Dynacirc SRO
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition and Formulation
- III. How Dynacirc SRO Works
- IV. Approved Uses and Indications
- V. Off-Label Uses and Emerging Applications
- VI. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- VII. Isradipine side effects
- VIII. Drug Interactions and Contraindications
- IX. Warnings, Important Precautions, and Careful Administration
- X. Special Population Considerations
- XI. Overdosage and Emergency Management
- XII. Storage, Handling, and Disposal
I. Introduction
Overview of Dynacirc SRO
Dynacirc SRO represents a paradigm shift in cardiovascular therapeutics. Isradipine, and therefore Dynacirc SRO, was primarily prescribed to treat hypertension (high blood pressure). Managing high blood pressure is crucial to reduce the risk of serious health problems, such as stroke, heart attack, and kidney disease.
- Innovative design and formulation.
- Precision-targeted therapeutic action.
- Robust clinical performance.
This compound has garnered attention for its multifaceted benefits in cardiovascular management.
II. Composition and Formulation
Active Ingredients and Their Roles
At the core of Dynacirc SRO lies an amalgamation of active pharmaceutical ingredients. Each constituent is meticulously selected to exert specific biochemical effects that collectively orchestrate vascular modulation and cardiac support. Their roles include:
- Isradipine
This synergistic interplay is fundamental to its clinical efficacy.
Inactive Ingredients and Excipients
Complementing the active components, a diverse array of excipients ensures the stability and optimal bioavailability of Dynacirc SRO. These inactive ingredients play pivotal roles in:
- Maintaining formulation integrity.
- Facilitating uniform drug dissolution.
- Optimizing absorption kinetics.
The integration of these ancillary constituents enhances the overall pharmacological profile.
Isradipine vs amlodipine
Isradipine and amlodipine are both types of calcium channel blockers that are effective in managing blood pressure. Additionally, amlodipine is prescribed for individuals with artery disease—a condition characterized by blocked arteries in the heart.
III. How Dynacirc SRO Works
Mechanism of Action
Calcium Channel Blockade
Isradipine mainly focuses its action on L-type calcium channels that are located within the muscle cells of blood vessels with a presence in the arterial walls. By obstructing these pathways, isradipine prevents the entry of calcium ions into the muscle cells.
Vasodilation
Essential for muscle contraction is the influx of calcium into the cells; isradipine induces relaxation in muscle cells by decreasing calcium entry. This state of relaxation causes vasodilation. A process where the blood vessels expand. The expansion of the blood vessels decreases resistance in the system, leading to a decrease in blood pressure.
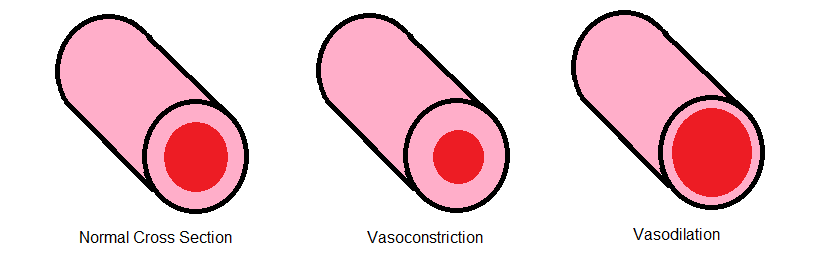
Effects on the Heart
While isradipine mainly targets the muscles, in blood vessel action, it may also exert certain impacts on the heart. Isradipine can enhance heart function indirectly by lowering afterload, which's the resistance the heart pumps against.
IV. Approved Uses and Indications
A. Primary Medical Indications
1. Cardiovascular Management
Dynacirc SRO is predominantly indicated for advanced cardiovascular management. Its application in this domain includes the regulation of cardiac function and the stabilization of vascular dynamics. The key benefits include:
- Optimization of myocardial performance.
- Regulation of systemic vascular resistance.
- Prevention of heart failure exacerbations.
This targeted approach reinforces its stature as a cornerstone in cardiovascular therapeutics.

2. Blood Pressure Regulation
Integral to its clinical utility is the role of Dynacirc SRO in blood pressure regulation. Through its vasodilatory properties, the medication:
- Effectively modulates systolic and diastolic pressures.
- Prevents hypertensive surges.
- Ensures vascular compliance is maintained.
The regulation of blood pressure is critical in mitigating cardiovascular risk and enhancing overall vascular health.
B. Secondary Uses in Clinical Practice
1. Adjunctive Therapy in Related Conditions
Beyond its primary indications, Dynacirc SRO serves as a valuable adjunct in various clinical contexts. It is utilized to complement standard treatment regimens in conditions such as:
- Metabolic syndrome.
- Chronic heart conditions.
- Other vascular disorders that compromise circulatory stability.
Its integration into broader therapeutic strategies underscores its versatility.
2. Comparative Effectiveness with Other Agents
Comparative studies have highlighted the advantageous profile of Dynacirc SRO when juxtaposed with alternative agents. Its benefits are reflected in:
- Superior tolerability and safety.
- Enhanced efficacy in modulating vascular tone.
- Fewer drug-drug interactions in polypharmacy contexts.
Such comparative effectiveness consolidates its standing as a preferred therapeutic option.
V. Off-Label Uses and Emerging Applications
A. Use in Unconventional Patient Populations
1. Management of Resistant Hypertension
In select clinical scenarios, Dynacirc SRO is utilized off-label for the management of resistant hypertension. This application leverages its potent hemodynamic modulation to overcome treatment recalcitrance. Its off-label benefits include:
- Enhanced stabilization of blood pressure.
- Reduction in hypertensive complications.
- Complementary support in refractory cases.
Such use exemplifies the compound's adaptability in challenging clinical environments.
VI. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
A. Standard Dosage Recommendations for Adults
B. Pediatric Dosage Adjustments
Geriatric Dosage: Older adults may require lower doses. It is common to start with the lower end of the dosing scale. It is very important that a doctor is consulted with for correct dosing.
C. Administration to Elderly Patients
Elderly patients present unique pharmacodynamic challenges that necessitate cautious dosage modifications. Clinical guidelines advocate:
- Incremental titration of dosages.
- Close observation for drug interactions and adverse effects.
- Frequent reassessment of therapeutic outcomes.
Such measures ensure that the benefits of Dynacirc SRO are realized while minimizing potential risks.
D. Administration Techniques and Best Practices
1. Oral vs. Injectable Forms (if applicable)
Dynacirc SRO is formulated in multiple delivery modes to accommodate patient preferences and clinical exigencies. The oral formulation offers ease and convenience, while the injectable form provides:
- Rapid onset of action.
- Precise dosing control.
- Enhanced bioavailability in critical settings.
These options empower clinicians to select the most appropriate route based on situational demands.
VII. Isradipine side effects
A. Common Side Effects
Frequency and Severity
The incidence of common side effects is documented in clinical trials with meticulous precision. Although most events are classified as mild to moderate, their frequency can be contingent upon patient-specific factors such as genetic predisposition and concurrent medications.
- Headache, dizziness, and slight nausea occur in a notable fraction of patients.
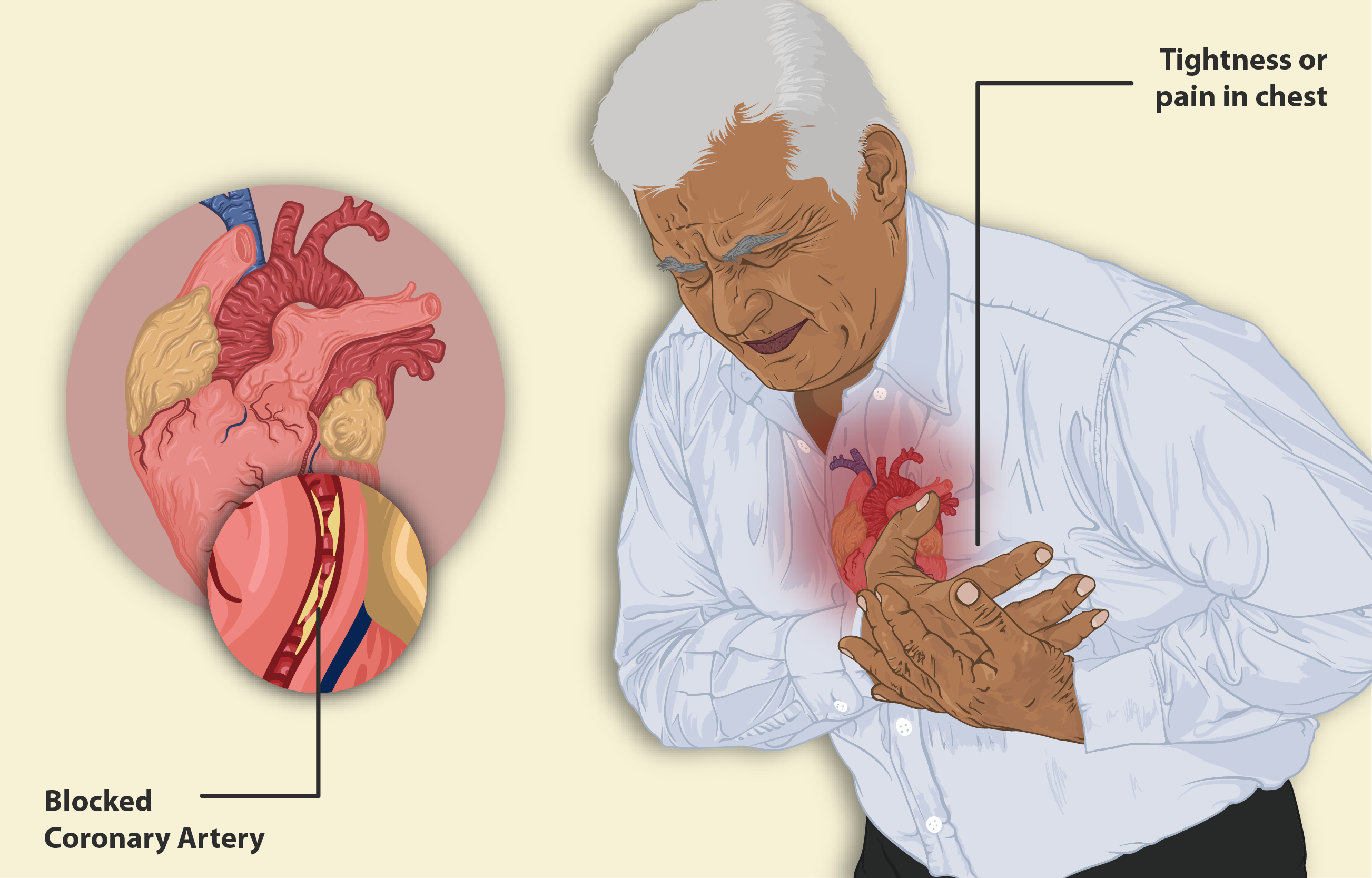
- Low blood pressure—dizziness, feeling faint or lightheaded, blurry vision;
- Worsening chest pain (angina)—pain, pressure, or tightness in the chest
Short and sporadic, these symptoms are often self-limiting; yet, their severity may escalate in predisposed individuals.

B. Rare and Serious Adverse Reactions
Monitoring and Reporting Requirements
Serious adverse reactions, though infrequent, mandate rigorous monitoring and prompt reporting. Healthcare professionals are urged to adopt a proactive surveillance strategy to identify early indicators of severe toxicity. In instances of atypical clinical presentations, comprehensive diagnostic evaluations are warranted.
- Paresthesia (numbness and tingling)
- Transient ischemic attack (TIA)Stroke.
- Musculoskeletal: cramps of legs/feet.
- Urogenital: nocturia.
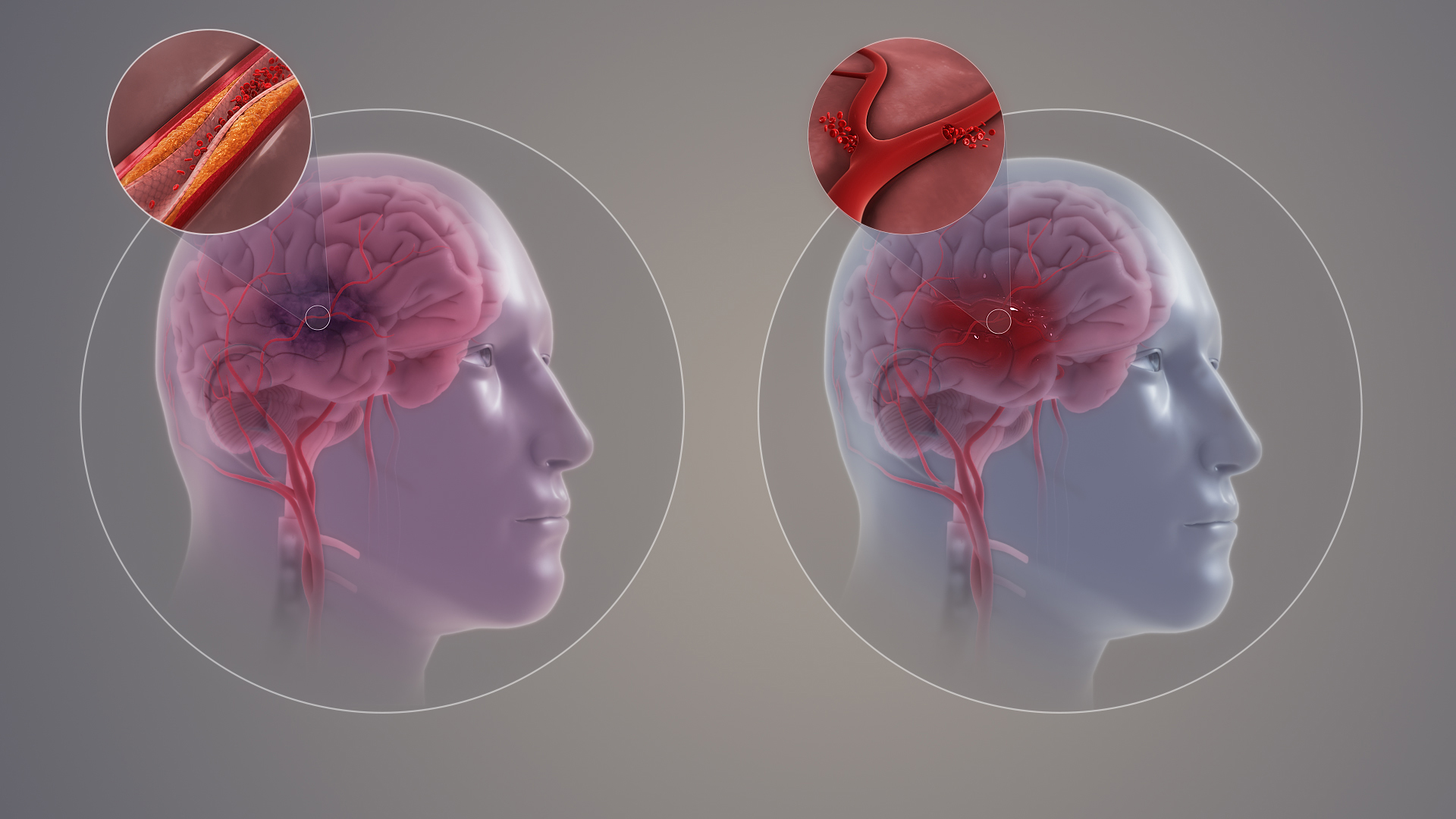
Long-Term Safety Considerations
Long-term administration of Dynacirc SRO requires assiduous evaluation of its cumulative safety profile. Longitudinal studies have illuminated potential concerns that include sustained organ system perturbations and progressive metabolic disturbances.
- Chronic monitoring of hepatic and renal function.
- Regular cardiovascular evaluations to preclude latent complications.
This comprehensive approach to safety ensures that any deleterious effects are detected and managed expeditiously.
VIII. Drug Interactions and Contraindications
A. Interaction with Other Medications
1. Effects on Co-administered Drugs
- Other Blood Pressure Medications: Combining isradipine with other antihypertensive drugs can lead to an increased risk of hypotension (low blood pressure). Careful monitoring is essential.
- Cimetidine: Cimetidine (a medication used for heartburn) can increase the levels of isradipine in the blood, potentially increasing the risk of side effects.
- Rifampin: Rifampin (an antibiotic) can decrease the levels of isradipine in the blood, potentially reducing its effectiveness.
- Drugs that affect the heart: Because isradipine affects the heart, care should be taken when it is used in combination with other medications that effect the heart. Such as certain antiarrhythmic drugs. Grapefruit Juice: Like some other calcium channel blockers, isradipine may interact with grapefruit juice.
- Grapefruit juice can increase the levels of isradipine in the blood, potentially leading to increased side effects.
B. Contraindications
Hypersensitivity:
If someone has a sensitivity (allergy known to isradipine or any other dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker, they should avoid using this medication.
Hypotension:
Isradipine has the ability to reduce blood pressure levels. It is typically not recommended for individuals with hypotension (extremely low blood pressure).
Certain Cardiac Conditions:
When it comes to treating blood pressure with medication,' it's crucial to be wary when dealing with patients who have specific heart conditions. Severe aortic stenosis may lead to a chance of experiencing blood pressure issues. Congestive heart failure can be improved by decreasing the afterload; however it may also lead to a decrease, in heart function, at doses potentially exacerbating the condition.
IX. Warnings, Important Precautions, and Careful Administration
General Safety Warnings and Alerts
The administration of Dynacirc SRO is accompanied by a spectrum of safety warnings. These alerts are disseminated to preempt any inadvertent complications and to inform healthcare providers of potential hazards. They include but are not limited to, cautions regarding:
- Rapid fluctuations in cardiovascular parameters.
- Potential exacerbation of pre-existing conditions.
The promulgation of these warnings is integral to ensuring a secure therapeutic environment.

X. Special Population Considerations
A. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
1. Safety and Risk Assessments During Pregnancy
Administration of Dynacirc SRO during pregnancy mandates a circumspect appraisal of both maternal and fetal risks. A thorough risk-benefit analysis is imperative, incorporating:
- Evaluation of gestational age and developmental milestones.
- Consideration of pre-existing obstetric complications.
- Multidisciplinary consultation for tailored risk assessment.
Decisions are predicated on incontrovertible clinical evidence and patient-specific nuances.
2. Considerations for Breastfeeding Mothers
In lactating mothers, the excretion of Dynacirc SRO into breast milk necessitates vigilant consideration. Key points include:
- Assessment of drug transfer to neonatal circulation.
- Monitoring of infant growth and developmental parameters.
- Implementation of alternative feeding strategies if required.
This strategic approach minimizes neonatal exposure while preserving maternal health.

B. Administration to Children and Adolescents
1. Pediatric Safety and Dosing Guidelines
Pediatric administration requires precise dosing regimens calibrated to the patient's age, weight, and developmental stage. This demographic is particularly susceptible to:
- Metabolic rate variability impacting drug clearance.
- Distinct pharmacodynamic responses.
- Enhanced sensitivity to potential side effects.
Careful titration and individualized dosing protocols are essential to optimize safety.
2. Monitoring Growth and Development
The longitudinal monitoring of growth and development in pediatric patients is paramount. Clinicians must:
- Track physical growth trajectories and developmental milestones.
- Evaluate cognitive and behavioral responses.
- Adjust therapeutic regimens based on periodic assessments.
This vigilant oversight ensures that the benefits of therapy are not overshadowed by developmental impediments.
C. Administration to Elderly Patients
1. Age-Related Pharmacological Considerations
In elderly patients, physiological changes associated with senescence necessitate tailored pharmacological strategies. Factors such as decreased renal function, altered hepatic metabolism, and diminished cardiac reserve compel:
- Incremental dose adjustments.
- Frequent reassessment of therapeutic efficacy.
- Enhanced monitoring for adverse reactions.
These considerations are critical to maintaining therapeutic integrity in an aging population.

2. Adjustments for Comorbidities
The presence of comorbid conditions further complicates the administration of Dynacirc SRO in elderly cohorts. A meticulous, individualized approach is required to:
- Integrate multi-drug regimens without compromising efficacy.
- Mitigate cumulative risks associated with polypharmacy.
- Ensure harmonious management of concurrent chronic illnesses.
This stratagem promotes a balanced, patient-centric therapeutic paradigm.
XI. Overdosage and Emergency Management
A. Recognizing Signs and Symptoms of Overdosage
Overdosage of Dynacirc SRO can precipitate a spectrum of clinical manifestations, ranging from subtle neurological disturbances to acute systemic decompensation. Early recognition is vital, characterized by:
- Profound hypotension and tachycardia.
- Exacerbation of central nervous system symptoms.
- Altered mental status and respiratory distress.
Rapid identification of these symptoms is imperative for prompt intervention.
XII. Storage, Handling, and Disposal
A. Recommended Storage Conditions
Temperature and Light Requirements
Optimal storage of Dynacirc SRO is critical to preserving its pharmacological integrity. The medication should be maintained in conditions that preclude exposure to:
- Excessive heat that may catalyze degradation.
- Direct light which could compromise chemical stability.
Short-term excursions outside prescribed conditions should be minimized to avert potency loss.
Shelf Life and Expiry Date Considerations
The shelf life of Dynacirc SRO is contingent upon stringent adherence to recommended storage parameters. Considerations include:
- Regular verification of expiry dates.
- Periodic quality assurance assessments to ensure efficacy.
This meticulous approach ensures that the medication remains both safe and effective throughout its designated lifespan.
B. Safe Handling Practices in Healthcare Settings
Within clinical environments, the handling of Dynacirc SRO necessitates scrupulous adherence to established protocols. Healthcare facilities must institute:
- Standard operating procedures for medication handling.
- Protective measures to prevent contamination or accidental exposure.
- Staff training sessions to reinforce safe handling practices.
Such protocols are indispensable for ensuring both patient and personnel safety.
Dynacirc SRO FAQ
- In which drug classification does DynaCirc belong?
- What is the drug isradipine used for?
- Is isradipine the same as amlodipine?
- How long does it take for isradipine to work?
- How much does isradipine lower blood pressure?
- What is the duration of action of isradipine?
- What is isradipine used for?
- When was isradipine FDA approved?
- How quickly does isradipine work?
- Does isradipine cause tachycardia?
- What is the half-life of isradipine?
- What is the onset of isradipine?
- What generation is isradipine?
- Does isradipine cause constipation?
- When is the best time to take a calcium channel blocker?
- What are the classifications of isradipine?
- How often can you give isradipine?
- What is the function of isradipine?
- How long does isradipine last?
- How quickly does isradipine work?
- What is the clinical use of isradipine?
- In which drug classification does DynaCirc belong?
- What is the drug isradipine used for?
- Is isradipine the same as amlodipine?
- How long does it take for isradipine to work?
- What is the duration of action of isradipine?
- What is isradipine used for?
- How quickly does isradipine work?
- Does isradipine cause tachycardia?
- What is the half-life of isradipine?
- What are the classifications of isradipine?
- What is the function of isradipine?
- How long does isradipine last?
In which drug classification does DynaCirc belong?
Dynacirc, a calcium channel blocker, is prescribed for managing hypertension, which is characterized by blood pressure levels.
What is the drug isradipine used for?
Isradipine is commonly prescribed on its own or in combination with medications like hydrochlorothiazide to manage blood pressure (hypertension). High blood pressure can strain the heart and arteries over time if not properly managed.
Is isradipine the same as amlodipine?
Isradipine and amlodipine are both types of calcium channel blockers used to manage blood pressure. However, amlodipine is additionally prescribed for individuals with artery disease associated with heart artery blockages.
How long does it take for isradipine to work?
2-3 hours
How much does isradipine lower blood pressure?
From 158/102 to 148/93 mm Hg (-10/-9 mm Hg)
What is the duration of action of isradipine?
It took over 12 hours after giving the dose for the effects to show up ultimately.
What is isradipine used for?
Isradipine is prescribed for hypertension. It belongs to a group of drugs known as calcium channel blockers, which function by easing the tension in the blood vessels, thereby reducing the workload on your heart.
When was isradipine FDA approved?
12/20/1990
How quickly does isradipine work?
Isradipine starts working within about 30 minutes after taking it and achieves its highest effect on blood pressure within 2 hours of being administered in this study dosage range without showing any dose-dependent decreases in blood pressure.
Does isradipine cause tachycardia?
Isradipine functions as a calcium channel blocker that specifically targets smooth muscle while causing minimal negative impacts on heart contractions or heart rate regulation mechanisms.
What is the half-life of isradipine?
The alpha has a life of around 1.5-2 hours, with a half-life of roughly 8 hours.
What is the onset of isradipine?
Peak serum concentration in 1 to 3 hours
What generation is isradipine?
Second generation calcium channel blocker
Does isradipine cause constipation?
Yes
When is the best time to take a calcium channel blocker?
Bedtime
What are the classifications of isradipine?
The group of calcium channel blockers known as dihydropyridine (or DHP).
How often can you give isradipine?
Twice daily
What is the function of isradipine?
Isradipine helps to relax the blood vessels allowing for blood and oxygen flow to the heart while also lessening its workload.
How long does isradipine last?
The alpha half life lasts 1 and a half, to 2 hours with a half life of about 8 hours.
How quickly does isradipine work?
2-3 hours
What is the clinical use of isradipine?
Isradipine is used to treat high blood pressure
In which drug classification does DynaCirc belong?
Dynacirc, a calcium channel blocker, is prescribed for managing hypertension also known as blood pressure.
What is the drug isradipine used for?
Isradipine is typically prescribed on its own or, in combination with medications like hydrochlorothiazide to manage blood pressure (hypertension). High blood pressure can strain the heart and arteries by increasing their workload over time and potentially impairing their functioning if unchecked for a period.
Is isradipine the same as amlodipine?
Isradipine and a common cholesterol drug called a statin are both choices for managing hypertension. A statin medication like alogliptin is also commonly prescribed to individuals with heart disease due to its effectiveness in treating arteries in the heart.
How long does it take for isradipine to work?
2-3 hours
What is the duration of action of isradipine?
It took over 12 hours after giving the dose.
What is isradipine used for?
Isradipine is prescribed for managing hypertension, belonging to a group of drugs known as calcium channel blockers that function to ease the strain on the heart by dilating blood vessels.
How quickly does isradipine work?
Isradipine starts working within, around 30 minutes after taking it and achieves its highest impact on blood pressure within 2 hours of being given. There were no decreases in blood pressure that varied based on the dose used in this research study.
Does isradipine cause tachycardia?
Isradipine acts as a blocker of calcium channels in smooth muscle cells without significant negative impacts on heart muscle contractions or heart rate regulation.
What is the half-life of isradipine?
The alpha has a duration of 1 point 7 to 2 hours and a final duration of around 8 hours.
What are the classifications of isradipine?
Calcium channel blockers are known as dihydropyridine (or DHPs).
What is the function of isradipine?
Isradipine helps to relax blood vessels, allowing for blood and oxygen flow to the heart while also reducing its workload.
How long does isradipine last?
The alpha decay process lasts for one and a half to 2 hours with a decay period of around 8 hours.




















