Atropine
- Introduction
- Uses of Atropine
- How It Works
- Off-label Use
- Dosage and Administration
- Composition
- Storage
- Interaction
- Warning
- Contraindication
- Careful Administration
- Important Precautions
- Administration to the Elderly
- Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
- Administration to Children
- Over Dosage
- Handling Precautions
- Side Effects
- Common Side Effects
- Conclusion
Introduction
Atropine has a remarkable history in medicine, dating back many centuries. It originated from the Atropa belladonna plant. Possesses intriguing chemical and physical attributes. With its form, Atropine appears colorless and tends to absorb moisture. Its strong bitterness serves as an indication of its qualities.
Uses of Atropine
The use of Atropine in medicine is extensive and diverse. It plays a role in treating various conditions. It has found particular importance in ophthalmology, where it is used to cause dilation of the pupils and relaxation of the eye muscles. In addition to its applications, Atropine has proven effective in treating bradycardia (slow heart rate), reducing excessive secretions during surgical procedures, and serving as an antidote for organophosphate poisoning. Furthermore, Atropine acting properties make it invaluable in emergencies. It can rapidly counteract nerve agents' effects and certain types of mushroom poisonings.
References:
1: Atropine - Definition, Properties, Uses, Side Effects and FAQs - Vedantu 2: Atropine (Atropine): Uses, Dosage, Side Effects, Interactions … - RxList 3: Atropine: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action | DrugBank Online 4: Atropine - Wikipedia
How It Works
The way Atropine works in the body is mainly by acting as a competitor to the acetylcholine receptors. This leads to physiological responses, such as an elevated heart rate, widening of the bronchi, and reduced movement and secretion in the digestive system.
Off-label Use
Exploring off-label use opens up many possibilities beyond what the FDA has approved. Off-label use refers to prescribing medications for conditions, age groups, or dosages that have not been officially approved. Some standard off-label uses for Atropine include reducing drooling in patients and treating certain gastrointestinal disorders. Numerous clinical studies have provided evidence supporting the effective use of Atropine in these unexplored areas. However, it is essential to emphasize the need for dosage and monitoring when venturing into these off-label applications.
References:
1: Pharmacological Management of Hypersalivation in Adults - RES Systems 2: The effect of sublingual atropine sulfate on clozapine-induced … 3: End-of-Life Care: Managing Common Symptoms | AAFP
Dosage and Administration
Administering Atropine requires precision. The recommended doses can vary depending on the condition being treated. For example, different dosages may be necessary when dealing with bradycardia or organophosphate poisoning. The drug can be administered through intravenous, intramuscular, or subcutaneous routes. Additionally, healthcare professionals often adjust the dosage based on the patient's weight and overall health to ensure the medication is effective while minimizing side effects.
Composition
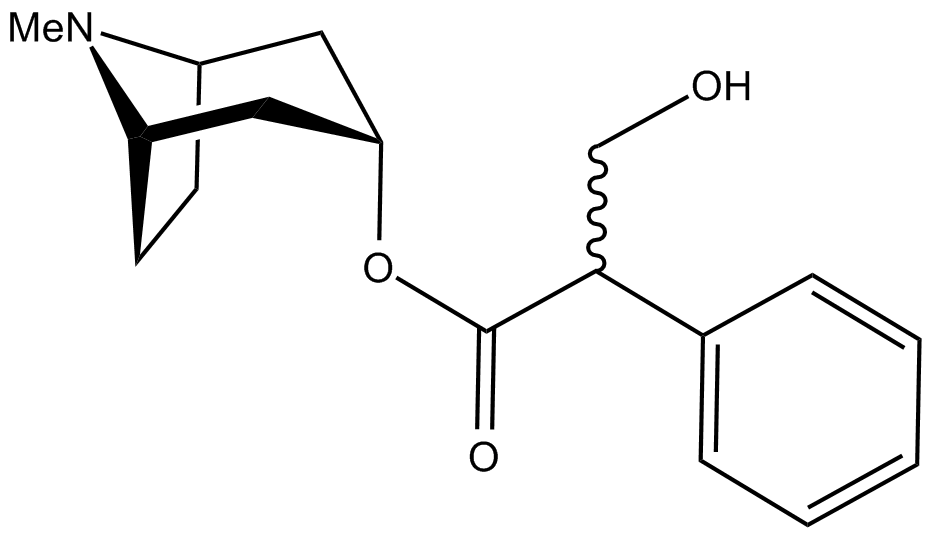
When we examine the chemical structure of Atropine closely, we discover that it is an alkaloid made up of both endo and exo isomers. Additionally, commercial preparations may include substances or diluents to improve the main compound's stability, solubility, or delivery.
Storage
It is crucial to store Atropine to maintain its effectiveness. The ideal storage conditions involve keeping it in a dark place, with no moisture. It's essential to pay attention to its shelf life and expiration date to ensure that it remains therapeutically effective. If you come across expired Atropine, it is recommended to dispose of it through medication take-back programs to prevent unintended use.
Interaction
The use of Atropine in therapy is not free from interactions. Various medications, such as antihistamines, antipsychotics, and certain antifungals, can interact with Atropine. These interactions may result in increased side effects or reduced effectiveness of the treatment. Therefore it is crucial to exercise caution when administering medications concurrently with Atropine.
Warning
Although Atropine is highly beneficial for purposes, it does come with certain risks. Misuse or excessive medication use can lead to hallucinations, rapid heart rate, and dangerous conditions. Identifying symptoms of reactions, such as blurry vision or difficulty urinating, allows for prompt intervention and necessary measures to be taken.
Contraindication
There are situations where it is not recommended to use Atropine. These include cases like angle closure glaucoma. Suppose someone has a sensitivity or allergy to the drug. Ignoring these restrictions not reduces the intended therapeutic effects but also increases the chances of adverse reactions occurring.
Careful Administration
Administering Atropine requires a balance of expertise and understanding. There are factors to consider when giving it, like the need for a clean environment and preventing contamination. Additionally, monitoring patients after administering the drug is essential to ensure no adverse reactions or overdoses. Keeping an eye on vital signs, especially heart rate and pupil dilation, is crucial.
Important Precautions
Before taking Atropine, it is essential to take precautions into account. These include checking the patient's medications, known allergies, and the specific condition being treated. In addition, it is crucial to refrain from activities like driving or operating machinery while under the influence of Atropine. It is also advisable to avoid substances, like alcohol, that can potentially intensify the effects of Atropine.
Administration to the Elderly
Geriatric care, a field of medicine, highlights the importance of considering specific factors when using Atropine. It is crucial to consider dosage adjustments due to the changes that occur with age, which can affect how the drug is processed and eliminated from the body. Healthcare professionals need to exercise clinical judgment as older patients often show increased sensitivity to medications ensuring a balance between potential risks and benefits.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
The relationship between Atropine and maternal health is complex. Recent studies provide some limited information on the effects of Atropine during pregnancy. Although it hasn't been directly associated with abnormalities, caution is advised. Safety concerns apply to both the mother and the fetus, emphasizing the need for effective doses and careful monitoring. When considering the use of Atropine in breastfeeding mothers, informed decision-making is necessary due to the transfer of the drug through breast milk.
Administration to Children
Pediatric patients, with their changing physiological characteristics, need customized approaches. Guidelines for dosing according to age are crucial to ensure effectiveness while maintaining safety. Considering their metabolic rates and organ functions, extra precautions must be taken to ensure the safety of these young patients.
Over Dosage
Regarding medications like Atropine, there is a real risk of overdosing. It's crucial to identify the signs and symptoms, ranging from having a mouth and blurry vision to experiencing intense restlessness and even hallucinations. If an overdose occurs, it's essential to contact emergency services and ensure the patient's airway is open. Medical interventions may involve using activated charcoal to provide care or resorting to mechanical ventilation in severe situations.
Handling Precautions
It is equally important to prioritize the safety of those administering Atropine just as we do for the protection of the patients. This involves taking precautions like wearing gloves and ensuring the drug does not contact the skin. In case of any exposure, following protocols such as immediately washing the affected area and seeking medical assistance without delay is crucial.
Side Effects
No matter how effective, every medication can have some side effects. In the case of Atropine, these side effects can range from ones like dry mouth to more severe ones like increased heart rate. It is difficult to determine the frequency of these side effects due to variations in different populations and dosages.

Common Side Effects
In terms of side effects, some manifestations are more commonly observed. The frequently mentioned side effects include experiencing a dry mouth having blurred vision, and difficulty with urinary retention. Strategies such as adjusting the dosage, providing treatment, and educating the patient are recommended to effectively manage and alleviate these side effects.
Conclusion
Atropine is highly regarded in the field due to its numerous applications. However, it is essential to use it because of its potent effects. Like with any medication, the "not harm" principle is crucial. Therefore ongoing education, monitoring, and prioritizing patient-centered care are essential for using it safely and effectively.