Finacea Gel
- I. Introduction to Finacea Gel
- II. Composition and Formulation of Finacea Gel
- III. How Finacea Gel Works: Mechanism of Action
- IV. Approved Uses of Finacea Gel in Dermatology
- V. Off-Label Uses and Emerging Applications
- VI. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- VII. Storage, Handling, and Precautionary Measures
- VIII. Side Effects and Safety Profile
- IX. Drug Interactions, Warnings, and Contraindications
- X. Important Precautions and Special Administration Considerations
- XI. Overdose Management and Emergency Response
I. Introduction to Finacea Gel
Overview and Therapeutic Purpose
Finacea Gel stands as a paragon of contemporary topical therapeutics in dermatology. It is meticulously engineered to alleviate the inflammatory sequelae associated with rosacea and similar cutaneous maladies. Rapid relief and sustained amelioration are hallmarks of its clinical application. Its benefits include:
- Reduction of erythema and irritation.
- Improvement of overall skin clarity.
Its therapeutic regimen is designed to confer both immediate and enduring benefits.
Historical Development and Clinical Background
The evolution of Finacea Gel is rooted in a rich tapestry of clinical inquiry and scientific rigor. Originating from pioneering research in inflammatory dermatopathology, the formulation has undergone extensive clinical trials that underscore its efficacy. Its developmental chronology is marked by iterative refinements and empirical validation, reflecting the culmination of decades of medical advancement.
- Inspired by groundbreaking clinical insights.
- Refined through rigorous research protocols.

II. Composition and Formulation of Finacea Gel
Active Ingredients and Their Dermatological Benefits
At the heart of Finacea Gel lies an array of active constituents, carefully selected for their potent therapeutic attributes. Chief among these is azelaic acid, renowned for its robust anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial prowess. This ingredient serves as the fulcrum of the gel's action, mitigating inflammatory cascades and moderating microbial proliferation.
- Azelaic acid: Reduces inflammation and microbial growth.
- Optimized concentration ensures maximal efficacy.
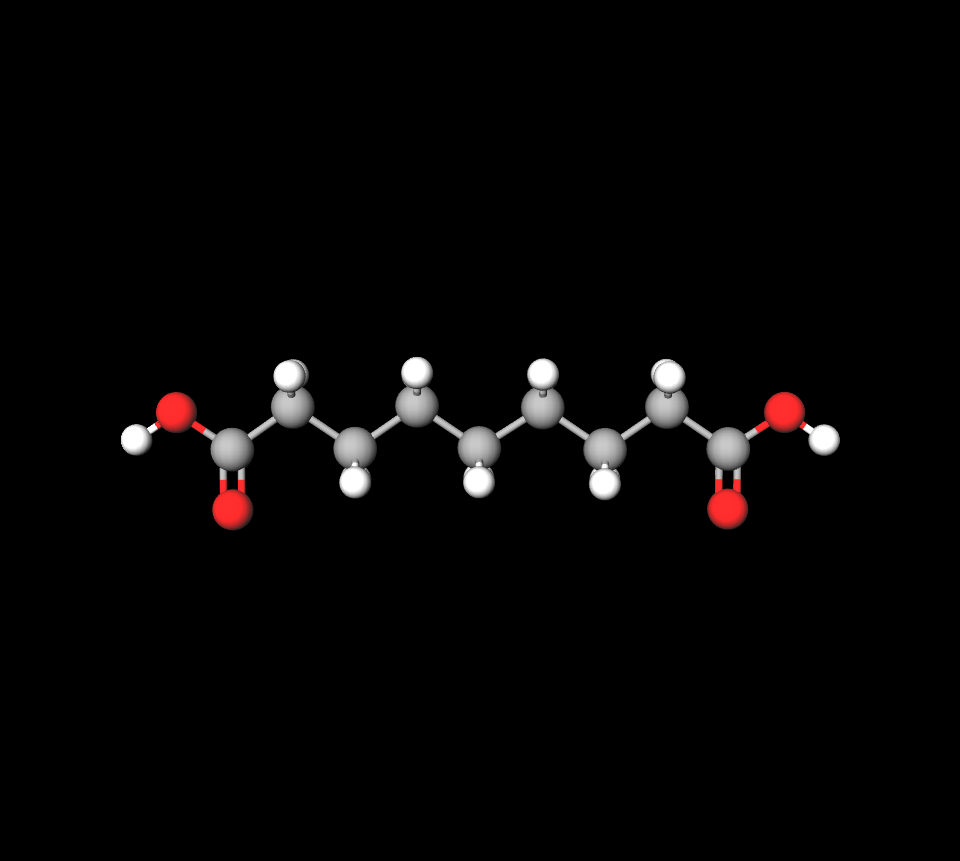
Inactive Ingredients and Their Functional Roles
Complementing the active agent is a suite of inactive excipients, each fulfilling a critical role. These constituents enhance the product's stability, facilitate uniform dispersion, and improve the overall textural experience upon application. Their synergistic function is instrumental in maintaining the gelâs integrity and performance.
- Emollients: Enhance skin hydration and comfort.
- Preservatives: Safeguard against microbial contamination.
Azelaic acid and retinol
The combination of azelaic acid and retinol for addressing acne and hyperpigmentation goals; just make sure not to apply them in your skincare routine! Azelaic acid works wonders in calming the skin and combatting acne while also helping to diminish hyperpigmentation marks; on the other hand, retinol boosts collagen production and minimizes the appearance of fine lines.
Azelaic acid and tretinoin
Tretinoin and azelaic acid share some traits; however, Tretinoin plays a role in boosting cell renewal and repair processes more significantly than azelaic acid does alone. The combination of Tretinoin and azelaic acid is particularly effective because the presence of azelaic acid can amplify the benefits of Tretinoin, in addressing acne issues addressing pigmentation concerns and improving skin brightness.
Azelaic acid and vitamin c
The mix of vitamin C and azelaic acid products help speed up the process of enhancing your skin tone and reducing marks by tackling the problem from different angles.
III. How Finacea Gel Works: Mechanism of Action
Anti-Inflammatory and Antimicrobial Properties
Finacea Gel employs a dual-action mechanism that elegantly intertwines anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects. Its formulation attenuates pro-inflammatory mediators while concurrently curbing bacterial colonization. This confluence of actions establishes a robust defense against the pathogenic underpinnings of rosacea.
- Inhibition of cytokine release.
- Reduction of bacterial proliferation.
Impact on Skin Texture and Bacterial Balance
The application of Finacea Gel results in a nuanced transformation of skin texture. Recalibrating the cutaneous microbiome promotes a harmonious bacterial balance while enhancing epidermal integrity. This dual benefit not only refines skin smoothness but also fortifies its natural barrier function.
- Restoration of dermal equilibrium.
- Promotion of a smoother, more luminous complexion.
IV. Approved Uses of Finacea Gel in Dermatology
A. Primary Use in the Treatment of Rosacea
Primarily, Finacea Gel is acclaimed for its efficacy in treating rosacea. This chronic dermatological condition, typified by persistent facial erythema and papulopustular eruptions, responds favorably to the gel's targeted intervention. Its usage is central to restoring a balanced and aesthetically pleasing skin tone.
- Directly addresses the inflammatory aspects of rosacea.
- Enhances facial radiance and diminishes redness.

B. Azelaic acid for acne
- Modulates sebaceous activity.
- Reduces both comedonal and inflammatory lesions.
C. Long-Term Maintenance and Skin Rejuvenation
Long-term application of Finacea Gel is associated with sustained skin maintenance and subtle rejuvenation. Its continuous use can lead to cumulative benefits, manifesting as improved dermal texture and resilience. The regimen is designed to preserve skin health over an extended period.
- Supports ongoing skin integrity.
- Encourages gradual cellular renewal and rejuvenation.
V. Off-Label Uses and Emerging Applications
A. Azelaic acid for hyperpigmentation
Emerging evidence suggests that Finacea Gel holds promise in the off-label treatment of hyperpigmentation and melasma. Its capacity to modulate melanogenic activity can lead to a diminution of discolored patches, restoring a more uniform complexion.
- Targets aberrant pigmentation with precision.
- Fosters an even-toned and radiant skin appearance.
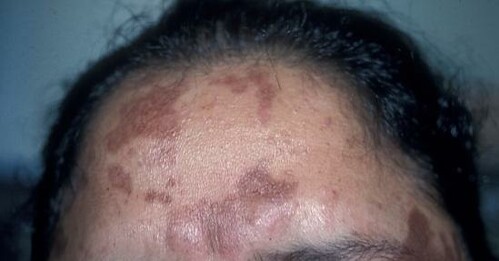
B. Azelaic acid perioral dermatitis
Beyond its primary uses, Finacea Gel is increasingly recognized as an effective adjunct in the management of various dermatological disorders. Its integrative application alongside other therapeutic modalities can enhance overall treatment outcomes.
- Synergizes with complementary topical agents.
- Provides an ancillary therapeutic benefit.
VI. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Recommended Dosage for Adult Patients
For adult patients, adherence to the recommended dosage is paramount. Finacea Gel is typically applied in a thin, even layer to the affected areas. The precise dosing regimen is designed to maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing adverse effects. It is a regimen that is succinct yet effective.
- Apply once daily for optimal results.
- Observe for any signs of irritation.

Step-by-Step Application Techniques for Optimal Results
A methodical approach is advised when applying Finacea Gel. Begin by cleansing the target area with a gentle, pH-balanced cleanser. Pat the skin dry, then proceed with a uniform application of a thin layer of the gel. This sequential process enhances absorption and efficacy.
- Cleanse, pat dry, then apply.
- Ensure even distribution for best outcomes.
Careful Administration: Tips to Maximize Absorption and Minimize Irritation
To optimize the performance of Finacea Gel, careful administration is essential. Employ gentle, circular massage techniques to facilitate absorption, while avoiding over-application that may lead to irritation. Vigilance in application can significantly enhance patient comfort and treatment efficacy.
- Utilize gentle massage motions.
- Monitor the skin's response regularly.
Adjustments Based on Skin Type and Severity
Individualization of treatment is critical. Adjustments to the dosage and frequency may be warranted based on the patients specific skin type and the severity of their condition. Consultation with a healthcare professional ensures a tailored regimen that addresses unique dermatological nuances.
- Consider lower concentrations for sensitive skin.
- Modify application frequency for severe manifestations.

VII. Storage, Handling, and Precautionary Measures
Proper Storage Conditions and Shelf Life
Finacea Gel must be stored under meticulously controlled conditions. Temperature stability and humidity control are paramount. The product is best preserved in a cool, dry environment away from direct sunlight. Its shelf life is strictly defined, ensuring optimal efficacy when stored correctly.
- Maintain a consistent ambient temperature.
- Avoid exposure to extreme climatic variations.
- Secure in its original packaging to deter contamination.
Compliance with these parameters guarantees the product's longevity and performance.
Handling Precautions to Maintain Product Integrity
Adherence to handling protocols is essential for preserving the therapeutic integrity of Finacea Gel. Caution is advised during application and storage to prevent any compromise in quality. The formulation is susceptible to environmental perturbations if mishandled.
- Minimize direct contact to avert contamination.
- Employ aseptic techniques during usage.
- Inspect containers for any signs of damage prior to use.
Vigilant handling ensures that the gel retains its intended potency and safety profile.
VIII. Side Effects and Safety Profile
Common Side Effects: Redness, Irritation, Dryness, and Peeling
Users may experience a constellation of common side effects. These include transient redness, mild irritation, dryness, and peeling of the skin. The presentation is typically self-limiting, resolving with continuous use.
- Redness that subsides within a few hours.
- Mild irritation that diminishes with appropriate moisturization.
- Dryness and peeling that can be alleviated with adjunctive care.
Monitoring these manifestations is vital to optimize the treatment regimen.
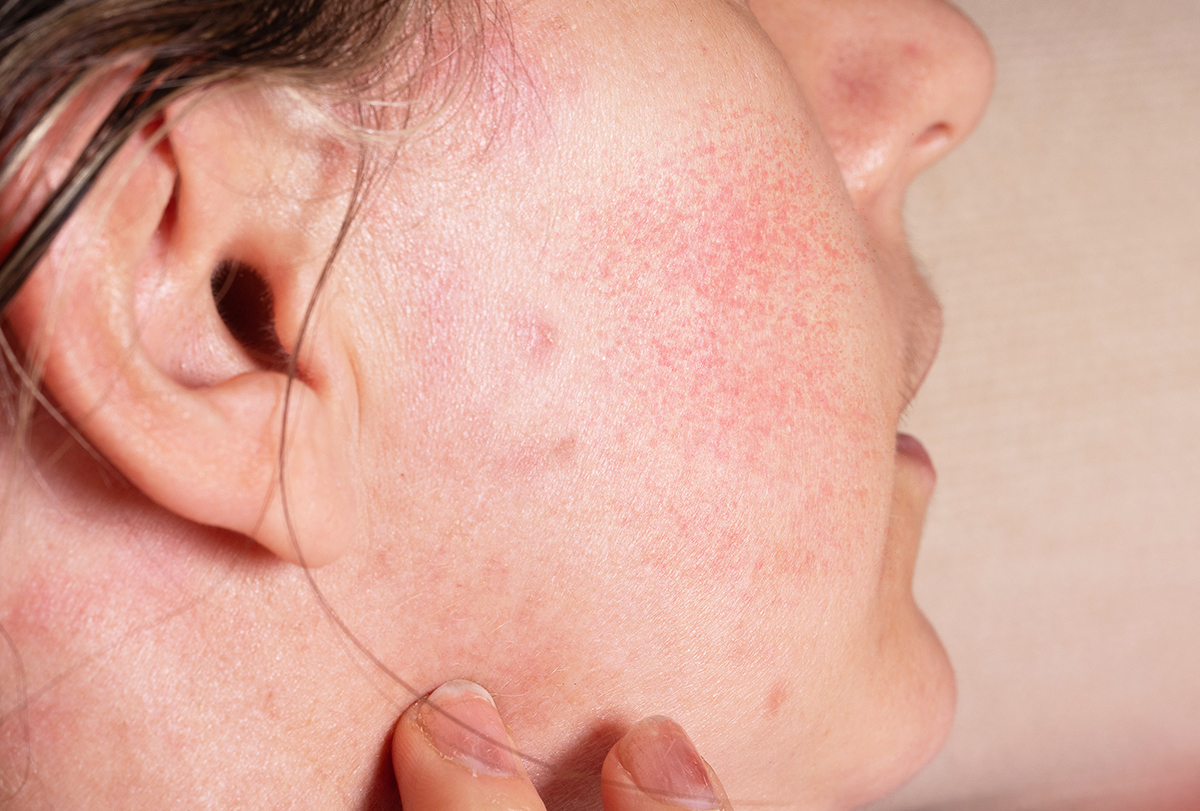
Rare and Serious Adverse Reactions: Identification and Management
Although uncommon, serious adverse reactions require immediate attention. Such events may include exacerbated inflammatory responses or unusual dermatological manifestations. Rapid identification and intervention are essential.
- Persistent irritation beyond initial application.
- Signs of hypersensitivity or allergic response.
- Any unexpected systemic symptoms.
Prompt management, including discontinuation of the gel and professional consultation, is advised.
IX. Drug Interactions, Warnings, and Contraindications
A. Known Interactions with Other Topical and Systemic Medications
Interactions with concomitantly administered medications must be scrupulously evaluated. Finacea Gel may interact with other topical agents and systemic drugs, thereby altering its pharmacodynamic profile. A comprehensive medication review is advised before initiation.
- Concurrent use with retinoids may potentiate irritation.
- Systemic antibiotics may influence microbial flora interactions.
Knowledge of these interactions supports judicious therapeutic planning.
B. Critical Warnings and Safety Alerts for Users
Users are advised to heed critical warnings associated with Finacea Gel. These safety alerts are designed to preempt adverse reactions and ensure proper usage. Awareness of these advisories is essential for informed consent and adherence.
- Do not apply to broken or compromised skin.
- Immediate cessation is warranted if severe irritation occurs.
- Azelaic acid can cause skin irritation, so using it with other potentially irritating topical products can exacerbate these effects. This includes: Astringents Exfoliants Harsh soaps or cleansers Products containing alcohol or spices
The dissemination of these warnings contributes to a safer treatment environment.
C. Contraindications in Specific Patient Populations
Certain populations may be contraindicated for the use of Finacea Gel. Pre-existing dermatological conditions or hypersensitivities necessitate careful screening. It is imperative to exclude patients with documented allergies to the active components.
- Individuals with known hypersensitivity to azelaic acid.
- Patients with acute dermatological infections.
Ensuring the absence of contraindications is foundational to patient safety.
X. Important Precautions and Special Administration Considerations
Administration in the Elderly: Dosage Adjustments and Monitoring
Administration in the Elderly: Dosage Adjustments and Monitoring
Special considerations apply when administering Finacea Gel to elderly patients. Age-related dermatological changes necessitate dosage adjustments and vigilant monitoring. The fragile nature of aging skin demands a more conservative approach.
- Initiate therapy with a reduced dosage.
- Monitor skin response frequently.
These modifications ensure both safety and therapeutic efficacy in geriatric populations.
Guidelines for Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Risk Assessment and Recommendations
For pregnant women and nursing mothers, the use of Finacea Gel requires a rigorous risk-benefit analysis. The potential for transdermal absorption mandates caution. Clinical prudence and individualized assessment are essential.
- Consultation with an obstetrician is mandatory.
- Alternative treatments may be considered if risk is elevated.
Adherence to these guidelines safeguards both maternal and neonatal health.
Pediatric Administration: Safety Considerations and Dosage Modifications
Pediatric administration of Finacea Gel demands a tailored approach. The developing skin of children is particularly sensitive to pharmacological interventions. Dosage modifications are essential to mitigate the risk of adverse effects.
- Start with the minimal effective dose.
- Monitor for signs of irritation or systemic exposure.
Strict adherence to pediatric guidelines promotes a safe and effective therapeutic course.
XI. Overdose Management and Emergency Response
Recognizing Signs and Symptoms of Overdosage
Overdose of Finacea Gel is a rare occurrence but must be promptly recognized. Signs include exacerbated skin irritation, marked erythema, and possible systemic manifestations. Early detection is crucial for mitigating complications.
- Unusual intensification of cutaneous reactions.
- Signs of systemic distress in severe cases.
Timely identification of these symptoms is essential for effective management.
Immediate Steps and First-Aid Measures
Immediate intervention is warranted in the event of an overdose. Rapid first-aid measures can substantially reduce adverse outcomes. The following actions should be taken without delay:
- Cease further application immediately.
- Administer supportive care to alleviate symptoms.
- Initiate topical or systemic treatments as directed by emergency protocols.
Swift and decisive action is imperative to counteract the effects of overdose.
Finacea Gel FAQ
- What is Finacea gel used for?
- How long does it take to see results from Finacea gel?
- Does Finacea gel fade dark spots?
- How effective is Finacea for acne?
- Can you use Finacea everyday?
- Can I leave azelaic acid overnight?
- Can I apply moisturizer after Finacea?
- Does azelaic acid gel remove dark spots?
- What moisturizer goes well with azelaic acid?
- Do I need a prescription for Finacea?
- How much Finacea gel to apply?
- What not to mix with azelaic acid?
- Can I use vitamin C with azelaic acid?
- Do I need sunscreen if I use azelaic acid?
- Can I apply azelaic acid on active acne?
- Does azelaic acid lighten skin?
- Can I mix azelaic acid with niacinamide?
- What happens if you use too much azelaic acid?
- Which is better, kojic acid or azelaic acid?
- Does azelaic acid flatten scars?
- What to avoid when using azelaic acid?
- What color is Finacea gel?
- When should I stop using Finacea?
- What is another name for Finacea?
- What happens if you don t wear sunscreen with azelaic acid?
- How does Finacea work?
- Does azelaic acid remove dark spots?
- Which is better for acne scars, vitamin C or azelaic acid?
- How long does azelaic acid take to clear acne?
- What happens if I use azelaic acid everyday?
- What is Finacea gel used for?
- How effective is Finacea for acne?
- Can you use Finacea everyday?
- Does Finacea lighten skin?
- How quickly does Finacea work?
- Does azelaic acid lighten skin?
- What happens if you use too much azelaic acid?
- Which is better, kojic acid or azelaic acid?
- What to avoid when using azelaic acid?
- When should I stop using Finacea?
- What happens if you don t wear sunscreen with azelaic acid?
- How does Finacea work?
- Does azelaic acid remove dark spots?
- Which is better for acne scars, vitamin C or azelaic acid?
- What happens if I use azelaic acid everyday?
What is Finacea gel used for?
Finacea is used to alleviate mild to moderate acne on the face. It can also treat papulopustular rosacea.
How long does it take to see results from Finacea gel?
4 weeks
Does Finacea gel fade dark spots?
Yes
How effective is Finacea for acne?
Users who applied Finacea gel experienced a decrease of 58 percent in the count of blemishes.
Can you use Finacea everyday?
You should apply the product consistently to the skin areas in the morning and at night for months.
Can I leave azelaic acid overnight?
Yes
Can I apply moisturizer after Finacea?
Yes
Does azelaic acid gel remove dark spots?
Yes
What moisturizer goes well with azelaic acid?
Ceramides, hyaluronic acid, or niacinamide
Do I need a prescription for Finacea?
Yes
How much Finacea gel to apply?
0.5 grams
What not to mix with azelaic acid?
alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), beta hydroxy acids (BHAs), and benzoyl peroxide
Can I use vitamin C with azelaic acid?
Yes
Do I need sunscreen if I use azelaic acid?
Yes
Can I apply azelaic acid on active acne?
Yes
Does azelaic acid lighten skin?
Azelaic acid serves as another skin-brightening agent by blocking tyrosinase activity in the skin cells. Apart from its impact on skin pigmentation azelaic acid has demonstrated effectiveness in alleviating acne and rosacea symptoms for patients.
Can I mix azelaic acid with niacinamide?
Yes
What happens if you use too much azelaic acid?
Your skin problem may become worse
Which is better, kojic acid or azelaic acid?
Azelaic acid and Kojic acid are both options for treating hyperpigmentation issues, with Azelaic acid being favored for its anti-inflammatory properties, making it a popular choice for addressing acne and rosacea concerns as well. It tends to be gentler for individuals with sensitive skin compared to Kojic acid.
Does azelaic acid flatten scars?
It can also help decrease inflammation and thus reduce redness caused by acne. It may also enhance cell production and lessen acne scarring.
What to avoid when using azelaic acid?
Products that contain cleansers and exfoliants with alcohol-based ingredients
What color is Finacea gel?
white to yellowish white
When should I stop using Finacea?
If there is no progress within two months or If the rosacea condition worsens.
What is another name for Finacea?
Azelaic Acid
What happens if you don t wear sunscreen with azelaic acid?
Azelaic acid continues to exfoliate the skin, causing regenerated skin cells to be more exposed on the surface and, therefore, more vulnerable to UV rays and sun exposure.
How does Finacea work?
Finacea gels azelaic acid functions by eliminating the bacteria linked to acne and rosacea on the skin, including propnibacterium, which thrives on the bodys sebum and generates acids and waste substances.
Does azelaic acid remove dark spots?
Yes, Azelaic acid has the ability to fade spots and hyperpigmentation effectively.
Which is better for acne scars, vitamin C or azelaic acid?
For individuals with skin to acne breakouts, dermatologists and users alike consider azelaic acid as the most reliable option.
How long does azelaic acid take to clear acne?
8-12 weeks
What happens if I use azelaic acid everyday?
Azelaic acid helps speed up skin cell renewal to clear out pores and decrease redness while fading spots.
What is Finacea gel used for?
Finacea is used to alleviate mild to moderate acne on the face and for treating papulopustular rosacea.
How effective is Finacea for acne?
58 percent of individuals using Finacea gel experienced a decrease in the number of facial lesions.
Can you use Finacea everyday?
Yes
Does Finacea lighten skin?
Using Azelaic acid (brand name; Finacea ) may lead to depigmentation in the treated areas of the skin due to its ability to inhibit melanin production, the pigment for skin coloration. Thereby resulting in a noticeable loss of skin color particularly prominent in individuals with darker skin tones.
How quickly does Finacea work?
It could require around 12 weeks to notice an improvement in the symptoms of rosacea.
Does azelaic acid lighten skin?
Azelaic acid is also a skin brightening ingredient that functions by blocking tyrosinase activity in the skin cells. Apart from its impacts on skin pigmentation, azelaic acid has also demonstrated effectiveness in managing acne and rosacea symptoms in patients.
What happens if you use too much azelaic acid?
Skin problems may worsen
Which is better, kojic acid or azelaic acid?
Azelaic acid and Kojic acid are both useful, for treating hyperpigmentation with the former known for its anti inflammatory benefits making it a popular choice for addressing acne and rosacea concerns especially among individuals, with dry or sensitive skin who may find it more gentle compared to Kojic acid.
What to avoid when using azelaic acid?
harsh cleansers, exfoliators, and products with alcohol
When should I stop using Finacea?
If there is no progress within 2 months or If the rosacea worsens
What happens if you don t wear sunscreen with azelaic acid?
Azelaic acid continues to exfoliate the skin resulting in skin cells on the surface that're more vulnerable to UV rays and sun exposure.
How does Finacea work?
The azelaic acid found in Finacea gel functions by eliminating the bacteria on the skin that is linked to acne and rosacea conditions. This particular bacteria, known as propiobacterium thrives on your skins oils generating fatty acids and waste substances in the process.
Does azelaic acid remove dark spots?
Sure thing! Azelaic acid has been known to aid in reducing the appearance of spots and hyperpigmentation on the skin.
Which is better for acne scars, vitamin C or azelaic acid?
For individuals, with skin to acne breakouts dermatologists and users commonly rely on azelaic acid, for its effectiveness and trustworthiness.
What happens if I use azelaic acid everyday?
Azelaic acid helps speed up the skins renewal process to clear pores blockages and decrease redness and dark spots.