Dobutamine HCL
- Introduction to Dobutamine
- Uses of Dobutamine
- Off-Label Uses of Dobutamine
- Understanding How Dobutamine Works
- Composition of Dobutamine
- Dosage and Administration of Dobutamine
- Side Effects of Dobutamine
- Interactions of Dobutamine with Other Medications
- Warnings and Contraindications
- Safe and Careful Administration of Dobutamine
- Dobutamine Administration to Specific Populations
- Managing Overdose of Dobutamine
- Storage and Handling Precautions for Dobutamine
Introduction to Dobutamine
Brief Overview of Dobutamine
Dobutamine is a medication used in the medical field for its essential role in heart care. It is derived from isoproterenol. It mainly works by stimulating the beta-1 adrenergic receptors of the heart. This stimulation leads to an improved output without causing a significant increase in heart rate.
Historical Development and Approval Status
Dobutamine, first created in the 1970s as a remedy for heart failure and circulatory shock, underwent extensive clinical trials before receiving FDA approval in the United States in 1978. Since then, this medication has gained recognition for improving myocardial contractility and enhancing blood flow in individuals with heart failure.
Uses of Dobutamine
Primary Use: Treatment of Heart Failure
Dobutamine is commonly used to treat acute heart failure. One of its benefits is that it enhances stroke volume and cardiac output while not placing excessive demands on oxygen. This, in turn, helps improve blood circulation and alleviate symptoms associated with heart failure3, including difficulty breathing and swelling in the extremities. Dobutamine can also be helpful for short-term management of acute heart failure syndromes and treat cardiogenic shock following surgery or a heart attack.
Other Recognized Uses in Cardiology
Dobutamine has applications in cardiology beyond its role in heart failure. For example, it is commonly used in stress testing to evaluate artery disease through Dobutamine stress echocardiography. This diagnostic method helps doctors assess how the heart responds to stress in a controlled environment. Additionally, Dobutamine can help improve performance after a heart attack or surgery, particularly for individuals experiencing low cardiac output syndrome.
Off-Label Uses of Dobutamine
Use in Hypovolemic Shock
Although Dobutamine is primarily used for managing heart conditions, it's also utilized off-label in treating hypovolemic shock. In cases where there is a decrease in blood or fluid volume in the body, Dobutamine can assist in preserving cardiac output and stabilizing blood pressure1.
Other Potential Off-Label Applications
Apart from its usage, Dobutamine may have potential benefits in various medical scenarios. However, it is essential to note that further research and verification are necessary to validate these applications. Some uses include enhancing kidney function during critical illness and treating septic shock in cases where other medications have not yielded the desired outcomes.
Understanding How Dobutamine Works
Mechanism of Action Explained
Dobutamine primarily works by stimulating adrenergic receptors in the heart, which boosts the contractility of the heart muscle and improves its pumping capacity. Unlike medications with similar effects, Dobutamine doesn't significantly impact heart rate, making it a favored option in various cardiac situations.
Dobutamine Article - StatPearls
Dobutamine's Impact on the Cardiovascular System
Dobutamine can enhance the heart's pumping capacity resulting in hemodynamics. This means it helps the heart overcome the forces to circulate blood throughout the body effectively. Consequently, it leads to an efficient cardiac output and alleviates symptoms commonly associated with reduced cardiac output, such as fatigue, shortness of breath, and fluid retention.
Composition of Dobutamine
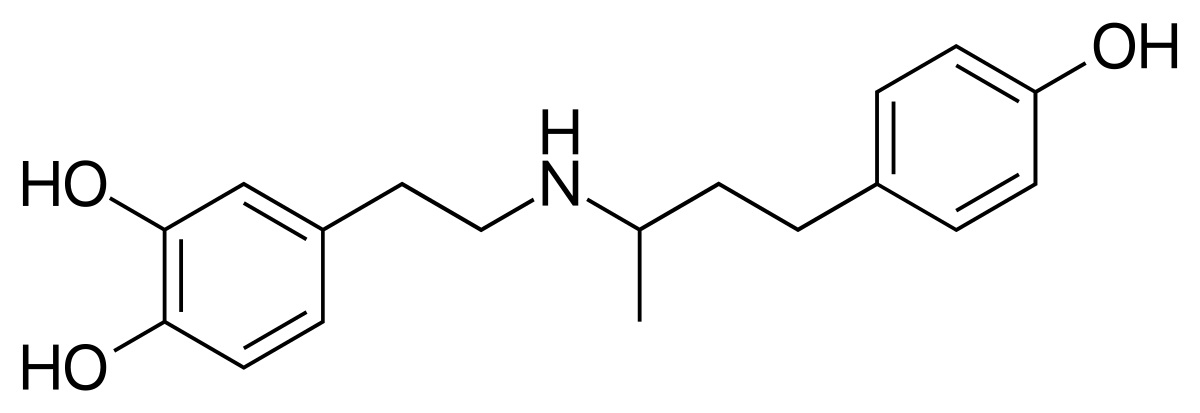
Active Ingredient: Dobutamine HCL
Dobutamine contains a compound called Dobutamine Hydrochloride (HCL), a powerful synthetic catecholamine. Its distinct chemical composition enables it to engage with beta-1 receptors, thereby supporting its impact on the cardiovascular system.
Understanding the Inactive Ingredients
The ingredients that are not active, also known as excipients, can vary depending on the formulation and maker of the Dobutamine medicine. Typically these might consist of stabilizing agents, pH adjusters, and preservatives. Even though they are not active themselves, these elements have a function in preserving the stability and shelf life of the drug.
Dosage and Administration of Dobutamine
Standard Dosage Guidelines
Dobutamine is usually given through an IV by a healthcare provider. The dose is carefully determined depending on the patient's weight, medical condition, and how they respond to treatment. Usually, the infusion begins at a rate and is adjusted based on the patient's reaction1.

Instructions for Optimal Administration
Dobutamine, being a medication, needs to be administered with caution. Typically it is mixed with a solution and given through an infusion pump to maintain a consistent and controlled flow. To ensure dosage, the patient's vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and electrocardiogram (ECG), are closely monitored during administration. Any necessary adjustments to the dosage are made accordingly.
Side Effects of Dobutamine
Common Side Effects and How to Manage Them
Dobutamine, similar to any medicine, may have some side effects. Although most are usually mild and temporary, it's essential to be mindful of them. Common side effects may include2:
- Increase in heart rate
- Higher blood pressure
- Headaches
- Feelings of nausea
- Chest discomfort
Generally, these side effects tend to subside on their own as the body adapts to the medication. However, seeking medical attention is advisable if they persist or worsen over time.

Rare but Serious Side Effects to Watch Out For
Sometimes Dobutamine might lead to adverse effects that demand urgent medical attention. These can include:
- Difficulties in breathing
- Heartbeat intense
- Dizziness
- Fainting
If you notice any of these symptoms, reaching out to a healthcare professional is crucial.
Interactions of Dobutamine with Other Medications
Potential Risks with Commonly Used Drugs
Dobutamine can interact with medications, changing their effects or increasing side effects. It is essential to inform healthcare providers about all your current medicines, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter products, and herbal supplements. Particular attention should be given to medications such2, as
- Beta-blockers
- Calcium channel blockers
- Specific antidepressants

Interaction of Dobutamine with Dietary Supplements
Although there is research on the interaction between Dobutamine and dietary supplements, you should inform healthcare professionals about any supplements you take. Some natural products may affect the system, which could potentially affect the effectiveness or safety of Dobutamine.
Warnings and Contraindications
Health Conditions that May Preclude Use of Dobutamine
Specific individuals with health conditions may need to refrain from using Dobutamine. These conditions encompass hypertension, certain forms of irregular heart rhythm, and significant narrowing of the aortic valve. It is crucial to disclose your medical history to your healthcare provider to mitigate any potential risks.
Lifestyle and Drug Contraindications to Consider
Confident lifestyle choices can also impact the safety of using Dobutamine. It's advisable to steer clear of alcohol while taking Dobutamine as it could worsen side effects such as dizziness or cause a rise in blood pressure. Moreover, smoking or using nicotine products might interfere with the effectiveness of the medication.
Safe and Careful Administration of Dobutamine
Important Precautions to Take
Make sure that a healthcare provider administers Dobutamine through an IV infusion. The information rate will be modified depending on how the person responds to the medication. Monitoring the heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG readings while undergoing treatment is essential.
The Importance of Monitoring Patient Response
Monitoring patients while administering Dobutamine is essential to ensure their safety and achieve the best treatment outcomes. Regular evaluations enable healthcare providers to make dosage adjustments and promptly address potential side effects, providing practical and safe treatment.
Dobutamine Administration to Specific Populations
Special Considerations for Elderly Patients
When it comes to using Dobutamine in patients, there are a few things to remember. How their bodies process and respond to medications can change with age, which means the effects of the drug might be different for them. This makes this group more prone to experiencing effects like increased heart rate and greater demand for oxygen in the heart muscle. That's why it's wise, to begin with a dose and slowly increase it based on how each individual responds.

Administration in Pregnancy and Lactation: What You Need to Know
Dobutamine should only be given to women if necessary. We have limited information on the use of Dobutamine during pregnancy. It's essential to carefully consider the potential risks to the baby versus the benefits for the mother. Likewise, we're unsure if Dobutamine is passed through breast milk. It's advisable to be cautious when administering Dobutamine to breastfeeding women and explore alternative treatment options.

Use in Pediatric Populations: Precautions and Guidelines
The use of Dobutamine in children has not been thoroughly studied to determine its safety and effectiveness. Just like with adults, the dosage for patients should be personalized according to their weight, clinical condition, and how they respond to treatment. It is crucial to monitor their vital signs throughout the process.

Managing Overdose of Dobutamine
Recognizing Signs of Overdose
While it is uncommon, an overdose of Dobutamine can happen. If someone experiences1
- Headaches
- Palpitations
- A significant increase in blood pressure
- Shortness of breath
It is essential to recognize these symptoms to manage an overdose effectively.
Immediate Steps and Long-Term Management of Dobutamine Overdose
If there is an overdose of Dobutamine, it is essential to stop the medication away and provide supportive care. Doctors may use beta blockers as a specific treatment strategy to counteract the sympathetic activity. In the term, it is usually necessary to monitor the cardiovascular condition until it stabilizes.
Storage and Handling Precautions for Dobutamine
Recommended Storage Conditions
It is advisable to store Dobutamine at room temperature in a dark place, preferably not in the bathroom. Keep it out of the reach of children and pets to avoid ingestion3.
Precautions to Ensure Safe Handling of Dobutamine Medication
Dobutamine is usually given in an environment, so healthcare workers must prioritize safety. They should avoid touching their skin or eyes and wear protective clothing if there is a chance of any spills. If there is contact, washing the affected area promptly with plenty of water is crucial.











