Augmentin IV Vial
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Composition
- 3. How Augmentin IV Vial Works
- 4. Uses of Augmentin IV Vial
- 5. Augmentin Dosage and Administration
- 6. Storage and Handling Precautions
- 7. Side Effects of Augmentin IV Vial
- 8. Warnings and Contraindications
- 9. Drug Interactions
- 10. Important Precautions
- 11. Administration in Special Populations
- 12. Overdosage and Management
1. Introduction
Overview of Augmentin IV Vial
Augmentin IV Vial is a potent antibacterial agent designed to combat a wide range of infections. With its intravenous formulation, it ensures rapid delivery of its active compounds, making it indispensable in acute clinical settings.
History and Development of Augmentin
Originally developed to address antibiotic resistance, Augmentin combines two active components to overcome bacterial defenses. Introduced in the late 20th century, it revolutionized treatment protocols by offering a dual-action mechanism.
Therapeutic Importance in Medical Practice
Widely utilized in hospital and outpatient settings, Augmentin IV Vial is a cornerstone in the treatment of severe bacterial infections. Its role extends beyond first-line therapy, often being a critical intervention for drug-resistant pathogens.
2. Composition
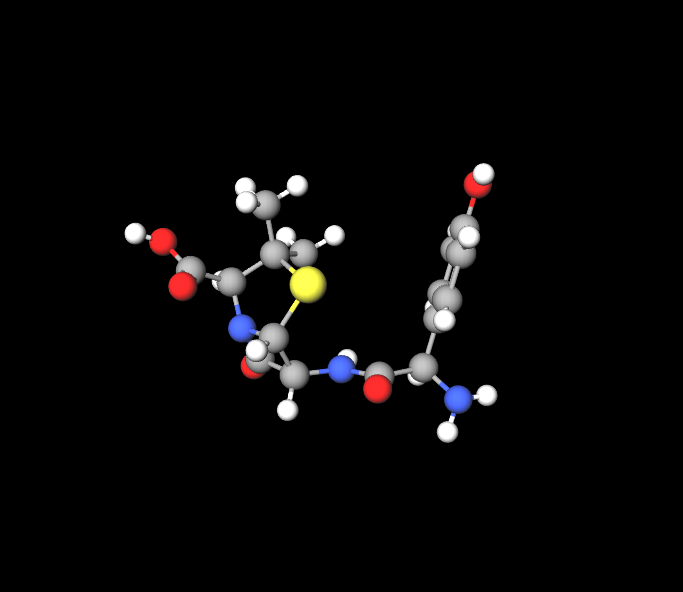
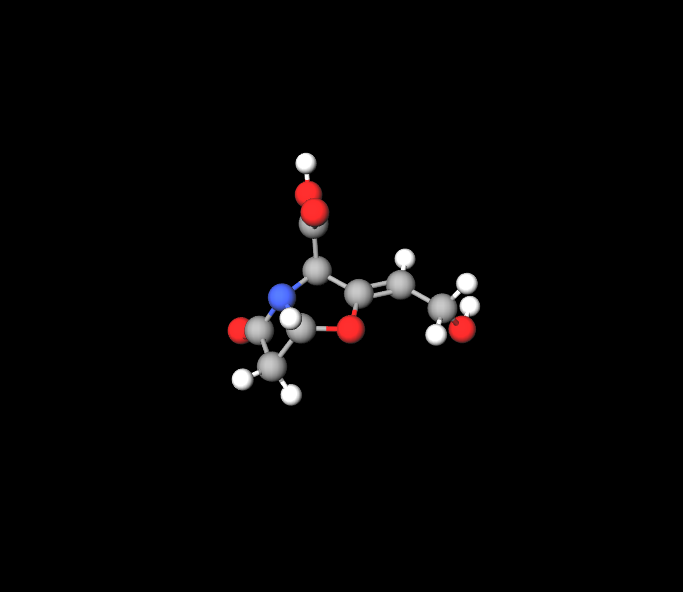
Active Ingredients: Amoxicillin and Clavulanic Acid
Each vial contains Amoxicillin, a penicillin-class antibiotic, and Clavulanic Acid, a beta-lactamase inhibitor. Together, they ensure a broader and more effective antibacterial spectrum.
Formulation Specifics for IV Administration
- Prepared as a lyophilized powder for reconstitution.
- Designed for controlled intravenous infusion to optimize bioavailability.
Pharmaceutical Classification
Classified as a combination antibiotic, Augmentin IV belongs to the beta-lactam/beta-lactamase inhibitor family, setting it apart in its ability to tackle resistant organisms.
Augmentin vs amoxicillin
Augmentin contains amoxicillin and clavulanate, which may make Augmentin more effective than amoxicillin alone for certain infections.
Amoxicillin vs penicillin
Both penicillin and amoxicillin are penicillin-class drugs. While the medicines penicillin V and penicillin G are naturally occurring penicillins, amoxicillin was made by chemically modifying penicillins to make them more powerful. As a result, amoxicillin tends to treat a broader range of bacterial infections.
Azithromycin vs amoxicillin
Azithromycin is commonly prescribed for infections like sinus infections, pneumonia, and certain sexually transmitted diseases, while amoxicillin is used for ear infections, pneumonia, and throat infections among others.
Cephalexin vs amoxicillin
Cephalexin is a cephalosporin antibiotic, and amoxicillin is a penicillin derivative.
Amoxicillin and ibuprofen
Amoxicillin and ibuprofen together to treat an infection and relieve pain or fever.
3. How Augmentin IV Vial Works
Mechanism of Action of Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin disrupts bacterial cell wall synthesis, leading to cell lysis. It targets penicillin-binding proteins, rendering it lethal to susceptible organisms.
Role of Clavulanic Acid in Combating Resistance
Clavulanic Acid inhibits beta-lactamase enzymes produced by resistant bacteria. This synergy ensures the efficacy of Amoxicillin against otherwise impervious strains.
Spectrum of Antibacterial Activity
The combination is effective against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus, E. coli, and anaerobes like Bacteroides fragilis.
4. Uses of Augmentin IV Vial
Treatment of Bacterial Infections
Augmentin for bronchitis
Augmentin is approved to treat certain types of respiratory infections. In some cases, this can include bronchitis. Bronchitis is often caused by a virus, so antibiotics are not usually effective in treating it.
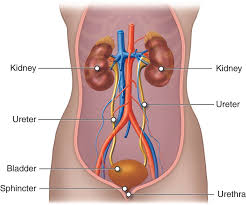
Augmentin for UTI
Effective in managing pyelonephritis and complicated UTIs caused by resistant pathogens.
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
Recommended for cellulitis, abscesses, and diabetic foot infections.
Augmentin for sinus infection
Bone and Joint Infections
Treats osteomyelitis and septic arthritis where oral antibiotics are insufficient.
Use in Surgical Prophylaxis
Helps reduce the occurrence of infections after surgery – in cases of orthopedic procedures.
Augmentin for tooth infection
Amoxicillin combined with Clavulanic acid, which is then sold under the brand name Augmentin, tackles an even broader spectrum of bacteria. Most dentists recommend taking 625mg of Augmentin three times daily as a treatment for dental infections.
Off-Label Uses
Treatment of Multi-Drug-Resistant Infections
Explored for infections caused by resistant gram-negative bacilli.
Experimental Use in Severe Sepsis or Septic Shock
Used adjunctively in life-threatening conditions, although evidence remains limited.
Augmentin for dogs
Pets were prescribed amoxicillin/clavulanate to address issues like skin infections and gum disease while also tackling soft tissue problems such as abscesses and wounds.

Augmentin for diverticulitis
Amoxicillin clavulanate could potentially be recommended as an alternative to using metronidazole with fluoroquinolone to lower the chances of experiencing side effects linked to fluoroquinolone.
5. Augmentin Dosage and Administration
Augmentin dose for adults
Typically administered at 1.2g every 8 hours, adjusted based on infection severity.
Augmentin pediatric dose
Children <40 kg: 20 mg/5 mg/kg/day to 60 mg/15 mg/kg/day given in 3 divided doses.
Adjustments for Renal and Hepatic Impairment
Dosage must be modified in patients with reduced kidney or liver function to prevent toxicity.
Step-by-Step Guide for IV Preparation and Administration
- Reconstitute vial with sterile water.
- Administer via slow IV infusion over 30 minutes.
Duration of Therapy for Common Infections
Ranging from 5-14 days, depending on infection type and patient response.
6. Storage and Handling Precautions
Recommended Storage Conditions
Store vials in a cool, dry place below 25°C.
Shelf Life of Prepared Solutions
Use within 20 minutes of preparation to ensure potency.
Proper Disposal of Unused Medication
Dispose of in accordance with local guidelines to minimize environmental impact.
7. Side Effects of Augmentin IV Vial
Common Side Effects
Gastrointestinal Disturbances
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
Augmentin rash
About 5 to 10 percent of children taking amoxicillin or Augmentin will develop a skin rash during medication. Most of these rashes are non-allergic and are typically caused by viruses.
Augmentin allergy
Raised, itchy, white, red, or discolored bumps after the first few doses of Augmentin may indicate an allergy to the medication. Requires immediate discontinuation and emergency intervention.
Liver Dysfunction and Cholestatic Jaundice
May present as elevated liver enzymes and yellowing of the skin.
Side effects of augmentin in females
However, vaginitis, including vaginal yeast infections, can sometimes occur after treatment with antibiotics, including Augmentin
8. Warnings and Contraindications
Known Hypersensitivity to Penicillins or Beta-Lactams
Contraindicated in patients with a history of severe allergic reactions to these agents.
History of Severe Allergic Reactions
Exercise extreme caution in patients with prior anaphylaxis to drugs in the same class.
Conditions Contraindicating Use
Avoid use in patients with significant hepatic dysfunction or mononucleosis, as it increases the risk of adverse effects.
Augmentin pregnancy category
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category B.
9. Drug Interactions
Interaction with Anticoagulants
Augmentin IV Vial may potentiate the effects of anticoagulants like warfarin. This interaction can increase the risk of bleeding complications, necessitating close monitoring of prothrombin time and INR levels. Adjustments to anticoagulant dosage may be required during concurrent use.
Effect on Oral Contraceptive Efficacy
Concurrent use of Augmentin IV Vial can reduce the efficacy of estrogen-based oral contraceptives. This occurs due to alterations in gut flora, impacting estrogen recycling. Patients should be advised to use additional contraceptive measures during the treatment period.
Interactions may occur when co-administered with other antibiotics, such as tetracyclines, which can antagonize the bactericidal activity of Augmentin. When used alongside antivirals like acyclovir, there is potential for renal function impact, requiring dosage adjustments and renal monitoring.
Augmentin and alcohol
Alcohol will not stop Augmentin from working. However, drinking alcohol could raise your risk of certain side effects from Augmentin. These include nausea, vomiting, and liver problems.
10. Important Precautions
Monitoring for Allergic Reactions During Therapy
Patients should be closely monitored for signs of hypersensitivity, such as rash, pruritus, or more severe reactions like anaphylaxis. Early identification and intervention can prevent complications.
Guidelines for Minimizing Gastrointestinal Side Effects
- Administer the dose with food to reduce gastrointestinal irritation.
- Encourage hydration to minimize the risk of diarrhea.
Probiotics may also be recommended to maintain gut flora balance during prolonged therapy.
Avoidance of Unnecessary Long-Term Use
Prolonged use can lead to superinfections and antimicrobial resistance. Therapy should always be guided by culture and sensitivity results where possible.
Foods to avoid when taking augmentin
There haven't been any documented cases of food interactions, with Augmentin – an antibiotic prescribed for infections; however certain foods may interfere with antibiotics such, as grapefruit juice and dairy products containing calcium or spicy foods.
Careful Administration
Special Considerations in Elderly Patients
Older adults are more susceptible to drug accumulation due to age-related renal decline. Renal function tests should guide dosing decisions to prevent toxicity.
Use in Patients with a History of Liver Disease
Augmentin IV Vial may exacerbate hepatic dysfunction. Regular liver function tests are advised in patients with pre-existing conditions.
Adjustments for Immunocompromised Individuals
Immunocompromised patients may require longer treatment durations or adjunctive therapies due to altered pharmacokinetics and diminished immune response.
11. Administration in Special Populations
Administration to Elderly
Dosage Modifications Based on Renal Function
Renal clearance declines with age, necessitating reduced dosages or extended intervals to prevent accumulation and adverse effects.
Increased Monitoring for Adverse Reactions
Older adults are more prone to side effects such as gastrointestinal disturbances or hepatic dysfunction. Regular assessments can mitigate these risks.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Safety Profile During Pregnancy
Augmentin is classified as category B, indicating no evidence of harm in animal studies. However, caution is advised, particularly during the first trimester.
Augmentin and breastfeeding
Small amounts of Augmentin components may pass into breast milk. Although generally considered safe, infants should be observed for signs of diarrhea or allergic reactions.
Administration to Children
Pediatric Dosage Guidelines
Considerations for Premature or Neonatal Patients
Neonates and premature infants may have immature renal and hepatic systems, requiring significant dose adjustments and careful monitoring for drug accumulation.
12. Overdosage and Management
Symptoms of Overdosage
Overdosage symptoms may include severe gastrointestinal disturbances, seizures, or acute renal dysfunction. Hypersensitivity reactions may also occur at higher frequencies.
Immediate Steps for Managing Overdose
- Discontinue administration immediately.
- Provide supportive measures such as hydration and electrolyte balance.
- Initiate hemodialysis in severe cases to remove the drug from circulation.
Long-Term Effects of Overdose and Their Treatment
Renal impairment and hepatic dysfunction are potential long-term effects. Follow-up care should include renal and hepatic function monitoring, with adjustments to future drug regimens as necessary.
Augmentin IV Vial FAQ
- What amoxicillin used for std?
- What amoxicillin treat?
- What amoxicillin for?
- What amoxicillin used for?
- How amoxicillin should be taken?
- How amoxicillin works in the body?
- How amoxicillin works on bacteria?
- How amoxicillin is made?
- How amoxicillin works?
- Can amoxicillin make you tired?
- Can amoxicillin cause diarrhea?
- Can amoxicillin cause uti?
- Can amoxicillin make you feel sick?
- Can amoxicillin cause constipation?
- Can amoxicillin treat uti?
- Are amoxicillin and cephalexin the same?
- Are amoxicillin and ampicillin the same?
- Are amoxicillin and augmentin the same?
- Are amoxicillin and penicillin the same?
- Will amoxicillin help a ear infection?
- Will amoxicillin treat pneumonia?
- Will amoxicillin treat strep?
- Will amoxicillin treat a cold?
- Why amoxicillin is used?
- Why amoxicillin after tooth extraction?
- Why amoxicillin with clavulanic acid?
- Why amoxicillin with food?
- Which amoxicillin is safe during pregnancy?
- What is clavulanic acid used for?
- Why is clavulanic acid added to amoxicillin?
- Is clavulanate a strong antibiotic?
- What bacteria does clavulanic acid cover?
- When should clavulanic acid be taken?
- What is the main side effect of amoxicillin-clavulanate?
- What to avoid while taking amoxicillin-clavulanate?
- How many amoxicillin-clavulanate can you take in a day?
- What is the difference between amoxicillin and clavulanate?
- What does amoxicillin clavulanic acid cure?
- Is clavulanic acid bad for liver?
- Why do you take clavulanic acid?
- Is clavulanic acid antibacterial?
- Who should not take clavulanic acid?
- Is amoxicillin-clavulanate bad for kidneys?
- What amoxicillin used for std?
- What amoxicillin treat?
- What amoxicillin for?
- What amoxicillin used for?
- How amoxicillin should be taken?
- How amoxicillin works in the body?
- How amoxicillin works on bacteria?
- How amoxicillin is made?
- How amoxicillin works?
- Can amoxicillin make you tired?
- Can amoxicillin cause diarrhea?
- Can amoxicillin cause uti?
- Can amoxicillin make you feel sick?
- Can amoxicillin cause constipation?
- Can amoxicillin treat uti?
- Are amoxicillin and cephalexin the same?
- Are amoxicillin and ampicillin the same?
- Are amoxicillin and augmentin the same?
- Are amoxicillin and penicillin the same?
- Will amoxicillin help a ear infection?
- Will amoxicillin treat pneumonia?
- Will amoxicillin treat strep?
- Will amoxicillin treat a cold?
- Why amoxicillin is used?
- Why amoxicillin after tooth extraction?
- Why amoxicillin with clavulanic acid?
- Why amoxicillin with food?
- Which amoxicillin is safe during pregnancy?
- What is clavulanic acid used for?
- Why is clavulanic acid added to amoxicillin?
- Is clavulanate a strong antibiotic?
- What bacteria does clavulanic acid cover?
- When should clavulanic acid be taken?
- What is the main side effect of amoxicillin-clavulanate?
- What to avoid while taking amoxicillin-clavulanate?
- How many amoxicillin-clavulanate can you take in a day?
- What is the difference between amoxicillin and clavulanate?
- What does amoxicillin clavulanic acid cure?
- Is clavulanic acid bad for liver?
- Why do you take clavulanic acid?
- Is clavulanic acid antibacterial?
- Who should not take clavulanic acid?
- Is amoxicillin-clavulanate bad for kidneys?
What amoxicillin used for std?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), it is recommended that people should consume 500 mg of amoxicillin three times daily for a week to treat conditions such as chlamydia.
What amoxicillin treat?
It is often used to treat infections such as chest infections like pneumonia) abscesses and stomach ulcers when used in combination, with other antibiotics and medications.
What amoxicillin for?
Doctors often recommend this medication for treating infections like pneumonia and dental abscesses; it can also be used alongside antibiotics and drugs to treat stomach ulcers effectively. It's commonly advised for children with ear and chest infections.
What amoxicillin used for?
It is often prescribed for infections, such as chest infections, pneumonia, dental abscesses, and stomach ulcers, when used in conjunction with other antibiotics and medications.Children are often advised to seek treatment for ear infections and chest infections.
How amoxicillin should be taken?
Experts often suggest taking it either every 12 hours or every 8 hours, which amounts to three times a day.
How amoxicillin works in the body?
Amoxicillin is part of a category of medications called penicillin antibiotics, which work by stopping the growth of bacteria in the body.
How amoxicillin works on bacteria?
Amoxicillin works by inhibiting the synthesis of mucopeptides within the cell wall—a network of acids that provides structural support to the cell wall. This causes the cell wall to weaken and break down over time until the bacteria is completely eliminated.
How amoxicillin is made?
Amoxicillin belongs to the category of aminopenicillins, which was created by adding an amino group to penicillin to address issues with resistance.
How amoxicillin works?
Amoxicillin is part of a category of medications called penicillin-type antibiotics. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria in the body.
Can amoxicillin make you tired?
After antibiotics kill off bacteria in your system, you may feel tired as your body works to regain its equilibrium.
Can amoxicillin cause diarrhea?
Amoxicillin could cause stomach discomfort, possibly lead to diarrhea in some instances.
Can amoxicillin cause uti?
No
Can amoxicillin make you feel sick?
Common side effects of amoxicillin often involve feeling nauseous and having diarrhea.
Can amoxicillin cause constipation?
Constipation is not typically listed as a side effect of taking amoxicillin medication. However the use of antibiotics can sometimes lead to constipation by disrupting the balance of bacteria, in the body and changing the gut microbiome.
Can amoxicillin treat uti?
Amoxicillin has the potential to treat infections effectively. Despite its efficacy as a treatment choice, it is not commonly prescribed for UTIs.
Are amoxicillin and cephalexin the same?
Both cephalexin and amoxicillin fall under the category of beta-lactam antibiotics. They vary in their classification, with cephalexin being a cephalosporin antibiotic and amoxicillin a penicillin derivative. They do share some targets in terms of organisms they combat, and they also exhibit distinct effectiveness against specific types of organisms.
Are amoxicillin and ampicillin the same?
Amoxicillin and ampicillin target a range of bacteria. They have comparable effectiveness levels while also showing interchangeable resistance patterns.
Are amoxicillin and augmentin the same?
Both medications have features. Amoxicillin is an antibiotic prescribed by doctors, and Augmentin is a combination of amoxicillin with either clavulanate or clavulanic acid to potentially boost its effectiveness against certain types of infections.
Are amoxicillin and penicillin the same?
Penicillin and amoxicillin are both part of the penicillin family of medications, although penicillin V and penicillin G are naturally found as penicillins. Amoxicillin has been chemically modified from penicillins to improve its effectiveness in treating infections.
Will amoxicillin help a ear infection?
Amoxicillin is commonly prescribed for ear infections. It may not be practical in all instances.
Will amoxicillin treat pneumonia?
It's pretty likely that you will be prescribed a drug called amoxicillin, which belongs to the group of penicillin antibiotics.
Will amoxicillin treat strep?
Healthcare professionals often use penicillin and amoxicillin to treat throat infections with antibiotics.
Will amoxicillin treat a cold?
Amoxicillin and other antibiotics don't work against flu viruses or other viral infections. Taking antibiotics when not needed can raise the risk of developing resistance to them.
Why amoxicillin is used?
It is often used to treat infections such as pneumonia and tooth abscesses.
Why amoxicillin after tooth extraction?
Amoxicillin can also reduce the chances of developing socket swelling and trismus following procedures.
Why amoxicillin with clavulanic acid?
Clavulanic acid helps stop bacteria from breaking down amoxicillin, allowing the antibiotic to work better.
Why amoxicillin with food?
Eating a meal along with Amoxicillin can help prevent any stomach issues that may arise.
Which amoxicillin is safe during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, Amoxicillin, as co-amoxiclav, along with penicillin V, is regularly utilized and is unlikely to harm the growing baby.
What is clavulanic acid used for?
Clavulanic acid boosts the potency of amoxicillin in combatting strains by eliminating the bacteria causing these infections. However, it does not work against viral infections such as cold or flu viruses.
Why is clavulanic acid added to amoxicillin?
Amoxicillin is part of a class of drugs called penicillin antibiotics. These drugs work by stopping bacteria growth in its tracks. Clavulanic acid falls into the category of beta lactamase inhibitor medications. It acts as a shield against bacteria breaking down amoxicillin.
Is clavulanate a strong antibiotic?
When clavulanate potassium is taken alone, its effectiveness is limited. When it is paired with amoxicillin, it expands its capabilities to fight infections caused by bacteria that release beta lactamase enzymes.
What bacteria does clavulanic acid cover?
Clavulanate works well against β lactamases in Gram-negative bacteria, on both genetic material and extra DNA strands.
When should clavulanic acid be taken?
Don't forget to take the pill before you eat or along with your meal bite.
What is the main side effect of amoxicillin-clavulanate?
If you're feeling stomach pain or diarrhea with blood in it (even if it occurs after your dose), notice pale or yellow skin with dark urine, and have symptoms such as fever or feeling confused and weak, these could be concerning signs to look out for. Other symptoms may include loss of appetite, abdominal pain, and decreased or no urination at all.
What to avoid while taking amoxicillin-clavulanate?
Augmentin is a type of antibiotic that is prescribed to combat infections in the body and is known to have the possibility of interactions when consumed alongside alcohol and warfarin (Coumadin and Jantoven). Moreover‚ it could potentially interact with two medications for gout‚ probenecid and allopurinol (which is also referred to as Zyloprim). ‚ The chances of experiencing any interaction when combined with birth control pills are relatively low.
How many amoxicillin-clavulanate can you take in a day?
Grown-ups and kids who are 40 kilograms or heavier in weight, should take 500 milligrams of amoxicillin and 125 milligrams of clavulanate every 8 hours or 875 milligrams of amoxicillin and 125 milligrams of clavulanate every 12 hours as directed by a healthcare provider. For children weighing more than 40 kilograms, a professional should decide the right amount and how often it should be taken.
What is the difference between amoxicillin and clavulanate?
Amoxicillin and clavulanate are believed to work against a variety of bacteria, compared to amoxicillin, but they may lead to gastrointestinal issues.
What does amoxicillin clavulanic acid cure?
AMOXICILLIN and CLAVULANIC ACID are antibiotics that doctors prescribe to help fight infections in various areas of the body, such as the ears, nose or throat, skin, or joints. When bacteria invade our bodies and make us sick, it leads to infections that require treatment with these medications.
Is clavulanic acid bad for liver?
Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid is widely recognized as a cause of liver damage from medications in adults. It also carries a potential for drug-induced liver problems in children even when administered frequently.
Why do you take clavulanic acid?
Clavulanic acid works by preventing bacteria-produced beta-lactamase enzymes from breaking down amoxicillin, thus helping combat infections that may be resistant to antibiotics without the use of acid.
Is clavulanic acid antibacterial?
Although it may not work well on its own, it does have an inhibitory impact on class A beta lactamases while not affecting class C enzymes at all.
Who should not take clavulanic acid?
Before beginning this course of medication, make sure to let the doctor or pharmacist know about your history. Be sure to mention any liver conditions (including those linked to amoxicillin/clavulanic acid) kidney issues (such, as needing dialysis) or a particular infection type (like mononucleosis).
Is amoxicillin-clavulanate bad for kidneys?
If you consume amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium, it may cause a condition known as nephritis, which is a form of kidney failure that results in decreased urine production.
What amoxicillin used for std?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, advises individuals to consume 500 mg of amoxicillin thrice for a week to treat infections such as chlamydia that are passed through sexual contact.
What amoxicillin treat?
It is often used to treat infections such as chest infections (including pneumonia), tooth abscesses, and stomach ulcers when paired with antibiotics and medications.
What amoxicillin for?
It is often prescribed for infections, such as chest infections (such as pneumonia) and dental abscesses. It can be used along with antibiotics and medications to treat stomach ulcers. It is also frequently advised for children to treat ear infections and chest infections.
What amoxicillin used for?
Doctors often prescribe this medication for infections such as chest infections like pneumonia, dental abscesses, and stomach ulcers when used alongside other antibiotics and medications. It is a recommendation for children to treat ear infections and chest infections with this medication.
How amoxicillin should be taken?
It's often suggested that you take it every 12 hours ( a day) or every 8 hours (three times a day).
How amoxicillin works in the body?
Amoxicillin is classified within a category of medications called penicillin antibiotics, which work by stopping the growth of bacteria in the body.
How amoxicillin works on bacteria?
Amoxicillin works by preventing the formation of mucopeptides in the cell wall. These structures are composed of acids supporting the cell wall's structure and integrity. This process weakens the cell wall, eventually destroying it and effectively eliminating the bacteria.
How amoxicillin is made?
Amoxicillin belongs to the class of aminopenicillins, which was created by adding an amino group to penicillin to address issues with resistance.
How amoxicillin works?
Amoxicillin is part of a category of medications referred to as penicillin-type antibiotics. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria.
Can amoxicillin make you tired?
When antibiotics eradicate bacteria in your system, you may feel tired as your body works to regain its equilibrium.
Can amoxicillin cause diarrhea?
Taking amoxicillin could cause stomach discomfort and severe diarrhea as side effects.
Can amoxicillin cause uti?
Using amoxicillin does not result in tract infections (UTIs).
Can amoxicillin make you feel sick?
Adverse effects commonly associated with taking amoxicillin involve feelings of nausea and instances of diarrhea.
Can amoxicillin cause constipation?
Constipation is not usually listed as a side effect of taking amoxicillin medication. However, antibiotics can sometimes cause constipation by disturbing the balance of bacteria in the body and changing the gut microbiome.
Can amoxicillin treat uti?
Amoxicillin may be effective in treating infections. However, it is not commonly prescribed for UTIs.
Are amoxicillin and cephalexin the same?
Both cephalexin and amoxicillin fall under the beta-lactam category but are classified differently. Cephalexin is a cephalosporin antibiotic, while amoxicillin is derived from penicillin medication. They treat some organisms, and each has its own specific range of effectiveness against different types of organisms.
Are amoxicillin and ampicillin the same?
Amoxicillin and ampicillin are able to combat a variety of bacteria and show levels of effectiveness against them.
Are amoxicillin and augmentin the same?
Amoxicillin and Augmentationin have some similarities as they both serve as medications for treating infections; amoxicillin is prescribed on its own, while Augmentationin combines amoxicillin with either clavulanate or clavulanic acid to potentially boost its capability against certain types of infections.
Are amoxicillin and penicillin the same?
Penicillin and amoxicillin are both part of the penicillin family of medications. Penicillin V and G are penicillins, while amoxicillin has undergone chemical modifications from its penicillin origins to boost its effectiveness in tackling different types of infections.
Will amoxicillin help a ear infection?
Amoxicillin is commonly prescribed for ear infections. It may not be effective in all situations.
Will amoxicillin treat pneumonia?
You will likely be prescribed a drug called amoxicillin, which belongs to the group of penicillin antibiotics.
Will amoxicillin treat strep?
Doctors often prescribe penicillin and amoxicillin to treat throat infections.
Will amoxicillin treat a cold?
Amoxicillin and other antibiotics don't work against the flu or other viral infections. Taking antibiotics when not needed can raise the risk of developing antibiotic infections.
Why amoxicillin is used?
It is frequently used to treat infections such as pneumonia and tooth abscesses.
Why amoxicillin after tooth extraction?
Taking amoxicillin can also reduce the chances of developing socket swelling and trismus following procedures.
Why amoxicillin with clavulanic acid?
Clavulanic acid inhibits enzymes from amoxicillin, enhancing the antibiotic's effectiveness in combating infections.
Why amoxicillin with food?
Having a meal while taking Amoxicillin is recommended to prevent stomach upset.
Which amoxicillin is safe during pregnancy?
Throughout pregnancy and while expecting a baby to develop safely in the womb, used medications include Amoxicillin as well as co-amoxiclav, and penicillin V, which are considered safe choices and unlikely to cause harm to the developing fetus.
What is clavulanic acid used for?
Clavulanic acid boosts the potency of amoxicillin in combating strains by eliminating the bacteria causing these infections. However, it is ineffective against viral infections such as cold or flu viruses.
Why is clavulanic acid added to amoxicillin?
Amoxicillin is part of a category of drugs called penicillin antibiotics, which stop bacteria from growing in the body. Clavulanic acid acts as a medication known as a beta-lactamase inhibitor to protect amoxicillin from being broken down by bacteria.
Is clavulanate a strong antibiotic?
When clavulanate potassium is taken by itself, its effects are limited. When it is paired with amoxicillin, however, it expands its capabilities to fight infections caused by bacteria that make beta-lactamase.
What bacteria does clavulanic acid cover?
Clavulanate works well against types of β lactamases in Gram-negative bacteria on both chromosomes and plasmids.
When should clavulanic acid be taken?
Don't forget to take the pill before you eat or along with your meal.
What is the main side effect of amoxicillin-clavulanate?
If you're feeling stomach issues or diarrhea with a texture (even if it occurs months after your dose), noticing pale or yellowish skin, dark urine, and additional signs like fever, confusion, and weakness can be concerning, too. Be sure to keep an eye out for appetite and abdominal pain along with decreased or no urination at all.
What to avoid while taking amoxicillin-clavulanate?
Augmentin is a type of antibiotic prescribed for treating infections in the body. It's important to be cautious when taking Augmentin along with alcohol and warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven) as there might be interactions between them. Other medications, like probenecid and allopurinol (also called Zyloprim), can also potentially interact when taken alongside Augmentin. However, the chances of any interactions happening are minimal if Augmentin is taken together with birth control pills.
How many amoxicillin-clavulanate can you take in a day?
For adults and children weighing 40 kilograms or more; Take 500 milligrams of amoxicillin and 125 milligrams of clavulanate every 8 hours or take 875 milligrams of amoxicillin and 125 milligrams of clavulanate every 12 hours as a healthcare provider instructs. For children, under 40 kilograms;. Consult a professional to determine the dosage and frequency.
What is the difference between amoxicillin and clavulanate?
Amoxicillin and clavulanate are believed to work against a range of bacteria compared to amoxicillin but may cause digestive side effects.
What does amoxicillin clavulanic acid cure?
AMOXICILLIN and CLAVULANIC ACID are medications used to treat infections that can affect areas of the body, including the ears, nose, and throat regions, as well as the skin, bones, muscles, joints, urinary tract, and respiratory system. When harmful bacteria enter the body and lead to sickness, bacterial infections can occur.
Is clavulanic acid bad for liver?
Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid is commonly recognized as a cause of liver damage from medications in adults; however, it can also present a risk of drug-related liver problems in children even with regular use.
Why do you take clavulanic acid?
Clavulanic acid neutralizes beta lactamase enzymes produced by bacteria, preventing them from breaking down amoxicillin through enzyme activity inhibition. This helps combat a variety of infections that might otherwise resist antibiotics without the presence of acid.
Is clavulanic acid antibacterial?
Although it may not work independently, it does exhibit inhibitory properties against class A beta-lactamases while excluding class C enzymes.
Who should not take clavulanic acid?
Before you begin taking this medication regimen, make sure to discuss your history with the doctor or pharmacist. Be sure to mention any liver problems (those linked to amoxicillin/clavulanic acid use), kidney issues (including if you need dialysis), or any particular infections (like infectious mononucleosis) you may have had.
Is amoxicillin-clavulanate bad for kidneys?
When you use amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium, it may cause a condition known as nephritis, which is a form of kidney failure that results in decreased urine production.