Desogestrel/ Ethinyl estradiol
- 1. Introduction to Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol
- 2. Composition of Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol
- 3. Uses of Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol
- 4. How Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol Works
- 5. Dosage and Administration
- 6. Side Effects of Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol
- 7. Common Side Effects of Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol
- 8. Warnings and Precautions
- 9. Contraindications
- 10. Important Precautions
- 11. Administration to Special Populations
- 12. Drug Interactions with Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol
- 13. Careful Administration
- 14. Overdosage and Management
- 15. Storage and Handling of Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol
1. Introduction to Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol
Overview of Combined Oral Contraceptives (COCs)
Oral contraceptive pills (OCP) containing both estrogen and progestin hormones are commonly used for birth control purposes in addition to regulating cycles and addressing issues effectively, with Desogestrel and Ethinyl Estradiol as important ingredients in this category.
Brief History and Development
Desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol were created to meet the demand for enhanced and lower-dose birth control choices in the 1980s. Desogestrel was considered a third-generation progestin with masculine effects compared to previous versions, while ethinyl estradiol, a synthetic estrogen, supplements Desogestrel's contraceptive effectiveness.
FDA Approval Status and Regulatory Guidelines
Desogestrel and Ethinyl Estradiol are both endorsed by the FDA as birth control options for women under 35 who are in good health and do not smoke regularly. The FDA approval signifies that these drugs are deemed safe and efficient according to criteria.

2. Composition of Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol
Active Ingredients
The main components of this birth control method are Desogestrel (a type of progestin hormone ) and ethinyl Estradiol (an estrogen hormone). These two substances collaborate to inhibit ovulation and maintain a cycle.
Inactive Ingredients and Fillers
Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol pills contain hormones and inactive components, like lactose and magnesium stearate, to maintain pill stability and aid absorption in our bodies.
Available Dosage Forms and Strengths
Blister packs containing either 21 or 28 pills typically include a mix of Ethinyl Estradiol at strengths, between 20 and 35 micrograms each pill dose for contraception with side effects.
Differences Between Various Brands
Many different brands provide combinations of Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol with varying concentrations of hormones, and the types of ingredients involved in the mixtures may vary. Certain brands might prioritize reducing side effects such as weight gain, while others provide extended cycle versions for decreased period frequency annually.
Desogestrel vs norethindrone
One benefit of desogestrel compared to norethisterone or levonorgestrel is that it offers a period of effectiveness. If a dose of norethisterone or levonorgestrel is delayed by more than three hours (more than 27 hours since the last pill was taken), it should be taken promptly, and the next dose should be taken according to the regular schedule.
Desogestrel vs drospirenone
The 4-milligram drospirenone pill results in reduced bleeding compared to the 0.075-milligram desogestrel pill and maintains strong contraceptive effectiveness even if a pill is missed within a 24-hour window.
Desogestrel vs norgestimate
Levonorgestrel and norethindrone interact directly with the progesterone receptor, while norgestimate and desogestrel function differently. Desogestrel needs to be activated in the liver to become norgestimate, and norgestimate and desogestrel are more specialized in their actions. They show fewer masculine effects when taken in doses that prevent ovulation.
3. Uses of Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol
Primary Use: Contraception
Menstrual Cycle Regulation
Hormonal Acne Treatment
Desogestrel and Ethinyl Estradiol are often recommended for managing acne issues when elevated androgen levels play a role in the condition's development. They are known to sebum production levels and enhance the overall clarity of the skin.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Management
This medication helps women with PCOS by controlling symptoms, like periods and excessive hair growth, through hormone level balancing while addressing acne issues.
Off-Label Uses: Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD)
This combination is sometimes used, off-label, to treat PMDD—a type of PMS that leads to mood changes.
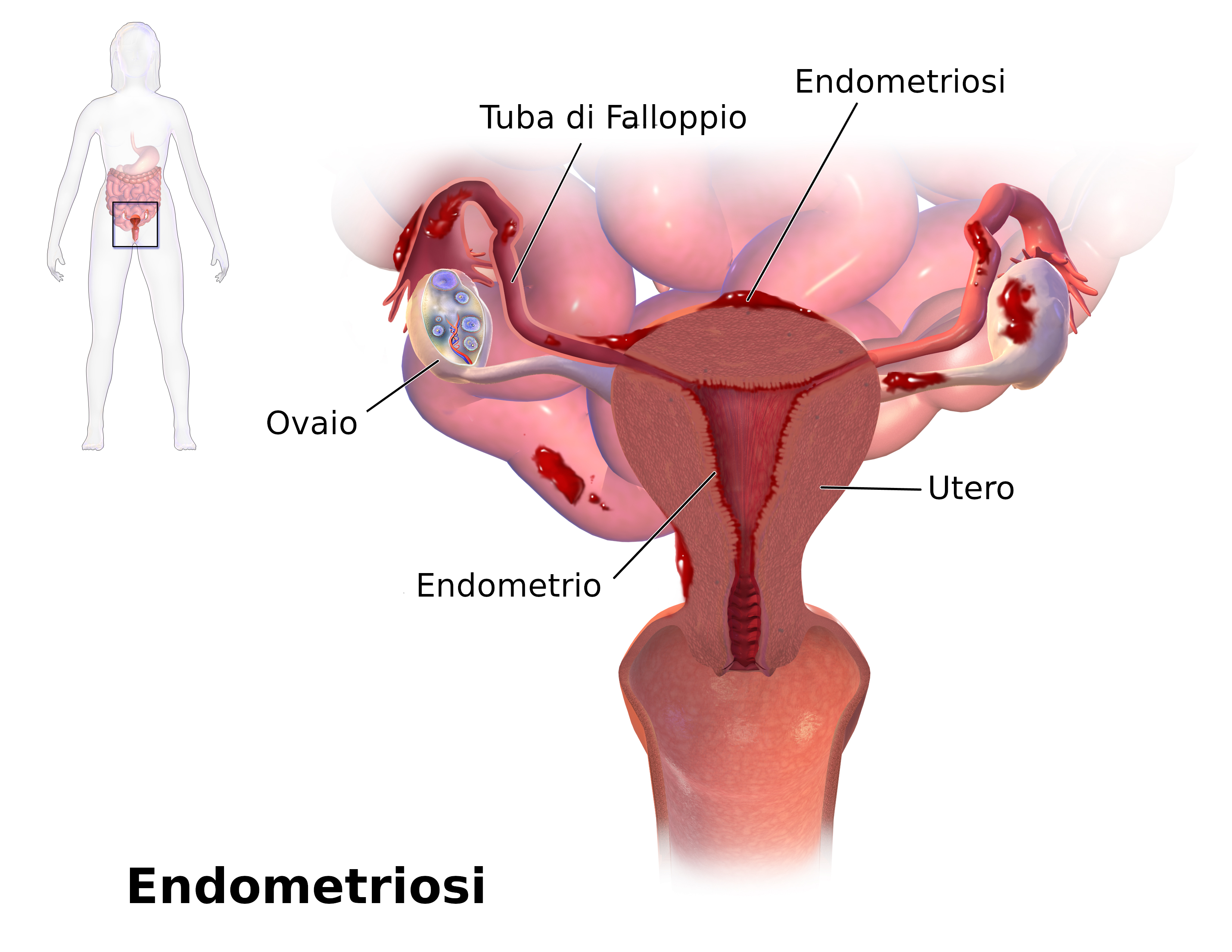
Off-Label Uses: Endometriosis Management
Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol is also used off-label to manage endometriosis, a condition where uterine tissue grows outside the uterus, leading to painful periods and other complications.
4. How Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol Works
Mechanism of Action: Suppression of Ovulation
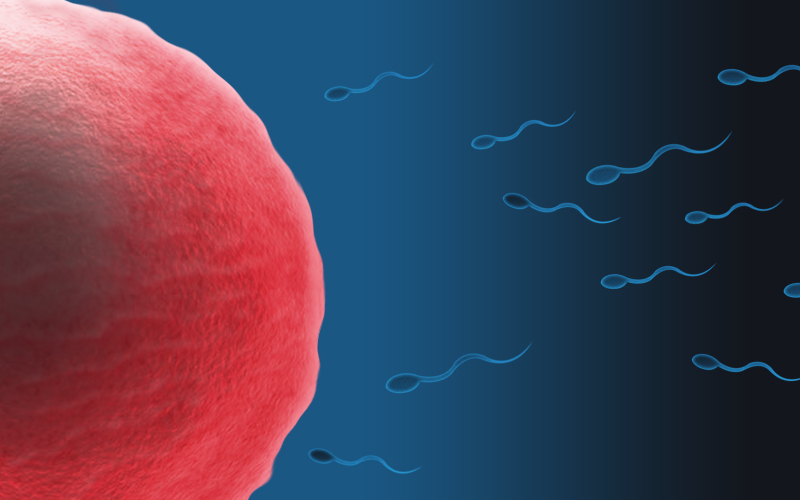
Desogestrel/ethinyl estradiol functions by inhibiting ovulation, hindering the ovaries from releasing eggs. This mechanism contributes to its success in preventing pregnancy.
Effect on Cervical Mucus and Endometrial Lining
It also increases the thickness of mucus, which can hinder the movement of sperm towards an egg, and changes the lining of the uterus to make it less conducive to implantation.
Hormonal Influence on the Body
The hormonal equilibrium created by Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol has a ranging impact on the body, from enhancing skin conditions like acne to promoting stability and easing menstrual discomforts.
5. Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosing Schedule for Contraception
The typical dosaging routine involves taking a pill a day at a consistent time daily to ensure the body maintains steady hormone levels.
Initiation of Therapy: First-Day vs. Sunday Start
You can start therapy either on the day of your period or on the Sunday after your menstrual cycle begins. Whichever suits you best and as recommended by your doctor.
Missed Dose Instructions
If you forget to take a pill on time you should take it soon as you remember. If you miss more than one dose, follow the instructions on whether to take doses or use backup contraception.
Adjustments for Special Populations (Obese, Smokers, etc.)
In cases involving individuals, like smokers or overweight women healthcare providers might suggest changing the dosage. We will use approaches to account for the higher likelihood of experiencing side effects such as blood clots.
6. Side Effects of Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol
Common Side Effects: Nausea, Breast Tenderness, Headaches
Feeling queasy and experiencing breast sensitivity and headaches are symptoms that often occur during the months of usage as your body gets used to the hormonal changes.
Less Common Side Effects: Mood Swings, Weight Changes
Changes in mood and fluctuations in weight can happen. They are usually not severe and tend to lessen with time. It is possible for some women to undergo alterations based on their unique sensitivities.
Serious Side Effects: Blood Clots, Stroke, Heart Attack
Severe adverse effects may include the potential for blood clots, stroke, and heart attacks among smokers and women aged 35 and older. It is crucial to seek care if any symptoms of these conditions surface.
Long-Term Side Effects and Risks
Extended use has been linked to a chance of types of cancer, like breast and cervical cancer; however, the overall risk is considered to be minimal.
7. Common Side Effects of Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol
Digestive Issues: Nausea, Vomiting
It's not unusual to experience stomach problems such as queasiness and throwing up when you take medication without eating. Having the pill with a meal can often ease these symptoms.
Breast-Related Symptoms: Tenderness, Enlargement
Reportedly common during the phases of treatment are instances of breast tenderness and a minor increase in size.
Skin Reactions: Acne, Pigmentation Changes
While this treatment is commonly prescribed for acne management, women may sometimes notice a worsening of acne or variations in skin tone.
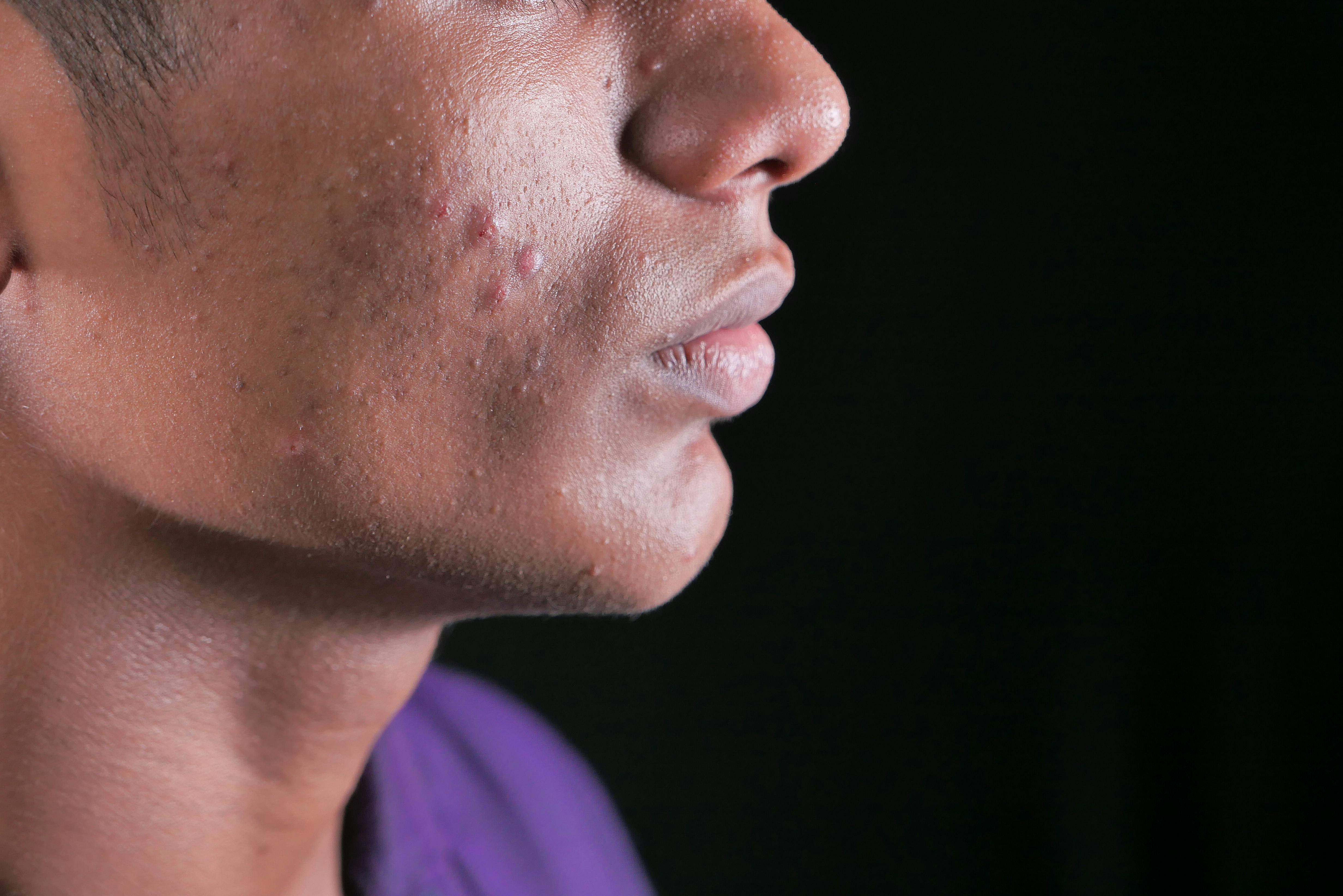
Menstrual Irregularities
Spotting or breakthrough bleeding may happen at times when you're starting out with the product—in the months of use—but these irregularities usually settle down as you continue using it regularly.
8. Warnings and Precautions
Cardiovascular Risks and Smoking
Women who smoke face a risk of experiencing heart-related issues, like stroke or heart attack, while taking this medication, so it's strongly recommended to quit smoking.
Risk of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE)
Women with a history of clotting disorders face a risk of VTE ( thromboembolism). It is essential to undergo assessment before starting any treatment, in these situations.
Considerations in Women with Hypertension or Diabetes
Women who have existing health issues such as high blood pressure or diabetes need to be observed because Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol could make these conditions worse.
Risk of Breast Cancer and Hormonal Influence
Extended usage could potentially increase the chances of hormone cancers, like breast cancer; thus, it is recommended for individuals who use it for a period to undergo regular breast examinations and mammograms for precautionary measures.
Stroke and Heart Attack in High-Risk Patients
Patients at risk of health complications— individuals with a background of cardiovascular issues—ought to weigh their options thoughtfully when choosing contraception in light of the increased likelihood of experiencing strokes and heart attacks.
9. Contraindications
Known Pregnancy
Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol should not be used during pregnancy as it can pose a risk to the baby's health, prompting women to cease its usage promptly upon confirming or suspecting pregnancy.
History of Blood Clots or Thrombotic Disorders
Individuals who have previously experienced thromboembolism (VTE), pulmonary embolism (PE), or any type of blood clotting issue should steer clear of Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol medication due to its content, which could substantially heighten the chances of another clot occurrence and potentially lead to life-threatening complications.
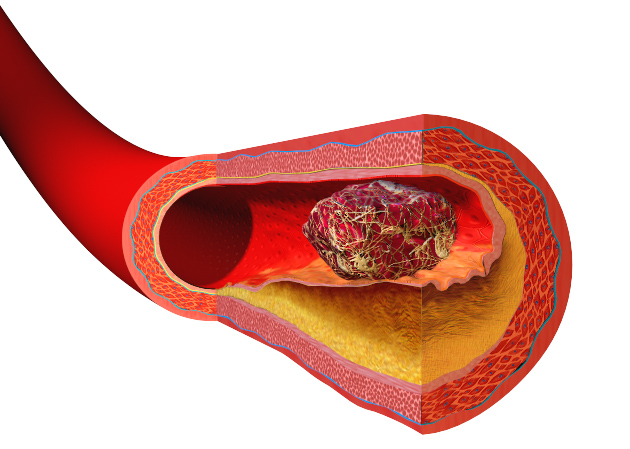
Liver Disease and Tumors
Severe liver damage, such as liver tumors, is a reason to avoid Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol use since the processing of estrogen and progestin mainly occurs in the liver; any liver issues could worsen conditions. Lead to more serious complications or cancers.
Uncontrolled Hypertension
When dealing with blood pressure, using this birth control method may worsen the situation by raising blood pressure levels further and increasing the chances of experiencing a stroke, heart attack, or other heart-related issues. It is advisable for women with this health condition to explore options for birth control methods.
Breast or Uterine Cancer
This medication should not be used for hormone cancers, like breast or uterine cancer, because the estrogen in it could fuel the growth of tumors that respond to hormones and worsen the condition.
10. Important Precautions
Routine Monitoring and Follow-up Visits
Regular medical checkups are important for women who are prescribed Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol to ensure they are tolerating the medication well and to monitor any complications that may arise over time.
Discontinuation Before Surgery
It is advised for women planning surgery or facing periods of immobility to stop taking Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol at least four weeks in advance to lower the risk of venous thromboembolism (blood clots), which tends to rise when movement is limited.
Recognizing Signs of Complications
People should learn about the symptoms of problems, like intense leg discomfort (a sign of potential DVT), abrupt difficulty in breathing (potential pulmonary embolism), or neurological issues such as sudden severe headaches or vision changes that could suggest a stroke.
11. Administration to Special Populations
Administration to Elderly Women: Risk vs. Benefit
While it is uncommon for doctors to recommend Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol to women in their years of life due to potential cardiovascular risks linked to this medication in females aged 50 and above, a thorough evaluation of the benefits and risks is essential before deciding on the appropriate treatment options, for this group.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol should not be used by women under any circumstances as they may pose risks to the baby's health. Nursing mothers should be cautious as the medication could reduce milk supply and transfer into breast milk, potentially impacting the infant's well-being. It is advisable for breastfeeding women to consider methods that are not hormone-based.
Administration to Adolescents: Safety and Efficacy
Over the years, Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol has been shown to be safe and reliable for birth control and regulating menstrual cycles. Nevertheless it is advised to monitor its usage among adolescents to ensure adherence and manage any side effects in this age group.
Considerations in Women with Underlying Medical Conditions
Special care should be taken for women who have underlying health issues, like diabetes or epilepsy, or have a history of depression when considering Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol, as it could interfere with their treatments or worsen their conditions.
12. Drug Interactions with Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol
Interaction with Antibiotics
Using antibiotics, like rifampin and certain types of tetracyclines, may lower the effectiveness of Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol by changing how the body processes it. Backup forms of contraception are recommended while taking antibiotics.
Interaction with Anticonvulsants
Antiepileptic medications, like phenobarbitone or carbamazepine, might decrease Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol levels in the bloodstream. Lessen its ability to prevent pregnancy effectively for women using these medications may require birth control methods.
Effect on Thyroid Medications
The combination of Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol may influence how thyroid hormone replacement therapy is absorbed and works in the body, potentially leading to the need for adjustments in the dosage of levothyroxine for women who are also using contraceptives.
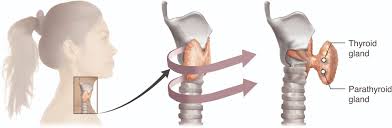
Herbal Supplements That May Affect Efficacy
St Johns Wort is a supplement that can reduce the effectiveness of Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol birth control pills and may increase the risk of contraceptive failure; therefore patients are recommended to refrain from using this herb while taking these medications.
13. Careful Administration
Careful Use in Women Over 35
Women who are 35 years of age or older should be careful when taking Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol if they smoke because their chances of experiencing heart-related issues, like stroke and heart attack, are much greater.
Careful Use in Women Who Smoke
Women who smoke and use contraceptives face a higher risk of thromboembolic events happening in their bodies compared to those who do not smoke or use contraceptives. It is advisable, for smokers over the age of 35, to avoid taking Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol due to the health risks associated with smoking.
Precautions in Women with Migraines
Women who experience migraines, especially those with aura, should be cautious when using contraceptives containing estrogen as they have a chance of developing strokes; it's advisable to explore options for women dealing with frequent or intense migraine attacks.
Monitoring Liver and Kidney Function
Regular monitoring of liver and kidney function is important when using Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol for a period of time, as any indication of liver or kidney issues may require stopping the medication.
14. Overdosage and Management
Symptoms of Overdose: Nausea, Vomiting, Vaginal Bleeding
Common signs of an overdose often entail feelings of nausea and vomiting along with bleeding occurrences; these symptoms typically resolve themselves over time, but seeking medical advice is advisable in severe instances.
Emergency Treatment for Overdose
In cases of an overdose situation occurring where immediate treatment is necessary for symptom relief, the use of activated charcoal could be considered to minimize absorption levels in instances; however, for cases involving oral contraceptive overdose incidents, this method is seldom necessary.
Long-Term Effects of Overdose
Usually, there aren't any lasting effects from taking Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol if you handle it properly. However a temporary hormonal imbalance could cause some menstrual irregularities to occur.
15. Storage and Handling of Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol
Proper Storage Conditions
Store Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol at room temperature in a dry place to maintain its effectiveness. Extreme temperatures can affect the ingredient's potency when exposed to direct light or moisture.
Disposal of Unused or Expired Medication
Make sure to dispose of any Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol that you no longer need or that has expired correctly—avoid flushing them down the toilet and opt for take-back programs or follow the pharmacy instructions for disposal instead.
Safe Handling and Packaging
When dealing with Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol medication, damaged packaging should be handled with caution to preserve the effectiveness and safety of the pills until they are needed for use.
Desogestrel/ Ethinyl estradiol FAQ
- What is desogestrel-ethinyl estradiol?
- How effective is drospirenone and ethinyl estradiol?
- What is norgestimate-ethinyl estradiol?
- What is drospirenone ethinyl estradiol?
- How effective is norgestimate-ethinyl estradiol?
- What is desogestrel-ethinyl estradiol?
- How to lower estrogen?
- How to increase estrogen naturally?
- What is the lowest dose of estrogen for menopause?
- What is estrogen dominance?
- When to increase estrogen dose?
- How to test estrogen levels?
- What is the difference between progesterone and progestin?
- How does progestin work?
- What does progestin do?
What is desogestrel-ethinyl estradiol?
Desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol combination is a method aimed at avoiding pregnancy by inhibiting the development of a woman's egg every month when consumed correctly in the form of birth control pills comprising desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol hormones.
How effective is drospirenone and ethinyl estradiol?
In two trials, findings suggest that roughly 1 out of every 100 women could become pregnant within the year of taking drospirenone and ethinyl estradiol tablets.
What is norgestimate-ethinyl estradiol?
Norgestimate and ethinyl estradiol are combined in a birth control pill that women take to avoid getting pregnant.
What is drospirenone ethinyl estradiol?
Drospirenone and ethinyl estradiol tablets consist of forms of estrogen and progesterone, which are designed to prevent pregnancy by halting the process of ovulation.
How effective is norgestimate-ethinyl estradiol?
The more accurately you adhere to the instructions given to you, the lower your likelihood of conceiving. According to findings, from investigations 1 in every 100 women could become pregnant within the initial year of using norgestimate and ethinyl estradiol tablets.
What is desogestrel-ethinyl estradiol?
Desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol combined are utilized to avoid pregnancy by serving as birth control pills containing two hormones. Desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol effectively prevent conception when taken correctly by inhibiting the development of a woman's egg every month.
How to lower estrogen?
Reduce your body percentage to improve your health and well being. Manage stress levels effectively for a lifestyle. Adopt an eating regimen by consuming a diet low in fats and high, in fiber while minimizing processed sugar intake to support your liver in processing estrogen. Control alcohol consumption by either cutting it out or consuming it in moderation to assist the liver in metabolizing estrogen.
How to increase estrogen naturally?
Various fruits, like apples and berries, are good options to include in your diet, along with grains such as barley and oats for added nutrition and fiber content in meals. Liquids like beer or red wine from plant sources can also be enjoyed for their flavors. Nuts and seeds like almonds and sunflower seeds are snacks packed with essential nutrients to energize you throughout your day.
What is the lowest dose of estrogen for menopause?
The typical suggested dosage of estradiol for individuals with estrogen levels ranges from 1 mg to 2 mg taken once a day.
What is estrogen dominance?
Some individuals may experience a deficiency in progesterone production, which can result in a condition known as estrogen.
When to increase estrogen dose?
When individuals experience loss of estrogen (prior to reaching 40 years old), they often receive doses to compensate for the natural production that their ovaries would customarily generate at that stage of life.
How to test estrogen levels?
When you undergo testing, it is typically at the healthcare provider's office or a laboratory setting. For an at-home test, though, saliva is typically used as the sample. In the case of a blood test, a medical practitioner will extract a blood specimen from a vein in your arm using a needle.
What is the difference between progesterone and progestin?
Progestin is a man-made version of progesterone that is utilized in the treatment of health issues related to hormones in the body's natural hormone production process for individuals regardless of their sex assigned at birth when insufficient or additional progesterone is required by the body.
How does progestin work?
Many progestins work to prevent pregnancy by reducing the release of a hormone called gonadotropin-releasing hormone (known as GnRH), which is produced by the hypothalamus. This hormone is also secreted by the gland along with luteinizing hormone (abbreviated as LH) and foetal stimulating hormone (referred to as FSH). This change in hormone levels impacts the cycle, ultimately inhibiting ovulation.
What does progestin do?
Many progestins work to prevent pregnancy by inhibiting the release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). This inhibition leads to changes in the cycle, ultimately stopping ovulation from occurring.






















