Eptoin, Phenytoin
- Introduction to Eptoin (Phenytoin)
- Phenytoin Mechanism of Action
- Uses of Eptoin (Phenytoin)
- Off-Label Uses of Eptoin (Phenytoin)
- Dosage and Administration of Eptoin
- Composition of Eptoin
- Phenytoin Side Effects
- Management of Side Effects
- Eptoin (Phenytoin) Interactions with Other Medications
- Storage Instructions for Eptoin
- Warnings and Precautions for Eptoin (Phenytoin)
- Phenytoin Contraindications
- Careful Administration and Monitoring
- Administration of Eptoin to Elderly Patients
- Administration of Eptoin During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Administration of Eptoin to Children
- Overdose of Eptoin (Phenytoin)
- Handling Precautions for Eptoin
Introduction to Eptoin (Phenytoin)
Overview of Eptoin as an Anti-Seizure Medication
Phenytoin-based medication known as Eptoin plays a role, in treating epilepsy by helping to control and prevent seizures through calming brain activity. Unlike antiepileptic drugs available on the market Eptoin stands out for its capacity to address both partial and generalized seizures effectively. Doctors commonly recommend Eptoin to patients with types of seizure conditions due to its demonstrated success in averting unmanageable electrical signals, in the brain.
History and Development of Phenytoin
Phenytoins discovery, in the century represented a significant step forward in treating neurological conditions like epilepsy when compared to the limited and often ineffective options available, before that time period.
In 1938 Phenytoin served as the pioneering sedating medication used extensively for managing epilepsy; this breakthrough transformed how seizure disorders were handled by offering patients a treatment option that didn't interfere with their daily activities.
Over time Phenytoin has seen adaptations including the creation of Eptoin which has improved its effectiveness and how it is absorbed by the body.
Importance of Eptoin in Epilepsy Management
The significant importance of Eptoin, in managing epilepsy should not be underestimated all. For those dealing with epilepsy issues keeping seizures in check is crucial for maintaining a quality of life. By using Eptoin patients can lead independent lives as it helps in lessening the frequency and intensity of seizures. Due to its properties that allow for long-term management and lower chances of breakthrough seizures it has become a choice among both patients and healthcare providers due, to its wide availability and proven effectiveness
Phenytoin Mechanism of Action
How Eptoin (Phenytoin) Works
The medication Eptoin works to control seizures by affecting neurons, in the nervous system that are involved in triggering seizure activity.
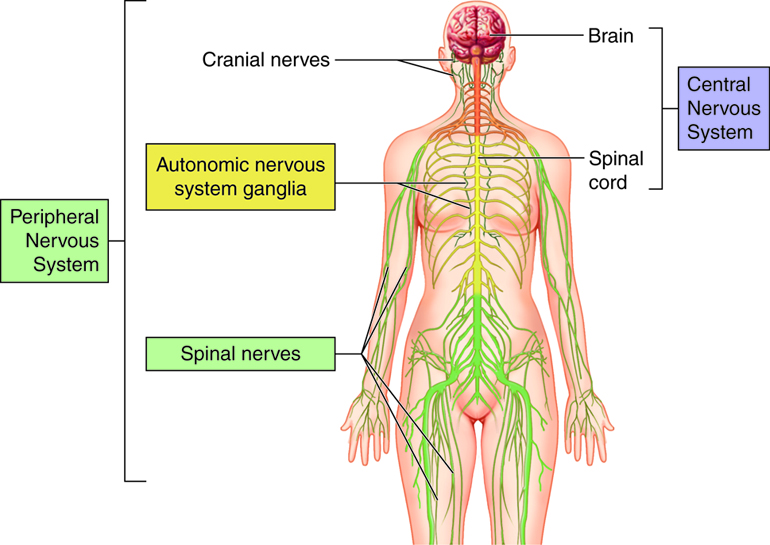
Mechanism of Action in the Central Nervous System
Eptoin works, by stabilizing the membranes of neurons through its impact on sodium ion channels that are crucial for communication processes. When there is a firing of neurons during seizures Phenytoin selectively blocks these channels to stop the entry of sodium ions. This control over sodium channels aids in restoring activity, in the brain and halting the spread of seizure episodes.
Stabilization of Neuronal Membranes
The way Eptoin works to stabilize membranes is crucial, in helping neurons go back, to their state after firing signals. It helps prevent the activity that usually happens during seizures. By making sure the electrical impulses are balanced out properly in the brain Phenytoin greatly lowers the chances of neurons becoming too active. Stops seizures from occurring often.
Inhibition of Repetitive Firing of Action Potentials
Apart, from stabilizing membranes Phenytoin also helps prevent the recurring firing of action potentials in a way. Seizures involve neurons firing rapidly and uncontrollably. Eptoin functions by restraining this behavior. Moderating the neuron activity efficiently lessens the duration and strength of seizures providing patients with an approach, to managing seizures.
Uses of Eptoin (Phenytoin)
Primary Use: Epileptic Seizures
Known for its effectiveness, in controlling seizures in the field of neurology Eptoin is an initial treatment option. Epilepsy is a condition characterized by repeated seizures. It is typically treated through extended use of medications with Phenytoin playing a vital role as a key element. Eptoin is employed to inhibit the patterns in the brain responsible, for these sudden and unforeseeable occurrences providing patients with a means to achieve stability.
Tonic-Clonic Seizures (Grand Mal)
Tonic-clonic (grand mal) seizures are considered one of the types of seizures due, to the intense muscle contractions and loss of consciousness they involve. Eptoin is crucial in managing these seizures by targeting the pathways responsible for these dramatic symptoms. For individuals suffering from these life-altering seizures Phenytoin can significantly reduce both the frequency and severity of these episodes empowering them to regain stability, in their routines.
Partial Seizures
When someone experiences seizures or focal seizures as they are commonly known, as well; it means that only a specific part of their brain is affected by these episodes of electrical activity in the brain cells allowing them to experience simple disruptions in movement or senses or even more complex episodes with changes in awareness levels. Eptoins ability to control these signals within areas of the brain makes it highly effective in managing partial seizures specifically by stabilizing these localized disruptions in brain activity and offering a targeted method, for dealing with seizures.
Treatment of Status Epilepticus
Status epilepticus is a situation where a seizure lasts for, over five minutes or when seizures happen rapidly without breaks in between them. This condition can be life-threatening and needs attention. Eptoin is commonly employed in cases to stop the prolonged electrical activity in the brain. Given through an injection Phenytoin acts quickly to stabilize brain cell activity and avoid damage. Its significance in handling status epilepticus highlights its role, in emergency neurological treatment.
Use in Seizure Prevention After Head Trauma or Surgery
Phenytoin for Seizures
Phenytoin's usefulness goes beyond treating epilepsy – it's also effective, in types of seizures and conditions other than epilepsy itself too. Its ability to handle both term and long-term seizures makes it a top choice for controlling convulsions. Eptoin guarantees control over seizures by interacting with sodium channels in neurons which makes it a reliable option, for ongoing treatment.
An Epilepsy Patient Is Being Treated with Phenytoin for His Seizures
Epilepsy patients receiving Phenytoin treatment prioritize long-term management of seizures as their goal, for health improvement. Eptoin plays a role in a treatment strategy by decreasing the frequency of seizures and enabling patients to carry out their daily routines with more consistency. Close monitoring and adjustments in dosage are essential, for maximizing effectiveness and minimizing any effects linked to prolonged therapy.
Phenytoin Osteoporosis
Patients who take Phenytoin for a period should be aware of the risk of osteoporosis developing as a side effect, over time due to reduced bone mineral density caused by long-term use of anticonvulsants like Phenytoin leading to an increased fracture risk. Healthcare providers need to monitor the bone health of patients undergoing prolonged Phenytoin treatment and consider measures such, as calcium and vitamin D supplements to prevent this potential side effect and ensure the overall health and well-being of patients taking Eptoin is maintained.
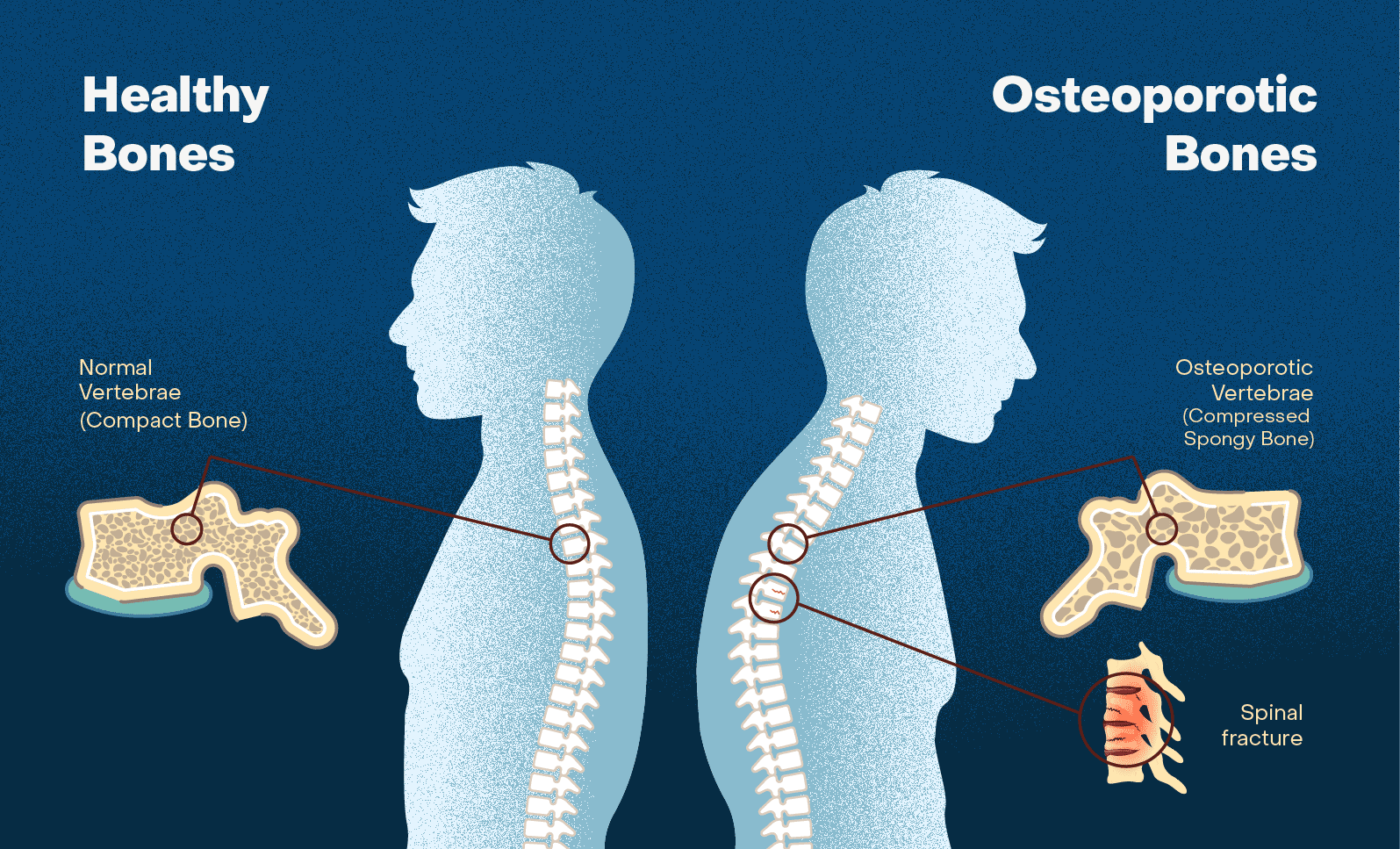
Off-Label Uses of Eptoin (Phenytoin)
Management of Trigeminal Neuralgia (Off-Label)
Trigeminal neuralgia is often referred to as one of the medical conditions out there and causes severe and unpredictable facial pain as a result of irritation, to the trigeminal nerve root in the head and neck region. While it has been conventionally treated with medications Eptoin has gained recognition as an approach for patients who do not respond well to initial treatment options. The capability of Phenytoin to regulate nerve signals through stabilizing membranes has proven to be a successful strategy, in reducing both the frequency and severity of painful episodes. Eptoin can offer relief to individuals dealing with this condition as a secondary benefit of the medication.
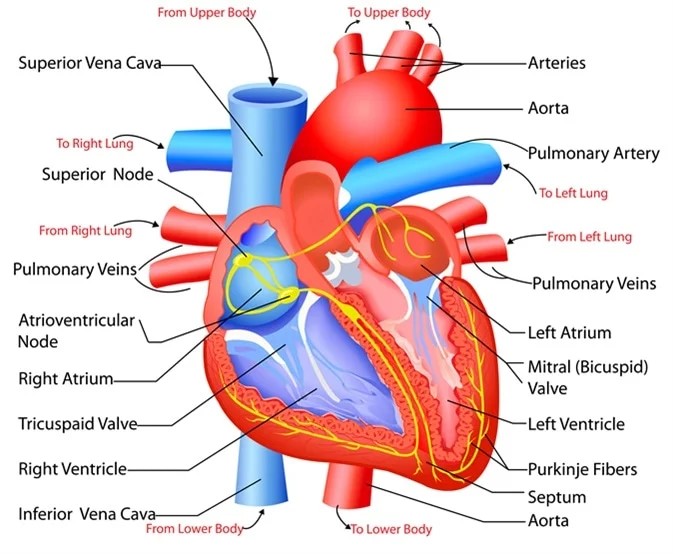
Cardiac Arrhythmias (Off-Label)
Eptoin is not used for purposes but has also shown effectiveness, in managing specific types of heart irregularities when other treatments are ineffective. Phenytoin's ability to stabilize sodium channels extends to the heart's tissues well. It can correct irregular electrical activities in the heart. By suppressing impulses Eptoin aids in restoring heart rhythms in conditions such, as ventricular arrhythmias. This alternative use provides a treatment option in urgent care scenarios where swift management of irregular heartbeat events is crucial.
Management of Bipolar Disorder
Individuals, with disorder often need mood stabilizers to manage their mood swings effectively so that they can lead a stable life mentally and emotionally in the long run. Enough Eptoin a medication typically used for purposes other than treating bipolar disorder directly has been considered as an additional treatment option for this psychiatric condition apart from the usual medications being offered.
It appears that the drugs ability to affect nerve cell excitability by altering sodium and calcium channels in the brain has shown to have benefits in controlling mood shifts. Although it is not widely recommended as a first-line treatment for disorder management yet when traditional therapies fail to produce desired results Eptoin can be considered as a strategy especially, in dealing with intense manic episodes and emotional instability.

Treatment of Neuropathic Pain
Neuropathic pain can be tricky to manage using methods because it stems from nerve damage. One unconventional yet effective approach involves Eptoin's ability to impact nerve signal transmission and improve types of pain conditions such, as diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia by calming down hyperactive nerves. Phentoin works by reducing the excitation of nerves and has shown promise in easing pain caused by conditions, like nerve injuries. This alternative treatment option may offer relief for individuals dealing with nerve discomfort when standard medications fall short.
Use in Cardiac Arrhythmias
In the field of cardiology the usefulness of Phenytoin, in treating heart irregularities highlights its adaptability. When traditional antiarrhythmic medications fail or are not recommended Eptoin helps regulate the heart's functions by adjusting ion exchange among heart cells. This makes it especially beneficial, in situations giving doctors a way to manage rapid and dangerous heart rhythm disturbances that could endanger a patient's life. However, it is used in specialized medical situations.
Migraine Prophylaxis
People who suffer from migraines and often experience headaches may consider using Eptoin as a preventive measure, off-label despite the fact that it is not widely known for this purpose. The ability of Phenytoin to stabilize disturbances in the brain can help reduce the frequency of migraine attacks by targeting the excitability that triggers migraines. Eptoin provides relief in cases where traditional migraine preventive treatments have been ineffective. Although additional research is needed to understand its effectiveness patients might find some benefit from this standard use, in specific situations.

Dosage and Administration of Eptoin
Phenytoin Dose
Dosing Eptoin, with Phenytoin requires an approach as it is essential to adjust the dosage to effectively manage seizures and reduce side effects in each patient's unique case. The dosage amount depends on factors such, as age and weight ensuring that the patient reaches the levels without any harmful effects.
Standard Dosage Guidelines for Adults
In adult's treatment, with Phenytoin initially involves taking between 300 to 400 mg in divided doses and adjusting the dosage according to how the patient responds and their blood levels of the drug. During therapy with Phenytoin for adults may vary from 100 to 600 mg per day based on requirements and needs. It is crucial to make adjustments to prevent spikes, in drug levels that could result in toxicity.
Pediatric Dosing Recommendations
Dosing for children usually depends on their body weight, in pediatrics care settings. Typically starting at 5 mg/kg/day divided into two or three doses per day. The maintenance dosage can vary between 4 to 8 mg/kg/day based on how the child responds and the Phenytoin levels in the blood. It's crucial to monitor children as they are still growing and developing which can lead to changes, in drug levels.
Dosage Adjustments for Renal or Hepatic Impairment
Patients, with kidney or liver issues need adjustments in their medication dosage because in these situations the way Phenytoin is broken down and removed from the body changes. This requires starting with doses and checking the drug levels often. In cases of liver issues the dose may need to be decreased by 25 to 50% because the liver processes the drug. Renal problems can also impact how quickly the drug is removed from the body. This is particularly relevant, in long-term treatment.
Special Instructions for Status Epilepticus Treatment
In instances of Status Epilepticus. An urgent situation. Phenytoin is injected directly into the veins, for treatment purposes. The suggested initial dose is 15 to 20 mg per kilogram of body weight. Is administered as a flow to quickly reach the needed therapeutic levels. Subsequent to the dose administration, an infusion, for maintenance may commence. Given the seriousness of this state prompt action and vigilant monitoring are essential to guarantee effectiveness and safety.
How to Take Eptoin: Oral and Intravenous Forms
The medication Eptoin can be given either by mouth or, through an IV based on the situation at hand. If taken orally in the form of tablets or capsules with food can help reduce stomach irritation. In emergency situations where quick seizure management's crucial intravenous administration is preferred. When using the form it is usually mixed with a solution. Administered slowly to prevent heart-related issues, like low blood pressure or irregular heartbeats.
Importance of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring for Phenytoin Levels
Monitoring the effectiveness of Eptoin, through drug monitoring (TDM) is crucial because Phenytoin has a therapeutic range where optimal serum concentrations typically fall between 10 to 20 mcg/mL. If the levels dip below this range ineffective seizure control may occur; conversely if levels exceed this range toxicity can manifest as symptoms like dizziness or nystagmus and potentially more serious issues such as ataxia or confusion may arise. Regular blood tests are essential to ensure that drug levels remain in the effective zone, for the well-being of the patient.
Composition of Eptoin
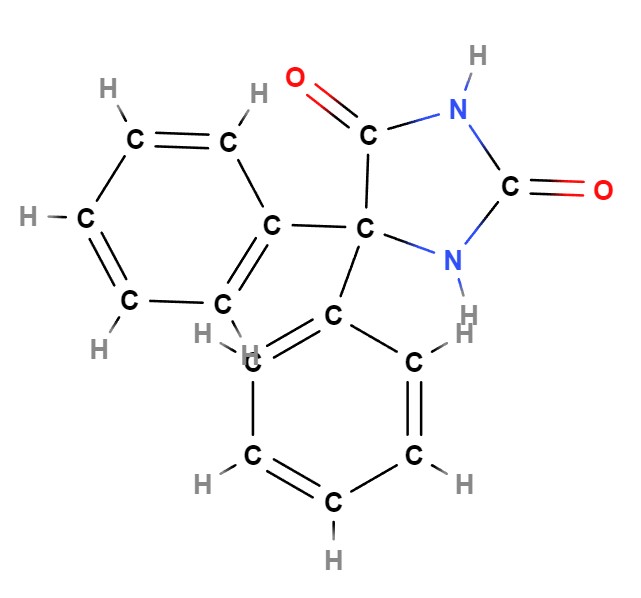
Active Ingredient: Phenytoin Sodium
The main component, in Eptoin is Phenytoin sodium which serves as an anticonvulsant by stabilizing membranes and preventing firing incidents in the body's neurological system. Phenytoin sodium takes on a salt form that improves its solubility and allows for use, in both injectable forms of the medication.
List of Excipients and Their Roles
- Lactose monohydrate is utilized as a filler ingredient.
- Magnesium stearate is used as a lubricant.
- Starch is commonly utilized as a substance that holds things together and helps them break down.
- The tablet's components help it stay intact and aid in absorption while also ensuring stability in the run.
Available Strengths and Forms (Tablets, Capsules, Injections)
There are strengths and forms of Eptoin to meet the diverse needs of patients.
Tablets are usually sold in 100 mg strengths.
- Capsules; Available, in strengths of 100 mg and 300 mg.
- Injections; Mainly administered in hospitals and come in vials, for administration.
There are types to allow for flexibility, in management that address both ongoing treatment and immediate assistance requirements.
Phenytoin Level
Ensuring the Phenytoin level stays within the recommended range is key, to managing seizures as discussed previously. Typically the ideal range falls between 10 and 20 mc g/mL. Levels than 10 mc g/mL might not adequately manage seizures while levels than 20 mc g/mL could lead to heightened side effects, like toxicity.
Fosphenytoin to Phenytoin Conversion
In emergencies, when quick administration is key to reducing the risk of irritation and ensuring effectiveness in treating seizures rapidly fosphenytion serves as a preferable choice due, to its ability to convert into Phenytoin in the body at a 1 to 1 ratio.
Normal Phenytoin Level
The typical therapeutic range, for Phenytoin in the blood is 10 to 20 mcg/mL as discussed earlier. It is important to maintain this level to prevent seizures without causing side effects. It is crucial to check blood levels through tests to keep track of these levels for patients with conditions, like pregnancy or organ problems that could affect how the drug is processed in the body.
Phenytoin vs Dilantin
Phenytoin and Dilantin are medications; Dilantin is just the brand name, for Phenytoin. They both contain the component and are used for the same medical purposes. However, the slight differences in ingredients and composition between generic Phenytoin and Dilantin may cause variations in how they're absorbed or tolerated by some patients. As a result, some medical professionals may choose one version over the other based on how each reacts, to it.
Phenytoin Side Effects
Phenytoin Side Effects Toxicity
Phenytoin is very good, at managing seizures it can be harmful if the levels in the blood go too high beyond what's considered safe for treatment purposes. These excess levels can show up in ways such as issues with movement control like stumbling or speech difficulties and involuntary eye movements called nystagmus.
Some people might feel confused or tired or even have problems, like seizures triggered by the drug itself. It's important to check the blood levels to avoid these effects because Phenytoin works best within a specific range of dosage that needs to be closely monitored. In situations involving toxicity issues urgent medical attention is crucial to lower blood levels and ease symptoms.
Phenytoin Side Effects Long-Term
Extended usage of Phenytoin is linked to lasting effects that could greatly affect a patient's daily life quality in significant ways, over time. Patients may experience gingival hyperplasia and hirsutism while also noticing changes in features becoming coarse due to prolonged use. Moreover, continuous use might influence bone strength negatively by increasing the likelihood of developing osteoporosis. It is advisable, for long-term users to undergo assessments to watch out for these issues enabling timely interventions when needed.
Overview of Potential Side Effects
Phenytoin can lead to side effects that range from common, to occurrences in individuals taking the medication for their condition Some patients may handle the drug without any major issues while others might face adverse reactions that vary in severity and frequency These side effects can range from mild problems like nausea to severe conditions, like Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) It is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers to be aware of the risks linked with Phenytoin usage
Phenytoin Gingival Hyperplasia
Excessive growth of gum tissue, around the teeth is often seen in individuals who use Phenytoin for a period of time—a condition known as gingival hyperplasia that can cause discomfort and oral hygiene difficulties and sometimes lead to issues if left untreated.
Maintaining hygiene and seeing a dentist regularly can assist in managing gingival hyperplasia; however, some patients may need to reduce their medication dosage or stop taking it altogether if this side effect becomes problematic.
Phenytoin Teratogenic Effects
During pregnancy, it is risky to use Phenytoin as it can cause birth defects, in the child during the three months of gestation period. The babies born to mothers who have taken Phenytoin may have deformities known as hydantoin syndrome which includes facial and skull anomalies along, with growth and developmental problems. It is important for women of age to thoroughly weigh the risks involved and explore treatment options when thinking about getting pregnant.
Common Side Effects
The common side effects often seen with Phenytoin include;
- Feeling queasy and throwing up are quite common when starting treatment due to stomach uneasiness.
- Patients might feel sleepy and lightheaded when starting doses of medication which could affect their ability to drive or use machinery in their activities.
- Regarding Gingival Hyperplasia – it's a problem that long-term users often face.
- Excessive hair growth known as hirsutism may develop in women, with long-term use of Phenytoin medication.
Over time, with extended treatment usage some individuals might observe an increase, in the thickness or roughness of their characteristics.
Serious Side Effects
Rare but severe side effects of Phenytoin are uncommon; however they can be life necessitate medical intervention.
- Loss of muscle coordination and balance known as ataxia may indicate Phenytoin toxicity and individuals experiencing these signs should promptly seek attention.
- When Phenytoin levels exceed the desired range, for treatment purposes intoxicity can lead to diplopia vision, as a symptom.
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (referred to as SJS); An uncommon serious allergic response characterized by skin blistering and affecting mucous membranes as well could result in fatality if not promptly addressed.
- In cases of Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (often referred to as TEN) which is a variant of SJS (Stevens-Johnson syndrome) it results in extensive skin necrosis and requires urgent medical attention right away if any severe skin reactions are noticed while taking Phenytoin; the medication should be stopped immediately and emergency medical help should be sought without delay.
Management of Side Effects
Monitoring and Early Detection
The secret, to handling the side effects of medications like Phenytoin lies in staying aware and catching any issues. Regular blood tests and keeping an eye out for symptoms reported by patients are crucial in spotting any reactions before they become serious.
For those undergoing long term treatment with this medication regular check-ups are important to address side effects like gingival hyperplasia, osteoporosis, or changes in features.
By monitoring the levels of Phenytoin in the bloodstream we can prevent the risk of toxicity and potential neurological symptoms such, as ataxia and nystagmus from arising. Detecting issues on allows healthcare providers to adjust medication doses promptly and avoid complications.
Addressing Mild Side Effects
Numerous Phenytoin related side effects can be bothersome. Are generally controllable, with measures. For instance;
- Digestive issues like nausea and vomiting can often be eased by consuming the medication along, with food.

- Initial drowsiness and dizziness tend to lessen as the body gets used to the treatment
Patients facing these effects may find relief by spreading out their medication intake throughout the day or adapting their schedules to steer clear of tasks demanding attention.
Treating Gingival Hyperplasia
Excessive growth of gum tissue known as gingival hyperplasia is an issue that can arise from taking Phenytoin over a period of time and requires consistent oral care practices like regular brushing and flossing along with routine dental check-ups to prevent any complications related to the conditions progression.
In instances of gingival hyperplasia procedures may be required to address the excessive gum tissue growth but adjusting the Phenytoin dosage or switching to an alternative anticonvulsant treatment can also help alleviate the severity of this side effect. Healthcare providers, in dentistry often work closely with prescribing physicians to ensure patients receive care in managing this side effect effectively.
Managing Hirsutism and Cosmetic Changes
Excessive facial hair growth and altered appearance, it may impact a person's self-confidence without causing harm or medically significant issues to the patient's health condition. Lowering the dosage of Phenytoin could potentially lessen the occurrence of these side effects in some situations. If individuals are troubled by these alterations in their appearance caused by medication effects they can consider options, like laser hair removal. Using creams to manage undesired hair growth. A doctor might suggest switching to an anticonvulsant if these cosmetic side effects become significantly troubling.
Prevention of Serious Skin Reactions
Rare but serious skin reactions, like Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN) can occur as a result of taking Phenytoin medication treatment; however, they are complications that warrant cessation of the drug upon the first indication of a rash or blistering appearance being noted as a crucial step in management.
Early detection is crucial since SJS and TEN can rapidly progress into life-threatening conditions. Hospitalization is usually required for management with care and appropriate wound healing practices alongside the use of corticosteroids or immunosuppressants. Educating patients about recognizing symptoms and seeking medical attention is vital, for preventing these severe reactions.
Addressing Phenytoin Toxicity
When someone experiences Phenytoin toxicity symptoms arise due, to a dose of the medication, which can be managed by lowering the dosage or temporarily stopping it to allow the drug levels in the blood to stabilize within the desired range again.
In situations where toxicity is severe intravenous fluids and activated charcoal can be administered to help eliminate Phenytoin from the body faster are used bo in some cases.
It's important to provide care for symptoms like difficulty with coordination slurred speech, and muddled words confusion until Phenytoin levels return back to normalize in check. In instances for cases, procedures like hemodialysis may be necessary to quickly reduce dangerous drug levels in the body toxins, from reaching dangerous levels.
Managing Bone Health in Long-Term Users
Extended use of Phenytoin can have an impact, on bone strength. May result in issues such as osteoporosis over time. To address this issue and lessen its effects; patients are often encouraged to add calcium and vitamin D supplements to their routine along with engaging in weight-bearing exercises to improve bone density. Routine bone density screenings play a role in identifying signs of bone weakening which allows healthcare professionals to recommend medications like bisphosphonates or other suitable treatments to prevent fractures. Ensuring the well-being of bones is vital, in maintaining a quality of life for individuals undergoing long-term Phenytoin treatment.
Collaborative Care for Complex Side Effects
Dealing with the consequences of Phenytoin generally involves an effort, from different healthcare professionals, like doctors pharmacists dentists, and others to handle both minor and major side effects effectively For instance a neurologist might tweak the dosage to lessen overall side effects while a dentist addresses gingival hyperplasia This team approach ensures that side effects are managed comprehensively enabling patients to still receive the advantages of seizure management while reducing the negative effects of adverse reactions
Eptoin (Phenytoin) Interactions with Other Medications
Phenytoin Interactions
Phenytoin is, like anticonvulsants in that it has a wide range of interactions with different medications which can impact their effectiveness or lead to potential side effects if not monitored closely by healthcare providers due to its effects on drug metabolizing enzymes such as those, in the cytochrome P450 system.
Drugs That Increase Phenytoin Levels
Some medications have the potential to raise the levels of Phenytoin in the bloodstream. May cause toxicity when not properly monitored. These medications hinder the enzymes that break down Phenytoin in the body which can result in increased Phenytoin concentrations leading to side effects, like ataxia or confusion, for patients.
Antifungal Medications
Antifungal medications, like fluconazole and ketoconazole belonging to the azole group are recognized for slowing down the breakdown of Phenytoin in the body leading to levels, in the bloodstream of patients taking them with Phenytoin medication; hence healthcare providers need to regularly check Phenytoin blood levels to prevent any harmful effects and might have to adjust the dosage accordingly to keep it within a safe treatment range.
Some Antibiotics
Certain types of antibiotics, like macrolides such as erythromycin and clarithromycin, can increase Phenytoin levels by blocking liver enzymes. It is important to be careful because high levels of Phenytoin could worsen its side effects and possibly cause nerve-related symptoms. Adjusting the dosage of either the antibiotic or Phenytoin may be necessary based on the situation, in a setting.
Cimetidine
When Cimetidine is used alongside Phenytoin to manage issues and hinder its metabolism significantly, it can cause a build-up of Phenytoin in the blood vessels. Monitoring the drugs regularly and adjusting the doses as needed is crucial to avoid any effects.
Drugs That Decrease Phenytoin Levels
Certain drugs, trigger the enzymes responsible for breaking down Phenytoin in the body which can lower its levels in the blood-stream and make it less potent against seizures increasing the chance of breakthrough seizures happening therefore patients need to be closely monitored to make sure they have proper seizure management while, on these drugs that interact with Phenytoin.
Carbamazepine
Carbamazepine is known as an anticonvulsant can impact the metabolism of Phenytoin which may lead to a reduction, in its effectiveness. This situation can create challenges in the treatment of epilepsy for patients, on medications. Doctors may have to adjust the dosage of Phenytoin or explore treatment options to ensure control of seizures.
Theophylline
The medicine Theophylline helps widen the airways and is commonly used to manage breathing issues, like asthma and COPD; it also impacts how the liver metabolizes Phenytoin medication which treats seizures and epilepsy symptoms in patients. The simultaneous use of these medications may result in than desired Phenytoin levels in the bloodstream thus heightening the chances of having seizures. Monitoring and dosage modifications are crucial, for maintaining a level of seizure control with these medications.
Interaction with Oral Contraceptives
Phenytoin can impact the effectiveness of contraceptives by speeding up their metabolism, which could increase the chances of pregnancies, for women using both medications together. To prevent this risk women are recommended to use hormonal contraception alongside Phenytoin and hormonal contraceptives. For individuals who depend on contraceptives and want to avoid interactions with other anticonvulsants that have fewer effects, this regard may be worth exploring.
Interaction with Alcohol and Its Effects on Phenytoin Metabolism
Consuming alcohol may cause changes, in how Phenytoin is processed in the body's metabolism system. Regularly drinking alcohol can trigger liver enzymes that might lower Phenytoin levels and compromise the management of seizures. On the other hand, drinking alcohol suddenly can slow down the breakdown of Phenytoin, in the body. This might result in blood levels of Phenytoin. Raise the chances of experiencing harmful effects. Patients are usually advised to be mindful of their alcohol consumption and steer clear of drinking while undergoing Phenytoin treatment.

Storage Instructions for Eptoin
Recommended Storage Conditions
It's recommended to store Eptoin at room temperature which is generally, between 15°C and 30°C (59°F to 86°F). To maintain its stability and effectiveness avoid sunlight by keeping it in a dry place as the storage conditions play a vital role in preserving the drugs quality; exposure, to extreme temperatures or moisture can lead to degradation.
Handling of Oral Tablets and Injectable Forms
It's important to keep tablets and capsules in their packaging until you're ready to use them to avoid any damage, from exposure to air and humidity. For forms of Phenytoin (a medication) it's crucial to store them in a controlled environment from light and use them promptly once the vial is opened. Following handling practices is key to maintaining the effectiveness and sterility of the medication. Important, in hospital settings where injectable forms are commonly utilized.
Precautions to Avoid Moisture and Heat Exposure
Phenytoin is easily affected by moisture this can lead to the deterioration of tablets and a decrease, in their efficacy over time if not stored properly in a closed container with a desiccant to absorb any excess moisture present in the environment. It is recommended that patients refrain from storing Eptoin in areas exposed to temperatures as this may lead to drug destabilization and reduce its effectiveness. Avoid keeping the medication in places like the bathroom or, near heat sources as these settings can potentially compromise the integrity of the medication.
Warnings and Precautions for Eptoin (Phenytoin)
Phenytoin Warnings
Phenytoin is known for its ability to manage seizures effectively. Comes with cautions that need thorough evaluation, in medical settings. The drugs narrow range of dosage levels and intricate ways it works in the body require observation to prevent issues. Healthcare professionals have the responsibility to weigh the benefits of its properties against dangers, especially for those at higher risk. Adjustments in dosage must be done accurately. Monitoring should be done regularly while educating patients is vital, in reducing effects during Phenytoin treatment.
Black Box Warning: Risk of Cardiovascular Complications with IV Administration
Phenytoin is marked with a box warning because of the potential, for heart issues when given through an IV line too quickly. Like sudden low blood pressure or irregular heartbeats that could lead to a cardiac arrest situation! This risk is even higher for folks with existing heart problems! To prevent these outcomes from happening during IV Phenytoin treatment sessions in scenarios like managing Status Epilepticus urgently it's crucial to go and keep a close eye on blood pressure and heart function at all times to navigate the fine line, between stopping seizures fast and ensuring cardiovascular safety.
Importance of Regular Liver Function Tests
Phenytoin undergoes breakdown, in the liver; therefore, the proper functioning of the liver is crucial for its administration. It is important to conduct liver function tests (LFTs) for individuals with existing liver issues or those undergoing prolonged treatment with Phenytoin. Phenytoin has been linked to liver damage known as hepatotoxicity, elevated liver enzymes might signal the need for dosage adjustment or discontinuation of treatment. Early identification of any liver dysfunction can help prevent damage, to the liver and ensure continued safe usage of Phenytoin.
Risks of Abrupt Discontinuation
Suddenly stopping Phenytoin may trigger rebound seizures. Even cause Status Epilepticus, A state that needs to be managed carefully by healthcare professionals and patients alike. Educating patients about following their medication schedules and avoiding discontinuation is crucial. When it comes to ending treatment, with Phenytoin tapering the dosage is recommended to decrease the chances of seizures coming back. This approach holds significance for individuals with epilepsy as a sudden halt, in medication could have devastating consequences.
Phenytoin-Induced Hypersensitivity Reactions
Phenytoin has been linked to reactions, like Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) which can have consequences including death if not detected early enough. Symptoms of these reactions usually include fever and rash along with swelling of the lymph nodes and potential damage to organs.
It's crucial to act at the sign of hypersensitivity by stopping the use of Phenytoin right away. There might be a risk of reactions with anticonvulsants from the hydantoin class as well. Therefore it's important to choose treatments for patients who are sensitive, to such medications.
Phenytoin Contraindications
Known Hypersensitivity to Phenytoin or Other Hydantoins
Individuals who have shown sensitivity, to Phenytoin or similar hydantoins like fosphenytoin should avoid using Eptoin as it could lead to reactions varying from mild skin irritations to severe systemic conditions such, as Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) or Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN). It's advisable for these patients to explore anticonvulsant options to steer clear of dangerous side effects that could be life-threatening.
Pre-Existing Blood Dyscrasias
Patients, with blood disorders like agranulocytosis or thrombocytopenia should avoid using Phenytoin as it can worsens their condition due to its known side effects such as aplastic anemia and leukopenia. Evaluation of patients with blood counts is crucial before starting Phenytoin treatment and regular CBC monitoring is essential, throughout the therapy process.
Severe Hepatic Impairment
Patients who have liver problems face a chance of experiencing Phenytoin toxicity because their bodies struggle to metabolize and eliminate the drug properly due, to impaired liver function being necessary for the drug's elimination process Therefore in individuals, with liver issues the drug may build up to dangerous levels For such patients it is advisable to explore other anticonvulsants that do not rely heavily on liver metabolism or to administer Phenytoin in much lower doses while monitoring them closely

Phenytoin Toxicity Treatment
Treating Phenytoin toxicity involves providing care and taking steps to decrease the levels of the drug in the bloodstream. In some cases taking the drug and keep a watch may be enough. In some cases activated charcoal can limit absorption and IV fluids can help speed up kidney clearance. In some situations, hemodialysis might be needed to quickly lower levels. Patients showing symptoms, like confusion or uncoordinated movements should be checked away for Phenytoin toxicity; adjusting treatment based on drug monitoring is important.
Careful Administration and Monitoring
Required Blood Level Monitoring for Therapeutic Range
Eptoin (Phenytoin) needs to be managed within a therapeutic range because it has a narrow margin of safety, in its effectiveness levels. It's necessary to monitor blood levels to make sure the serum concentrations stay between 10 to 20 mcg/mL. Below this range might not control seizures effectively and above it could lead to toxicity risks. Managing Phenytoin toxicity is crucial in long-term treatment plans. Emphasizes the importance of monitoring, for patient care.
Phenytoin Toxicity Symptoms
Experiencing toxicity may happen when Phenytoin levels go beyond the recommended range and result in indicators, like eye movements ( difficulty speaking clearly (slurred speech), and mental confusion – which are usually the initial signs of high blood concentrations of the medication being present. As the toxicity worsens over time symptoms like lack of coordination (Ataxia) shaking movements (tremors) and cognitive function impairment can emerge. If not treated promptly and effectively if toxicity from Phenytoin occurs it could escalate to health issues requiring adjustments, in dosage or stopping the medication entirely.
Corrected Phenytoin Level
Patients who have albumin levels or kidney problems need to calculate the adjusted Phenytoin level because Phenytoin binds strongly to proteins, in the body and reduced albumin can lead to an estimation of free Phenytoin levels in the blood stream. This adjusted level helps determine the drug concentration in the blood and is particularly important for patients with conditions, like chronic illnesses or advanced age that affect protein binding abilities.
Renal and Hepatic Impairment Considerations
Both issues, with the liver and kidneys can have an impact on how the body processes Phenytoin medication. If someone has liver problems it may take longer for their body to break down the drug properly. This can result in the drug building up in their system. Posing a risk of harmful effects. Likewise kidney problems can affect how Phenytoin is eliminated from the body. This may mean adjusting the dosage and keeping an eye on monitoring the drugs levels in the body. It's important to check on both liver and kidney function to prevent any effects, in these groups of patients.
Monitoring for Signs of Toxicity
Regularly observing patients for signs of effects is crucial when overseeing individuals undergoing long-term treatment, with Phenytoin medication with early warning signs including;
- Nystagmus; When someone experiences eye movements it is frequently an indicator of Phenytoin toxicity.
- When intoxication increases speech can slow down. Become hard to comprehend.
- Elevated levels of Phenytoin can lead to issues varying from disorientation to significant confusion.
Act promptly when these signs show up to avoid any issues.
Administration of Eptoin to Elderly Patients
Age-Related Sensitivity to Side Effects
As people get older and their bodies change with age they might be more sensitive, to the side effects of Phenytoin. This could lead to increased feelings of dizziness, confusion, or difficulty moving around which in turn raises the chances of falling and getting hurt. Moreover, as we age our bodies may struggle to break down and eliminate medications effectively. Because of this it's crucial to adjust doses and begin with amounts to prevent any negative effects, from happening.
Dosage Adjustments in Elderly Due to Decreased Clearance
In individuals, with reduced liver and kidney function Phenytoin stays in the body longer due to clearance rates which can result in a build-up of the drug over time requiring lower doses for safe and effective seizure management while avoiding harmful side effects. Regular monitoring of drug levels and periodic evaluation of liver and kidney function are essential for efficient treatment of seizures, in the population.
Increased Risk of Drug Interactions
Older patients frequently use medications which can lead to interactions, with Phenytoin. The prescribed medications, like blood thinners, antibiotics, and high blood pressure drugs might interact with Phenytoin by either raising its levels leading to a risk of toxicity or decreasing its effectiveness by speeding up metabolism. Healthcare professionals need to examine all medications and make dose adjustments to prevent adverse interactions.
Administration of Eptoin During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Risk of Teratogenic Effects: Phenytoin and Fetal Hydantoin Syndrome
Phenytoin is considered a teratogen. Is known to be linked to hydantoin syndrome when taken during pregnancy. Leading to issues such, as growth deficiencies and cognitive impairments, in babies exposed to Phenytoin before birth. The highest risk of birth defects occurs in the stages of pregnancy; therefore it is crucial to weigh the pros and cons before using Phenytoin in expectant mothers.
Guidelines for Use in Pregnant Women with Epilepsy
Pregnant women, with epilepsy face a task in handling seizures during pregnancy as it involves a balance to ensure the well-being of both the mother and the fetus. It is important to weigh the risks associated with seizures, against the potential of Phenytoin medication. In situations other anticonvulsants might be a choice. However, if Phenytoin is deemed necessary it is advised to use the dose possible and consider supplementing with folic acid to decrease the chances of neural tube defects.
Excretion into Breast Milk and Precautions for Breastfeeding Mothers
Phenytoin is released into breast milk in quantities; though the levels found in breastfed babies are generally low; there is a chance of effects occurring. It is advisable, for breastfeeding mothers to keep an eye out for any signs of Phenytoin toxicity in their infants such, as drowsiness or fussiness. In situations where newborns are involved or if higher doses are needed by the mother; other feeding methods may be suggested as a measure.

Phenytoin Nursing Interventions
Mothers who are taking Phenytoin should be informed about the risks of exposing their babies to the drug through breast milk. Should ensure that both the mother and baby receive proper monitoring care. It is crucial, for nurses to help ensure that the prescribed doses are followed correctly and to assist in managing any side effects while offering guidance on monitoring the baby's health. Open communication between healthcare providers and nursing staff is vital, for administering Phenytoin to pregnant and breastfeeding women.
Administration of Eptoin to Children
Pediatric Dosage Guidelines
When giving Eptoin (Phenytoin) to kids it's important to think about their age, size, and how they react to the treatment. The dosage, for children is often based on their weight starting at around 5 mg per kilogram per day and divided into two or three doses. Doctors might change this amount based on how the child's seizures are controlled and their Phenytoin levels in the blood. Kids have a range for treatment, as adults so it's important to keep track of their levels regularly to avoid giving too little or too much medication.
Special Considerations for Long-Term Use in Children
Long-term use of Eptoin, in kids requires monitoring because continuous Phenytoin treatment can greatly affect their growth and development in ways. Children are at risk for side effects like gum overgrowth and excessive hair growth. However taking Phenytoin could also lead to changes in bone health making individuals more prone to fractures and osteoporosis, in life. To minimize these risks it is advised for children undergoing long-term Phenytoin therapy to have check-ups and bone health evaluations.
Monitoring Growth and Development in Pediatric Patients
Children taking Phenytoin need to be checked to make sure the medicine isn't impacting their mental growth negatively. Their growth should be monitored regularly. Their developmental progress was closely followed. If any issues or delays are noticed in their development milestones or growth parameters doctors might think about changing the medication plan or looking into choices.
Overdose of Eptoin (Phenytoin)
Symptoms of Phenytoin Overdose
An overdose of Phenytoin is a situation that may show neurological and bodily symptoms. To begin with symptoms, like dizziness, nystagmus, and intense ataxia can be observed. As the toxicity increases further severe signs such, as confusion, mumbled speech, and a deep lethargic state might become apparent. In instances a Phenytoin overdose could lead to a coma, problems, and potentially fatal outcomes if not quickly addressed.
Severe Ataxia
Severe ataxia is an indicator of Phenytoin overdose. Is defined by a lack of coordination and balance, in patients leading to difficulty with walking and basic activities due, to motor function impairment necessitating urgent medical assessment to avoid worsening toxicity levels.
Coma
In instances of overdose situations individuals might enter a state of unconsciousness. The suppressive impact of Phenytoin, on the brain's system can result in a lack of alertness in the patient. Prompt action is necessary when a coma caused due to Phenytoin toxicity occurs, as an extended period of unresponsiveness could trigger issues that may not be reversible such as lasting damage, to the system.
Respiratory Depression
An excessive amount of Phenytoin can have an effect, on brains functions by causing respiratory depression in individuals who may show signs of breathing slowly and shallowly; this could lead to a lack of oxygen in the body and potentially respiratory failure if not addressed promptly with urgent medical intervention such as assisted breathing support or intubation, until the levels of Phenytoin decrease.
Emergency Management and Treatment Options for Overdose
Dealing with an excess of Phenytoin requires ensuring the patient's airway is stable and that they are breathing properly and have blood circulation flow restored to normal levels as soon, as possible. If the overdose occurred recently. Activated charcoal is given promptly after ingestion of Phenytoin overdose may help by binding to the substance, in the stomach and preventing absorption. In situations where necessary gastric lavage could be considered. It is typically only recommended for patients who seek emergency care shortly after ingestion to prevent any complications.
Role of Activated Charcoal and Gastric Lavage
Activated charcoal is often used as a first line approach, for treating an overdose of Phenytoin medication by binding to the drug in the stomach to reduce its absorption into the body systemically. In cases of an overdose where a large amount of Phenytoin has been ingested within a short time frame gastric lavage may be considered as part of the treatment plan though it is less common nowadays. These treatments are usually paired with measures such, as fluids and constant monitoring of vital signs to aid in the patient's recovery process.
Handling Precautions for Eptoin
Proper Handling of Injectable Forms
Injectable Eptoin solutions need handling to guarantee safety and effectiveness levels are maintained throughout administration processes. A healthcare provider needs to give these injections in a controlled environment, like a hospital to monitor any reactions that may arise. Slowly administering the medication after proper dilution is crucial to prevent heart issues, like blood pressure and irregular heart rhythms. Healthcare workers must also prepare the injection site correctly to minimize the chance of infections occurring.
Safe Disposal of Unused or Expired Medication
To ensure safety and prevent ingestion or harm to the environment when dealing with expired Eptoin medication it is recommended that patients do not flush them down the toilet or throw them in the trash. Discarding them in such a manner it is advised to return expired or unused medication, to a pharmacy or adhere to regulations, for proper drug disposal.
Precautions to Avoid Accidental Overdose
To avoid overdosing incidents, Eptoin medication storage is vital in a place away from children or others who might mistakenly consume it by accident. It is crucial to label the medication and follow the prescribed doses diligently since mistakes in taking it can easily result in amounts entering the body system. Patients and caregivers need to be informed about the significance of sticking to dosage timings and being able to identify indicators of an overdose, for prompt action.
Eptoin, Phenytoin FAQ
- What to avoid when taking PHENYTOIN?
- A nurse would instruct patients taking PHENYTOIN to report which side effects?
- What is PHENYTOIN?
- What is PHENYTOIN used for?
- How does PHENYTOIN work?
- What does PHENYTOIN do?
- What to avoid when taking PHENYTOIN?
- What is PHENYTOIN used to treat?
- What are PHENYTOIN levels?
- What are PHENYTOIN tablets used for?
- Why are PHENYTOIN levels checked?
- When are PHENYTOIN levels taken?
- What are PHENYTOIN sodium pills used for?
- What are PHENYTOIN sodium tablets?
- Can PHENYTOIN cause hyponatremia?
- Can PHENYTOIN cause seizures?
- Can PHENYTOIN capsules be opened?
- Can PHENYTOIN be crushed?
- Can PHENYTOIN cause hypotension?
- How does PHENYTOIN work?
- How does PHENYTOIN cause gingival hyperplasia?
- How does PHENYTOIN cause hirsutism?
- How does PHENYTOIN cause folic acid deficiency?
- How does PHENYTOIN cause megaloblastic anemia?
- What is PHENYTOIN sodium extended used for?
- What does PHENYTOIN do to your body?
- When should PHENYTOIN be taken?
- When is PHENYTOIN given?
- Where is PHENYTOIN used?
- Where is PHENYTOIN metabolized?
- PHENYTOIN belongs to which class of drug?
- Why is PHENYTOIN not given with dextrose?
- Why is PHENYTOIN contraindicated in myoclonic seizures?
- Is PHENYTOIN a sodium channel blocker?
- What are the side effects of PHENYTOIN toxicity?
- Is PHENYTOIN an inducer or inhibitor?
What to avoid when taking PHENYTOIN?
Stay away, from alcohol because it could worsen the side effects of PHENYTOIN, and grapefruit juice might mess with the way the drug works in your body too. Also steer clear of handling machinery before you figure out the impact of PHENYTEIN on you as it could make you feel dizzy or sleepy. Certain medications like blood thinners and birth control pills should be avoided unless your doctor gives the light due, to interactions.
A nurse would instruct patients taking PHENYTOIN to report which side effects?
Patients need to let their healthcare provider know about any skin rashes they experience. If they feel unusually tired or dizzy during the treatment process. They should also watch out for gums (gingival hyperplasia) difficulty, in moving, and any indications of a severe allergic response. Additionally necessary to keep an eye out for changes, in mood or thoughts of self-harm and check for symptoms of toxicity including vision problems and confusion.
What is PHENYTOIN?
Phenytoin is a medication used to treat seizures in people, with epilepsy by stabilizing brain activity and preventing signals that trigger seizures.
What is PHENYTOIN used for?
Phenytoin is prescribed for managing tonic-clonic ( grand mal) complex partial seizures and seizures happening during or, after neurosurgical procedures.
How does PHENYTOIN work?
Phenytoin functions, by blocking sodium channels, in the brain to decrease the occurrence and strength of activity; thereby averting the electrical bursts that trigger seizures.
What does PHENYTOIN do?
Phenytoin works to prevent and manage seizures by stabilizing the membranes of neurons and restricting the propagation of seizure activity, in the brain.
What to avoid when taking PHENYTOIN?
Patients should steer clear of alcohol and medications that may interact with PHENYTOIN if they feel drowsy and avoid activities that need alertness during this time periods. Additionally, foods in folic acid should be closely monitored as PHENYTOIN has the potential to lead to folic acid deficiency symptoms
What is PHENYTOIN used to treat?
What are PHENYTOIN levels?
The levels of PHENYTOIN, in the bloodstream must be checked regularly to make sure they are in the range, for treatment and to prevent any risks of toxicity or insufficient seizure management.
What are PHENYTOIN tablets used for?
Phenytoin tablets are prescribed to manage and reduce seizures by stabilizing brain activity in people, with epilepsy or those recuperating from neurosurgery.
Why are PHENYTOIN levels checked?
Doctors monitor PHENYTOIN levels to make sure the medication is, at a helpful level to prevent both harm from too much or too little treatment, for seizures.
When are PHENYTOIN levels taken?
Phenytoin levels are usually checked once a consistent dosage plan is set up or when there are dosage adjustments or signs of side effects or toxicity symptoms.
What are PHENYTOIN sodium pills used for?
Phenytoin sodium tablets are prescribed to help prevent and manage seizures by decreasing activity, in the brain.
What are PHENYTOIN sodium tablets?
PHENYTOIN sodium tablets are a type of medication that is taken orally and mainly used for treating seizure disorders.
Can PHENYTOIN cause hyponatremia?
Hyponatremia is not an issue, with phenytoin; however electrolyte imbalances can still. May require close monitoring, for specific patients.
Can PHENYTOIN cause seizures?
Taking PHENYTOIN or missing doses can unexpectedly trigger seizures so it's crucial to maintain the right blood levels and avoid interactions, with other medications.
Can PHENYTOIN capsules be opened?
It's important not to open capsules unless your healthcare provider tells you to do so because changing the form could impact the way the medication is absorbed and its effectiveness.
Can PHENYTOIN be crushed?
It is usually advised not to crush PHENYTOIN unless a healthcare provider gives instructions because changing the dosage form can impact the absorption and effectiveness of the drug.
Can PHENYTOIN cause hypotension?
PHENYTOIN has the potential to induce blood pressure levels when administered intravenously and should be approached with care in a supervised setting.
How does PHENYTOIN work?
Phenytoin functions, by blocking voltage gated sodium channels, in nerve cells to stop the signals that trigger seizures.
How does PHENYTOIN cause gingival hyperplasia?
Phenytoin may lead to overgrowth by triggering an excess of gum tissue growth possibly linked to alterations, in collagen metabolism and cellular proliferation, in the gums.
How does PHENYTOIN cause hirsutism?
Phenytoin may cause hirsutism or increased hair growth because it has androgen properties that stimulate hair follicles.
How does PHENYTOIN cause folic acid deficiency?
Phenytoin disrupts the process of folic acid metabolism by blocking its absorption in the intestines This can result in a shortage of folic acid and potential complications associated with it.
How does PHENYTOIN cause megaloblastic anemia?
Phenytoin can result in anemia by hindering the absorption of folic acid, for the creation of red blood cells and causing the production of larger and less mature red blood cells.
What is PHENYTOIN sodium extended used for?
Phenytoin sodium extended is prescribed for managing tonic partial seizures by delivering a slow release of the medication to maintain long-term control, over seizures.
What does PHENYTOIN do to your body?
When should PHENYTOIN be taken?
It's important to take PHENYTOIN at some time every day whether, with or, without food to ensure blood levels and effective seizure management.
When is PHENYTOIN given?
Phenytoin is given to manage seizures. It can be used as a treatment, for epilepsy or to prevent seizures during and, after brain surgery.
Where is PHENYTOIN used?
Phenytoin is often prescribed in settings to treat epilepsy post surgery or during emergencies to manage seizures.
Where is PHENYTOIN metabolized?
Phenytoin is mainly broken down in the liver by P450 enzymes.
PHENYTOIN belongs to which class of drug?
Phenytoin is categorized as a medication that works by blocking sodium channels in the body.
Why is PHENYTOIN not given with dextrose?
Phenytoin should not be mixed with dextrose as it may form a precipitate in the solution which can lower the drugs effectiveness and lead to issues when administered intravenously.
Why is PHENYTOIN contraindicated in myoclonic seizures?
Avoid using phenytoin, for seizures as it might make the condition worse by causing frequent seizure episodes, in certain individuals.
Is PHENYTOIN a sodium channel blocker?
PHENYTOIN works as a sodium channel blocker that aids in decreasing impulses in the brain and stopping seizures from occurring.
What are the side effects of PHENYTOIN toxicity?
Is PHENYTOIN an inducer or inhibitor?
Phenytoin acts as an enzyme inducer, for the P450 system and can lower the effectiveness of other drugs by speeding up their metabolism.