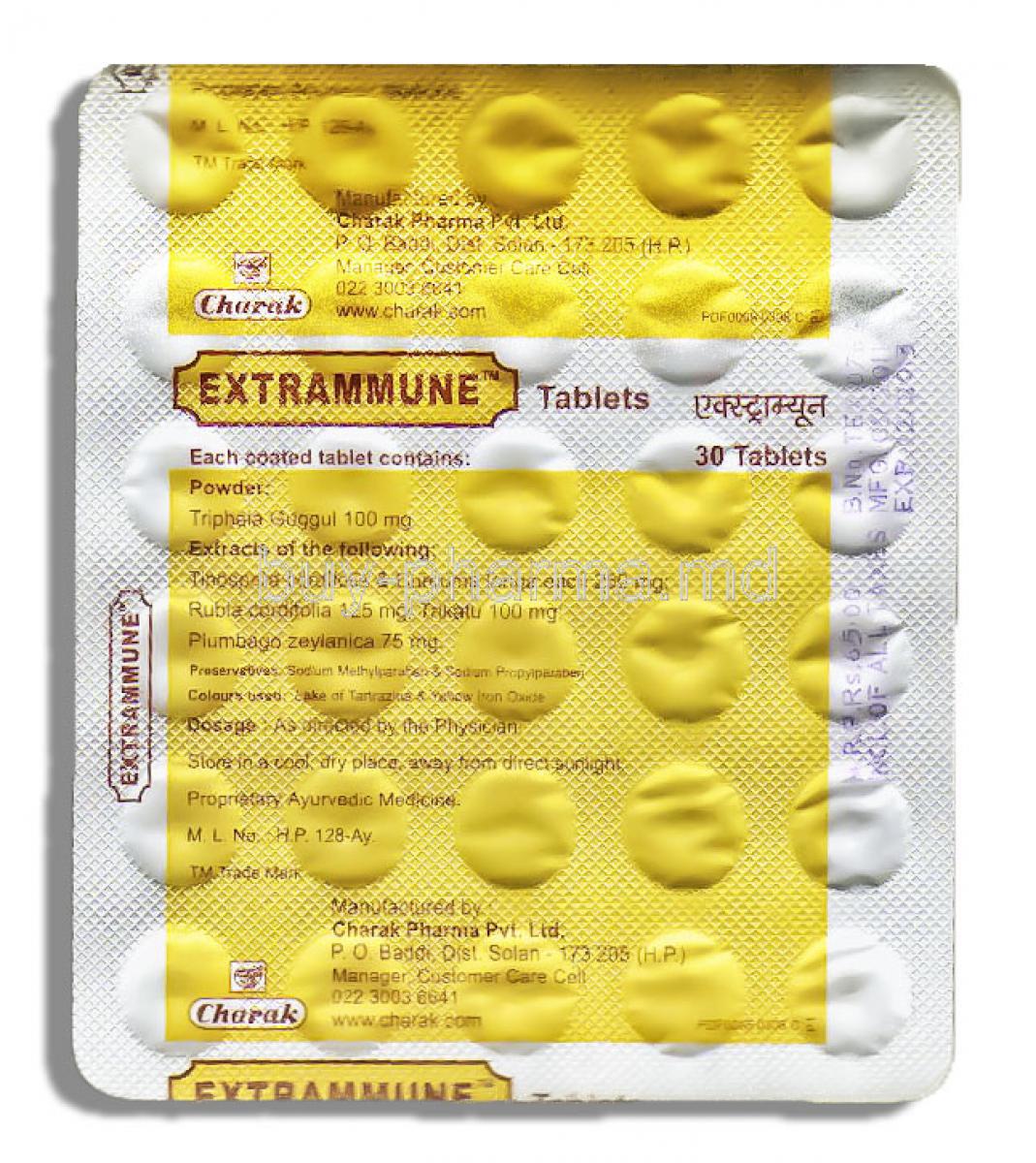
Extrammune
- I. Introduction
- II. Uses of Extrammune
- III. How It Works
- IV. Dosage and Administration
- V. Composition
- VI. Off-label Use of Extrammune
- VII. Side Effects
- VIII. Common Side Effects
- IX. Interactions with Other Medications
- X. Warnings and Contraindications
- XI. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
- XII. Administration to Specific Populations
- XIII. Overdosage
- XIV. Storage Instructions
- XV. Handling Precautions
I. Introduction
Historical background and development of Extrammune
Extrammunes origins can be traced back to laboratory investigations and clinical experiments focused on improving the body's immune responses. Starting as a puzzle, it has transformed over time into a remarkable medical achievement. This progress was not accidental—rather a product of careful research, trials, and unwavering determination.
Its primary role in the medical field
Extrammune plays a role in the diverse realm of medical treatments by serving as a fundamental component of immunotherapy. Thanks to its groundbreaking effects, it is recognized as an elixir that empowers our body's natural defense mechanisms against harmful pathogens. This goes beyond being a regular treatment; it represents a transformative change in our understanding and reinforcement of the body's immune system.
II. Uses of Extrammune
Main indications and benefits for patients
Extrammune stands out from medications on pharmacy shelves; it brings hope to many. It boosts the system strengthening the body's defenses against external threats. Moreover, it reduces the occurrence of illnesses making patients more resistant. There is also potential for it to improve symptoms in situations where the immune system is compromised.
References:
- Best Ayurvedic Immunity Booster Syrup – Extrammune - Charak1
- Extrammune Tablet - Uses, Dosage and Effects | mfine2
- Extrammune Syrup - Ingredients, Indications, Dose, Side effects3
- Extrammune Tablet: Uses, Ingredients, Dose, Side Effects - AyurMedInfo4
Disease conditions where Extrammune proves most effective
Some situations demonstrate the effectiveness of Extrammune; cases of immunodeficiency disorders where the body's natural defense system is weak post-surgical scenarios to promote healing and minimize the risk of infection and chronic illnesses where immunity may be compromised due to long-term medication or the disease itself.
References:
- What is Immunodeficiency and its causes and related conditions?1
- Immunodeficiency Disorders: Symptoms, Types, and More - Healthline2
- Overview of Immunodeficiency Disorders - Immune Disorders - Merck Manuals3
- Overview of Immunodeficiency Disorders - The Merck Manuals4
III. How It Works
Mechanism of action in the body
Extrammune doesn't just work; it orchestrates. When administered, it acts as an immunomodulator boosting both the cellular elements of our immune system. It's like a conductor leading an orchestra, ensuring all the different resistant components work together in harmony and synergy.
Cellular and molecular interaction details
Going deeper into how it works, Extrammune operates at the level. It enhances the function of macrophages and triggers B cells to increase the production of antibodies. Additionally, it stimulates the creation of cytokines, crucial molecules for communication between cells during immune responses.
IV. Dosage and Administration
Recommended dosages for various conditions
Extrammune is a medication, but its effectiveness depends on the correct dosage. The recommended dosage varies depending on the condition being treated. A higher dosage is often necessary for immunodeficiency disorders due to the weakened system. In surgical scenarios, a moderate dosage is given to promote healing without risking potential overdose effects. For conditions, the dosage is adjusted based on the medications being taken and the severity of the disease.
Instructions for administration
Extrammune, although compelling, must be administered. It is best to take it orally for optimal absorption and bioavailability. Taking it with meals can help reduce any gastrointestinal side effects. It's essential to take it at the time every day to maintain a consistent level of the medication in your bloodstream.
Adjustments based on patient needs and feedback
Like any other medication, Extrammune may require dose adjustments. Observing any feedback from the patients regarding possible side effects is essential. Regularly evaluate the blood parameters to ensure no abnormalities caused by the treatment. Customize the doses according to the patient's age, weight, and overall health condition.
V. Composition
Key active ingredients and their concentrations
Extrammune is the result of research and is known for its exceptional list of ingredients. It contains components like Immunoglobulins, crucial in supporting a robust immune system. It also includes precursors that help facilitate effective communication, between cells and specific enzymes that contribute to vital reactions involved in immune responses.
List of excipients or inactive components
Apart from the components, Extrammune also contains additional substances that facilitate effective drug administration. These include binding agents that help the tablet stay intact, fillers that give it its desired size, and preservatives that extend the product's shelf life while preserving its potency.
VI. Off-label Use of Extrammune
Popular off-label indications
Although Extrammune is primarily used for its intended purposes, it has also been utilized in approved ways. These include treating reactions by harnessing its ability to modify the immune system. Additionally, it has been employed in skin disorders due to its capacity to regulate immune responses. Furthermore, it has shown potential in managing gastrointestinal disorders by influencing both immunity and inflammation.
References:
- Best Ayurvedic Immunity Booster Syrup – Extrammune - Charak1
- Autoimmune Skin Conditions: Types, Symptoms, Causes - Verywell Health2
- Gastrointestinal Diseases: Symptoms, Treatment & Causes - Cleveland Clinic3
- Gastrointestinal Disease: Types, Symptoms, and Treatment - Verywell Health4
Research and studies supporting off-label use
There have been studies and personal accounts that have emphasized the possible additional advantages. Research shows that it can help lessen the intensity of reactions, particularly in cases where traditional treatments haven't worked. It may also improve skin conditions due to its impact on the immune system. Additionally, it seems to alleviate symptoms in gastrointestinal disorders, although scientists are still unsure about how it works.
References:
- Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Efficacy of Treatment With Hyperimmune Plasma Obtained From Convalescent Antibodies of COVID-19 Infection - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov1
- Boost Immune System with Extrammune - Charak2
- Extrammune Tablet - Uses, Dosage and Effects | mfine3
Risks associated with off-label administration
Using medications for purposes than their approved indications, although showing potential benefits, does come with certain risks. One such risk is the worsening of symptoms, particularly when the exact mechanism of action is not well understood. Additionally, there is knowledge regarding the possible side effects of off-label use. Furthermore, there is uncertainty surrounding potential drug interactions due to the lack of research in off-label scenarios.
References:
- Off-Label Drug Use: Why Do Doctors Prescribe Them? - Drugwatch1
- What is off-label drug use? Risks, benefits, and examples2
- Off-Label Prescription Drugs Use: Benefits and Risks - WebMD3
- Taking off-label medication - Mayo Clinic Health System4
VII. Side Effects
Overview of potential adverse reactions
Differentiating between minor and serious side effects
It is crucial to distinguish between different side effects. Some side effects, such as mild nausea, occasional headaches, and fatigue, are temporary and may go away on their own. On the hand, there are serious side effects that require immediate medical attention. These include reactions like hives or difficulty breathing, severe gastrointestinal disturbances, and neurological abnormalities like seizures.

VIII. Common Side Effects
Frequently reported side effects by patients
Although Extrammune is highly regarded for its abilities patients have reported experiencing specific side effects, including gastrointestinal discomfort mild skin rashes, and dizziness.
Management and mitigation strategies
Reducing the impact of these side effects is possible with approaches; Taking the medication with food may help minimize digestive issues. Nonprescription antihistamines can help alleviate responses. Staying hydrated and getting rest can assist in managing feelings of dizziness and fatigue.
IX. Interactions with Other Medications
Drugs known to interact with Extrammune
Interactions between drugs can be pretty complex in pharmacology, so it's essential to stay alert. Some specific medications that could diminish or enhance the effects of Extrammune include immunosuppressants, specific antivirals, and particular antibiotics.
Mechanism of interaction and potential outcomes
Mechanisms support the complex interplay of drug interactions. One of these mechanisms involves the modulation of enzymes, where certain drugs can enhance or hinder the metabolism of Extrammune, thereby affecting its effectiveness. Another mechanism involves alterations in binding affinity, where certain drugs may compete for the receptors resulting in the attenuation or amplification of therapeutic outcomes.
Recommendations when co-administering with other drugs
It's important to stay vigilant and record all the medications you're taking. Make sure to share this list with your healthcare providers. Also, be aware of any changes in your health that may occur after starting a medication. It's an idea to have regular blood tests done to make sure that the levels of the medicines in your body are still in the therapeutic range.
X. Warnings and Contraindications
Conditions where Extrammune should not be used
There are situations in which it is not recommended to use Extrammune. These include patients who have known allergies to any of its components and individuals with autoimmune disorders, as excessive stimulation could worsen their condition.
Potential risks for certain populations
Certain groups of people may have a risk, such as individuals with a history of severe allergies. Also those, with liver or kidney issues, which could potentially affect how the medication is processed in their bodies.
XI. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
Monitoring needs during therapy
Continual monitoring during therapy is essential; blood tests to assess its effects and identify any unexpected reactions. Consistent patient input to monitor and address any discomforts.
Steps to ensure patient safety during treatment
Ensuring safety is of utmost importance. It is crucial to provide patients with information regarding side effects. Additionally, it is essential to establish and maintain lines of communication so that patients can express any concerns they may have. Regularly evaluating the need for and dosage of Extrammune based on feedback is also essential.
XII. Administration to Specific Populations
a. Elderly Patients
Elderly patients require attention due to their distinct physiological characteristics. It is essential to consider the possibility of dosages due to changes in metabolism and to monitor them for an increased risk of side effects closely.
b. Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
This group of people wants to consider the pros and cons; Initial information indicates that it's wise to be cautious in the stages of pregnancy. If breastfeeding, it's essential to talk with your healthcare provider about the risks since there isn't enough precise data on how Extrammune is excreted in breast milk.
c. Children
Administering medication to children requires consideration of various factors. One crucial aspect is adjusting the dosage based on their weight. It's also essential to monitor for any differences in side effects that may arise. Additionally, regular assessments of their growth and development play a role in ensuring the safety of the medication being used.
XIII. Overdosage
Symptoms of Extrammune overdose
Understanding the complexities of administering medication demands attention, especially when dealing with potent drugs like Extrammune. Accidentally taking much can lead to various symptoms, including changes in breathing patterns like shallow breaths or even temporary pauses in breathing (apnea). It can also cause trembling, seizures, confusion, and even loss of consciousness (coma). Additionally, it may result in problems like severe nausea, vomiting, and intense abdominal pain.
Emergency management and treatment options
In the event of an overdose, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. The critical aspect of treatment revolves around the following steps; 1. Stabilizing the patient; Ensuring that essential vital signs such as breathing and heart rate are within range. 2. Gastric lavage; This traditional method, commonly called stomach pumping, can be highly beneficial if an overdose occurs recently. 3. Providing care; This includes administering intravenous fluids supplying oxygen when needed, and prescribing medications to alleviate specific symptoms. 4. Monitoring; It is essential to constantly observe the patient's condition to promptly address any potential complications arising after the overdose. These measures are essential in managing an overdose situation with timely medical intervention.
XIV. Storage Instructions
Recommended storage conditions for maintaining potency
To maintain the effectiveness and strength of Extrammune, it is crucial to follow the recommended storage conditions. These instructions must be strictly followed without negotiations; Temperature Control; It is best to keep Extrammune in an environment ideally between 15 25°C. Avoiding Moisture; The storage area for the medication should be free from humidity to ensure its efficacy. Shielding from Light; Prolonged exposure to sunlight can harm the chemical structure of Extrammune. Therefore it should be stored in an environment. It is vital to prioritize these guidelines to preserve the quality and potency of Extrammune.
Shelf life and expiration considerations
The effectiveness of a drug is closely linked to how fresh it's. The expiration date is not just a suggestion; after this date, the medicine may not work well, and harmful breakdown substances could develop. Extrammune usually remains effective for 24 to 36 months if stored correctly. Inspecting the drug for any changes in its appearance, such as alterations in form, color, or texture is essential. If you notice any of these changes, it's best to dispose of the medication.
XV. Handling Precautions
Safe handling procedures for healthcare professionals
It is crucial to handle drugs with care, considering the balance between their effectiveness and safety. To ensure safety measures, gloves are recommended when handling Extrammune to prevent absorption through the skin. Additionally, maintaining an environment around the drug can play a significant role in preventing unintended infections. If the drug is in form or reconstituted, precautions should be taken to avoid inhaling particles.
Proper disposal and environmental concerns
Protecting the environment and ensuring safety are two essential responsibilities. When disposing of biohazard materials, such as used vials or containers, they should be placed in designated bins. It's crucial not to flush products like Extrammune down toilets or drains. It's always an idea to consult local guidelines, as different regions may have specific protocols for pharmaceutical disposal. Following these guidelines is not a legal requirement but also an ethical obligation.