Benibuz, Benidipine
Introduction
Benibuz, also known by its commercial name Benidipine represents the pinnacle of advancements in the fight against hypertension, a common cardiovascular condition. Its role in treating blood pressure is crucial providing hope to millions globally by helping them control their health and improve their well-being. The journey of research and testing that led to the development and approval of Benidipine highlights its effectiveness and safety, for consumption.
Blood-pressure
Composition
The creation of Benibuz involves a combination of both active and inactive components to achieve the best results with minimal side effects. At the core of this medicine lies Benidipine Hydrochloride, a calcium channel blocker essential for managing high blood pressure. Alongside this key ingredient are inactive components that contribute significantly to the drug's effectiveness absorption, in the body and how well patients can tolerate it. These elements showcase the sector's dedication to producing comprehensive medications.
How It Works
Benidipine works by blocking calcium ions from entering the smooth muscle and heart cells leading to the widening of arteries and lowering blood pressure. Unlike drugs in its class, Benidipine has a unique effect on both the blood vessels and the heart.
When taken orally Benidipine goes through a process in the body involving absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. It is absorbed efficiently into the bloodstream and distributed throughout the body including tissues that control blood pressure metabolized in the liver and then excreted through the kidneys. This process ensures a prolonged antihypertensive effect
. Compared to calcium channel blockers Benidipine stands out due to its distinct effects on vascular smooth muscle and heart cells as well as its favorable metabolic pathway. These unique properties give it an advantage, in managing hypertension.
Uses
Benidipine, a medication is commonly used to treat high blood pressure and chest pain(1). These health issues affect people worldwide and have a notable impact on heart health and overall well-being(2). With its way of working Benidipine not only reduces blood pressure (3)but also offers various advantages for heart health highlighting its significance, in contemporary treatment approaches.
2. DrugBank - Benidipine
3. National Library of Medicine - Antioxidative effects of benidipine hydrochloride in patients with hypertension independent of antihypertensive effects. Relationship between blood pressure and oxidative stress
Primary Indications: Hypertension and Angina Pectoris
Benidipine is most effective in treating blood pressure(1) a condition known for its link to heart problems. It is also used to manage angina(2), a chest pain caused by blood flow to the heart due, to coronary artery disease. By treating these conditions Benidipine helps prevent and control diseases and related deaths.
1. Science Direct - Benidipine
2. PubMed - Clinical efficacy of benidipine for vasospastic angina pectoris
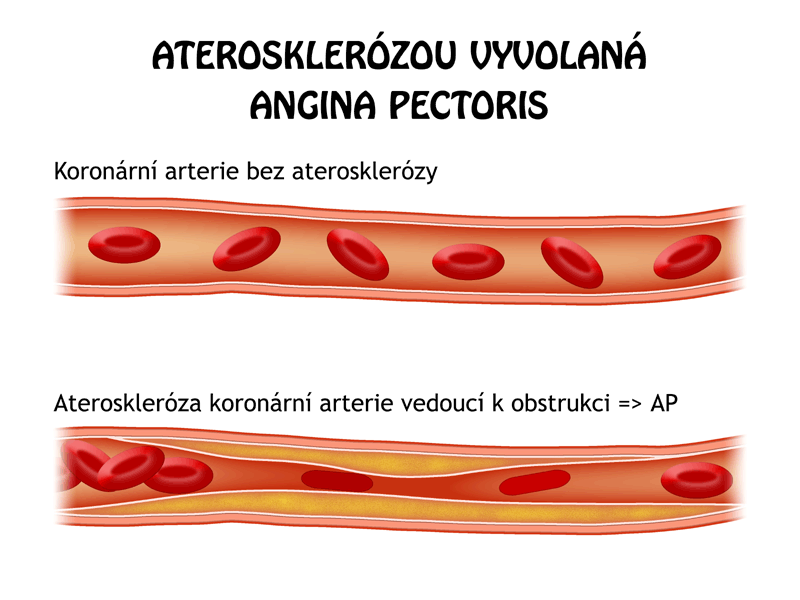
Angina Pectoris
Mechanism of Action: How Benidipine Lowers Blood Pressure
The effects of Benidipine in lowering blood pressure and relieving angina symptoms are due to how it works as a calcium channel blocker. It specifically blocks the entry of calcium ions into heart and blood vessel muscle cells through L-type calcium channels. This leads to the widening of blood vessels reducing resistance in blood vessels and ultimately lowering blood pressure.
Additionally, the impact of the drug on the heart muscle helps reduce the heart's workload and oxygen usage easing angina symptoms by reducing contractility and arterial tension. By improving oxygen supply to heart tissue it helps alleviate angina symptoms. Benidipine also improves the body's profile without causing reflex tachycardia, a common side effect seen with other medications, for high blood pressure.
Benefits in Cardiovascular Health
Benidipine offers advantages in the field of heart health beyond simply lowering blood pressure. Its ability to widen blood vessels improves flexibility in arteries. Eases the workload on the heart leading to a reduced risk of conditions like hypertensive heart disease and stroke.
Additionally, the effectiveness of the drug in enhancing blood flow makes it valuable for individuals with heart conditions boosting their ability to exercise and decreasing the occurrence of angina episodes.
Overall Benidipine plays a role in treating high blood pressure and angina showcasing its significant impact on modern medicine with its distinctive mode of action and excellent safety record as essential tools, for healthcare professionals tackling these common health issues.
Off-label Uses
The world of pharmaceuticals is full of examples where medications are used for more, than what they were approved for. Benidipine, which is mainly used to treat blood pressure and chest pain is a perfect example of this. Its additional uses highlight the range of effects it has on the body prompting further investigation into its wider therapeutic benefits.
Potential Off-label Applications of Benidipine
The potential applications of Benidipine beyond its approved uses cover a range showcasing its diverse mechanisms of action. Medical professionals have looked into using it for conditions like the Raynaud phenomenon, which causes blood flow to limbs due to vasospasms and nephropathy where its kidney-protecting properties may be helpful. Furthermore, studies on its ability to prevent atherosclerosis have spurred research on its benefits for patients with artery disease going beyond just managing angina
There's also an exploration into how it could help those with chronic kidney disease by increasing blood flow to the kidneys through vasodilation.In addition, it's being considered for patients with arterial disease to improve circulation, in the limbs and has shown promise in treating diabetic retinopathy by enhancing microcirculation.
Research and Evidence Supporting Off-label Uses
There is growing evidence to support the use of Benidipine for purposes not originally intended by its developers. This evidence is largely based on clinical trials and retrospective analyses. These studies shed light on the drug's ability to improve symptoms and alter disease progression in conditions outside of its scope.
For example, research indicates a decrease in proteinuria among patients with nephropathy hinting at a potential protective effect on the kidneys that warrants further exploration. Similarly, initial studies have noted enhancements in symptoms and disease indicators among individuals, with arterial disease and the Raynaud phenomenon.
Considerations and Limitations in Off-label Prescribing
The use of Benidipine in ways not approved shows promise, but it's crucial to proceed cautiously. When considering using the Benidipine off-label it's important to have a grasp of its effects thoroughly review available evidence and carefully assess individual patient factors.
Being transparent with patients about using Benidipine off-label is vital to ensure they fully understand and consent. It's essential to evaluate the quality and quantity of evidence supporting off-label use to prioritize safety and effectiveness.
Examining drug interactions and situations where Benidipine should not be used is critical due to the increased risk of side effects beyond approved uses.
Proper documentation of reasons for off-label use expected results and patient agreement is necessary for protection and ethical medical practice.
In summary, exploring the off-label use of Benidipine offers insights into addressing medical needs. Ongoing research may reveal more, about its potential across various conditions expanding treatment options.
Dosage and Administration
Benidipine plays a role in treating hypertension and angina pectoris requiring careful consideration of dosage and how it is administered to achieve the best treatment results, with minimal side effects. Following recommended guidelines is essential to ensure the effectiveness of the medication and the safety of the patient.
Standard Dosage Recommendations
The usual starting dose of Benidipine usually begins at a level and then increases gradually depending on how the patient reacts to it and how well they can tolerate it.
When treating blood pressure the initial dose generally begins at 4 mg per day with the possibility of increasing it to a maximum of 8 mg, per day based on how effective it is and how the patient responds.
In the management of angina pectoris similar dosing approaches are used, adjusted according to the seriousness of the condition and individual patient factors.
Adjustments for Specific Populations
It is crucial to adjust the dosage for certain groups to manage risks and improve the effectiveness of Benidipine. Older individuals, those with kidney issues, or people with liver problems may need doses due to changes in how their bodies process and respond to the medication.
These dose modifications require an approach that highlights the significance of evaluating each patient thoroughly. Starting patients on the smallest effective dose and gradually increasing it is recommended.
Regular monitoring and adjusting dosages as needed are essential for patients, with kidney or liver complications.
Administration Guidelines for Optimal Efficacy
For results, it is recommended to take Benidipine regularly either in the morning or evening whether with or, without food. Following a schedule improves how the drug works in your body helping to keep your blood pressure stable over time. It's important for patients to swallow the tablet whole and not crush or split it to ensure that the drug effects are released properly.
Side Effects
Although most patients tolerate Benidipine well there is a possibility of experiencing side effects, which can vary from being minor, to serious. It is important to be aware of and effectively manage these responses to ensure the comfort and safety of the patients.
Overview of Common Side Effects
Common side effects of Benidipine often consist of headaches, dizziness, flushing, and palpitations. These symptoms are usually mild and temporary typically improving as the body gets used to the medication. Less frequent but possible are digestive issues, like nausea and stomach discomfort.
Managing Mild to Moderate Side Effects
Dealing with mild, to side effects usually includes treating the symptoms without necessarily stopping Benidipine. If you feel dizzy or lightheaded it's recommended to get up from sitting or lying down to help with orthostatic hypotension. Staying well hydrated and making temporary dose changes can also help in handling these side effects.
Serious Adverse Effects and Emergency Responses
Rare but severe side effects necessitate medical care. These may involve pronounced blood pressure, fainting, and allergic responses marked by skin rash, itching, or swelling, especially in facial areas, like the tongue or throat. When faced with situations it is crucial to promptly discontinue the medication and seek immediate medical help to safeguard the patient well being.
Common Side Effects
The frequent side effects associated with Benidipine highlight the importance of monitoring and providing supportive care to address these reactions.
- Common issues like headaches and dizziness are often seen, reflecting the body's adjustment to the medication's effects.
- While flushing and palpitations can be uncomfortable they usually resolve on their own. Indicate the impact of the drug on the cardiovascular system.
- Managing symptoms such as nausea and stomach pain can be improved by taking Benidipine with food.
To improve tolerance to Benidipine it is crucial to focus on preventive measures and effectively manage symptoms. Regular check-ups and open communication between healthcare providers and patients are vital, for adapting treatment strategies as necessary. Ensuring optimal care outcomes.

Dizziness
Interactions
Exploring how Benidipine interacts with substances is crucial to guarantee its effectiveness and reduce negative outcomes. This part focuses on the interactions between Benidipine and other drugs or food offering advice, on effectively handling these interactions.
Drug-Drug Interactions: Common and Significant
Benidipine has the potential to interact with medications changing how they work or potentially increasing the chances of negative responses. Specifically, when used alongside blood pressure-lowering drugs it can enhance its effectiveness in lowering blood pressure requiring close observation and potential adjustments in dosage. Moreover, interactions, with substances that inhibit or stimulate CYP3A4 enzymes can influence Benidipine levels in the bloodstream affecting its effectiveness and safety.
Drug-Food Interactions: Dietary Considerations
When taking Benidipine it's important to note that food can play a role in how the medication works in your body. For example, grapefruit juice might affect how Benidipine is absorbed potentially making its effects stronger and increasing the likelihood of side effects. It is recommended to stick to a diet and seek advice from healthcare providers before making any major changes, to your eating habits.
Managing Potential Interactions
- It is crucial to check the medications a patient is currently taking to spot any possible interactions.
- When making changes to the treatment it's important to watch out for any changes in how the medications work or if there are any negative reactions.
- Having conversations with patients about the significance of informing them about new medications like over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements is vital, for handling interactions effectively.
Warnings and Precautions
Approaching the administration of Benidipine requires consideration especially when dealing with patients who have existing health conditions or are undergoing extended treatment. This part emphasizes the factors to consider in terms of assessing risks and monitoring needs.
Pre-existing Conditions and Risk Assessment
Patients who have had heart problems like heart failure or those with kidney or liver issues might need changes, in their medication dosage or different treatment options. It's crucial to evaluate the risks and benefits before starting Benidipine treatment.
Monitoring Requirements for Long-term Use
Long-term use of Benidipine requires monitoring of blood pressure kidney function and liver enzymes to promptly identify any negative developments. Regular assessments enable actions to maintain the safety and efficacy of the treatment plan.
Important Precautions
When giving Benidipine to groups of people and, in specific environmental or lifestyle situations it's important to follow safety precautions to protect the health of patients.
Specific Populations and Vulnerable Groups
Extra care should be taken when recommending Benidipine for at-risk populations such as seniors, expectant mothers, breastfeeding women and children. Customizing the treatment, for these groups helps guarantee their well-being and enhances the effectiveness of the treatment.
Environmental and Lifestyle Considerations
Various environmental elements and personal habits, like smoking and alcohol use have the potential to impact how well Benidipine works and the side effects it may cause. It is essential for patients to be educated on the significance of leading a lifestyle and refraining from activities that could diminish the positive effects of the medication.
Careful Administration
It's important to be cautious when giving Benidipine to those who are more vulnerable, to negative effects. This helps in getting the most out of its treatment benefits while keeping the patients safe.
Guidelines for Elderly Patients
Elderly individuals might show sensitivity to Benidipine so it's recommended to start with lower doses and adjust gradually depending on how they tolerate it and respond. It's important to watch for low blood pressure and monitor their kidney function carefully in this group.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
The safety of Benidipine, for women and nursing mothers has not been confirmed. It should only be prescribed if the benefits outweigh the risks to the baby after considering treatment options carefully.
Special Considerations for Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Benidipine, in children still needs investigation to reach a definitive conclusion. When considering its administration to this age group it is crucial to weigh the advantages against the associated risks while closely monitoring and adjusting the treatment according to each child's individual requirements.
Contraindications
It is essential to know the restrictions associated with Benibuz (Benidipine) to keep patients safe and achieve treatment results. Clearly outlining both relative contraindications helps healthcare professionals make well-informed choices during patient care.
Absolute Contraindications: Conditions and Drug Interactions
Patients who have a known sensitivity to Benidipine or any of its ingredients along with those with left ventricular dysfunction or unstable heart failure should not take this medication. It is crucial to avoid drug interactions that could pose risks, such, as those involving strong CYP3A4 inhibitors as they are considered absolute contraindications.
Relative Contraindications: When Caution Is Needed
When dealing with contraindications it is important to be cautious when using Benidipine. Patients with moderate liver issues kidney problems or a tendency towards orthostatic hypotension should be carefully evaluated and dosage adjustments may be necessary. It is crucial to balance the advantages of treatment against the risks, in such situations.
Handling and Storage
The effectiveness and safety of Benidipine depend on how it's handled and stored factors that guarantee the maintenance of its pharmacological properties.
Proper Storage Conditions to Ensure Drug Stability
It's best to store Benidipine at room temperature shielded from light and moisture to ensure it stays stable and effective. Use the packaging to safeguard the medication from external elements that might affect its quality.
Handling Precautions for Safety
It's important to take precautions to avoid exposure to Benidipine, especially for those who are not prescribed the medication. Both healthcare providers and patients need to make sure that the medicine is stored away, from children and that any leftover or expired medication is disposed of properly.
Overdosage
In case of an overdose, it is crucial to know the actions to take in order to minimize any possible negative consequences.
Symptoms of Overdosage and Immediate Actions
Symptoms of taking too much Benidipine could lead to serious low blood pressure, slow heart rate, and lightheadedness. It's important to act by providing supportive care like giving activated charcoal early on and keeping an eye on vital signs to avoid any further issues.
Medical Interventions and Supportive Care
Treatment for an overdose of Benidipine focuses on providing support to help normalize blood pressure and heart rate. Depending on the severity of the situation interventions such, as administering fluids using vasopressors and in extreme cases considering cardiac pacing may be necessary.
Administration to Special Populations
Unique groups of people require customized methods, for giving Benidipine to guarantee it is safe and effective.
Adjustments and Monitoring for Elderly Patients
Elderly individuals might require lower starting doses and careful adjustments when taking Benidipine due, to sensitivity. It is recommended to check blood pressure and kidney function to reduce the chances of negative outcomes.
Safety and Efficacy in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
The safety of Benidipine, for women and nursing mothers has not been confirmed. It is recommended to use it during pregnancy only if the benefits outweigh the risks to the fetus and caution should be exercised when given to nursing mothers.
Dosing and Safety in Pediatric Patients
The safety and efficacy of Benidipine in children has not been definitively proven. When considering its use in this group it is important to weigh the benefits, against the risks while closely monitoring for any negative effects.
Conclusion
Benibuz (Benidipine) signifies progress in treating high blood pressure and chest pain capturing the intricate nature of contemporary medications. Though its use in settings is clearly outlined, following recommendations regarding restrictions, storage, and usage is crucial. The future path of research and utilization is expected to concentrate on broadening its healing capabilities guaranteeing that Benidipine remains an asset, in inpatient treatment.