Diamicron/ Diamicron MR, Gliclazide
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Uses of Diamicron/Diamicron MR
- 3. How Diamicron/Diamicron MR Works
- 4. Dosage and Administration
- 5. Composition and Formulations
- 6. Diamicron Side Effects
- 7. Common Side Effects
- 8. Off-label Uses of Gliclazide
- 9. Drug Interactions
- 10. Warnings and Precautions
- 11. Special Considerations for Specific Populations
- 12. Overdosage of Diamicron/Diamicron MR
- 13. Storage and Handling of Diamicron/Diamicron MR
1. Introduction
Overview of Diamicron/Diamicron MR
Diamicron and Diamicron MR are oral hypoglycemic drugs prescribed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. As a member of the sulfonylurea class, Diamicron contains the active ingredient gliclazide, which is known for its hypoglycemic properties. The drug is available in two forms: Diamicron, a continuous release form, and Diamicron MR, a modified release form designed to provide a long-lasting effect throughout the day.
Brief History and Development of Gliclazide
Gliclazide was first developed in the late 1960s and has since become a cornerstone of diabetes treatment. The development marked a significant advance in the treatment of type 2 diabetes, improving blood sugar control and reducing the risk of hypoglycemia compared to previous sulfonylureas. Over the decades, the introduction of Diamicron MR has improved its therapeutic index, increased patient adherence, and reduced fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
Importance of Gliclazide in Diabetes Management
Gliclazide plays a strategic role in diabetes management due to its dual action of stimulating insulin secretion and protecting pancreatic beta cells. Its favorable safety profile, especially in cardiovascular outcomes, solidifies its position as a preferred long-term treatment option.
2. Uses of Diamicron/Diamicron MR
Approved Uses for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Off-label Uses in Other Medical Conditions
Gliclazide has been investigated for off-label use in conditions such as PCOS and neonatal diabetes to improve insulin resistance. These applications are still under investigation and should be used cautiously outside of its approved indication.
Comparison with Other Sulfonylureas and Antidiabetic Agents
Gliclazide stands out among sulfonylureas for its lower risk of hypoglycemia and potentially favorable cardiovascular effects. It is a cost-effective option compared to newer antidiabetic drugs, making it more accessible to a wider range of patients. However, choosing between Gliclazide and other medications should be based on individual patient needs.
3. How Diamicron/Diamicron MR Works
Mechanism of Action in Lowering Blood Glucose Levels
Gliclazide stimulates insulin release from pancreatic beta cells by binding to sulfonylurea receptors, closing ATP-sensitive potassium channels, depolarizing the cell membrane, and causing calcium ions to enter, ultimately leading to insulin secretion and hypoglycemic effects.

Role of Gliclazide in Beta-Cell Stimulation and Insulin Secretion
Gliclazide not only promotes insulin secretion but also increases the sensitivity of beta cells to glucose, leading to tighter regulation of insulin release in response to blood glucose levels. This helps reduce the risk of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
Long-term Benefits of Diamicron MR in Glycemic Control
Diamicron MR extended-release formulation provides long-term benefits such as stable blood glucose levels, reduced risk of nocturnal hypoglycemia, and preservation of beta-cell function. These benefits are crucial for the sustained management of Type 2 Diabetes.
4. Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosage for Adults
The typical starting dose for Diamicron is 40 to 80 mg daily, with gradual titration based on glycemic response. For Diamicron MR, it is 30 mg once daily. The maximum recommended dose is 320 mg per day for Diamicron and 120 mg per day for Diamicron MR.
Guidelines for Initial Dosing and Dose Adjustment
Gliclazide therapy initiation should consider patient factors like age, renal function, and severity of hyperglycemia. Dose adjustments should prevent hypoglycemia, with blood glucose monitoring. Dose splitting may be needed for optimal control in some cases.
Administration Recommendations for Special Populations
- Elderly patients: Should begin with the lowest dose to avoid hypoglycemia.
- Renal impairment: Dosing adjustments are required based on creatinine clearance levels.
- Liver dysfunction: Use with caution, monitoring for signs of drug accumulation.
Differences Between Diamicron and Diamicron MR in Dosing
Diamicron MR's modified-release technology allows for once-daily dosing, providing a consistent therapeutic effect. Immediate-release Diamicron may require multiple daily doses based on the patient's glycemic control.
5. Composition and Formulations
Active and Inactive Ingredients in Diamicron/Diamicron MR
The active ingredient in Diamicron and Diamicron MR is Gliclazide, with inactive ingredients like lactose, hypromellose, and magnesium stearate contributing to stability and absorption. Excipients differ slightly between formulations.
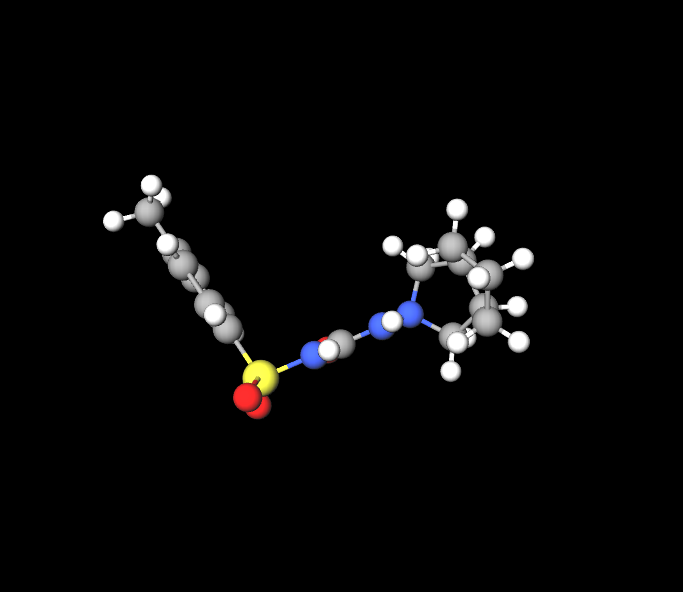
Available Forms and Strengths
Diamicron tablets come in 40mg and 80mg doses, and Diamicron MR comes in 30mg and 60mg doses, offering customizable treatment options for patients.
Differences in Formulation Between Diamicron and Diamicron MR
Diamicron MR utilizes a hydrophilic matrix to control the release of Gliclazide over 24 hours, providing smoother pharmacokinetics and better patient compliance compared to immediate-release Diamicron.
Diamicron vs metformin
Gliclazide is not as effective as metformin for weight loss in obese, non-insulin-dependent diabetic patients, but the difference is minimal. It is still a suitable oral hypoglycemic agent for obese diabetics who are not able to manage their condition through diet alone.
6. Diamicron Side Effects
Common Side Effects and Their Frequency
Common side effects of Diamicron and Diamicron MR may include hypoglycemia, gastrointestinal issues, and headaches. Hypoglycemia is more prevalent in patients who don't follow dietary guidelines or adjust medication for strenuous activities.
Serious Side Effects and Potential Risks
Rare but serious side effects of diabetes medication include severe hypoglycemia, liver enzyme elevation, and hematologic issues. Patients should be educated on symptoms and seek medical help if experiencing these reactions.
Long-term Safety Profile of Gliclazide
Gliclazide is well-tolerated for long-term use, but monitoring is necessary to detect potential adverse effects, especially in patients with other health conditions.
Strategies to Minimize or Manage Side Effects
To minimize side effects, adherence to prescribed doses, monitoring blood glucose levels, and lifestyle changes are essential. Educating patients on the role of diet and exercise with Gliclazide therapy can further reduce risks.
7. Common Side Effects
Hypoglycemia: Incidence, Prevention, and Management
Hypoglycemia is a common side effect of Gliclazide use, which can be managed by adjusting the dose and timing of medication. Symptoms include dizziness, sweating, and confusion, and can be relieved by consuming fast-acting carbohydrates.
Gastrointestinal Disturbances
Common gastrointestinal side effects of medications include nausea, diarrhea, and dyspepsia. These symptoms are typically mild and temporary, often improving with continued use or dosage adjustments.
Dermatological Reactions
Dermatologic reactions such as rash, itching, and photosensitivity may occur in patients taking medication and should be monitored.
Other Frequently Reported Adverse Effects
Common side effects of the medication also include headache, dizziness, and fatigue. It is important to inform a healthcare provider if these symptoms become bothersome or worsen over time.
8. Off-label Uses of Gliclazide
Potential Benefits in Non-diabetic Conditions
Gliclazide is being explored for its potential benefits in conditions outside Type 2 Diabetes, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and neonatal diabetes, by improving insulin sensitivity and metabolic disturbances in PCOS.
Clinical Evidence Supporting Off-label Uses
Clinical evidence for off-label use of Gliclazide is mainly derived from small studies or anecdotal reports. More research is required to determine its effectiveness and safety in non-diabetic conditions.
Risks Associated with Off-label Use of Diamicron
The off-label use of Diamicron poses risks of unexpected side effects and drug interactions. Healthcare professionals should closely monitor and understand the possible benefits and risks associated with using this medication for unapproved purposes.
9. Drug Interactions
Interactions with Other Antidiabetic Medications
Gliclazide can interact with other antidiabetic drugs, such as insulin and metformin, increasing the risk of hypoglycemia. Combination therapy requires careful management and regular monitoring of blood glucose levels.

Effects of Gliclazide When Combined with Cardiovascular Drugs
When combined with certain cardiovascular drugs like beta-blockers or ACE inhibitors, Gliclazide may increase its blood glucose-lowering effects, necessitating dosage adjustments. However, some diuretics may make Gliclazide less effective, so careful monitoring is needed.
Potential Interactions with Herbal Supplements and Over-the-counter Medications
Herbal supplements and over-the-counter medications can affect the effectiveness of Gliclazide. For instance, St. John's Wort can reduce its efficacy, while NSAIDs can increase its hypoglycemic effects. Patients should seek advice from their healthcare provider before taking new medications or supplements.
Impact of Alcohol and Dietary Factors on Gliclazide Efficacy
Alcohol can increase the risk of severe hypoglycemia when combined with Gliclazide. Patients should limit alcohol consumption. Dietary habits, such as meal timing and composition, can affect Gliclazide's effectiveness and require personalized dietary guidance.
10. Warnings and Precautions
Contraindications: When Not to Use Diamicron/Diamicron MR
Diamicron and Diamicron MR are effective but not appropriate for everyone. Patients with a hypersensitivity to Gliclazide, Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus, diabetic ketoacidosis, or severe renal/hepatic impairment should avoid these medications. They have an increased risk of hypoglycemia and could worsen underlying conditions.
Warnings for Patients with Pre-existing Medical Conditions (e.g., Liver or Kidney Disease)
Patients with liver or kidney disease should be closely monitored when taking Diamicron or Diamicron MR due to the potential for accumulation of the drug in the body. Healthcare providers must carefully evaluate the benefits versus the risks and consider alternative treatments to minimize the risk of adverse effects like severe hypoglycemia.
Careful Administration in Patients with Risk Factors for Hypoglycemia
Individuals who are predisposed to hypoglycemia should use caution when taking Diamicron/Diamicron MR. Their risk of low blood sugar is increased due to factors such as irregular meal patterns or strenuous physical activity. It is important for these individuals to monitor their blood glucose levels regularly and be educated on recognizing symptoms of hypoglycemia to prevent potentially dangerous situations.
Importance of Regular Monitoring and Follow-up
Regular monitoring and follow-up are crucial for patients taking Diamicron or Diamicron MR to effectively manage diabetes. This includes routine blood glucose tests and assessments of renal and hepatic function to detect potential adverse effects early on. Follow-up visits allow healthcare providers to adjust dosages, review adherence, and address any concerns.
11. Special Considerations for Specific Populations
Administration to Elderly Patients: Dosage Adjustments and Monitoring
Elderly patients require special consideration when taking Diamicron or Diamicron MR due to age-related declines in renal and hepatic function. Lower starting doses, gradual titration, and vigilant monitoring are necessary to prevent hypoglycemia in this population.
Use During Pregnancy and Lactation: Safety Profile and Guidelines
Gliclazide use is generally not recommended during pregnancy due to a lack of data on safety in pregnant women. Insulin is preferred for strict glycemic control. Gliclazide is also not recommended during lactation due to unknown excretion in human milk and potential risk to nursing infants.
Considerations for Pediatric Use: Efficacy and Safety Concerns
Diamicron and Diamicron MR have not been proven safe and effective for children. Therefore, Gliclazide is not advised for use in pediatric populations. Other treatments with established safety profiles should be used instead for managing diabetes in younger patients.
Gliclazide in Patients with Comorbid Conditions: Adjustments and Precautions
When prescribing Gliclazide for patients with comorbid conditions like cardiovascular disease or concurrent infections, healthcare providers need to carefully consider dosage adjustments and close monitoring to prevent drug interactions and worsening of the underlying condition. It is important to take a comprehensive approach and consider the overall health status of the patient.
12. Overdosage of Diamicron/Diamicron MR
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation of Gliclazide Overdose
An overdose of Gliclazide can lead to severe hypoglycemia with symptoms like sweating, tremors, confusion, and loss of consciousness. Prolonged hypoglycemia can cause neurological damage or death, requiring immediate intervention to prevent long-term complications.
Gliclazide maximum dose
The maximum daily dose for gliclazide is 320mg. If exceeding 160mg, split into two equal doses for safety.
Immediate Management and Treatment Options
Management of a Gliclazide overdose includes giving oral or intravenous glucose depending on the severity of hypoglycemia. Continuous glucose monitoring is crucial until the patient stabilizes, and hospitalization may be necessary for prolonged observation to prevent the recurrence of hypoglycemia.
Long-term Consequences of Overdose and Follow-up Care
Patients who overdose on Gliclazide may experience long-term consequences such as cognitive impairment or neurological deficits if not promptly treated. Follow-up care should include monitoring blood glucose levels and adjusting medication to prevent future incidents.
13. Storage and Handling of Diamicron/Diamicron MR
Proper Storage Conditions to Maintain Efficacy
It is important to store Diamicron and Diamicron MR in a cool, dry place below 25°C to maintain the effectiveness of the medication in managing blood glucose levels. Improper storage can degrade the active ingredient, reducing efficacy.
Handling Precautions to Avoid Contamination
It is crucial to take precautions when handling Diamicron or Diamicron MR to avoid contamination. Tablets should be handled with clean, dry hands to prevent exposure to contaminants that may affect the medication's effectiveness. Always securely close the packaging after use.
Guidelines for Disposing of Expired or Unused Medication
Expired or unused Diamicron/Diamicron MR should be disposed of according to local regulations to prevent environmental contamination. Pharmacies may offer take-back programs for safe disposal, avoiding risks to others and the environment by not disposing of medications in household waste or sewage systems.
Diamicron/ Diamicron MR, Gliclazide FAQ
What is Diamicron used for?
An oral hypoglycemic drug (hypoglycemic drug). Diamicron 80 mg is used to maintain blood sugar at a reasonable level in adults with insulin-resistant diabetes that is not controlled by diet, exercise, and weight loss.
What is the best time to take Diamicron?
All or half of Diamicron 60 mg MR tablets should be taken with food because the risk of hypoglycemia increases if the meal is taken for a long time, if there is no food, or if the carbohydrate intake is low. It is recommended to take the medicine at breakfast time.
Is Diamicron safe for kidneys?
Kidney disease or poor kidney function can cause this substance to accumulate in the body and cause side effects..
Can I take Diamicron twice daily?
Since the half-life of gliclazide in humans is 20 hours, the drug can be administered twice a day. Circulation occurs mainly in the urine: less than 1% of the dose is found unchanged in the urine..
Can you take metformin and Diamicron together?
It showed that Metformin and Diamicron can effectively control blood sugar levels in most patients with type 2 diabetes with a low risk of hypoglycaemia..
Can I stop Diamicron?
People treated with gliclazide MR may lose blood sugar control during illness or stressful situations, such as injury or surgery. In these cases, the doctor can stop the medicine and prescribe insulin to make the condition better.