Diacerein
- I. Introduction to Diacerein
- II. Composition and Structure of Diacerein
- III. Mechanism of Action: How Diacerein Works
- IV. Uses of Diacerein: Approved and Off-Label
- V. Dosage and Administration of Diacerein
- VI. Special Populations: Administration and Precautions
- VII. Interaction of Diacerein with Other Substances
- VIII. Side Effects of Diacerein: Common and Rare
- IX. Contraindications and Warnings for Diacerein Use
- X. Storage, Handling, and Disposal of Diacerein
I. Introduction to Diacerein
A. What is Diacerein: Definition and Therapeutic Class
Diacerein is classified as an anthraquinone derivative and belongs to the therapeutic category of anti-arthritic agents. It is primarily used in the management of osteoarthritis, aiming to address the inflammatory processes that contribute to cartilage degradation.
B. Historical Background and Development
It was emerging initially from the rhubarb plant with medicinal properties. Diacerein came to light during the 1980s. They were originally devised as a protective agent for cartilage. It distinguished itself by inhibiting Interleukin 1β – a significant pro-inflammatory cytokine linked to osteoarthritis pathophysiology through rigorous clinical trials and comprehensive meta-analysis studies over time. Its efficacy as an osteoarthritis treatment has become widely recognized and integrated into mainstream management strategies.
C. Importance in the Medical Field
Diacerein holds great significance beyond its conventional use in managing osteoarthritis. It offers a promising alternative for patients who cannot tolerate or do not respond to standard anti-arthritic medications. Additionally, due to its ability to regulate inflammatory reactions, Diacerein could help address other conditions characterized by inflammation and degeneration.
II. Composition and Structure of Diacerein
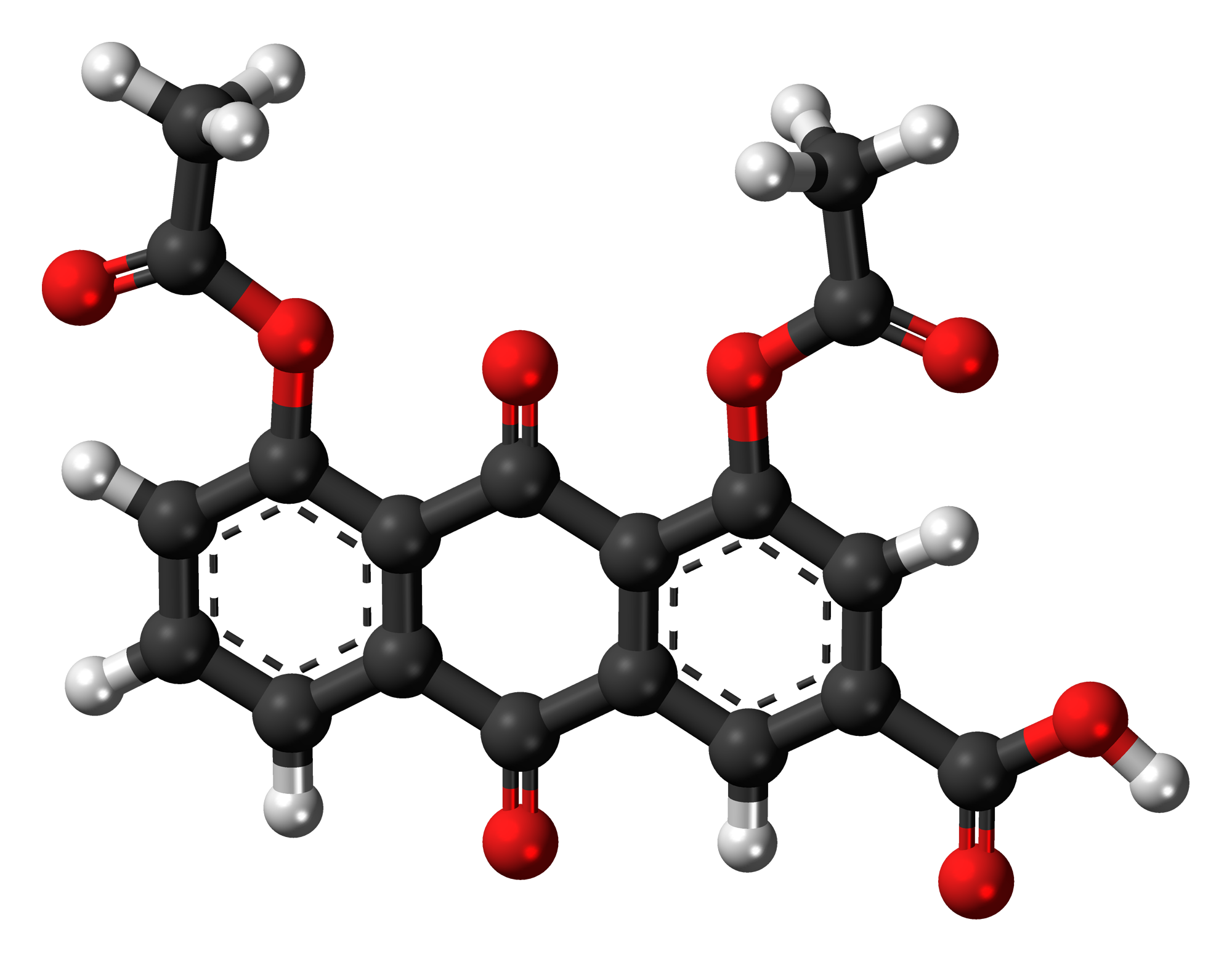
A. Chemical Structure and Properties
Diacerein, a compound derived from rhein, is composed of an intricate arrangement of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Its chemical formula is C19H12O8. This substance has low solubility in water but shows improved solubility in organic solvents suggesting its hydrophobic nature. Moreover, it has a yellowish color and forms crystals.
B. Metabolism and Bioavailability
Following oral ingestion. Diacerein undergoes an extensive metabolic conversion resulting in complete transformation into rhein. The primary mediators of this biotransformation are intestinal flora - microorganisms inhabiting our gut. This metabolic conversion holds immense importance as it is responsible for conferring therapeutic effects associated with Diacerein use onto its active metabolite - rhein. However, this significance of achieving sufficient systemic availability of Diacerein remains a challenge due to substantial first-pass metabolism in hepatic tissue and variations caused by concurrent food intake influencing its absorption rate. Delayed-release formulations have been devised to optimize pharmacokinetic properties and ensure appropriate systemic distribution of this medication.
III. Mechanism of Action: How Diacerein Works
A. Interaction with Cellular Structures
After oral administration, Diacerein is mainly transformed into its active metabolite, rhein. The therapeutic effectiveness of Diacerein lies in the intricate interplay of rhein with cellular structures. Rhein primarily interacts with the cellular machinery responsible for inflammation and matrix remodeling, thus playing a crucial role. It explicitly regulates enzymes like metalloproteinases and exhibits an inhibitory impact on pro-inflammatory mediators.
B. Influence on Inflammatory Response
The role of Diacerein in mitigating the inflammatory response should not be underestimated. It exerts its effects through various anti-inflammatory pathways. Firstly it inhibits the activity of Interleukin 1β (IL 1β), a critical pro-inflammatory cytokine involved in the development of osteoarthritis. Additionally, Rhein, the active metabolite of Diacerein, suppresses the production of other harmful cytokines like tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF α). Furthermore, Diacerein reduces the synthesis of Prostaglandin E2. It leads to a decrease in inflammation and pain. These combined actions result in a potent anti-inflammatory effect that effectively suppresses the widespread inflammation in conditions such as osteoarthritis.
C. Impact on Cartilage and Bone Health
An essential characteristic of Diacerein is its ability to protect cartilage and bone structures. This is achieved through several mechanisms. Firstly, Rhein, a component of Diacerein, can inhibit the synthesis of proteases that break down the cartilage matrix. This helps prevent cartilage erosion and maintains the integrity of the joints. It is believed that Diacerein may also potentially prevent subchondral bone sclerosis, a common feature in osteoarthritis. These combined effects make Diacerein an excellent therapeutic agent for managing diseases involving the degradation of cartilage and bone, such as osteoarthritis.
IV. Uses of Diacerein: Approved and Off-Label
A. Standard Uses: Osteoarthritis Management
Diacerein is commonly used to treat osteoarthritis—a long-term joint condition characterized by cartilage deterioration and inflammation(source). Diacerein helps alleviate symptoms like joint pain, swelling, and stiffness by reducing the activity of inflammatory chemicals and preventing cartilage breakdown(source). Moreover, it plays a crucial role in disease-modifying osteoarthritis drugs (DMOADs) which can potentially delay the progression of the disease and offer relief from symptoms(source).
B. Off-label Applications: Exploring Unapproved Benefits
In addition to its traditional use, Diacerein has been explored for a variety of non-approved purposes. The drug's potent anti-inflammatory and cartilage-preserving properties offer potential opportunities for treatment in different areas:
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Preliminary research indicates that Diacerein might help alleviate synovial inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis, a more aggressive and widespread form of the condition(source).
Inflammatory Bowel Disease: There is an ongoing investigation into the potential role of Diacerein in inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis due to its potent anti-inflammatory action(source). However, it is essential to highlight that these applications are still under investigation, and further research is needed to verify their effectiveness.
C. Emerging Research and Potential Future Applications
Ongoing research is uncovering the potential therapeutic benefits of Diacerein. One exciting area is its impact on Diabetic Nephropathy. Studies indicate that Diacerein can reduce inflammation and fibrosis, two key processes in this condition(source). Additionally, there is reason to believe that Diacerein could be beneficial in managing cardiovascular disorders with inflammatory components thanks to its anti-inflammatory properties(source). However, it is essential to note that further clinical trials are required before these uses can be validated and we can fully comprehend the implications of Diacerein therapy in these conditions.
V. Dosage and Administration of Diacerein
A. Standard Dosage Guidelines
Typically, Adult individuals have been prescribed a standard dose of 50 mg of Diacerein taken orally twice daily. It is generally endorsed for consumption after meals to optimize its effectiveness. Nevertheless, it should be kept in mind that these instructions serve as an overall guideline, and medical professionals may adjust the dosage based on each patient's unique response and ability to tolerate the drug.
B. Adjustments for Specific Populations
Dosage adjustments may be necessary for specific populations. If a patient has hepatic or renal impairment, it might be necessary to reduce the dose. Similarly, individuals experiencing severe gastrointestinal side effects may need dose adjustments. However, it is essential to remember that any changes should only be made under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
C. Route of Administration and Timing
Diacerein should be ingested orally following meals for improved absorption and reduced occurrence of gastrointestinal side effects. Moreover, sticking to a regular medication schedule can effectively sustain an optimal level of the drug in the body, resulting in enhanced therapeutic outcomes.
VI. Special Populations: Administration and Precautions
A. Administration to Elderly Patients
With elderly patients being more prone to comorbid conditions and altered drug metabolism patterns, it becomes imperative to exercise a vigilant approach when administering Diacerein therapy. Intense monitoring of side effects should primarily focus on gastrointestinal complications. Accordingly, possible dose adjustments may need consideration based on an individual's tolerance levels and responsiveness toward the medication's effectivity.
B. Diacerein Use in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Currently, there is not enough substantial evidence concerning the safety profile of Diacerein in pregnant women and nursing mothers. Henceforth. It would be more prudent for individuals undergoing these stages to refrain from utilizing Diacerein throughout their pregnancy and breastfeeding unless the prospective benefits significantly outweigh any possible risks. Prioritizing consultation with a healthcare professional can help ensure an informed decision-making process.
C. Pediatric Use and Considerations
The usage of Diacerein in children has not yet been proven to be safe and effective. Therefore it is generally not recommended to use Diacerein in pediatric patients. It should be done with careful medical supervision in the rare instances where it is considered.
D. Careful Administration: Comorbidity Factors
Patients with comorbidities like liver disease, renal impairment, or gastrointestinal disorders should be closely monitored and may need to adjust their dose of Diacerein. Therefore it is essential to discuss these conditions with a healthcare provider before starting the treatment.
VII. Interaction of Diacerein with Other Substances
A. Known Drug-Drug Interactions
Although Diacerein is considered relatively safe, it is important to be aware that it can interact with certain medications. In particular, if you are also taking hepatotoxic or nephrotoxic drugs alongside Diacerein, there may be an increased risk of liver or kidney damage. To ensure your safety, it is crucial to inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. This will help prevent any potential interactions from occurring.
B. Interaction with Food, Alcohol, and Dietary Supplements
C. How to Manage Potential Interaction Risks
It is of utmost importance to inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are currently taking and any dietary supplements and lifestyle habits such as alcohol consumption. This is necessary to manage any potential risks that may arise from interactions effectively. Additionally, it is recommended to monitor your condition regularly, follow the prescribed dosage and timing and promptly report any side effects. These actions can significantly assist in managing interaction risks.
VIII. Side Effects of Diacerein: Common and Rare
A. Common Side Effects: Frequency and Management
Diacerein, like all medications, has the potential to cause side effects. However, its worth noting that not everyone will experience these side effects. The most common ones include gastrointestinal discomfort such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, or nausea. Fortunately, these discomforts are usually temporary and can be mitigated by taking the medication after meals and staying properly hydrated. If these symptoms persist or worsen, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for further guidance.
B. Less Common Side Effects: Recognition and Response
Occasionally. Individuals may experience less common side effects like skin reactions like rash or itching. And abnormalities in liver function. In rare instances, patients might observe their urine turning yellow or orange, which usually poses no significant harm. If any unusual or severe symptoms arise, seeking immediate medical attention is crucial.
C. Reports of Overdosage: Symptoms and Treatment
Though instances of Diacerein overdose are uncommonly reported, they can potentially cause exacerbated side effects like severe diarrhea or skin reactions. Thus, it becomes critical to expeditiously seek medical care when an overdose is suspected, as obtaining prompt assistance greatly influences effective management. Generally, treatment would entail employing symptomatic and supportive measures.
IX. Contraindications and Warnings for Diacerein Use
A. Absolute and Relative Contraindications
Diacerein should be avoided in patients who have a known hypersensitivity to it or any of its components. It is also commonly not recommended for individuals with severe liver or kidney disease. As well as those suffering from inflammatory bowel diseases or bowel obstruction. Due to the possibility that the drug may worsen these conditions.
B. Warnings: Situations Where Caution is Required
It is recommended to exercise caution when administering Diacerein to patients who have a previous medical record of gastrointestinal conditions such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's' disease. This is due to the potential for worsening symptoms. Additionally, it is essential to be cautious when prescribing Diacerein to patients with compromised renal or liver function. To ensure the safety of these individuals, regular monitoring may be necessary.
C. Important Precautions for Safe Usage
Following the prescribed dosages and schedules when taking any medication is of utmost importance. Abruptly stopping the medication without consulting a healthcare professional should be avoided if there are any new symptoms or side effects. They should be reported promptly. Additionally, patients should inform their healthcare provider about any other medications they are taking to prevent possible drug interactions.
X. Storage, Handling, and Disposal of Diacerein
A. Optimal Storage Conditions
To ensure the preservation and effectiveness of Diacerein, it is advised to store it at room temperature. It should avoid excessive heat, moisture, and direct light. To prevent any unintended ingestion, it is strongly recommended to keep this medication out of reach of children and pets.
B. Safe Handling Procedures
To ensure safety with Diacerein, it is crucial to refrain from touching the eyes or mouth right after handling the capsules. Additionally, always remember to wash your hands before and after use. If the tablet breaks or gets crushed, please make sure to avoid any contact with the skin or eyes.
C. Proper Disposal of Unused or Expired Medication
Unused or expired Diacerein should be disposed of properly and not flushed down the toilet or thrown into the trash. Take-back programs for the secure disposal of new medication are provided by numerous pharmacies as an alternative, individuals can inquire with local waste disposal authorities for instructions on how to safely dispose of medications.






















