Exjade
- Introduction
- Uses
- How It Works
- Off-label Use
- Side Effects
- Common Side Effects
- Dosage and Administration
- Composition
- Storage
- Interaction
- Warning
- Contraindication
- Careful Administration
- Important Precautions
- Administration to Elderly
- Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
- Administration to Children
- Overdosage
- Handling Precautions
Introduction
The history and development of Exjade have brought advancements to the field of pharmacology. This medication was initially created to meet the growing need for iron chelation agents and has since undergone extensive clinical trials and modifications. Over the years, researchers have thoroughly evaluated its pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics, solidifying its importance in the community. The purpose of Exjade is primarily centered around its ability to remove excess iron from the body. This is particularly crucial for patients with conditions like thalassemia or sickle cell anemia who regularly receive blood transfusions. By managing iron overload, Exjade helps prevent organ damage.
Uses
Exjade is a medication that is used to treat chronic iron overload caused by blood transfusion1. It is also used in chelation therapy, which aims to remove metals from the body1. By acting as an iron chelator, Exjade binds to and helps eliminate surplus iron, reducing the risk of complications such as heart problems or liver diseases1.
Here are some references that provide more information about Exjade:
- Medscape: A comprehensive resource that provides dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more.
- WebMD: A trusted source that offers information about the uses, dosage, side effects, and warnings associated with Exjade.
- European Medicines Agency: The official website of the European Medicines Agency, which provides a summary of the product characteristics for Exjade.
- Understanding EXJADE (deferasirox) Film-Coated Tablets: A patient information leaflet that provides information about the uses, dosage, side effects, and warnings associated with Exjade.
- MIMS Philippines: A reliable source that offers detailed prescribing information for Exjade.
How It Works
How Exjade works is quite interesting. It acts as a chelation agent that binds to iron, forming a complex. This complex along with the captured iron is then excreted through the kidneys and feces effectively reducing the amount of iron, in the body.
Off-label Use
Exjade is primarily used for iron chelation1. However, some doctors have found it helpful in treating conditions such as aluminum toxicity and lead poisoning, even though these uses are not officially approved1. Several studies have suggested that Exjade may be effective in these areas1. It is important for physicians to exercise caution and carefully evaluate patients before prescribing it off-label. Regular monitoring is crucial in these cases1.
Here are some references that provide more information about Exjade:
- Medscape: A comprehensive resource that provides dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more.
- WebMD: A trusted source that offers information about the uses, side effects, and warnings associated with Exjade.
- European Medicines Agency: The official website of the European Medicines Agency, which provides a summary of the product characteristics for Exjade.
- Understanding EXJADE (deferasirox) Film-Coated Tablets: A patient information leaflet that provides information about the uses, dosage, side effects, and warnings associated with Exjade.
- MIMS Philippines: A reliable source that offers detailed prescribing information for Exjade.
Side Effects
Possible Immediate Side Effects: When starting Exjade, you may experience the following: Discomfort or pain in the abdomen. Skin. Itching. Possible Long-term Side Effects: Exjade could result in liver problems and kidney complications if taken for a period. Identifying Symptoms and Seeking Medical Advice: If you experience nausea, unusual fatigue, or notice yellowing of the eyes, it is crucial to seek medical advice promptly.
Common Side Effects
Here is a list of the commonly reported side effects; 1. Vomiting 2. Diarrhea 3. Vertigo To manage and alleviate these side effects it is often recommended to seek symptomatic relief consider dose adjustments and in some cases, use supplementary medications as necessary.
Dosage and Administration
Here are the revised instructions regarding the recommended dosage, proper administration, and adjusting dosage over time for patients with iron overload. The usual starting dose for patients with transfusional iron overload is 20 mg/kg daily. However, the specific dosage may be adjusted based on the individual's iron burden and how they respond to treatment. To take Exjade correctly, consuming it on a stomach is essential. You can disperse the tablet in water, orange, or apple juice. Monitoring serum ferritin levels and liver function while taking Exjade is necessary. Dose adjustments should be made carefully to ensure optimal iron levels are achieved. These guidelines aim to provide treatment while considering each patient's unique circumstances.
Composition
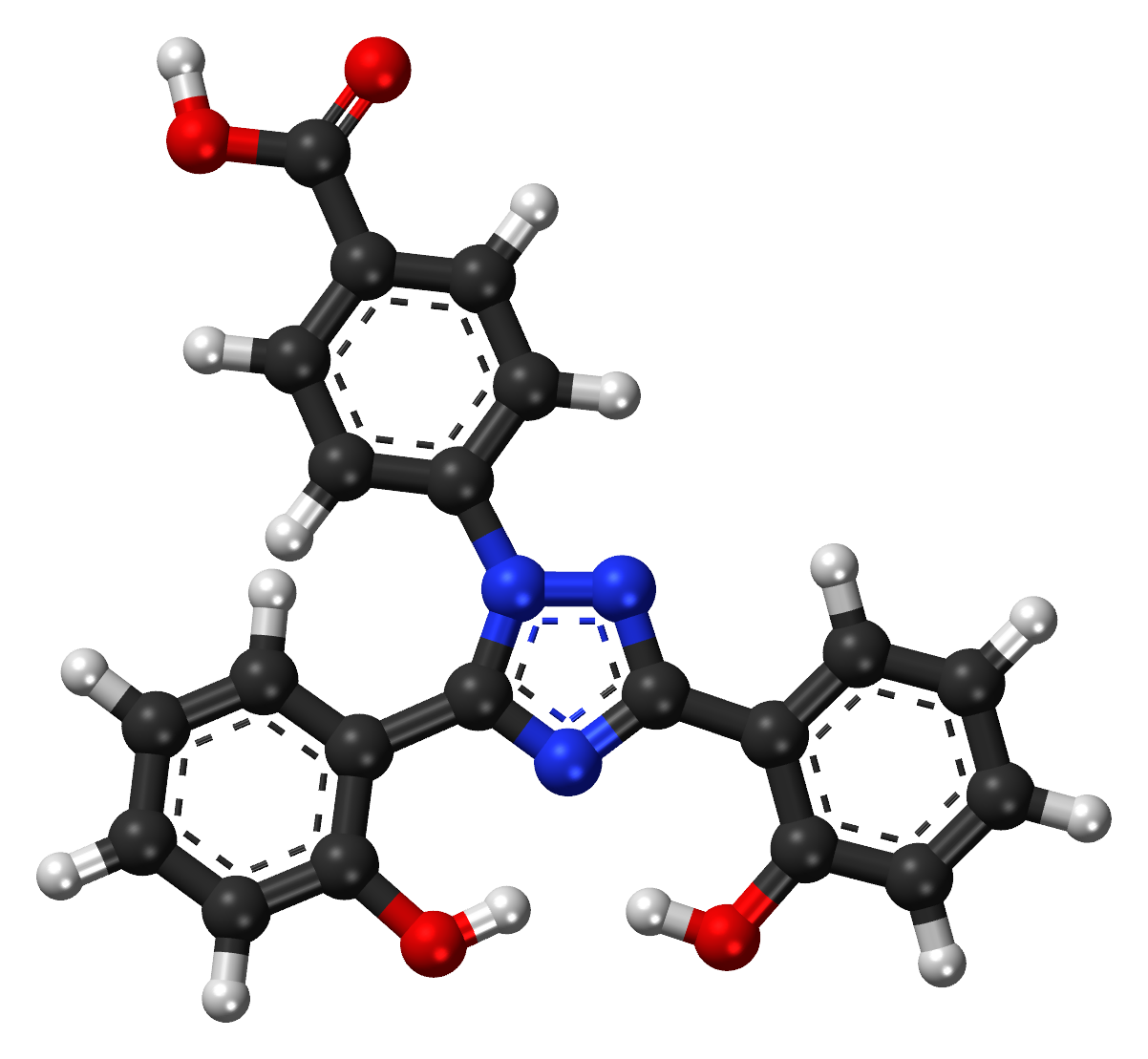
The primary active component found in Exjade is deferasirox. Additionally, the tablet contains nonactive ingredients with no therapeutic effects but are included to help with the formulation. Regarding its properties, deferasirox acts as a potent iron chelator promoting iron balance in individuals with iron overload and reducing the oxidative stress experienced by organs.
Storage
To ensure that Exjade remains effective, it is essential to store it at room temperature and keep it away from moisture. Additionally always check the expiration date, on the package before using Exjade as expired medication may not be as effective and could potentially cause harm. It's also crucial to store Exjade in a place where children cannot access it.
Interaction
Medications that may interact with Exjade: When taking Exjade, it's vital to be aware of medications that could affect its effectiveness. Some common drugs that might have interactions include antacids containing aluminum rifampicin (an antibiotic) and cholestyramine (a bile acid sequestrant). Effects of combining Exjade with alcohol and other substances: Drinking alcohol while taking Exjade could worsen liver-related side effects. Avoiding drugs or illicit substances that can strain the liver or kidneys when you are on Exjade is also essential. Foods or supplements to avoid while taking Exjade: Consuming high-iron foods, like meats, may reduce the drug's effectiveness. Additionally, when taken in quantities, specific supplements, such as vitamin C, can increase iron absorption and make it more challenging for Exjade to do its job effectively.
Warning
There are risks and potential adverse reactions associated with Exjade despite its effectiveness. These reactions include liver disorders, elevated liver enzymes, kidney impairments, increased serum creatinine levels, and severe skin reactions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome. It is essential to avoid or closely monitor the use of Exjade in individuals who have a hypersensitivity to the drug's existing severe renal disorders or high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Medical supervision should be maintained in cases.
Contraindication
There are medical conditions and situations in which it is not recommended to take Exjade. These include malignancies (severe forms of cancer). Patients who are in the advanced stage of bone marrow fibrosis. Individuals who have experienced documented hypersensitivity reactions to the medication.
Careful Administration
Specific individuals, such as those with existing liver or kidney conditions, specific genetic mutations, or a history of drug allergies, require care when undergoing Exjade therapy. It is essential to monitor and follow up on these patients by conducting regular blood tests to assess their hematological status, liver function tests to evaluate the health of their liver, and renal function evaluations to ensure their kidneys are functioning correctly. This approach is crucial for both the success of the treatment and the patient's safety.
Important Precautions
Before starting treatment, it is essential to perform initial tests to assess liver function, measure serum creatinine levels, and conduct a urinalysis. Throughout the treatment, regular blood tests will be done to monitor parameters, and monthly measurements of serum ferritin levels will be taken to ensure that the therapy is effective.
Administration to Elderly
Dosage Adjustments and Important Factors: As people age, their bodies change, which can impact how medications affect them. To prevent any issues or increased side effects, adjusting the doses of medicines for older individuals may be necessary. Concerns and Safety Measures for the Elderly: The elderly population is more susceptible to experiencing effects on their kidneys or liver from certain medications. Therefore, monitoring these individuals for any potential risks or complications is crucial.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Risks to Unborn Baby: Exjade, which falls under Category C drugs, has shown adverse effects in studies conducted on animals. Although there is research on its impact on humans, we cannot completely rule out potential risks to the fetus. Recommendations for Usage and Alternatives: Exjade may be prescribed if absolutely necessary. However, it would be wiser to consider harmful alternatives and closely monitor the mother's condition during treatment.
Administration to Children
Dosages for children need to be adjusted according to their weight and the amount of iron in their body. It is essential to monitor the safety and effectiveness of these dosages. Clinical studies have shown that the drug is effective for children. It is still crucial to be cautious due to their developing physiological systems.
Overdosage
Signs and Symptoms of Taking Much: Taking too much medication can lead to gastrointestinal problems, dizziness, or a rash. In severe cases, it may cause liver damage or kidney dysfunction. What to Do in Case of Overdose: If an overdose occurs, it is essential to stop taking the medication. Seek attention for symptomatic treatment and consider hospitalization for monitoring and supportive care if necessary.

Handling Precautions
Please make sure to store Exjade safely out of the reach of the children. If you have any unused tablets, please dispose of them according to the regulations for pharmaceutical waste in your area. Healthcare providers and caregivers should be aware of all drug interactions, contraindications, and special considerations related to Exjade to prioritize patient safety and successful treatment outcomes.