Betaferon Injection
- Introduction to Betaferon Injection
- Uses of Betaferon Injection
- Off-Label Uses of Betaferon Injection
- Composition and Active Ingredients
- Mechanism of Action: How Betaferon Works
- Dosage and Administration
- Storage and Handling Precautions
- Warnings and Contraindications
- Interactions with Other Medications
- Interferon side effects
- Important Precautions Before Starting Betaferon
- Administration in Specific Populations
- Overdose Management
- Careful Administration Practices
Introduction to Betaferon Injection
Overview of Betaferon
Betaferon is a known drug used for treating multiple sclerosis (MS). It acts as an immunomodulator that helps decrease the occurrence and intensity of relapses in individuals with relapsing forms of MS. The production of Betaferon is done meticulously to slow down disease advancement and enhance the well-being of patients.
Therapeutic Classification
Betaferon belongs to the group of medications known as interferon beta . It is created artificially to mimic the functions of proteins found naturally in the body that regulate reactions. Betaferon is classified as a type of treatment that disease-modifying therapy (DMT), indicating its focus on changing the development of MS or solely relieving symptoms.
Historical Background and FDA Approval
Betaferon was first introduced in 1990 as one of the pioneering therapies for multiple sclerosis (MS). The FDA gave its approval in 1993. This marked progress in how this long-term condition is managed. The effectiveness and safety of Betaferon have been extensively recorded through years of application.
Uses of Betaferon Injection
Treatment of Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis (RRMS) interferon
Betaferon is mainly used for individuals with RRMS, which stands for relapsing-remitting sclerosis. The prevalent type of MS condition among patients diagnosed with this neurological disorder. It aids in decreasing the occurrence of relapses. Hinders the progression of physical disabilities over time.
Delaying Disease Progression in Clinically Isolated Syndrome
For individuals with clinically isolated syndrome (also known as CIS), Betaferon has demonstrated effectiveness in postponing a confirmed sclerosis (MS) diagnosis, emphasizing the importance of early intervention to minimize lasting neurological impact.
Management of Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis (SPMS)
Individuals with SPMS may find that betaferon can decrease the frequency of relapses in situations where ongoing inflammatory activity is present. Though it may not halt progression entirely, it is an asset in managing the disease.
Off-Label Uses of Betaferon Injection
Treatment of Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD)
Betaferon has been investigated as a remedy for Treatment of Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD) disease in which a disorder impacts the optic nerves and spinal cord. This immunomodulatory impact shows potential despite not being a treatment option.
Potential Use in Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (CIDP)
Studies indicate that Betaferon could be advantageous for people with CIDT (Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy). The potential of Betaferon in diminishing inflammation presents a path for research and exploration.
Interferon covid
Interferons have been noted to have an impact on the pathogenesis of SARS Covid.
Other Investigational Uses in Autoimmune Diseases
Ongoing research is being conducted to evaluate how effective Betaferon is, in treating conditions showing promising initial results, in regulating immune responses across different diseases.
Composition and Active Ingredients
Active Ingredient: Interferon Beta-1b
The main ingredient in this medication is interferon beta, a man-made protein designed to imitate the immune-regulating proteins found naturally in the body. It is crucial for the drug's positive impacts on health.
Inactive Ingredients and Preservatives
- Sodium chloride
- Human albumin
- Sodium hydroxide
These components ensure stability and enhance the medication's usability.
Formulation Details
Betaferon comes in a dried form that needs to be mixed with a liquid before use to make dosing precise and administration simple.
Mechanism of Action: How Betaferon Works
Immunomodulatory Properties
Betaferon works by regulating responses, decreasing the function of cells that cause inflammation, and supporting mechanisms that help control the system's activity. This is essential for managing the autoimmune response in multiple sclerosis (MS).\
Reduction of Inflammatory Cytokines
The medication reduces the number of proteins, like interleukin–2 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, that are linked to the development of sclerosis.
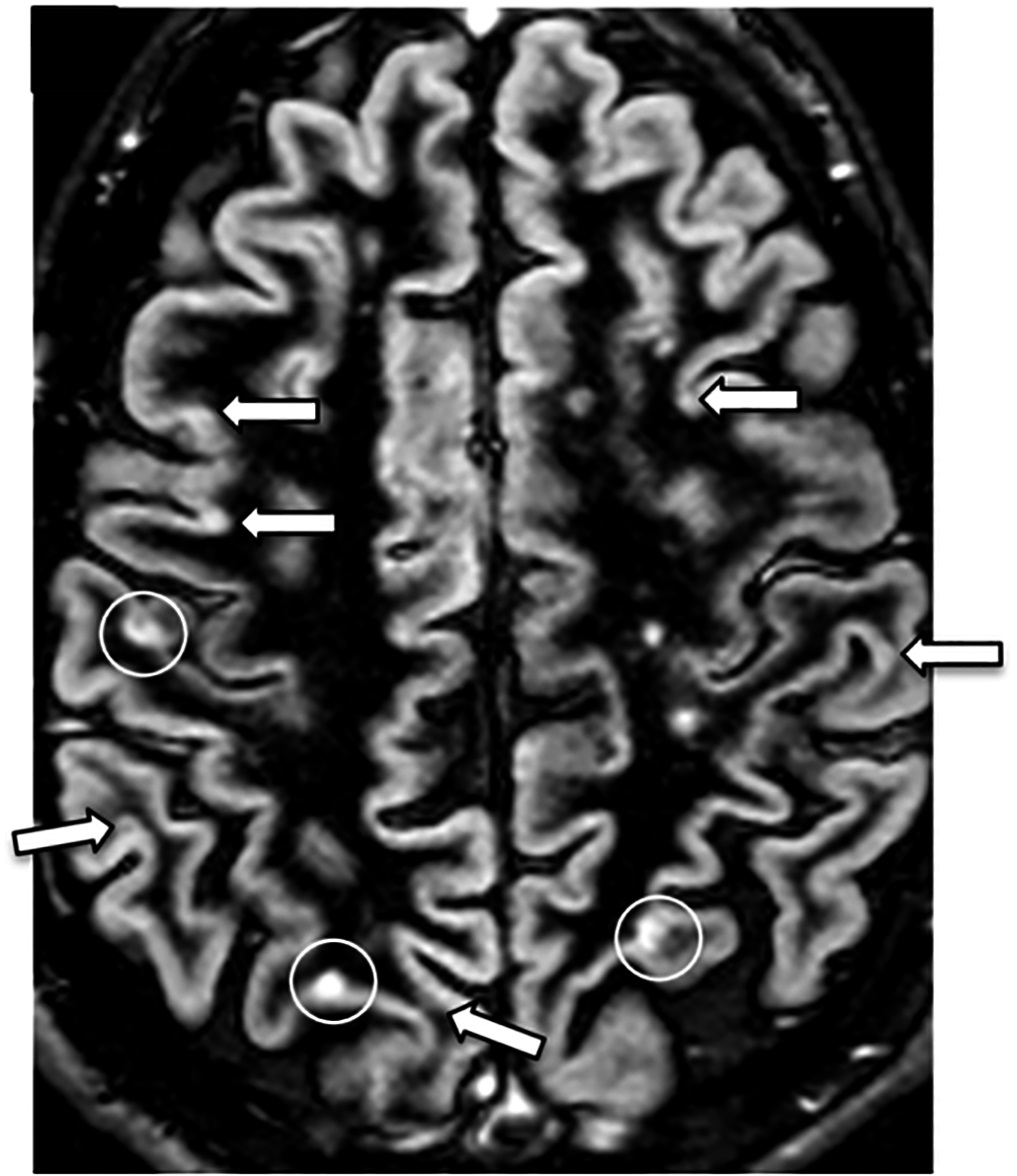
Prevention of Demyelination and Nerve Damage
Betaferon helps to maintain the health of the myelin sheath and nerve fibers by influencing responses and safeguarding function against damage.
Interferon therapy
Interferon treatment involves using proteins in the laboratory to assist the body system in combatting cancer cells as well as viruses and other types of infections.
Interferon innate or adaptive
Interferons, known as IFNs, are cytokines that are controlled at the level and play a role in the body's natural defense against viruses.
Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosage for Adults
The usual dose is 250 micrograms ( 8 million IU) given as an injection every second day, with potential need, for dosage changes depending on individual response levels.
Instructions for Self-Administration
Patients are taught how to give themselves the injection to reduce any discomfort they may feel during the process. It is important to switch up where the injections are given to avoid irritating the skin.
Frequency of Dosing and Duration of Treatment
Treatment usually needs to be continued and requires checkups to assess its effectiveness and make any necessary dosage changes accordingly. For the best possible results, it is essential to follow the dosing schedule.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Optimal Storage Conditions
Betaferon should be stored at temperatures between 2 and 8 degrees Celsius (36 and 46 degrees Fahrenheit). If a refrigerator is not accessible, it can be kept at room temperature for periods as long as it is shielded from light.
Stability and Expiry Information
Betaferon that has been reconstituted should be used away. Kept in a refrigerator for up to three hours at most. Make sure to follow the expiration dates closely to ensure its effectiveness.
Safe Disposal of Used Syringes
Be sure to dispose of used needles in designated sharps containers to prevent harm and help protect the environment's safety.
Warnings and Contraindications
Absolute Contraindications
Betaferon is contraindicated in individuals with a known hypersensitivity to interferon beta-1b or any of its components. Severe hepatic impairment, decompensated liver disease, and untreated depression are also absolute contraindications to its use.
Conditions Requiring Caution
Patients who have a past of seizures, heart issues, or thyroid problems should be cautious when using Betaferon medication. Regular monitoring is required for individuals with existing liver problems or blood abnormalities while undergoing treatment.
Risk of Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, may occur. Patients experiencing symptoms such as difficulty breathing, severe rash, or swelling should discontinue treatment immediately and seek medical attention.
Interactions with Other Medications
Potential Drug-Drug Interactions
Betaferon could interact with medications that suppress the system and increase the chance of infections occurring severely. When using Betaferon alongside interferons or antiviral drugs it is important to evaluate the potential risks involved.
Effect of Betaferon on Other Therapies
The immunomodulatory effects of Betaferon can influence the efficacy of vaccines, particularly live attenuated vaccines, which are generally contraindicated. Interaction with hormonal therapies or anticoagulants may necessitate dose adjustments.
Monitoring Requirements
Patients taking Betaferon should have blood tests to check their liver function and blood cell counts as well as monitor their thyroid activity for early detection and treatment of any possible issues.
Interferon side effects
Common Side Effects
- Injection Site Reactions: Redness, pain, or swelling at the injection site is common. Proper injection techniques can help minimize discomfort.
- Flu-Like Symptoms: Fever, chills, and muscle aches may occur during the initial weeks of treatment but often subside with continued use.
- Headaches and Fatigue: These symptoms are frequently reported and can be managed with hydration and rest.

Rare but Serious Side Effects
While rare, some patients may experience:
- Liver Dysfunction: Elevated liver enzymes can indicate hepatotoxicity, requiring close monitoring and possible dose adjustment.
- Severe Allergic Reactions: Anaphylaxis, though infrequent, is a life-threatening condition necessitating immediate intervention.
Interferon side effects long-term
Autoimmune conditions, disturbances, heightened susceptibility, to infections, cardiovascular incidents and blood disorders are health concerns to watch out for.
Important Precautions Before Starting Betaferon
Baseline Liver Function and Blood Count Tests
It's important to get baseline tests done for liver enzymes and complete blood counts before starting Betaferon therapy to have a reference point for monitoring purposes.
Monitoring for Depressive Symptoms
It's important to check if patients have any history of depression or thoughts of suicide before starting treatment. It is crucial to conduct health assessments throughout therapy as depressive symptoms could worsen.
Avoidance of Live Vaccines
Avoid using vaccines as they might not offer protection and could raise the chances of negative reactions; exploring other vaccination approaches is best.
Administration in Specific Populations
Administration to Elderly Patients
Age-Related Adjustments in Dosage
As people grow older, their bodies may need amounts of medication because of changes in how their bodies process and get rid of drugs.
Monitoring for Increased Sensitivity to Side Effects
As people age, some may be more sensitive to side effects, like liver issues or tiredness, and may need to be checked often.
Use During Pregnancy and Lactation
Safety Profile for Pregnant Women
It is recommended to use Betaferon during pregnancy only if the benefits outweigh the risks involved. Concerns about its effects on development require an evaluation of risk and benefit factors.

Recommendations for Nursing Mothers
There is no information regarding the presence of Betaferon in breast milk, so it is advisable for mothers who are breastfeeding to seek advice from their healthcare provider before starting treatment.
Pediatric Use
Efficacy and Safety in Children
Betaferon is not frequently prescribed for children because there is information on how effective and safe it is for younger patients requiring specific protocols to be followed when considering its use in this population.
Overdose Management
Signs and Symptoms of Overdosage
Taking too much Betaferon may lead to flu-like symptoms, extreme tiredness, and liver issues; it could also make neurological symptoms worse.
Immediate Steps to Take
If someone thinks they've taken much of the medicine it's essential to stop using it away and get help from a doctor. Providing care is key, in handling the symptoms of an overdose.
Supportive and Symptomatic Treatment
Symptomatic care is crucial for treatment. It may involve providing fluids and using fever-reducing medications for temperatures while also monitoring liver function levels. Hospitalization might be required in some instances.
Careful Administration Practices
Proper Injection Techniques
Patients need to learn injection methods to lower infection risks and improve treatment compliance, including the crucial step of using alcohol swabs before administering injections.
Avoiding Contamination During Preparation
Reconstitute the dried powder in a space to avoid contamination, and do not reuse syringes or vials.
Rotating Injection Sites
To reduce the chances of experiencing reactions at the injection site, patients are advised to switch between injection sites. Typical areas for injections include the thighs, arms and abdomen.
Betaferon Injection FAQ
- What is betaferon used for?
- Betaferon can be prescribed for adults with active?
- When is interferon released?
- What interferon does?
- What interferon attaches to a cell?
- What interferon is used for hepatitis c?
- How interferon inhibits viral replication?
- How interferon beta-1b works?
- Can interferon treat cancer?
- Can interferon cause hypothyroidism?
- Can interferon cause dementia?
- Can interferon cause neuropathy?
- Can interferon cause cancer?
- Interferon are produced by?
- Are interferon cytokines?
- Are interferon innate or adaptive?
- Are interferon species specific?
- Why does interferon cause depression?
- Why is interferon unusual?
- Which interferon is used in multiple sclerosis?
- Which interferon for ms?
- Which interferon activates macrophages?
What is betaferon used for?
Betaferon is a medication prescribed for adults dealing with sclerosis (MS).
Betaferon can be prescribed for adults with active?
Betaferon is recommended for adults who have relapsing-remitting sclerosis (MS).
When is interferon released?
Cells release interferons (IFNs) when viruses, bacteria, parasites, or tumor cells are detected.
What interferon does?
Interferons play a role in supporting the system's ability to combat infections, cancers, and autoimmune conditions.
What interferon attaches to a cell?
IFNs alpha and beta attach to a receptor located at the cell surface and are known as type 1 IFNs; in contrast, IFN gamma attaches to a receptor and is categorized as type 2 IFNs.
What interferon is used for hepatitis c?
Interferons alpha (IFNs α ) and lambda (IFNs λ ) are commonly employed to treat hepatitis.
How interferon inhibits viral replication?
Interferons work to stop viruses from multiplying by creating a defense mechanism within the cells of the host.
How interferon beta-1b works?
Interferon beta boosts the production of MHC I proteins, which helps in showcasing antigen-derived peptides effectively.
Can interferon treat cancer?
Adjuvant therapy, with interferon, is a form of cancer treatment administered following surgery to assist in delaying or preventing the cancer from returning.
Can interferon cause hypothyroidism?
In individuals receiving IFNα therapy, hypothyroidism presents in 2.4- 19 percent of cases, among those who already have thyroid autoimmunity.
Can interferon cause dementia?
IFN alpha therapy often leads to a combination of mood changes, along with memory issues and slower cognitive function, which can resemble a form of cortical dementia.
Can interferon cause neuropathy?
Rarely do patients undergoing treatment with IFN-α experience neuropathy, which is an unusual side effect in this context.
Can interferon cause cancer?
IFNs may impact, or even have negative consequences, on eliminating cancer. They could potentially aid in the evasion of cancer cells from the immune system.
Interferon are produced by?
White blood cells, known as lymphocytes, play a role in the system. Specifically focusing on T cells, killer (NK) cells, and killer (K) cells alongside macrophages contribute significantly to the body's defense mechanisms.
Are interferon cytokines?
Interferons, known as IFNs, are cytokines that are controlled by gene expression and play roles in the body's defense against viruses.
Are interferon innate or adaptive?
Interferons (IFNs), which are controlled by gene expression, act as components in the body's defense against viruses.
Are interferon species specific?
Interferons consist of a group of proteins that are similar in structure and unique to each species. They work to boost the system when the body detects invaders, such as viruses, bacteria, parasites, and cancer cells.
Why does interferon cause depression?
IFNa treatment reduces tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), which is needed as a coenzyme in the production of serotonin and other neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine; this could potentially lead to an increased risk of depression.
Why is interferon unusual?
Interferons stand out for their nature as proteins that play a role in the body's defense mechanisms, serving multiple purposes.
Which interferon is used in multiple sclerosis?
Beta interferons, which are referred to as disease-modifying therapies (DMTs), are used to treat relapsing sclerosis (MS) and, in certain instances, secondary progressive MS as well.
Which interferon for ms?
Beta interferons, also known as disease-modifying therapies (DMTs), are commonly used to treat relapsed n g scaler o sis (MS). In certain instances, they may also be prescribed for secondary progressive MS patients.
Which interferon activates macrophages?
Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), a type of interferon, triggers the activation of macrophages.