Dyamide, Torsemide
- Introduction
- Composition and Chemical Structure
- Torsemide Brand
- Torsemide Generic Name
- Torsemide Half Life
- Torsemide vs Furosemide
- Torsemide vs Bumetanide
- Torsemide vs Lasix
- Torsemide vs Bumex
- Soaanz vs Torsemide
- Torsemide Mechanism of Action
- Torsemide Uses
- Off-Label Uses
- Torsemide Dosage and Administration
- Side Effects of Torsemide
- Precautions and Warnings
- Torsemide Interactions
- Special Populations
- Handling and Storage
- Overdose and Emergency Management
Introduction
Join us as we dive into Torsemide's role as a medication for treating various health issues, such as heart failure and swelling in the body (edema). This piece explores the details of torsemide, from its classification to how it works and its wide range of uses, to help healthcare providers and students improve their understanding of pharmacology and improve patient outcomes.

Overview of Torsemide
Torsemide is a loop diuretic known for its effectiveness in removing surplus fluid from the body, which is necessary in conditions like heart failure and kidney or liver diseases. Compared to medications, it boasts a higher bioavailability of around 80-90 % and a longer-lasting effect, making it a favored choice for long-term treatment regimens.
Pharmacological classification and relevance in clinical use
Torsemide is a loop diuretic that mainly acts on the ascending limb of the loop of Henle in the kidney's nephron system. It blocks the sodium potassium chloride cotransporter to prevent the reabsorption of sodium and chloride ions while promoting water excretion. This process not only helps reduce fluid but also improves symptoms related to conditions like congestive heart failure and liver or kidney disease. The unique pharmacological characteristics of torsemide make it a vital component in treating management issues by offering an approach to therapy.
Scope of the article
- Explore the pharmacokinetics of Torsemide. Discuss how they affect care in a clinical setting.
- Compare research findings that showcase how Torsemide performs in comparison to diuretics.
- Lets talk about how Torsemide can be included in the treatment plans, for health conditions.
- Be sure to list reactions and restrictions while emphasizing the importance of closely monitoring the patient's condition.
To sum up the discussion, torsemide plays a role in treating disorders that call for action. Healthcare professionals specifically choose it for its properties and treatment benefits. It stands out as a pick for those seeking swift and successful interventions in conditions related to fluid retention. The upcoming sections will delve deeper into these aspects and shed light on the ways torsemide is utilized in real-world medical settings.
Composition and Chemical Structure
Torsemide is a loop chemically known as 1-isopropyl-3-[(4-m-toluidino-3-pyridyl)sulfonyl] urea. It has robust diuretic and antihypertensive effects due to its unique structure, which aids in quick absorption and thorough renal clearance.
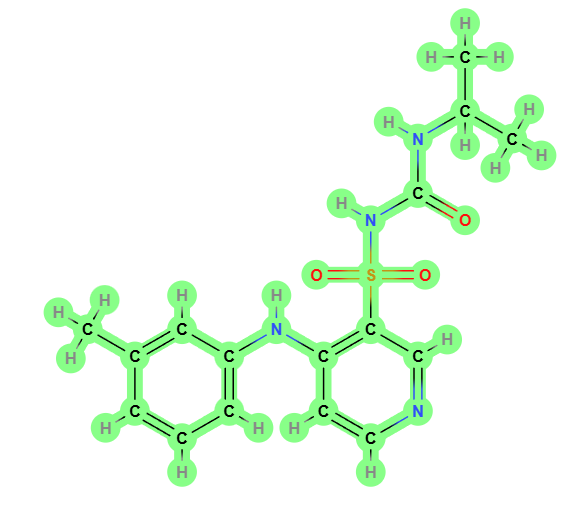
Active Ingredients in Torsemide
Torsemide contains the torsemide molecule, which encourages diuresis by disrupting the sodium potassium chloride cotransporter system in the renal tubular lumen. This component's effectiveness in managing fluids in medical scenarios is notable.
Formulation Specifics
- Torsemide can be found in tablet format, with dosages varying between 5 mg and 100 mg.
- The oral medications may contain ingredients, like lactose and magnesium stearate, to help maintain the tablet's effectiveness and absorption in the body.
Overview of Pharmacokinetics
Torsemide works quickly. It lasts a time due to its high bioavailability of around 90%. The liver mainly processes it. Eliminated through the kidneys with an amount being excreted in the bile.
Torsemide Brand
Torsemide is sold under brand names in the market. 'Demadex' is one of the known ones. This helps differentiate it from other diuretics and emphasizes its distinct therapeutic characteristics.
Torsemide Generic Name
In the realm of pharmacology and clinical records Torsemide is commonly known as 'torsemide' and devoid of any brand association.
Torsemide Half Life
Torsemide vs Furosemide
Torsemide and Furosemide are both loop diuretics. However, torsemide has a lasting effect and higher bioavailability than Furosemide, which could lead to better clinical results when managing fluid retention.
Torsemide vs Bumetanide
When looking at Torsemide in contrast to Bumetanide, Torsemide exhibits a half-life resulting in a protracted diuretic impact, which proves advantageous in the treatment of enduring ailments like heart failure.
Torsemide vs Lasix
Lasix and torsemide differ in how they work in the body and their effectiveness for patients. Torsemide's extended half-life makes it suitable for use and can enhance patient compliance, as opposed to Lasix, which may need to be taken multiple times a day.
Torsemide vs Bumex
The generic name Bumetanide (marketed as Bumex) is akin to Torsemide; however, Torsemide is generally favored for use over Bumex because it usually needs frequent doses due to its shorter effectiveness duration.
Soaanz vs Torsemide
Soaanz is a version of Torsemide that contains the main component but may have different additional ingredients that could enhance digestive comfort or change how the medication is released to offer customized treatment choices for each patient's requirements.
Torsemide Mechanism of Action
Torsemide works as a type of diuretic that mainly acts by preventing the Na K‐2Cl symporter in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle from functioning. This blockage stops the reabsorption of sodium, potassium, and chloride, which is essential to its diuretic effect. The outcome is a higher release of water, sodium chloride, and potassium through urine, leading to a decrease in the build-up of fluid in tissues and spaces.
How Torsemide Functions in the Body
When you take Torsemide by mouth, it is absorbed quickly and starts working immediately. It reaches its highest levels in the blood within an hour, leading to a rapid start of urine production. This quick effect can relieve the signs linked to having too much fluid in the body, making patients feel better and lowering the chances of serious problems like pulmonary edema and ascites.
Pathways Affected by Torsemide
- Torsemide affects the balance in the nephron by increasing the excretion of sodium and chloride compounds, which may result in shifts in water balance within cell membranes.
- The function of the kidneys is to improve blood flow to the kidneys and help with filtration processes, which aids the kidneys' ability to excrete sodium effectively.
- Torsemide helps alleviate strain on the heart and reduces blood pressure by decreasing blood volume in patients with high blood pressure.
Comparison with Other Diuretics
Torsemide is often compared to Furosemide and Bumetanide for its effectiveness among loop diuretics family members; however, it stands out due to its action duration and better absorption rate compared to the others mentioned above, which makes it a suitable option for managing medical conditions that need consistent diuretic effects without the need for frequent intake like in the case of Furosemide that might require multiple daily administrations of doses; Moreover when pitted against Bumetanide Torsemides higher renal clearance capability and extended half-life make it a viable choice for patients, with varying renal functions.
Torsemide Uses
Primary Approved Uses of Torsemide
- Patients with heart failure often receive prescriptions for Torsemide to help alleviate symptoms like swelling and difficulty breathing.
- Treatment for kidney dysfunction is commonly employed to manage swelling in individuals with kidney issues such as this syndrome.
- People with liver cirrhosis find relief with Torsemide, which aids in decreasing build-up in the belly (ascites) as well as in the lower extremities.
Efficacy in Treating Specific Conditions
Torsemide has shown effectiveness in lowering hospitalization rates for individuals suffering from heart failure by effectively reducing plasma volume and lowering the risk of acute decompensated heart failure episodes. The drug's positive influence on levels and kidney function is crucial for the care of patients with chronic renal failure, as it helps stabilize their conditions over prolonged periods.
Benefits Over Alternative Treatments
When it comes to diuretics, like Furosemide or Bumetanide, in comparison to Torsemide, many clinicians favor Torsemide due to its benefits.
- Torsemide has a bioavailability of around 90% compared to Furosemide's lower bioavailability levels, leading to more steady therapeutic results.
- Extended Action Duration: The extended period of effectiveness decreases the need for medication administration and may enhance patients' adherence to the prescribed treatment schedule.
- Response Consistency Improvement: Torsemide exhibits variability among patients, resulting in consistent and steady reactions when managing fluids.
Off-Label Uses
Torsemide is commonly prescribed for managing retention linked to heart failure and other conditions. It is also used off-label for various purposes beyond its FDA-approved indications due to its effectiveness in handling fluids in the body and offering healthcare providers flexibility in treating complex situations.
Common Off-Label Applications
- Managing blood pressure often involves using torsemide, a diuretic that helps control blood pressure and regulate fluid levels in patients.
- Due to its properties, torsemide can help lower high calcium levels in the bloodstream, reducing hypercalcemia.
- Acute Hyperkalemia helps remove potassium in situations of life-threatening hypercalcemia.
Research Supporting Off-Label Use
Recent studies have started to uncover the advantages of torsemide in fields beyond its applications. The research indicates that torsemide can successfully reduce blood pressure in patients with hypertension when other diuretics have not been effective. Additionally, studies have observed its capacity to assist in the elimination of calcium and potassium, suggesting its potential as a versatile treatment option.
Patient Outcomes and Case Studies
Clinical case studies offer insights into how Torsemide is used beyond its approved indications in real-world settings. For instance, a series of cases involving patients with high blood pressure showed significant improvements in their blood pressure levels when they switched from other loop diuretics to Torsemide.
Moreover, Stories about using Torsemide to treat calcium levels linked to cancer suggest that its quick diuretic effects play a role in managing symptomatic hypercalcemia by preventing kidney issues and reducing the health risks associated with elevated calcium levels.
Torsemide Dosage and Administration
The appropriate amount of Torsemide should be adjusted with caution depending on the ailment being addressed and the patient's reaction. Kidney function considerations are also taken into account in the dosage adjustment process detailed here for heart failure and swelling conditions, as well as the favored methods of delivery and dosage modifications for demographic segments.

Recommended Dosages for Different Conditions
- Patients with congestive heart failure are usually started on a dose of 10 to 20 mg initially. This dosage can be changed according to how they respond to diuretics.
- Edema Treatment Note for Liver Cirrhosis or Renal Failure: The Initial dosage for managing edema linked to liver cirrhosis or kidney issues typically falls between 10 and 40 mg per day.
Modes of Administration
Torsemide is mainly given by mouth in the form of tablets or liquid; for individuals who struggle to swallow pills, intravenous versions are also accessible for situations like acute hospital care where oral intake isn't possible.
Adjustments for Various Demographic Groups
Adjusting the dosage might be needed for groups of people based on their characteristics.
- Older patients might need to start with doses as their kidney function could be decreased.
- Patients who have issues with their kidneys may require changes in dosage depending upon the severity of their impairment to avoid diuresis.
Torsemide Maximum Dose per Day
It is advised not to go beyond 200 mg as the daily limit for Torsemide intake since taking doses won't offer benefits and could raise the chances of side effects occurring.
Torsemide Dosing Frequency
Torsemide is usually given once a day because it stays active for some time; however, in severe situations or as advised by a healthcare professional, the dose may be split into two daily administrations to enhance the diuretic's effectiveness and reduce the risk of side effects.
Side Effects of Torsemide
As with any medication, torsemide can cause side effects ranging from mild to severe. Understanding these effects cannot be overstated, as it helps healthcare professionals manage them and ensure the safety and health of patients. This section offers insights into serious side effects such as hyponatremia, their long-term impacts, and approaches to dealing with them.

Overview of Side Effects
Torsemide may lead to imbalances and dehydration while also affecting blood pressure levels as side effects; common symptoms such as increased urination frequency, dizziness, and headaches are often reported but usually improve once the body adapts to the medication.
Torsemide Hyponatremia
Low blood sodium levels, known as hyponatremia, can be a reaction to Torsemide medication for older individuals or those with kidney problems. Signs of hyponatremia consist of headaches, confusion, seizures, and tiredness, which should be addressed promptly by professionals.
Torsemide Side Effects Long-term
- Chronic usage of Torsemide may affect kidney function. Monitoring of renal parameters is required to ensure proper functioning.
- Prolonged treatment could lead to lasting disruptions in levels of potassium, magnesium, and calcium.
- Long-term use of torsemide in high doses can cause hearing problems and other loop diuretics and raise concerns about potential hearing loss in patients with existing kidney issues.
Common versus Severe Side Effects
Strategies for Management and Mitigation
Here are some practical ways to handle and reduce the effects of Torsemide:
- Regularly checking levels, kidney function, and blood pressure can help detect and manage potential side effects.
- Fine tuning the dosage of Torsemide can frequently help ease side effects while maintaining its effectiveness, as a medication.
- Teaching patients about the importance of maintaining a fluid and electrolyte intake can help them avoid issues linked to dehydration and imbalances in electrolyte levels.
Precautions and Warnings
Treatment of conditions like edema and heart failure with Torsemide requires consideration due to its diuretic properties and effectiveness in managing these ailments. The following segment details the contraindications, precautions, and special advisories for individuals to promote the administration of Torsemide.

Torsemide Contraindications for Use
- Anuria is a condition where patients are unable to produce urine. It's advised not to use Torsemide in such cases.
- Due to its similar sulfonamide structure, patients who have had reactions to sulfonylureas or sulfonamides in the past might also react to torsemide.
- Patients who are at risk of coma or have electrolyte imbalances should avoid using this medication.
Necessary Precautions Before Prescribing
Before starting treatment with Torsemide medication
- Make sure to check the patient's kidney function before giving Torsemide, as it can affect how the kidneys work and potentially worsen existing conditions.
- Make sure to check the levels of electrolytes and focus on potassium since the medication may cause a drop in electrolyte levels.
- Check the medicines currently taken by the patient to prevent any interactions with NSAIDs and lithium.
Special Warnings for At-Risk Populations
Special care must be taken when recommending Torsemide to populations.
- As people get older, they are at risk for issues with their levels and kidney function, which means it's essential to keep a close eye on and make changes to medication doses as needed.
- For individuals with diabetes, it's essential to be aware that Torsemide may impact blood sugar levels, necessitating monitoring and potential adjustments to diabetes medications.
- People who have had gout in the past should be watched closely for flare-ups, as Torsemide may raise acid levels in the body.
Torsemide Interactions
Managing Torsemide effectively involves being aware of how it may interact with drugs and substances such as over-the-counter medications, supplements, and lifestyle factors like drinking alcohol. This part explains these interactions. Provides advice on how to handle them to avoid effects and maintain the desired treatment outcomes.

Common Interactions and Their Implications
- Using diuretics and blood pressure medications, with diuretics or drugs that lower blood pressure can increase the chances of experiencing significant drops in blood pressure and disruptions, in electrolyte levels.
- Torsemide has the potential to enhance the impacts of digitalis medications by causing a loss of potassium, in the body which requires monitoring of electrolyte levels.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) have the potential to lessen the effectiveness of Torsemide in its antihypertensive roles, possibly elevating the chances of kidney issues occurring.
How to Manage Potential Drug Interactions
To handle these interactions efficiently and effectively in healthcare settings:
- Make sure to review all medications to find any interactions before beginning Torsemide treatment.
- Regularly check blood pressure and kidney function to modify the dosage as needed and reduce the chances of interactions.
- Inform patients about the importance of informing their healthcare providers about any medicines they are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements.
Interaction with Non-Prescription Drugs and Supplements
The use of prescription medications and dietary supplements may impact the effectiveness of Torsemide.
- Licorice may worsen the potassium loss induced by torsemide, which can impact the heart and muscles.
- Taking calcium supplements might affect how well Torsemide can lower calcium levels in the blood.
Torsemide and Alcohol
Consumption of alcohol can enhance the effects of Torsemide. Raise the chances of dehydration and low blood pressure. It may also worsen the drug's ability to harm the liver, especially in individuals with existing liver issues. Patients using Torsemide are recommended to restrict or refrain from alcohol intake to mitigate these dangers.
Special Populations
When it comes to prescribing Torsemide medication, it's essential to be mindful of groups, like individuals expecting and breastfeeding mothers as well as children. Considering these factors is crucial to guaranteeing safety and effectiveness while reducing risks linked to drug administration among these populations.
Elderly: Adjustments and Considerations
When dealing with individuals receiving Torsemide treatment‚ it is crucial to exercise caution as there is a likelihood of encountering renal and electrolyte imbalances issues requiring careful management and adjustments as needed, such as;
- Commencing treatment at the dosage to assess how the body responds and tolerates it.
- It's essential to keep an eye on kidney function and electrolyte levels to address any issues that may arise.
- Checking for indications of dehydration or low blood pressure is crucial when undergoing extended treatment or taking diuretics concurrently.

Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Safety and Recommendations
There is no information about the use of torsemide in pregnant women. To ensure safety during nursing, it should be prescribed only if the benefits outweigh the risks of nursing.
- Torsemide is eliminated through the breast, which may impact the baby's baby's health, so it might be better to consider using a different medication instead.
- If the necessity arises to use it, it will impact the baby.

Torsemide Nursing Considerations
Nurses have the function of overseeing patients who are prescribed Torsemide. Their duties encompass:
- Keeping track of levels. Weighing yourself daily to check effectiveness and avoid dehydration.
- Making sure patients grasp the way to take their medication to enhance its benefits to the fullest extent possible.
Torsemide Nursing Interventions
Some of the nursing interventions that work well are:
- Ensuring that the medicine is taken consistently at the schedule to keep a steady level of the drug in the system.
- Teaching the individual about the indications of imbalances and when to reach out to a healthcare provider.
Torsemide Nursing Implications
Understanding the pharmacological effects of torsemide is essential for nurses to provide patient care.
- Swiftly identifying signs of overdose or adverse reactions is crucial.
- Tuning fluid and dietary suggestions according to how the patient is reacting to the therapy provided.
Pediatric Use: Guidelines and Dosage Adjustments
When prescribing Torsemide to children, the dosage must be adjusted, and any side effects must be monitored, as outlined in the guidelines provided.
- Adjust the dosage according to the individuals weight ensuring regulation to prevent diuresis.
- Regularly observing the progress of growth and developmental milestones to identify any effects of the medication.

Handling and Storage
It is crucial to handle and store torsemide properly to ensure its effectiveness and safety are maintained over time. This section outlines the needed storage conditions and best practices for handling to guarantee the medication's continued efficacy and safety throughout its designated shelf life period.
Proper Storage Conditions
Remember to keep Torsemide in a dry spot from sunlight and moisture to avoid it breaking down over time. Use the recommended storage temperature of around 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). Keep the tablets in their packaging until you're ready to use them to shield them from light and moisture.

Shelf Life and Stability
The typical lifespan of torsemide tablets is around 24 to 36 months starting from the manufacturing date when kept in the recommended storage conditions. Patients should be informed to inspect the expiry date on the bottle and not use the medication after this date to ensure its efficacy.
Safe Handling Practices
When working with Torsemide medication safety measures should be adhered to as follows:
- Be cautious not to handle the tablets with your hands since moisture could impact the effectiveness of the medication.
- Avoid using tablets that have altered color or exhibit any indications of decay.
- Remember to seal the container every time you use it to avoid air and moisture exposure.
- Make sure to get rid of any unused medication by using a drug take-back program if possible.
Overdose and Emergency Management
Knowing the actions to handle a Torsemide overdose is crucial in avoiding health issues. In this part, you'll find information on the signs of an overdose, the steps for aid treatments provided by medical professionals, and ways to manage the situation in the long-term post-overdose event.

Symptoms of Overdose
Signs of taking too much Torsemide can differ in strength. Usually show excessive loss of fluids and electrolytes as the main indicators:
- Severe dehydration is characterized by thirstiness and a dry mouth, along, with decreased urine output.
- Severe disruptions, in levels can result in symptoms such, as fatigue, lightheadedness, mental fog or muscle spasms.
- In situations of hypovolemia, dehydration can lead to blood pressure and fainting, which might progress to a state of shock.
First-Aid and Medical Interventions
If you suspect an overdose of Torsemide has occurred, immediate action should be taken.
- Please call for help immediately. Take the patient to a hospital away.
- Supportive care should be given by laying the patient down with their legs elevated to address blood pressure and avoid the onset of shock.
- If the person is awake and can swallow enough fluids by mouth, give them liquids to reduce dehydration.
Medical treatments will target stabilizing the patient's state by administering fluids through IV to address dehydration and electrolyte imbalances while closely observing signs and renal function.
Long-Term Management of Overdose Symptoms
Dealing with the lasting impacts of taking too much Torsemide requires a series of actions.
- It's essential to monitor levels and kidney function regularly to ensure that any remaining imbalances are addressed promptly.
- Consider modifying the amount of Torsemide prescribed or reconsidering its necessity to avoid a repeat of an overdose incident.
- Providing guidance and education to the patient and their caregivers about the significance of following dosages and being able to identify indications of an overdose.
Dyamide, Torsemide FAQ
- Can Torsemide be crushed
- Can Torsemide cause hyponatremia
- Can Torsemide cause low blood pressure
- Can Torsemide cause constipation
- Can Torsemide cause diarrhea
- Can Torsemide be cut in half
- Can Torsemide cause shortness of breath
- Can Torsemide cause hyperkalemia
- Can Torsemide be taken twice a day
- Can Torsemide cause leg cramps
- Can Torsemide cause hearing loss
- Can Torsemide and Spironolactone be taken together
- Does Torsemide increase creatinine
- How long does Torsemide stay in your system
- How long does Torsemide make you pee
- How long does it take for Torsemide to reduce swelling
- How Torsemide works
- How many Torsemide per day
- How is Torsemide different from Furosemide
- How much Torsemide is too much
- How does Torsemide affect kidneys
- Is Torsemide potassium sparing
- Is Torsemide hard on the kidneys
- What is Torsemide used for
- What are Torsemide pills for
- What is Torsemide prescribed for
- What is Torsemide used to treat
- What does Torsemide do for the body
- What is Torsemide taken for
- When to switch from Lasix to Torsemide
- When should Torsemide be taken
- When does Torsemide start working
- When does Torsemide peak
- When is Torsemide taken
- When to use Torsemide over furosemide
- When to take Torsemide tablet
- When to stop Torsemide
- When to give Torsemide
- Which is safer Torsemide or Furosemide
- Which is stronger Torsemide or Bumex
- Which is stronger Torsemide vs Furosemide
- Which is stronger Torsemide or Lasix
- Which is better Torsemide or Furosemide
- Which is better Torsemide or Hydrochlorothiazide
- Which is better Torsemide or Spironolactone
- Which is better Torsemide or Bumex
- Why Torsemide is preferred over Furosemide
- Why Torsemide is used
- Why use Torsemide instead of Lasix
- Why is Torsemide prescribed
- Why is Torsemide not working
- Why is Torsemide given
- Why we use Torsemide
Can Torsemide be crushed
Torsemide should not be crushed; it is best to take it as directed and swallow the tablet as usual.
Can Torsemide cause hyponatremia
Indeed! Torsemide can cause hyponatremia as a side effect.
Can Torsemide cause low blood pressure
Indeed! Torsemide can lead to a drop in blood pressure as a side effect.
Can Torsemide cause constipation
Torsemide usually doesn't lead to constipation; instead, it often leads to increased urination due to its effects.
Can Torsemide cause diarrhea
Yes indeed! Torsemide may lead to experiencing diarrhea as a side effect.
Can Torsemide be cut in half
Certainly! Torsemide tablets can be halved if they have a score mark from the manufacturer, allowing it to be done that way. Please make sure to refer to the product guidelines or seek advice from healthcare before making any changes to your medication routine.
Can Torsemide cause shortness of breath
Sure thing! Torsemide may cause breathlessness when it causes fluid changes or imbalances in electrolytes.
Can Torsemide cause hyperkalemia
Torsemide usually doesn't cause hypercalcemia; it's more prone to hypokalemia, which occurs when potassium levels in the blood are lowered.
Can Torsemide be taken twice a day
Certainly! Torsemide can be consumed two times daily under the guidance of a healthcare professional when a higher daily dosage is necessary for fluid control.
Can Torsemide cause leg cramps
Torsemide may lead to leg cramps as a side effect because of electrolyte imbalances, like levels of potassium or magnesium.
Can Torsemide cause hearing loss
Torsemide may lead to hearing impairment as a side effect; it is usually reversible and more prone to happen with elevated dosages or quick intravenous delivery.
Can Torsemide and Spironolactone be taken together
Sure! Torsemide and Spironolactone are compatible for treating conditions such as heart failure. They provide both diuretic and potassium-sparing benefits under the supervision of a healthcare professional, who ensures safety and effectiveness while monitoring for any adverse reactions or drug interactions.
Does Torsemide increase creatinine
Yes, torsemide can increase creatinine levels.
How long does Torsemide stay in your system
Torsemide usually remains in the body for three and a half to four hours, as its life span is within that timeframe. However, its impact on urine output(diuresis) can last from six to eight hours.
How long does Torsemide make you pee
The increase in urination due to Torsemide usually lasts for around 6 to 8 hours following ingestion of a dose.
How long does it take for Torsemide to reduce swelling
The impact of torsemide on diminishing swelling or edema may become apparent within a few hours of consuming the medication. Depending on the specific ailment being addressed, the noticeable decrease in swelling manifests within the week of consistent usage.
How Torsemide works
Torsemide is a diuretic known as a loop that aids in the removal of fluid from the body by disrupting the reabsorption of sodium and water in the loop of Henry in the kidneys. This process results in urine output. It helps decrease fluid retention while also reducing blood pressure levels.
How many Torsemide per day
The amount of torsemide needed may vary depending on the illness being addressed. It is usually taken daily in doses ranging from 5 mg to 200 mg, depending on the individual's situation and how they respond to a treatment regimen prescribed by a healthcare professional.
How is Torsemide different from Furosemide
Torsemide lasts longer in the body and is better absorbed than Furosemide, which can result in consistent effects over time and potentially be more beneficial for specific individuals.
How much Torsemide is too much
Taking too much Torsemide medication can be dangerous as it may cause effects like dehydration and kidney issues if the daily dose exceeds 200 mg in most cases. Advice from a healthcare provider regarding the dosage is essential for usage.
How does Torsemide affect kidneys
Torsemide works on the kidneys by boosting urine production by blocking sodium and water reabsorption in the loop of Henle, which is part of the kidney filtration process. This action is beneficial for reducing retention and controlling conditions such as heart failure and hypertension. However, overusing or misusing Torsemide can result in dehydration and imbalances in electrolytes, which may strain the kidneys or worsen existing kidney problems.
Is Torsemide potassium sparing
Torsemide doesn't preserve potassium like some diuretics—it's actually a loop diuretic that can cause potassium levels to drop.
Is Torsemide hard on the kidneys
Torsemide may pose difficulties for kidneys in individuals with kidney issues as it has the potential to impact kidney functionality and fluid equilibrium, necessitating observation.
What is Torsemide used for
Torsemide is prescribed for swelling ( buildup), often linked to heart failure or liver and kidney issues. It is also utilized to control blood pressure.
What are Torsemide pills for
Torsemide tablets are used to help decrease swelling caused by retaining fluids (edema) and to control high blood pressure.
What is Torsemide prescribed for
Torsemide is often recommended to help manage swelling and hypertension in individuals.
What is Torsemide used to treat
Torsemide is prescribed for managing retention and hypertension.
What does Torsemide do for the body
Torsemide helps decrease fluid in the body and lower blood pressure.
What is Torsemide taken for
Torsemide is prescribed to treat swelling and hypertension issues.
When to switch from Lasix to Torsemide
Consider transitioning to Torsemide or Lasix when you require an effective diuretic option with improved absorption rate and lasting effects or when aiming for better patient adherence—particularly in instances of diuretic resistance, advanced heart failure, or chronic kidney disease. Seek advice from a healthcare provider for tailored recommendations.
When should Torsemide be taken
Torsemide is best taken once a day in the morning to avoid the need to urinate at night.
When does Torsemide start working
Torsemide typically begins to take effect around one hour after it is taken orally.
When does Torsemide peak
Torsemide reaches its levels in the body 1 to 2 hours after it is taken by mouth.
When is Torsemide taken
Torsemide is taken once daily in the morning.
When to use Torsemide over furosemide
Consider opting for torsemide instead or Furosemide for its higher absorption rates and longer-lasting effects in instances of diuretic resistance or conditionslike heart failure and chronic kidney disease.
When to take Torsemide tablet
Take a Torsemide tablet once daily in the morning.
When to stop Torsemide
If there are any side effects when blood pressure is consistent, discontinue the use of Torsemide with the guidance of a healthcare professional once the swelling subsides.
When to give Torsemide
Administer Torsemide to treat swelling (edema), heart failure, or high blood pressure (hypertension) or, as a management option, for kidney disease.
Which is safer Torsemide or Furosemide
Torsemide is often considered an option compared to Furosemide because it stays active for more extended periods, is better absorbed by the body, and poses a reduced risk of disrupting electrolyte levels.
Which is stronger Torsemide or Bumex
In terms of strength, Bumex (also known as Bumetanide) is more powerful than Torsemide, being 40 times more potent per milligram.
Which is stronger Torsemide vs Furosemide
Torsemide is more potent than Furosemide, being approximately twice as strong when compared to milligrams.
Which is stronger Torsemide or Lasix
Torsemide is more potent than Lasix (also known as Furosemide); it exhibits double the potency on a milligram-to-milligram basis.
Which is better Torsemide or Furosemide
Torsemide is often viewed as superior to Furosemide because it lasts longer in the body and is absorbed consistently and efficiently.
Which is better Torsemide or Hydrochlorothiazide
Torsemide is usually more effective in treating swelling and heart failure because it has an impact compared to Hydrochlorothiazide, which is commonly chosen for handling mild high blood pressure.
Which is better Torsemide or Spironolactone
Torsemide is effective in removing fluid from cases of edema and heart failure; on the other hand, Spironolactone is more effective in preventing potassium depletion and treating conditions such as hyperaldosteronism.
Which is better Torsemide or Bumex
Torsemide provides diuretic effects compared to Bumex (also known as Bumetanide), which is more potent and acts more quickly when removing excess fluids during acute situations.
Why Torsemide is preferred over Furosemide
Torsemide is often chosen over furosemide because it lasts longer in the body and is easier to take by mouth while also having a consistent effect on the body's processes and a lower chance of developing resistance to diuretics.
Why Torsemide is used
Torsemide is prescribed for treating swelling linked to heart failure, liver cirrhosis, and kidney disease and for controlling high blood pressure.
Why use Torsemide instead of Lasix
Torsemide is often preferred over Lasix (Furosemide) as it has a lasting effect once taken orally and is absorbed consistently in the body, resulting in more predictable diuretic outcomes.
Why is Torsemide prescribed
Torsemide is commonly used to treat swelling linked to heart, kidney, or liver issues and to control blood pressure effectively.
Why is Torsemide not working
Torsemide might not be effective because of issues such as the dosage amount or kidney problems that could affect its function; it could also be impacted by interactions with medications or the body's development of resistance to diuretics.
Why is Torsemide given
Torsemide is prescribed for treating swelling and fluid buildup resulting from issues such as heart failure, liver cirrhosis, and kidney disease for controlling high blood pressure.
Why we use Torsemide
Torsemide is commonly prescribed to address swelling and water retention linked to conditions like heart failure and liver cirrhosis, as well as kidney disease and high blood pressure control.