Femcal 500
- Introduction to Femcal 500
- Composition and Active Ingredients
- How Femcal 500 Works
- Uses of calcium carbonate
- Off-Label Uses of Femcal 500
- Calcium carbonate Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Common Side Effects of Femcal 500
- Serious Side Effects and Risks
- Drug Interactions and Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Special Considerations for Different Patient Groups
- Storage and Handling Precautions
- Calcium carbonate overdose Management and Treatment
- Patient Care and Monitoring
Introduction to Femcal 500
Overview of Femcal 500
The Femcal 500 medication is created to assist in maintaining the levels of calcium in the body. It is commonly recommended for those with calcium deficiencies or conditions, like osteoporosis, which affect bone health and metabolism by replenishing calcium stores to uphold skeletal strength and overall bodily equilibrium.
Therapeutic Classification and Primary Purpose
This medicine belongs to the calcium supplements and substances that promote bone health regulation. It is commonly recommended for individuals lacking calcium in their diet, those with malabsorption issues, or those with calcium requirements because of medical situations, like pregnancy or breastfeeding periods.
Importance in Medical Treatment
- Essential for bone mineralization and strength.
- Plays a pivotal role in neuromuscular functions and cardiovascular health.
- Supports enzymatic activity necessary for metabolic processes.
Composition and Active Ingredients
Key Active Ingredients in Femcal 500
The main ingredient in Femcal 500 is calcium carbonate, which is easily absorbed by the body for calcium intake, with an addition of vitamin D to help with absorption and utilization in the body.
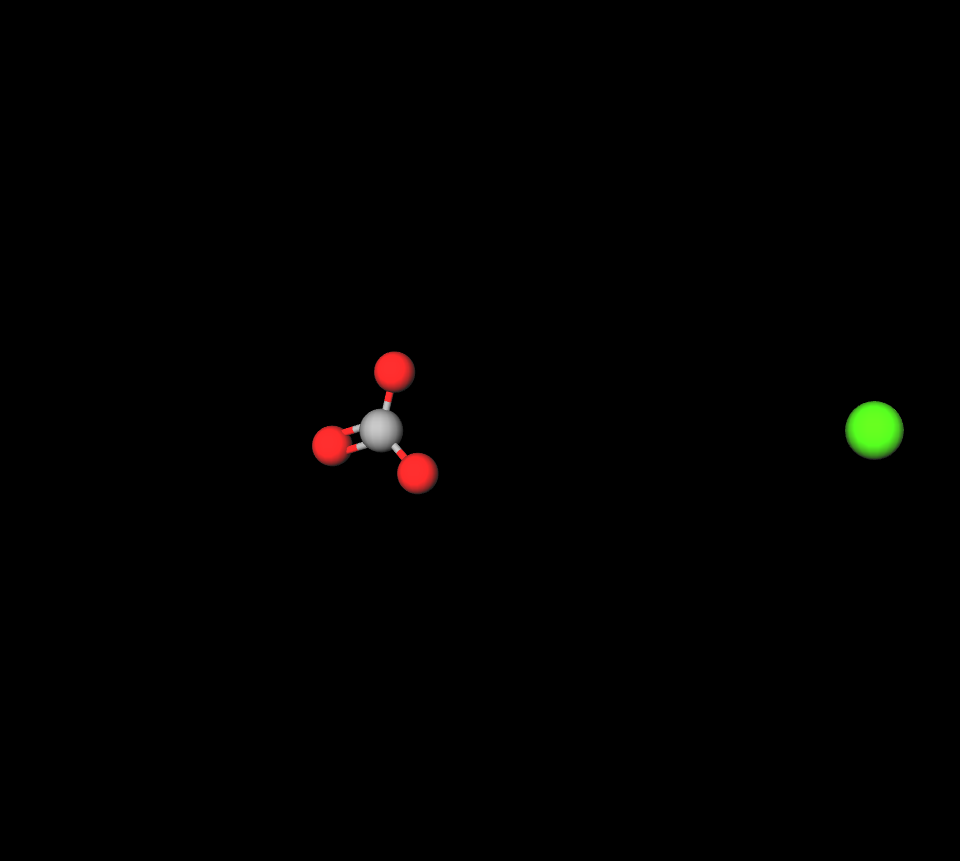
Ph of calcium carbonate
The pH level of calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) is 9.91, showing consistency in pH levels above 2. Its solubility remains relatively constant within the pH range of 5 to 10.
Mechanism of Action of Each Ingredient
- Calcium Carbonate: Neutralizes gastric acid and provides a concentrated source of calcium, which is absorbed in the intestines.
- Vitamin D3: Facilitates the intestinal absorption of calcium and ensures its proper deposition in bones.
Additional Components and Their Functions
The Femcal 500 tablets might also include ingredients like microcrystalline cellulose to help with the tablet's structure, magnesium stearate for lubrication, and croscarmellose sodium for dissolution.
Calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid
Calcium Carbonate and Hydrochloric Acid Reaction | CaCO3 + HCl Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is a metal carbonate compound and reacts with hydrochloric acid (HCl) to produce carbon dioxide (CO2), calcium chloride (CaCl2) and water.
Vinegar and calcium carbonate
When vinegar interacts with calcium carbonate, a chemical reaction process occurs where the acetic acid and calcium carbonate separate and then recombine to form compounds.

Calcium carbonate vs sodium bicarbonate
Calcium carbonate typically has an ability to neutralize acid per gram compared to sodium bicarbonate, which makes it potentially better at easing heartburn and indigestions; on the other hand, sodium bicarbonate (commonly known as baking soda) is often favored for its quicker effects but may lead to increased sodium intake due to its makeup.
Calcium gluconate vs calcium carbonate
Calcium carbonate is commonly utilized for managing heartburn and digestive issues while also serving as a supplement to boost calcium levels in the body. On the other hand, Calcium gluconate is a dietary supplement to increase calcium in the body. It is used to treat hypocalcemia and cardiac arrest.
Calcium vs calcium carbonate
Calcium carbonate is calcium often seen in supplements and food products.
Calcium carbonate vs calcium phosphate
Calcium carbonate is often the option; however, calcium phosphate might be more suitable for individuals with low phosphate levels as it is a crucial component of bones and teeth.
How Femcal 500 Works
Pharmacodynamics and Mechanism of Action
Once calcium carbonate is consumed and reaches the stomach, it breaks down to release calcium ions. These ions are then taken in by the intestine with the help of vitamin D to be absorbed. The absorbed calcium travels through the bloodstream to support functions in bones, muscles, and other tissues within the body.
Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion (ADME)
- Absorption: Primarily occurs in the duodenum and jejunum, facilitated by active transport mechanisms.
- Distribution: Calcium is bound to proteins and transported to target organs.
- Metabolism: Calcium itself is not metabolized but regulated by parathyroid hormone (PTH) and calcitonin.
- Excretion: Eliminated through feces (unabsorbed portion) and urine (regulated renal excretion).
How It Differs from Other Similar Medications
The Femcal 500 supplement stands out due to its calcium content and excellent absorption compared to forms of calcium like calcium citrate, making it a more effective treatment option with the added benefit of vitamin D₃ for improved therapeutic results.
Uses of calcium carbonate
Primary Medical Indications
Femcal 500 is primarily used for the prevention and treatment of calcium deficiency-related disorders, including:
Conditions Treated with Femcal 500
In addition to bone disorders, this supplement is effective in managing conditions such as:
Efficacy and Clinical Studies Supporting Use
Studies conducted in trials have shown that taking calcium supplements paired with vitamin D can notably decrease the likelihood of fractures among individuals. Various research has confirmed the impact of this combination, on enhancing bone strength and overall skeletal wellness.
Off-Label Uses of Femcal 500
Alternative Medical Conditions Treated
Femcal 500 is sometimes prescribed off-label for conditions such as:
- Premenstrual syndrome (PMS)-related symptoms
- Muscle cramps and spasms
- Hypertension management

Research and Clinical Trials Supporting Off-Label Use
Research indicates that getting calcium in your diet could play a role in controlling blood pressure and lowering the chances of heart-related issues. Additionally, taking calcium supplements has been associated with better muscle performance for people who are physically active.
Risks and Benefits of Off-Label Prescription
Using medications for purposes other than those approved by health authorities can be helpful in some situations; however, it is important to be careful to prevent issues like levels of calcium in the blood or the development of kidney stones and potential interactions with other drugs.
Calcium carbonate Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Calcium carbonate dosage per day
- Calcium carbonate dosage for adults: 500-1000 mg per day, divided into doses.
- Pregnant and lactating women: Up to 1200 mg per day.
- Osteoporotic patients: 1000-1500 mg daily.
How to Take Femcal 500 Correctly
To maximize absorption:
- Take with meals to enhance bioavailability.
- Avoid consuming with high-oxalate foods such as spinach.
- Use as directed by a healthcare provider.
Dosage Adjustments Based on Patient Factors
Adjustments to the dosage might be needed for people with kidney issues or older patients who are also using medications that impact calcium levels in the body.
Missed Dose Instructions
If you forget to take a dose of the medication on time and remember when it's not too close to your scheduled dose time, just go ahead and take the missed dose then. Make sure not to take two doses at once.
What to Do in Case of Overdose
Signs of taking too much include feeling sick to your stomach and throwing up, as well as feeling confused and having trouble with your kidneys working properly. You need to see a doctor right away.
Common Side Effects of Femcal 500
Frequently Reported Side Effects
- Gastrointestinal discomfort
- Constipation
- Hypercalcemia symptoms (e.g., thirst, frequent urination)
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Side Effects
Short-Term: Mild digestive disturbances.
Long-Term: Potential kidney stone formation and vascular calcification with excessive use.

When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek advice promptly if you have feelings of nausea or dizziness or if you notice any irregularities in your heartbeat.
Serious Side Effects and Risks
Severe Allergic Reactions and Anaphylaxis
Although rare, hypersensitivity reactions to Femcal 500 can manifest as severe allergic responses. Symptoms may include:
- Urticaria (hives) and pruritus (intense itching).
- Angioedema swelling of the face, lips, or tongue.
- Respiratory distress, wheezing, or difficulty in breathing.
- Anaphylactic shock, in extreme cases, requires immediate medical intervention.
Individuals with a known hypersensitivity to any component of Femcal 500 should avoid its use. Rapid administration of epinephrine and antihistamines is necessary in cases of anaphylaxis.
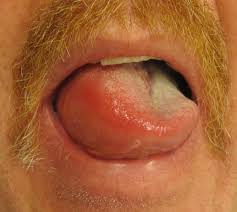
Organ-Specific Adverse Reactions
Femcal 500, when misused or taken in excessive amounts, may exert strain on specific organ systems, leading to severe complications.
- Renal System: High calcium levels can result in nephrocalcinosis, nephrolithiasis (kidney stones), and renal impairment.
- Gastrointestinal Tract: Excessive supplementation may cause nausea, vomiting, constipation, and abdominal cramps.
- Cardiovascular System: Hypercalcemia-induced cardiac arrhythmias, hypertension, or vascular calcifications may arise with prolonged high-dose use.
Long-Term Risks and Complications
Prolonged intake, especially without medical supervision, can lead to chronic health concerns:
- Soft tissue calcification, particularly in arteries and heart valves.
- Gastrointestinal disturbances leading to malabsorption syndromes.
- Increased risk of kidney dysfunction and progressive nephropathy.
Drug Interactions and Contraindications
Common Drug Interactions
Femcal 500 has the potential to alter the pharmacokinetics of several medications:
- Bisphosphonates: Reduced absorption leading to decreased efficacy.
- Tetracycline and Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics: Forms insoluble complexes, reducing antibiotic potency.
- Thiazide Diuretics: May increase serum calcium levels, heightening the risk of hypercalcemia.
- Glucocorticoids: Decreased calcium absorption, leading to potential deficiencies.
Effects of Combining Femcal 500 with Other Medications
Concurrent administration of certain drugs requires careful monitoring:
- Vitamin D analog may amplify calcium absorption, increasing toxicity risk.
- Iron supplements calcium may hinder iron absorption; advisable to stagger intake.
- Antacids simultaneous use may exacerbate gastrointestinal side effects.
Medical Conditions That Contraindicate Use
Patients with the following conditions should avoid or use Femcal 500 with extreme caution:
- Hypercalcemia or hyperparathyroidism.
- Chronic kidney disease or nephrolithiasis.
- Cardiac arrhythmias influenced by electrolyte imbalances.
Warnings and Precautions
Precautions Before Starting Treatment
Before initiating therapy, a comprehensive medical evaluation should be conducted to assess:
- Pre-existing conditions that may influence calcium metabolism.
- Potential drug interactions that could alter therapeutic outcomes.
- Dietary calcium intake to prevent excessive supplementation.

Potential Risks in Specific Patient Groups
People who have issues with their kidneys or heart health and those with metabolic conditions need to be watched over.
Monitoring and Safety Measures
- Routine serum calcium and renal function tests.
- Periodic assessment of bone mineral density for long-term users.
- Monitoring of cardiovascular health, particularly in elderly individuals.
Special Considerations for Different Patient Groups
Administration to Elderly Patients
As people grow older, they might experience a decrease in calcium absorption. Become more prone to hypercalcemia a condition of calcium levels, in the blood stream. Its advised to start with a dose and make adjustments gradually for their treatment.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
During pregnancy and breastfeeding periods, doctors often recommend Femcal 500 to meet the calcium needs of both the mother and the baby. However, it's important to avoid taking much to prevent issues, like fetal hypercalcemia.
Administration to Children
Pediatric applications are recommended for fulfilling calcium requirements related to growth emphasizing the importance of dosage to maintain bone development and prevent any disruptions.
Calcium carbonate nursing considerations
When looking after patients who're prescribed calcium carbonate medication, nurses keep an eye on any potential side effects, evaluate how well the patient is responding to the treatment, and provide guidance to the patient on correctly using the medication.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Recommended Storage Conditions
Femcal 500 should be stored under optimal conditions to maintain potency:
- Temperature: Below 25°C (77°F), away from direct sunlight.
- Humidity: Keep in a dry environment to prevent degradation.
How to Safely Handle Femcal 500
Remember to store from children and steer clear of much heat or moisture exposure.
Proper Disposal Methods
Dispose of unused pills, by utilizing pharmaceutical take back programs to avoid pollution.
Calcium carbonate overdose Management and Treatment
Symptoms of Femcal 500 Overdose
- Severe hypercalcemia leading to confusion, lethargy, and muscle weakness.
- Gastrointestinal distress, including nausea and vomiting.
- Cardiac arrhythmias in extreme cases.
Emergency Treatment and Medical Interventions
Dealing with an overdose involves; Please provide me with the input text so I can begin the paraphrasing process for you as requested. Administering fluids, through an IV to help increase the excretion of calcium, from the body. Taking loop diuretics, like furosemide should be done with oversight. Using calcitonin as a treatment, for cases of high calcium levels that do not respond to therapies.
Long-Term Effects of Overdose
Overdoing it without supervision can result in kidney stone formation and heart problems that may not be reversible in the run.
Patient Care and Monitoring
Regular Check-Ups and Monitoring Requirements
- Biannual assessment of calcium levels.
- Kidney function tests to prevent nephrotoxicity.
- Bone density scans for osteoporotic patients.
Managing Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Side effects should be addressed through:
- Dietary modifications to balance calcium intake.
- Hydration to prevent renal complications.
- Adjustment of dosage based on patient response.
When to Discontinue Femcal 500
Discontinuation is advised in cases of:
- Persistent hypercalcemia despite dosage reduction.
- Severe gastrointestinal intolerance.
- Development of nephrolithiasis or cardiovascular complications.
Femcal 500 FAQ
- What is the use of Femcal 500?
- What is calcium carbonate used for?
- Is calcium carbonate safe to take daily?
- When should I take calcium carbonate?
- What is a common side effect of calcium carbonate?
- What are the benefits of calcium carbonate supplement?
- Who should take calcium supplements?
- Who Cannot take calcium carbonate?
- Can calcium carbonate cause kidney stones?
- Which is better calcium or calcium carbonate?
- What foods should you avoid when taking calcium carbonate?
- Is calcium carbonate safe for heart?
- What is the side effect of taking calcium carbonate?
- When should I take calcium carbonate morning or night?
- How much calcium carbonate per day?
- Is calcium carbonate bad for the kidneys?
- Does calcium carbonate affect urine?
- Does calcium carbonate cause gallstones?
- Who should avoid calcium carbonate?
- Do eggs have calcium carbonate?
- What are the benefits of taking calcium carbonate?
- What to avoid when taking calcium carbonate?
- Does calcium carbonate raise blood pressure?
- Does calcium carbonate affect sleep?
What is the use of Femcal 500?
Femcal 500mg Tablet is known for its ability to address a range of health issues stemming from calcium levels in the body, such as Vitamin D deficiency, osteoporosis (characterized by bones) hypoparathyroidism (where the parathyroid glands produce insufficient calcium levels in the body) and latent tetany (an ailment affecting muscles due, to low blood calcium levels).
What is calcium carbonate used for?
Calcium carbonate is a type of food people take when they don't get calcium from their diet.
Is calcium carbonate safe to take daily?
It is commonly believed that calcium carbonate is safe for use as a calcium supplement.
When should I take calcium carbonate?
Remember to consume calcium carbonate alongside your meals as the stomach acids produced during eating aid in the absorption of calcium carbonate by the body.
What is a common side effect of calcium carbonate?
Experiencing constipation or feeling gassy and burping are side effects to be aware of when taking this medication; if any of these symptoms persist or worsen over time, it's best to inform your doctor or pharmacist away.
What are the benefits of calcium carbonate supplement?
Calcium carbonate is a type of antacid medicine, in either capsule or tablet form, that helps alleviate issues like heartburn and upset stomach caused by stomach acid production by lowering the acid levels in your stomach while potentially boosting calcium levels in your system.
Who should take calcium supplements?
Taking calcium supplements can benefit individuals who face a risk of osteoporosis or those with calcium intake in their diets.
Who Cannot take calcium carbonate?
Using calcium carbonate is not recommended if you have hypersensitivity reactions or conditions, like kidney stones or high levels of calcium in your urine or blood; low phosphate levels in the blood or lack of stomach acid (achlorhydria) may also be contraindications for its use due to interactions with medications, like digoxin.
Can calcium carbonate cause kidney stones?
Calcium alone is not to blame for the formation of stones in the body; when insufficient calcium is consumed, the body resorts to breaking down bones to release calcium, ensuring a level in the bloodstream, which can then result in excretion through urine and lead to the crystallization process that forms stones.
Which is better calcium or calcium carbonate?
Calcium carbonate supplements are often considered the cost option as they have the highest concentration of elemental calcium (approximately 40%) by weight.
What foods should you avoid when taking calcium carbonate?
Consumption of foods in acids such as spinach or rhubarb or phytic acid found in bran and whole grains could potentially reduce the absorption of calcium in the body, so it is advisable to take calcium supplements with food to enhance its absorption rate.
Is calcium carbonate safe for heart?
Some indications taking calcium supplements may raise the likelihood of having a heart attack.
What is the side effect of taking calcium carbonate?
Please consult a healthcare professional if you experience symptoms such as hives or have trouble breathing along with swelling in your face or throat area.
When should I take calcium carbonate morning or night?
Morning or night
How much calcium carbonate per day?
The recommended dosage is 800 milligrams taken orally, up to three times as required, with a daily intake of 2400 milligrams.
Is calcium carbonate bad for the kidneys?
Patients often turn to calcium carbonate supplements that are easily accessible without a prescription for their health needs. Regular and excessive consumption of these supplements has caused a rise in cases of milk–alkali syndrome (MAS). The symptoms of MAS are ambiguous. It can be overlooked easily if not detected enough. Undiagnosed MAS can lead to kidney damage that may become irreversible, in the run.
Does calcium carbonate affect urine?
The excretion of phosphate in urine showed a decrease when calcium carbonate was administered.
Does calcium carbonate cause gallstones?
Gallstones contain an amount of calcium carbonate.
Who should avoid calcium carbonate?
If you are experiencing any of the health issues listed below, be sure to consult with your doctor or pharmacist before using this product – levels of calcium (hypercalcemia), kidney problems (including kidney stones), low stomach acid levels (achlorhydria), heart conditions, diseases of the pancreas and a specific lung condition called sarcoidosis.
Do eggs have calcium carbonate?
The shell of an egg consists mainly of crystals composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
What are the benefits of taking calcium carbonate?
Calcium carbonate is often taken as a supplement when the body doesn't get calcium from the diet to support bones and overall bodily functions, like muscles and the nervous system.
What to avoid when taking calcium carbonate?
Possible interactions with this medication may occur with items like digoxin or specific phosphate binders (such as calcium acetate) and supplements, like potassium phosphate or sodium polystyrene sulfonate.
Does calcium carbonate raise blood pressure?
No
Does calcium carbonate affect sleep?
Calcium has been found to have an impact on our sleep patterns. It is especially important during the REM phase of sleep.