Clip, Tranexamic acid
- Introduction
- Overview of Tranexamic Acid
- Composition of Tranexamic Acid
- How Tranexamic Acid Works
- Uses of Tranexamic Acid
- Off-Label Uses of Tranexamic Acid
- Tranexamic Acid Dosage and Administration
- Tranexamic Acid Side Effects
- Tranexamic Acid Interactions with Other Medications
- Warnings and Tranexamic Acid Contraindications
- Important Precautions
- Administration to Special Populations
- Overdose Information
- Handling and Storage Precautions
- Careful Administration Practices
Introduction
Tranexamic acid has become well-known in the field of medicine for its effectiveness in decreasing bleeding and treating bleeding disorders. The article explores the background of this chemical compound while highlighting its impact on modern medicine.

Overview of Tranexamic Acid
Tranexamic acid is a compound derived from the amino acid lysine. It works mainly by blocking the conversion of plasminogen into plasmin, a molecule that breaks down fibrin in the blood clot formation process. By stopping fibrin from breaking down, tranexamic acid helps maintain clot stability and reduces bleeding to some extent.
- The Characteristics of chemicals
- Understanding how the coagulation cascade functions
- The study of how drugs move through the body and are processed
Brief History and Development
Tranexamic acid was first found in the 1960s by Utako Okamoto, a scientist working with her husband to develop a solution for reducing bleeding during procedures and post-surgery recovery. Exploring the creation and practical uses in experiments. The changing applications of medicine have occurred throughout the years.
Importance in Modern Medicine
Tranexamic acid has become incredibly important in today's medical field for situations where quick action is needed to avoid blood loss. Its uses cover a range of health issues and surgeries.
- In trauma and emergency surgery, it is essential to use techniques that help prevent bleeding.
- The function of overseeing flow and genetic blood clotting conditions.
- In the fields of dentistry and dermatology new applications are, on the rise.
Ultimately, tranexamic acid continues to play a role in treating bleeding because of its ability to prevent blood clot breakdown. Its evolution from a discovery to a medication highlights its essential contribution to improving healthcare and preserving lives.
Composition of Tranexamic Acid
Tranexamic acid is an antifibrinolytic known for its ability to reduce bleeding effectively by stabilizing blood clots.
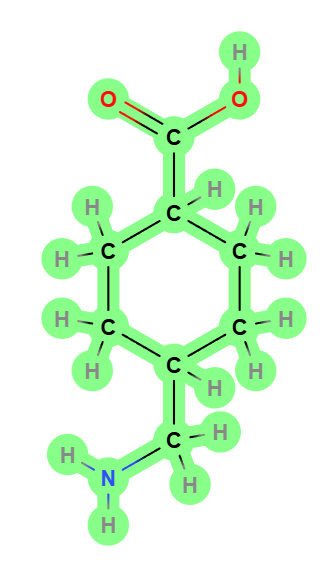
Chemical Structure
The structure of acid focuses on the amino acid lysine, which has been adjusted to improve its connection with plasminogen. This hinders the transformation of plasminogen into plasmin and protects the stability of fibrin in blood clots.
Active Ingredients
Acids' main component is their namesake molecule, which acts as a player in preventing fibrinolysis breakdown processes within the body's systems. Its effectiveness in treatments is attributed to this ingredient present in various healthcare scenarios.
Formulations Available
Tranexamic acid comes in forms designed to suit medical situations.
- Oral tablets are often recommended for treating bleeding and after dental surgeries.
- In scenarios, like surgeries and cases of trauma treatment injections are used.
- Topical remedies are commonly used in dermatology clinics to address issues with skin discoloration and melasma.
Tranexamic Acid Natural Alternative
Although tranexamic acid is artificial in a lab setting, substitutes with antifibrinolytic attributes are available as well. Take the bioflavonoids present in fruits, for example. They can enhance the strength of blood vessel walls and slightly lessen bleeding. Nonetheless, these natural options may not provide the precise effects of tranexamic acid but could be beneficial for minor situations or as supplementary treatment.
How Tranexamic Acid Works
Tranexamic Acid Mechanism of Action
Tranexamic acid interferes with the activation of plasminogen by binding to its Kringle domains. This prevents the conversion of plasminogen into the enzyme that breaks down fibrin, helping to keep blood clots stable.
Effect on Blood Clotting Process
Tranexamic acid has an impact on the process of blood clotting.
- It helps keep blood clots stable by stopping the fibrin protein from breaking down which's crucial, for forming clots.
- Effectively decreases blood loss during surgeries and in situations such as bleeding incidents.
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
The way tranexamic acid moves in the body shows that it is absorbed quickly into the bloodstream and reaches its levels within an hour of being taken. The drug's effects on stopping bleeding happen fast and last for a time, depending on how it is given.
Tranexamic Acid Before and After
In depth analysis of how tranexamic acid's used shows improvements, in patient outcomes.
- Prior, to treatment individuals might encounter bleeding and irregularities in the formation of blood clots.
- Following the treatment administration often results in a decrease, in bleeding incidents and an increase, in the stability of blood clotting is frequently observed.
This comparison clearly shows the importance of acid in improving patient care through the effective management and prevention of excessive bleeding.
Uses of Tranexamic Acid
Medical Indications
Tranexamic acid is commonly recommended for situations in which there is a risk of bleeding or when bleeding is already an issue.
- Menorrhage substantially decreases the amount of blood flow in women experiencing periods.
- Hereditary Angioedema doesn't serve as a treatment option, but it can be helpful in lessening the number of attacks in specific individuals.
- In emergency medical care settings, trauma management involves the use of medications to prevent bleeding in patients with injuries, which have been shown to increase significantly the chances of survival when given promptly following the injury occurrence.
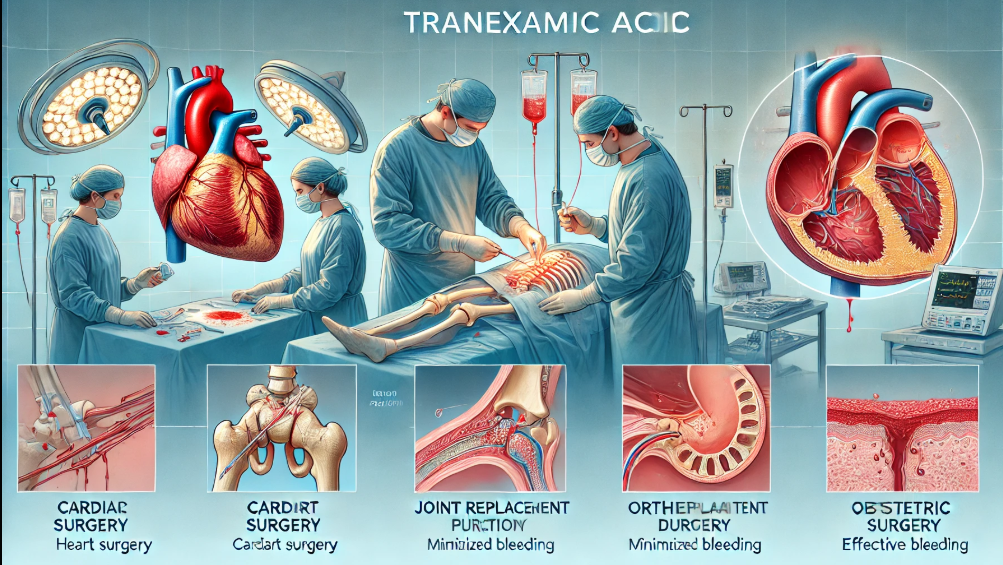
Surgical Applications
Tranexamic acid plays a role in environments and is especially valuable during procedures that are prone to significant blood loss.
- Cardiac surgery is performed to decrease the need for blood transfusions and lower the risk of bleeding complications.
- Orthopedic surgery plays a role in minimizing the requirement for blood transfusions during surgeries like hip or knee replacement procedures.
- Obstetric surgery dramatically reduces the chances of postpartum bleeding following deliveries and other obstetric surgeries.
Tranexamic Acid for Dental Bleeding
In dentistry, tranexamic acid helps control bleeding in individuals with blood clotting disorders or those having intricate tooth extractions.
- Mouthwash, commonly utilized to minimize bleeding and after procedures, is referred to as oral rinse.
- After dental procedures are done and dusted with like a rockstar, in the world or any other world for that matter, whatever floats your boat, postoperative care swoops in like a hero to save the day. It's about keeping things nice and tidy inside your mouth to help you recover smoothly and safely without any surprises of bleeding more than necessary.
Tranexamic acid's wide range of uses showcases its adaptability and efficiency in medical situations. This makes it a crucial resource for managing sudden and ongoing bleeding issues in healthcare settings.
Off-Label Uses of Tranexamic Acid
Tranexamic acid is used for purposes that are not officially approved in medicine. It has proven valuable in nonstandard situations due to its antifibrinolytic properties, which bring notable advantages to patients' well-being in different areas of medicine.
Tranexamic Acid in Dermatology
More and more dermatologists are now using acids to address melasma and other hyperpigmentation issues.
- Managing Melasma: Tranexamic acid is used either orally or topically to diminish the visibility of skin patches that are often worsened by sun exposure.
- Post-procedural bleeding is applied after procedures to reduce bleeding and bruising, which improves recovery and outcomes.

Tranexamic Acid for Postpartum Hemorrhage
Although not commonly recognized for this purpose specifically. Tranexamic acid has demonstrated effectiveness in treating postpartum hemorrhage.
- This condition is a contributor to mortality on a global scale. Providing care after giving birth can significantly lessen the risk of excessive bleeding in mothers and lead to better results overall.
Tranexamic Acid for Angioedema
Although tranexamic acid is not a treatment for angioedema, it is used preventively to lessen the intensity and occurrence of episodes.
- Using it preventively can assist in handling the symptoms linked to this condition that could be life-threatening
Use in Orthopedic Surgery
Tranexamic acid is commonly utilized in surgery to minimize blood loss in joint replacement procedures and spinal surgeries.
- Joint replacements significantly reduce the necessity for blood transfusions and enhance the speed of recovery in hip and knee replacement surgeries.
- Spinal surgery helps minimize bleeding, which can improve results and decrease complications.
Tranexamic acid's expanding range of uses in fields such as dermatology and orthopedics highlights its versatility. Enhance treatment results across different medical disciplines.
Tranexamic Acid Dosage and Administration
Tranexamic acid plays a role in treating bleeding disorders. It requires precise dosages based on conditions and patient demographics to achieve effectiveness and reduce risks.

Dosage Guidelines for Different Conditions
The dosage of tranexamic acid differs based on the ailment being addressed.
- Excessive menstrual bleeding can be managed by taking 1300 mg three times a day throughout your menstrual cycle.
- In preparation for surgery, prevention measures involve giving a dose of 10 to 15 mg/kg followed by a similar dose every 6 to 8 hours after the operation is completed.
Tranexamic Acid Maximum Dose
It is advised not to exceed 4 grams of acid per day, and the dosage should be divided to minimize the risks of adverse effects, such as thromboembolic events, that may arise with higher doses.
Tranexamic Acid Dose for Bleeding
Dealing with bleeding situations in a management setting:
- For adults with bleeding issues, administer 1 gram through an IV drip in 10 minutes initially; then, consider giving another 1 gram if the bleeding persists.
- For kids weighing 10 mg/kg of body weight, 10 mg/kg should be administered initially, followed by a continuous infusion as per the response to treatment.
Routes of Administration
Tranexamic acid can be given using methods based on the medical requirements.
- You can easily take it in tablet form.
- Intravenous administration is ideal, for response, in scenarios when immediate systemic impact is needed.
- Apply topically for skin or mucosal bleeding in a localized manner.
Adjustments for Specific Populations
Changes in the amount of acid might be required for specific demographics.
- To prevent the medication from building up in the body, dosage adjustments should be made according to the patient's function and creatinine clearance rate.
- Older patients may require observation and adjustments in medication doses because their kidney function may be decreased.
- When giving medicine to children, the dosage must be calculated according to their weight and illness.
This detailed review guarantees that healthcare professionals can safely and effectively use acid for a range of patients and medical scenarios.
Tranexamic Acid Side Effects
Tranexamic acid plays a role in treating bleeding issues; however, it does come with side effects that vary in severity from common, mild ones to rare yet serious ones that can significantly affect a patient's well-being. Being aware of these responses is vital for both healthcare professionals and patients.

Common Side Effects
When individuals take acid for bleeding relief purposes, they may encounter various usual side effects.
- Frequent complaints include problems like queasiness and stomach upset leading to vomiting and diarrhea episodes.
- Mild rashes and other allergic reactions may occur. They usually go away quickly.
Less Common but Serious Adverse Reactions
Some rare adverse reactions may necessitate intervention.
- Tranexamic Acid and Weight Gain Concerns: It's not typical for acid to cause weight gain, but any sudden changes in weight should be checked by a doctor.
- Tranexamic Acid and Seizures Concerns exist regarding the possibility of seizures in individuals prescribed doses or those having risk factors such as renal dysfunction.
Tranexamic Acid Long-term Side Effects
Extended use of acid may result in the development of severe health complications.
- Extended utilization has been associated with vision issues that ought to be checked by an expert.
- Thromboembolic Incidents: While uncommon, there is a chance of blood clots forming, potentially causing thrombosis or pulmonary embolisms, particularly in people with a predisposition.
Keeping an eye on these side effects is essential to ensure the acid treatment is safe and works well for the patient.
Tranexamic Acid Interactions with Other Medications
Tranexamic acid is a type of medication that helps with blood clotting and can interact with drugs in ways that may impact how well they work and how safe it is for patients to use them effectively.

Common Drug Interactions
Certain drugs might disrupt how tranexamic acid works. Raise the chances of experiencing side effects.
- When using contraceptives together, there is a chance of experiencing blood clotting issues because of the blood clot-promoting effects of estrogen.
- When using acid, be cautious, as it may increase the chances of bleeding if combined with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Medications such as warfarin or heparin may interact with acid in ways that could reduce its effectiveness or raise the risk of bleeding.
Interaction Mechanisms
When tranexamic acid interacts with drugs, it usually affects how those medications work in the body, either by changing their effects or how they are processed.
- Pharmacodynamic interactions occur when tranexamic acid and another medication impact a process such as blood clotting. These interactions can result in increased or decreased effects of both drugs.
- Pharmacokinetic interactions can change how tranexamic acid is absorbed into the body and distributed or metabolized within it, impacting its blood levels and effectiveness in treatment.
Management of Tranexamic Acid Drug Interactions
To effectively handle these drug interactions, one must approach them with deliberation and strategic foresight.
- Assessing Risks and Benefits: Consider the need to use medications at the time by weighing the potential advantages and disadvantages.
- Consistently monitor patients for any signs of side effects or if the treatment is not working as well.
- Adjusting Dosages: To prevent interactions, consider changing the doses of acid or other medications that may interact with it.
Ensuring the handling of interactions involving acid is crucial for preventing issues and attaining the intended treatment benefits, safeguarding patient well-being and treatment effectiveness.
Warnings and Tranexamic Acid Contraindications
Tranexamic acid is a medication for controlling bleeding. It should be handled carefully in specific situations to ensure patient safety and maximize its effectiveness.

Absolute Contraindications
In cases, it is best to avoid the use of acid because of the potential for severe adverse outcomes.
- Patients with thromboembolic disease, such as vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, are advised to steer clear of tranexamic acid as it could worsen these conditions.
- Those who have experienced events in the past face a risk when taking this medication due to their medical history of clotting issues.
- Patients who have known allergies to the components of acid should avoid using it because they may be hypersensitive to the medication.
Conditional Warnings
When using acid in situations or conditions, it is essential to consider its usage and follow the specific warnings provided carefully.
- Patients with kidney problems may need to adjust their medication dosages to avoid the drug building up in their system and causing effects.
- When using acid along with medications that can impact the clotting system, like anticoagulants or birth control pills, caution is recommended.
Risks in Specific Conditions
Patients with issues require careful supervision when given tranexamic acid.
- People with a history of heart issues should be carefully monitored because tranexamic acid might increase clotting tendency in theory.
- Seizure Conditions. Some studies indicate that using amounts of acid could lead to more frequent seizures in individuals who have a history of seizures.
Tranexamic Acid and Alcohol
When alcohol is taken along with acid at the same time, it can heighten the chances of experiencing stomach-related issues like feeling sick and throwing up. It may also interfere with clotting, which could lower the effectiveness of tranexamic acid in managing bleeding concerns. Healthcare professionals must be aware of these alerts and restrictions to guarantee the use of acid that suits each patient's unique requirements and health conditions.
Important Precautions
Before Starting Treatment
Before giving Tranexamic acid to a patient
- Make sure there are no allergies to acid or similar drugs to avoid any allergic reactions.
- Let's start by running some blood tests in the lab to check your clotting function before we begin any treatment.
Monitoring During Treatment
It's essential to monitor things to spot any side effects and evaluate how well the medication is working.
- It is essential to monitor clotting factors regularly to identify any issues with blood clotting, such as clot formation or a tendency to bleed more than usual.
- Remember to check your kidney function regularly. Tranexamic acid is mainly eliminated through the kidneys, and depending on how well your kidneys are working, you may need to adjust your dosage.
- Watch out for reactions, such as changes in vision or stomach issues, and be alert for any possible blood clot symptoms.
Special Considerations
When utilizing acid, it's essential to take into account a few factors.
- During pregnancy, it is advisable to use acid when necessary and after a careful evaluation of the risks and benefits involved in its usage.
- Elderly individuals might need medication doses as their kidney function decreases with age.
- Adhere to weight-based dosage instructions in accordance with medical condition guidelines when administering medications to children. Check the medicines you're taking to ensure they won't affect how tranexamic acid works or increase the chances of side effects.
Following these safety measures and monitoring recommendations diligently helps ensure the efficient use of acid, minimizing risks and maximizing therapeutic advantages.
Administration to Special Populations
Special care must be taken when giving acid to groups, taking into account their individual physiological and pharmacological characteristics to ensure the treatment's safety and efficacy.
Elderly Patients
When administering acid to patients, various things must be taken into consideration.
- Dosage Adjustment Note: Lower doses might be needed because older adults often experience reduced kidney function, which can impact how medications are cleared from the body.
- Keeping an eye on things is essential as we age because we may experience problems such as blood clots or heart-related issues.
- Carefully examining all prescribed medications is crucial to address interactions, especially considering the use of multiple drug treatments.

Tranexamic Acid in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Using acid while breastfeeding requires careful thought.
- During pregnancy, tranexamic acid should be used with caution, considering the benefits and risks to the baby. It falls under Pregnancy Category B, which suggests that it may not harm the fetus based on animal studies.
- The presence of acid in human breast milk is not well understood as of yet, so it is advisable to be cautious when giving it to breastfeeding mothers.

Tranexamic Acid Nursing Implications
In today's healthcare practices, the administration of acid to patients has become a task for nurses. This responsibility entails evaluating backgrounds and overseeing patients' health.
- Patient Evaluation; Thoroughly reviewing the patients history to pinpoint any reasons that may prevent usage or pose risks, for responses.
- Teaching Patients: Educating individuals on how to identify side effects and stressing the significance of reporting them.
Tranexamic Acid Nursing Interventions
Ensuring safety and maximizing the effectiveness of medications hinges heavily upon the implementation of nursing interventions.
- Assessing Effectiveness: This involves monitoring how tranexamic acid works as a treatment and modifying care strategies accordingly based on the results.
- Management of Negative Effects: Identify and handle any side effects by offering supportive assistance and making necessary adjustments to the dosage when required.
Following these instructions can reduce dangers and improve the effectiveness of tranexamic acid treatment for elderly individuals and those in vulnerable groups, like pregnant women and nursing mothers.
Overdose Information
It's essential for healthcare professionals and patients to grasp the consequences of taking tranexamic acid in order to handle the situation promptly and effectively, as overdosing can result in serious complications if not dealt with quickly and correctly.

Symptoms of Overdose
Excessive acid intake can lead to a variety of symptoms that reflect its impact on the blood clotting system and other bodily functions.
- Sudden decreases in blood pressure can result in hypotension. May lead one into a state of shock.
- Events related to blood clot formation in the body may lead to issues like blockages in the veins or arteries, which can affect the heart or lungs.
- Impacts can have neurological consequences, such as disorientation and faintness, at dosage levels.
Emergency Management
Urgent steps need to be taken to handle a dose of acid.
- Seeking help is vital, in this situation; it's crucial to either contact emergency services or take the patient to the nearest emergency room as soon, as possible.
- Caring for the patient involves monitoring their signs and ensuring their symptoms are managed effectively through treatments, like administering fluids or medications to help stabilize their condition.
- In cases of taking tranexamic acid for which no designated cure is available, the treatment options may involve actions to avoid absorption, like gastric lavage or giving activated charcoal if done within a proper time frame after consumption.
Preventive Measures
To avoid an overdose, several tactics need to be put into action;
- Patients should be informed about the importance of following the recommended doses and the dangers associated with taking medication.
- Healthcare professionals need to oversee the dispensing of prescriptions to guarantee that the dosages are suitable, for the patients condition and associated risk factors.
- Regularly ensuring that patients stick to their medication is crucial for safety concerns in groups like older people or individuals with limitations who are at a higher risk of accidental overdose.
Healthcare professionals can protect against the outcomes that can occur from tranexamic acid overdose by comprehending the symptoms and emergency procedures necessary for its management and by taking action.
Handling and Storage Precautions
Properly managing and storing acid is crucial to maintaining its effectiveness and reducing risks linked to its usage. Following the recommended protocols guarantees the stability and safety of the drug for patient treatment.
Proper Storage Conditions
Preserving the integrity of acid necessitates particular conditions.
- Please store the product in a place with a room temperature between 15 °C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) away from sunlight and heat sources.
- To prevent moisture damage, store the medicine in its packaging until you're ready to use it.
- It's best to avoid sunlight to keep the ingredients from breaking down due to light sensitivity concerns.

Handling Guidelines
When working with acid in healthcare environments, it is essential to take precautions.
- Remember to have dry hands when handling to avoid contamination.
- Do not use it if the package looks opened or damaged, as this might impact the medication's sterility and effectiveness.
- Maintain sterility by using techniques when preparing doses of forms.
Disposal Recommendations
It's essential to dispose of acid to avoid any accidental exposure or harm to the environment.
- Remember to adhere to the regulations in your area when disposing of acid to protect the environment and ensure safety.
- Participate in medication disposal programs if possible to safely get rid of any expired tranexamic acid medications that you may have at home.
- Seek Advice from Pharmacists. If you are unsure how to dispose of it, you can always seek advice from a pharmacist about disposal practices.
By following these recommended steps for handling and storing acid properly in healthcare settings and at home, both healthcare professionals and patients can help maintain the effectiveness and safety of the medication while also promoting safety by disposing of it correctly.
Careful Administration Practices
It's essential to manage the use of acid during treatment procedures to ensure that it works well and is safe. Your approach should involve dosages, preventing common mistakes, and effectively educating patients and ensuring their cooperation.
Ensuring Correct Dosage
Mastering the art of tranexamic acid treatment lies in calculating and administering the proper dosage.
- Dosage calculation is crucial. It should be carefully determined, considering the patient's weight and medical condition, to ensure effectiveness while reducing risks.
- The patient's reaction to treatment and test outcomes should be continuously monitored to modify the dosage as required—during circumstances like surgery or when dealing with fluctuating renal function levels.
Avoiding Common Errors
Avoidance of errors in managing acid is crucial to prevent outcomes and ensure successful treatment.
- Remember to review the medication label and double-check the dosage calculations before administering the medication to avoid any mistakes in dosing.
- Follow the recommended guidelines for how the treatment is given, whether it's through injections into the vein, taken by mouth, or applied to the skin.
- To get the results and reduce any possible issues that may arise. To optimize outcomes and lower mortality rates in cases like trauma scenarios, it is crucial to administer acid within the specified time window.
Patient Education and Compliance
Ensuring that patients receive education plays a role, in improving their adherence, to treatment and overall health outcomes.
- Educating patients on the way to use acid is crucial and should include guidance on timing aspects – crucial for conditions such as heavy menstrual bleeding or postpartum hemorrhage.
- Patients should be advised about side effects and the significance of informing their healthcare provider about them.
- Ensuring compliance continuity through check-ins and gentle nudges can help patients maintain their medication regimen as instructed by addressing any issues that may cause them to deviate from it.
By focusing on these methods of administration in healthcare settings, providers can improve the safety and effectiveness of tranexamic acid treatment, resulting in improved results and reduced chances of negative impacts.
Clip, Tranexamic acid FAQ
- Does Tranexamic Acid work
- Does Tranexamic Acid cause weight loss
- Does Tranexamic Acid exfoliate
- Is Tranexamic Acid an active
- Is Tranexamic Acid safe during pregnancy
- How long does it take for Tranexamic Acid to stop your period
- How does Tranexamic Acid work for heavy periods
- How long does Tranexamic Acid stay in your system
- How fast does Tranexamic Acid work
- How long does it take for Tranexamic Acid to work
- What not to mix with tranexamic acid
- What percentage of Tranexamic Acid is effective
Does Tranexamic Acid work
Tranexamic acid has been found to be successful in lessening bleeding in situations like heavy periods and after surgery or injury.
Does Tranexamic Acid cause weight loss
Nope! Tranexamic acid doesn't lead to weight loss. Its primary purpose is to manage or prevent bleeding, and it doesn't impact weight loss.
Does Tranexamic Acid exfoliate
Tranexamic acid doesn't work as an exfoliant; its primary purpose is to control or prevent bleeding and enhance skin brightness in skincare routines rather than for exfoliating purposes.
Is Tranexamic Acid an active
Tranexamic acid is commonly used in skincare products because it reduces inflammation and enhances skin radiance.
Is Tranexamic Acid safe during pregnancy
During pregnancy, Tranexamic acid is usually deemed safe for situations like excessive bleeding when the benefits are greater than the risks; nevertheless, it should only be taken with guidance from a healthcare professional.
How long does it take for Tranexamic Acid to stop your period
Tranexamic acid can potentially lessen bleeding within 2 to 3 hours of consumption; noticeable alterations in menstrual flow might require a few days of consistent usage to become evident.
How does Tranexamic Acid work for heavy periods
Tranexamic acid decreases bleeding by preventing the disintegration of blood clots in the uterus. This stabilizes clot formation and reduces blood loss.
How long does Tranexamic Acid stay in your system
Typically, the body usually gets rid of acid within 11 hours following the final dose.
How fast does Tranexamic Acid work
Tranexamic acid may start to decrease bleeding around 2 to 3 hours after being taken.
How long does it take for Tranexamic Acid to work
Tranexamic acid usually begins to take effect around 2 to 3 hours after it is taken orally.
What not to mix with tranexamic acid
It's important to avoid combining acid with birth control pills that contain estrogens because it can raise the chance of developing blood clots.
What percentage of Tranexamic Acid is effective
Using a 5 percent concentration of Tranexamic Acid has shown effectiveness in skincare when applied topically in reducing pigmentation and enhancing skin tone.