Aromasin
- I. Introduction
- II. Uses of Aromasin
- III. How Aromasin Works
- IV. Off-label Use of Aromasin
- V. Dosage and Administration
- VI. Composition
- VII. Side Effects
- VIII. Common Side Effects
- IX. Interactions
- X. Warnings and Contraindications
- XI. Careful Administration
- XII. Important Precautions
- XIII. Administration to Special Populations
- XIV. Over Dosage
- XV. Storage
- XVI. Handling Precautions
I. Introduction
The origin and development of Aromasin also known as exemestane, can be traced back to research focused on treating estrogen-dependent ailments, specifically breast cancer. Aromasin quickly gained recognition as a drug in the field of endocrine therapies. Its primary use lies in its effectiveness against breast cancer in postmenopausal women. Aromasin acts as a therapy by suppressing the synthesis of estrogen, thus slowing down the growth of cancer cells that are dependent on this hormone.
II. Uses of Aromasin
Aromasin is an anti-cancer medication that has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the following uses:
- Treating women with early breast cancer that is estrogen receptor positive as part of adjuvant therapy.
- Treating breast cancer in postmenopausal women whose condition has worsened after taking tamoxifen1.
Aromasin is considered a standout among aromatase inhibitors, like letrozole and anastrozole, because it has a unique mechanism of action that allows it to permanently deactivate the aromatase enzyme1. In contrast, its non-steroidal counterparts only bind temporarily, requiring dosing1.
Here are some references that provide more information about Aromasin:
- Medscape: This website provides detailed information about Aromasin, including its dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more.
- FDA: This document contains the highlights of prescribing information for Aromasin, including its approved uses, dosage, and administration.
- Wikipedia: This page provides a comprehensive overview of Aromasin, including its pharmacology, clinical use, and side effects.
- Drugs.com: This website offers comprehensive information about Aromasin, including its uses, dosage, and side effects.
III. How Aromasin Works
IV. Off-label Use of Aromasin
Various clinical trials and studies have highlighted the potential of Aromasin in off-label applications, such as managing ovarian cancer, increasing follicular sensitivity for infertility treatments, and countering gynecomastia in men1. For example, a study demonstrated progression-free survival rates when using Aromasin for ovarian cancer management1.
Here are some references that provide more information about Aromasin:
- Medscape: This website provides detailed information about Aromasin, including its dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more.
- FDA: This document contains the highlights of prescribing information for Aromasin, including its approved uses, dosage, and administration.
- Wikipedia: This page provides a comprehensive overview of Aromasin, including its pharmacology, clinical use, and side effects.
- Drugs.com: This website offers comprehensive information about Aromasin, including its uses, dosage, and side effects.
V. Dosage and Administration
Here are the recommended dosages for conditions: For women who have gone through menopause and have either early-stage or advanced breast cancer, the standard dose is 25mg daily after eating. However, the dosage may vary depending on the clinical situation and other medications. It's essential to consult a healthcare professional to determine the dosage based on individual circumstances. Dosage adjustments may be necessary for individuals with kidney or liver impairments. Collaborating with a clinician is crucial to customize the dosage appropriately. To ensure results, it is recommended to take Aromasin at the same time every day, preferably after a meal, as this can enhance absorption. It is also advised to avoid consuming grapefruit or its derivatives during treatment to prevent interactions that may increase drug concentration levels.
VI. Composition
The critical ingredient in Aromasin is exemestane, a substance that deactivates aromatase. In addition to that, Aromasin contains inactive ingredients like mannitol crospovidone and magnesium stearate. These ingredients help maintain the stability of the drug and extend its shelf life so that it can be delivered effectively. While Aromasin is the brand-name version of this medication, alternatives are available that contain the same active ingredient, exemestane. These generic versions are considered equivalent to Aromasin but may have minor differences in nonessential components.
VII. Side Effects
Side effects are a possibility with any medication, including Aromasin. These can vary from discomforts like hot flashes and fatigue to more serious concerns such as osteoporosis or cardiac events. It's important to distinguish between side effects like insomnia and joint pain and rarer ones like liver issues, severe skin reactions, or potential heart problems. If you experience any symptoms, staying attentive and consulting with a medical professional for guidance is essential.
VIII. Common Side Effects
Here is a list of side effects associated with Aromasin despite its effectiveness in treating specific conditions. Patients may experience the following: flashes, Joint pain or stiffness, Fatigue, Mild nausea, Depression, Insomnia, and Sweating If you're dealing with these side effects, some may improve over time. However, if your symptoms persist or worsen, it's essential to seek intervention. To manage these effects, you can try using fans or other cooling methods for flashes, engaging in gentle exercise to alleviate joint pain, or seeking professional guidance for depression. Remember that any unusual or severe symptoms should prompt medical consultation.
IX. Interactions
Some drugs can interact with Aromasin and affect its effectiveness. These include estrogen medications, antifungal medicines like ketoconazole, and certain antibiotics like erythromycin. It is essential to avoid consuming grapefruit or any derivatives of it as they can increase the concentration of Aromasin in the blood. It is also advised to avoid using supplements like St. Johns Wort with Aromasin. Additionally, it is recommended to refrain from consuming alcohol as it may worsen side effects.
X. Warnings and Contraindications
There are situations and conditions where it is not recommended to use Aromasin. If a patient has a hypersensitivity to the ingredients of Aromasin, it should not be used. Additionally, premenopausal women, patients with liver disease, or those with certain endocrine disorders may be advised against using it. Patients with osteoporosis or cardiovascular issues must exercise caution when considering Aromasin, as it can potentially worsen bone loss or strain functions.
XI. Careful Administration
If someone has liver or kidney problems, it may be necessary to adjust the medication dosage due to changes in how their body processes and eliminates drugs. To ensure the treatment results and avoid any possible issues, it is essential to regularly monitor bone density, liver function, and lipid levels.
XII. Important Precautions
Recommended health monitoring during treatment: In addition to the tests mentioned earlier, it is crucial to monitor for any changes in cardiovascular health, mood swings, or gastrointestinal issues. When discontinuing or pausing treatment, it is essential to consider adverse reactions, severe hypersensitivities, or any signs of endocrine dysfunction that may require stopping the treatment. In situations, it is advisable to discontinue the therapy, under medical supervision gradually.
XIII. Administration to Special Populations
a. Administration to the Elderly
When it comes to adjusting medication doses for patients, it's vital to consider the effects of aging on drug absorption and metabolism. Therefore, starting treatment with doses and gradually increasing them based on tolerances is a wise approach. Studies involving individuals have shown that they experience similar effectiveness from medications but may be more prone to specific side effects, particularly those related to bone density reduction.
b. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Dangers and suggestions: It is not recommended to take Aromasin during pregnancy because it can harm the fetus. It is also advised that breastfeeding mothers avoid using it as it is possibly passed into breast milk. Instead, consider safer treatments during pregnancy and lactation, such as specific selective estrogen receptor modulators.
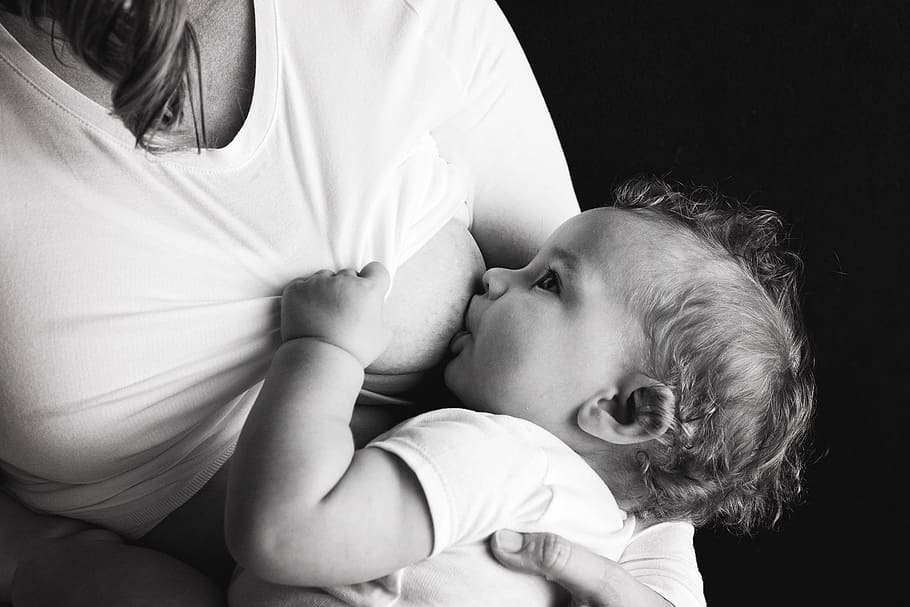

c. Administration to Children
Based on the research and findings, we don't have enough extensive trials in children to fully understand the safety and effectiveness of Aromasin in this age group. We have limited information about its safety profile. There are indications that it may cause disruptions in the endocrine system and affect growth. However, more studies are needed to grasp the long-term implications of using Aromasin in pediatric populations.
XIV. Over Dosage
Signs of taking too much Aromasin: If you consume an excessive amount, you may experience tiredness, dizziness, stomach problems, and potential imbalances in your hormones. What to do immediately and treatment options: It is essential to seek help immediately if you overdose. The treatment will focus on managing the symptoms and closely monitoring your condition. Long-term effects and follow-up care: If the overdose becomes chronic, it can disrupt your hormone levels. This may require term hormonal therapies and regular monitoring of your health.
XV. Storage
It is advisable to store Aromasin in a dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture, ideally within the temperature range of 15°C to 30°C. Although Aromasin has shelf stability, its therapeutic effectiveness may decrease if consumed after the expiration date.
XVI. Handling Precautions
To ensure handling and proper disposal of Aromasin, it is essential to avoid direct contact, especially if the medication is broken or crushed. When disposing of Aromasin, it should be done following waste guidelines. To prevent ingestion or exposure, it is recommended to keep Aromasin out of the reach of children, store it in its original container, and remain vigilant to avoid any potential spills.