Azathioprine, Azathioprine Tablet
- Introduction to Azathioprine
- Composition of Azathioprine Tablets
- How Azathioprine Works
- Uses of Azathioprine
- Off-Label Uses of Azathioprine
- Dosage and Administration of Azathioprine Tablets
- Side Effects of Azathioprine
- Interactions with Other Medications
- Contraindications and Cautions
- Special Precautions in Administration
- Management of Azathioprine Overdosage
- Storage and Handling Precautions
- Withdrawal Symptoms of Azathioprine
Introduction to Azathioprine
Azathioprine is a medicine in the array of drugs. It plays a vital role in treating autoimmune disorders and facilitating organ transplants. It regulates the immune system to curb harmful reactions that could harm tissues in autoimmune illnesses or cause organ rejection after transplantation. This medication originated in the 1950s. Signifies a breakthrough in medical progress. Since it first came into existence,Azathioprine has played a role in improving patients' lives by offering a way to deal with long-term conditions involving the immune system.
Overview of Azathioprine as a Medication
Azathioprine is an immunosuppressant. It typically reduces the body's response by disrupting DNA synthesis and preventing cell growth that may cause inflammation and harm. This medication is often recommended for treating ailments like arthritis and Crohn's disease or supporting organ well-being.
Brief History and Development
The discovery of Azathioprine emerged from the quest for chemotherapy medications during the twentieth-century era. With its focus on cancer therapy, the drug's immunosuppressive characteristics were eventually harnessed to enhance the outcomes of organ transplants, enabling a groundbreaking shift in healthcare practices and improving the success rates of organ transplant procedures.
Importance in Modern Medicine
Azathioprine plays a role in medicine as it effectively treats autoimmune diseases and supports organ transplant procedures by being versatile in its applications for various conditions. It positively affects patients’ health outcomes and enhances their quality of life.
Composition of Azathioprine Tablets
Azathioprine tablets are designed to provide a specific amount of the immunosuppressive substance, and various inactive ingredients help maintain the medicine's stability and effectiveness.
Active Ingredients and Their Roles
Azathioprine is the main active component in cells, disrupting DNA replication and decreasing cell growth and function.
Inactive Components and Their Functions
The tablet also includes ingredients such as magnesium stearate, starch, and lactose to help maintain the tablet's structure integrity and ensure dosages while improving absorption into the body.
Azathioprine Half Life
The way Azathioprine moves through the body shows that it stays active for 5 hours before its metabolites take over and continue to work for some time.
Azathioprine Alternatives
Based on their condition and how they respond to treatment, patients who cannot tolerate azathioprine may be given options like methotrexate or biologics such as infliximab.
Azathioprine vs Mercaptopurine
Azathioprine acts as a precursor to Mercaptopurine in the body through metabolic processes, and the selection between the two hinges on patient needs and tolerance levels.
Azathioprine and 6-Mercaptopurine
Azathioprine and 6-Mercaptopurine play roles in treating leukemia and autoimmune disorders by affecting the system differently based on individual patient needs and responses to treatment. Thorough knowledge of Azathioprine is crucial for its use in medical scenarios where immune regulation is essential.
How Azathioprine Works
Azathioprine is a component in treating immune-related conditions. It regulates the immune system to control abnormal immune reactions that cause various health issues.
Mechanism of Action in the Immune System
The essence of Azathioprine's function is its capacity to block purine synthesis to create DNA and RNA molecules in the body. This blocking mechanism slows down cell division in multiplying cells, such as those found in the immune system. As a result of this action, lymphocyte growth is. Immune reactions are moderated.
Effects on Cellular Processes and Immune Response
Azathioprine inhibits cell growth in the body, helping reduce inflammation and prevent damage to tissues in autoimmune disorders. It works by disrupting cell growth, thus reducing the immune reaction.
Uses of Azathioprine
Primary Indications in Autoimmune Disorders
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Reduces joint inflammation and damage.
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Controls systemic inflammation and prevents flares.
Role in Organ Transplantation Management
The immunosuppressive effects play a role in preventing the body from rejecting the transplanted organ after surgery by helping it adapt and ensuring the organ's well-being, which is crucial for the patient's overall survival.
Overview of Approved vs. Experimental Uses
Azathioprine is commonly used to treat conditions such as hepatitis and inflammatory bowel disease. It is now also being studied for its potential benefits in other immune-related illnesses as its therapeutic applications continue to grow and evolve.
Azathioprine for Cats
Azathioprine for Dogs
The drug treats autoimmune disorders in dogs, showcasing its effectiveness in handling long-term digestive issues and immune-related hemolytic anemia.

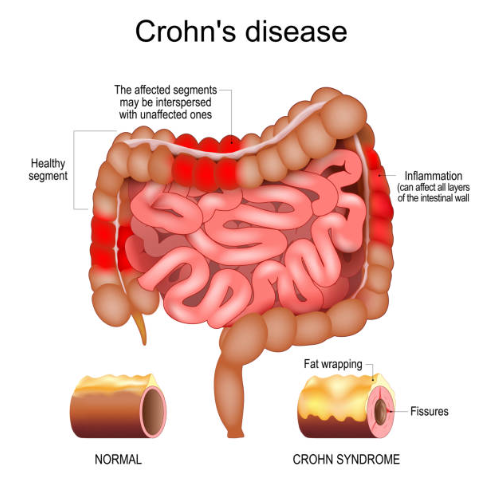
Azathioprine for Crohn's
Azathioprine is widely used to manage Crohn's disease. It sustains remission and avoids flare-ups, greatly enhancing the quality of life for those affected.
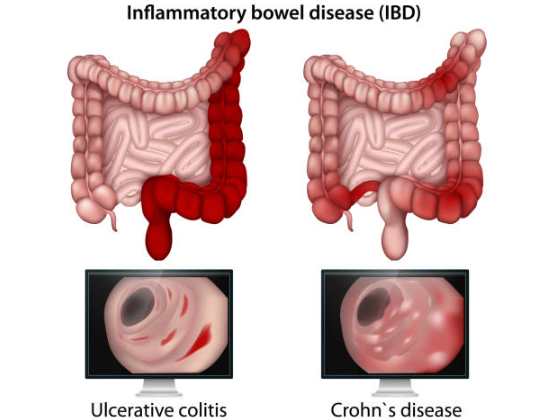
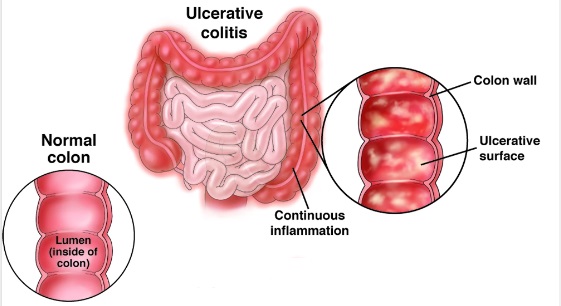
Azathioprine for Ulcerative Colitis
In colitis, well, it plays a crucial role by helping to sustain remission without the need for steroids.
Azathioprine IBD
In the management of bowel disease (IBD), it is crucial to ensure that remission is sustained for effective long-term control of the condition.
Azathioprine Fatigue
While Azathioprine is helpful in treating conditions, it can cause fatigue as a side effect, which could impact one's adherence to medication and overall well-being.
Azathioprine Lupus
Azathioprine plays a role in treating lupus erythematosus by serving as a long-term therapy that helps control symptoms and reduce the likelihood of flare-ups in this complex autoimmune condition. This in-depth examination of Azathioprines' uses and benefits for conditions highlights its essential contribution to modern drug therapy and brings optimism to individuals dealing with immune-related disorders.
Off-Label Uses of Azathioprine
The flexibility of Azathioprine goes beyond its intended uses. Due to continuous research and observations in clinical settings, alternative treatment areas are being explored.
Exploration of Less Common Applications
Azathioprine has uses beyond its intended purposes, such as treating severe atopic dermatitis and certain skin conditions, as well as autoimmune hemolytic anemia cases.
Research Studies and Findings Supporting Off-Label Use
Numerous studies have shown that Azathioprine is effective in applications. One example is its proven benefits in treating cases of atopic dermatitis, as highlighted by research studies showing notable symptom improvement and fewer flare-ups.
Dosage and Administration of Azathioprine Tablets
Successful administration of Azathioprine relies on a customized dosage plan to meet each patient's requirements and specific medical circumstances.

Guidelines for Initial Dosing and Adjustments
- Usually, when starting a medication regimen with a patient, it is practice to begin with a low dose to check for any adverse reactions and then increase it gradually until the desired treatment outcome is achieved.
- Adjusting the dosage is important. It should be based upon how the treatment is working and any side effects that happen along the way. It's suggested to keep a check of blood counts and liver enzymes to help with these adjustments.
Administration Techniques and Best Practices
Azathioprine tablets should be consumed twice a day, either with or without food, to ensure the medication's stomach tolerability; however, taking them with food may reduce any gastrointestinal discomfort often associated with their use. Keeping a regular schedule also helps sustain the proper drug levels in the bloodstream effectively.
Starting Dose of Azathioprine
For adults, starting a medication regimen with tailored dosages adjusted to body weight is practice, usually falling between 1.0 and 2.5mg/kg/day. This method ensures treatment plans can be customized according to individual responses and tolerances.
Azathioprine Dosage for Adults
For grownups, the amount prescribed may change based on the purpose. How one reacts to the medicine usually falls between 1.0 and 3.0 mg/kg/day. The goal of this dosage is to strike a balance between effectiveness and keeping side effects at bay.
Azathioprine Dog Dose
Azathioprine is commonly used in medicine to treat immune-related conditions in dogs. Dosages vary between 0.5 and 2.0 mg/kg/day based on health factors and treatment response. Comprehensive dosing guidelines and careful administration help achieve outcomes for various diseases when using Azathioprine as an adaptable treatment option.
Side Effects of Azathioprine
Azathioprine is quite powerful. It comes with a range of side effects that can vary from mild to severe and affect how well patients follow their treatment plan and need close monitoring.

Common Side Effects Encountered by Patients
The common side effects often seen are issues, with the stomach like feeling queasy and throwing up and blood related effects such as a drop, in blood cells known as leukopenia that could raise the risk of infections.
Potential Severe Adverse Reactions
- Liver damage can occur, leading to the need for liver function tests due to Hepatotoxicity.
- Pancreatitis is a condition that can sometimes happen when using Azathioprine and needs medical care, though it's uncommon.
Azathioprine Side Effects Long-Term
Using Azathioprine for a period may heighten the chances of contracting infections and raise the risk of developing conditions like lymphoma and skin cancers over time.
Azathioprine Side Effects Eyes
Eye problems are not expected. They may involve eye discomfort and eye-light alterations that are to be assessed to exclude any potential severe issues.
Azathioprine Side Effects in Dogs
In dogs undergoing treatment with medications, they may experience side effects similar to those in humans, like decreased bone marrow function and digestive system disturbances or liver toxicity, which highlights the importance of precise dosages and vigilant monitoring.
Azathioprine Hair Loss
Hair thinning or loss may not affect everyone. It can happen and usually gets better once you stop taking the medication or adjust the dosage.

Azathioprine Weight Gain
Weight increase is not typically linked with Azathioprine treatment. However, it's important to keep track of any changes in weight, as they could signal underlying health concerns.

Interactions with Other Medications
Common Drug Interactions and Their Implications
Azathioprine can interact with medications such as allopurinol used for treating gout and can significantly raise the chances of effects occurring; likewise, warfarin, a blood might see its effectiveness boosted when taken alongside Azathioprine.
Managing Polypharmacy in Patients on Azathioprine
To ensure management, it is important to assess all prescribed medications and over-the-counter drugs that the patient is using and make adjustments to the treatment plan if needed to reduce potential interactions and promote the safe utilization of Azathioprine.
Azathioprine and Alcohol
Drinking alcohol can make the harmful effects of Azathioprine on the liver worse; therefore, it's usually recommended that patients restrict or avoid alcohol to reduce strain on the liver. This detailed examination of Azathioprine's side effects and interactions highlights the importance of dosing and thorough patient education to improve treatment effectiveness and lower adverse outcomes.
Contraindications and Cautions
Successful use of Azathioprine relies on an approach to its dosing and administration due to factors that need to be considered for patient safety and treatment effectiveness.

Conditions Under Which Azathioprine Should Not Be Used
Azathioprine should not be given to patients who are allergic to the medication or any of its parts. It should also be avoided in those with liver or kidney issues because of how it is processed and removed from the body.
Genetic Factors Influencing Treatment Safety
Certain inherited tendencies, like TPMT (thiopurine methyltransferase) deficiency, can significantly affect the safety of using Azathioprine as a treatment option. People with TPMT activity face a likelihood of experiencing severe and potentially life-threatening myelosuppression when they receive typical doses of Azathioprine.
Foods to Avoid While Taking Azathioprine
Consuming caffeine and grapefruit juice can affect how Azathioprine is metabolized. To lower the chance of acid buildup in your body, you should cut back on foods in purines, like red meat and seafood.
Azathioprine Toxicity Symptoms
Symptoms of toxicity may manifest as severe gastrointestinal distress, jaundice, and pronounced leukopenia that require prompt medical care to avoid further issues.
Special Precautions in Administration
When giving Azathioprine, it's important to take precautions based on the patient's characteristics to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the treatment.
Precautions for Elderly Patients
Older patients might have energy problems and other health issues that require careful adjustments to the dosage of Azathioprine during treatment and frequent checks on their kidney and liver functions.

Azathioprine Nursing Considerations
Nurses need to watch for signs of infection and blood-related changes in patients while being proactive in handling side effects. They must ensure patients understand the significance of following doses and report any reactions promptly.

Guidelines for Pediatric Administration
When treating children with conditions such as arthritis, azathioprine medication dosages need to be calculated with precision according to their body surface area, and keeping a close eye on any signs of growth suppression or developmental delays is essential.

Management of Azathioprine Overdosage
Excessive intake of Azathioprine may result in potentially life-threatening issues that require identification and intervention to be crucial.

Signs and Symptoms of Overdosage
Symptoms such as nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, and a notable decrease in blood cells may indicate a severe health concern requiring prompt medical attention.
Immediate Actions and Antidote Information
If someone overdoses on Azathioprine medication by mistake or intentionally takes much of it beyond the prescribed dose limit, appropriate initial support measures should be started without delay. While there isn't an antidote, Azathioprine actions like performing gastric lavage to flush out the stomach contents, giving activated charcoal to limit further absorption, and providing supportive treatment to ensure proper hydration and electrolyte balance may be necessary.
By following these steps accurately, Azathioprine can be used effectively, reducing potential dangers and maximizing its beneficial effects for individuals needing this powerful immunosuppressive drug.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Storing and handling Azathioprine correctly is important to keep it practical and safe. Following these instructions can prevent contact and preserve the drug's quality.
Recommended Storage Conditions
Azathioprine tablets need to be stored at room temperature between 15 °C and 25°C (59°F and 77°F) away from light and moisture in a container with the lid tightly closed to prevent ingestion by children or pets.

Safety Measures During Handling and Disposal
- While managing Azathioprine medication, it's recommended to steer off skin contact or inhale dust from the tablets, essential for safety reasons when handling the medicine. Healthcare professionals are encouraged to wear gloves while administering the medication.
- When you no longer need or have expired Azathioprine, dispose of it to prevent environmental harm. For hazardous waste, it's best to take it to a pharmacy or medical center that can handle its disposal according to the local rules.
Withdrawal Symptoms of Azathioprine
Although Azathioprine is nonaddictive, stopping it suddenly may cause the return of the symptoms of the disease it was controlling before its discontinuation; being aware of these effects can help in devising strategies for managing the withdrawal phase.

Side Effects of Stopping Azathioprine
Ceasing Azathioprine abruptly could result in a worsening of the ailment it was intended to treat – for instance, heightened Crohn's disease or rheumatoid arthritis symptoms could occur prominently in patients due to increased immune system activity triggers, causing symptom aggravation or flare-ups to happen more frequently. As such, a choice to discontinue Azathioprine should always be made under the guidance of experts, with a plan that may involve gradually reducing doses or switching to alternative therapies to control the condition effectively.
Following these recommendations for storing and handling Azathioprine medication and for withdrawing it correctly helps maintain the effectiveness and safety of the therapy for patients who need long-term management of their immune-related conditions.
Azathioprine, Azathioprine Tablet FAQ
- Can Azathioprine affect your teeth
- Does Azathioprine cause weight gain
- Does Azathioprine cause hair loss
- How long does Azathioprine stay in your system after stopping
- How long does Azathioprine take to work
- How long can you stay on Azathioprine
- Is 100mg of Azathioprine a high dose
- Is Azathioprine a steroid
- Is Azathioprine a biologic
- Is Azathioprine a chemo drug
- What is Azathioprine?
- What does Azathioprine do?
- What is Azathioprine used for?
- What is a low dose of Azathioprine
- What is a high dose of Azathioprine
- What is Azathioprine used for in dogs
- What are the most common side effects of Azathioprine
- Which medication action would the nurse identify as the purpose of Azathioprine
Can Azathioprine affect your teeth
Certainly! Azathioprine can impact your teeth and could result in problems, like gum disease and mouth ulcers, that might impact your dental well-being.
Does Azathioprine cause weight gain
Azathioprine usually doesn't lead to an increase in body weight.
Does Azathioprine cause hair loss
Yes indeed! Azathioprine may lead to hair loss as a side effect.
How long does Azathioprine stay in your system after stopping
Azathioprine is usually eliminated from the body after discontinuation; however, its influence on the system may linger for several days.
How long does Azathioprine take to work
It can take anywhere from weeks to months for Azathioprine to fully take effect in treating conditions such as autoimmune disorders.
How long can you stay on Azathioprine
You may continue taking Azathioprine for years as it proves effective and your body tolerates it well, but make sure to have regular checkups with your healthcare provider to monitor any possible side effects and evaluate its ongoing efficacy.
Is 100mg of Azathioprine a high dose
Indeed, a dosage of 100 milligrams of Azathioprine is generally regarded as being on the side in terms of medication quantity.
Is Azathioprine a steroid
Azathioprine is not a steroid; it's a type of medication that helps suppress the system.
Is Azathioprine a biologic
Azathioprine isn't classified as a biologic; it's actually a drug that disrupts DNA synthesis to impact the immune system's functioning.
Is Azathioprine a chemo drug
Azathioprine is classified as a type of chemotherapy medication because it can inhibit or stop cell growth and division processes in the body. It is typically employed as an immunosuppressant for treating cancer; however, it does exhibit some similarities in its mechanisms with traditional chemotherapy medications.
What is Azathioprine?
Azathioprine is a drug mainly employed for immunosuppression, organ transplants, and conditions like arthritis and Crohn's disease by preventing the overgrowth of immune cells responsible for inflammation and harm.
What does Azathioprine do?
Azathioprine works by slowing down DNA production in cells, which decreases their growth and function levels. This process aids in stopping the system from targeting its tissues in autoimmune conditions or rejecting transplanted organs.
What is Azathioprine used for?
Azathioprine prevents rejection following organ transplants and manages autoimmune disorders such as arthritis and inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, along with lupus, by regulating the system to protect against self-tissue attack or transplant organ rejection.
What is a low dose of Azathioprine
The usual range for an amount of Azathioprine is between 25 and 50 milligrams as prescribed based on the individual's health condition and weight, with adjustments made according to how they react to the treatment and their test outcomes.
What is a high dose of Azathioprine
High doses of Azathioprine can usually fall between 2 and 3 mg per kg of body weight daily. The typical range for a 70 kg individual would be 140 to 210 mg each day. This amount is commonly prescribed for conditions or as a preventative measure against organ rejection after a transplant and necessitates close observation for any adverse reactions.
What is Azathioprine used for in dogs
Dogs are given Azathioprine mainly to control diseases, like immune-mediated anemia and certain skin conditions caused by the immune system or inflammatory bowel disease, by reducing the immune system activity against the body's cells and tissues.
What are the most common side effects of Azathioprine
Some of the side effects of Azathioprine are
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Lower white blood cell count (Leukopenia)
- Increased vulnerability to infections
- Abnormal liver enzyme levels
- Rash
Which medication action would the nurse identify as the purpose of Azathioprine
The nurse aims to use Azathioprine for immunosuppression purposes. This drug reduces the activity of the system to prevent it from harming the body tissues in autoimmune diseases or rejecting donated organs, like transplants. Azathioprine works by limiting the growth of cells called lymphocytes, which are essential in immune responses. This decrease in immune cell activity assists in treating disorders and prolongs the functioning of transplanted organs.