Gardasil Pre-filled Injection
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Uses of Gardasil Pre-filled Injection
- 3. How Gardasil Pre-filled Injection Works
- 4. Dosage and Administration
- 5. Composition of Gardasil Pre-filled Injection
- 6. Storage and Handling Precautions
- 7. Side Effects of Gardasil Pre-filled Injection
- 8. Interaction with Other Medications and Vaccines
- 9. Warnings and Contraindications
- 10. Important Precautions
- 11. Administration to Specific Populations
- 12. Overdose of Gardasil Pre-filled Injection
- 13. Handling Precautions for Healthcare Professionals
- 14. Off-label Uses and Emerging Applications
1. Introduction
Overview of Gardasil Pre-filled Injection
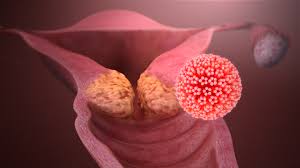
The Gardasil pre-filled shot is a vaccine created to offer defense against different types of human papillomavirus (HPV). Known for its effectiveness in warding HPV-linked illnesses, it has become a player in vaccination campaigns.
Historical Development and Approval
The development of Gardasil marked a breakthrough in vaccine research. First approved by the FDA in 2006, it emerged after years of meticulous research and clinical trials. This vaccine has since received global recognition and has been integrated into national immunization programs worldwide.
Importance in Preventive Healthcare
Gardasil plays a role in reducing the number of other cancers by combatting HPV infections effectively and contributing to public health efforts aimed at preventing these diseases.
2. Uses of Gardasil Pre-filled Injection
Primary Use: Prevention of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infections
Prevention of Cervical Cancer and Other HPV-Related Cancers
The vaccine plays a role in preventing cancer and also provides defense against vulvar and vaginal cancers as well as anal cancers extending its benefits beyond just the cervix.
Prevention of Genital Warts
Expanded Uses: Prevention of Anal, Vulvar, and Vaginal Cancers
Off-label Uses: Emerging Research and Potential Applications
Emerging research explores Gardasil's potential in preventing non-cancerous HPV-related conditions, underscoring its evolving role in medical practice.
3. How Gardasil Pre-filled Injection Works
Mechanism of Action
Utilizing virus particles (VLPs), Gardasil imitates the HPV virus's behavior to trigger the system to generate neutralizing antibodies without causing any infection.
Role of HPV Types Covered by the Vaccine
Gardasil offers protection against the oncogenic and non-oncogenic HPV types6 And 11 as well as 16 and 18.
Immune Response and Long-term Protection
4. Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosage for Adolescents and Adults
The typical treatment plan involves administering either two or three doses based on the individual's age at the start of the vaccination process.
Recommended Dosing Schedule
- Two-dose schedule: For individuals aged 9â14 years.
- Three-dose schedule: For individuals aged 15 years and older or those with immunocompromising conditions.
Administration Route and Technique
Gardasil is usually given with a needle, into the shoulder muscle while following procedures to ensure it works safely and effectively.
Adjustments for Special Populations
Certain groups of people with weakened systems may need customized treatment plans to ensure they get the possible protection against illnesses.
5. Composition of Gardasil Pre-filled Injection
Active Ingredients and Their Functions
The active components consist of VLPs sourced from HPV strains 6, 11, 16, and 18 that act as antigens to trigger the response.
Inactive Ingredients and Stabilizers
Inactive ingredients such as amorphous aluminum hydroxy phosphate sulfate act as adjuvants to enhance immune response.
Differences Between Gardasil and Gardasil 9
Gardasil provides protection against four types of HPV viruses; however, Gardasil 9 offers increased coverage by including five extra oncogenic HPV strains for protection.
Gardasil and cervarix
Both Cervarix and Gardasil protect against HPV strains 45 and 52 that are linked to cancer; however, Cervarix is shown to be more efficient in preventing these types of HPV infections.
6. Storage and Handling Precautions
Ideal Storage Conditions
Gardasil should be stored at 2°C to 8°C and protected from light to maintain its stability and efficacy.
Guidelines for Safe Transport and Use
It is essential to keep the chain intact when transporting vaccines to ensure their efficacy remains high throughout the process of administration after they have been taken out of refrigeration.
Preventing Contamination
Following a protocol when handling syringes is crucial to avoid contamination and maintain safety by disposing of them.
7. Side Effects of Gardasil Pre-filled Injection
Overview of Potential Adverse Effects
In some cases, Gardasil is well tolerated; however similar, to vaccines, it might result in mild to moderate side effects for certain individuals.
Common Side Effects: Pain, Swelling, and Fever
Rare but Serious Side Effects: Allergic Reactions
Although rare, anaphylactic reactions may occur. Patients should be observed for 15 minutes post-vaccination.
Long term side effects of gardasil
Extensive research has shown that Gardasil has a good safety record, over time and no significant health concerns have been linked to its usage.
8. Interaction with Other Medications and Vaccines
Potential Drug Interactions
While Gardasil pre-filled injection is typically considered safe, for use in individuals receiving medications may experience interactions with the effectiveness of the vaccine being reduced due to drugs like corticosteroids or chemotherapy agents that can weaken the immune response during treatment consultation with a healthcare provider, for personalized advice is recommended.
Interactions with Other Vaccines
It's okay to give Gardasil along with vaccines, like hepatitis B or meningococcal vaccines, without affecting its effectiveness. The key is to give the shots at body areas to reduce any reactions in one spot. It's important to follow the immunization rules when planning combined vaccine schedules.
Precautions for Patients with Pre-existing Conditions
Individuals with long-term health issues, like autoimmune disorders or heart conditions, should have an assessment done before getting the Gardasil vaccine to ensure their safety and well-being in the process.
9. Warnings and Contraindications
Absolute Contraindications: Known Allergies
Individuals with a sensitivity to any components of Gardasil should not use it; this includes yeast or aluminum-based adjuvants. In cases of reactions occurring treatment should be sought promptly to avoid serious consequences.

Situations Requiring Careful Administration
Patients who have had Guillain Barré syndrome in the past or suffer from conditions should be given medication carefully with careful observation to prevent any negative reactions.
Risks for Patients with Immunosuppressive Conditions
Immunocompromised individuals might not have a reaction to the Gardasil vaccine despite its overall advantages; thus, healthcare professionals should discuss the potential constraints of the effectiveness of the vaccine with patients in such situations.
Gardasil vaccine in pregnancy
It is advised not to receive the HPV vaccine while pregnant; this includes Gardasil 9 well.

10. Important Precautions
Monitoring After Administration
Post-vaccination monitoring for at least 15 minutes is essential to detect immediate adverse reactions such as syncope or anaphylaxis. Observation protocols ensure prompt management of any unexpected incidents.
Counseling Patients on Vaccine Efficacy
Patients should be informed about Gardasil's high efficacy in preventing HPV-related diseases, while emphasizing the need for regular screenings, such as Pap smears, to maintain comprehensive cervical health.
Addressing Concerns About HPV-Related Stigma
Healthcare professionals should address the potential stigma surrounding HPV vaccination, emphasizing its role as a preventive measure rather than a reflection of lifestyle choices. Clear communication fosters acceptance and understanding among diverse patient populations.
11. Administration to Specific Populations
Administration to Children and Adolescents
The vaccine works best if given before being exposed to HPV. It is usually advised for children between 9 and 14 years. Getting vaccinated early provides protection and in most cases two doses are enough for kids, in this age range.
Guidelines for Elderly Patients
Although Gardasil is not typically advised for individuals, as part of practice it might be an option for those who continue to face a risk of HPV infection. It is important for healthcare providers to carefully assess the advantages for this group of people.
Safety and Recommendations for Pregnant and Nursing Mothers
Gardasil is not recommended during pregnancy due to limited safety data. Nursing mothers may receive the vaccine, as studies suggest no adverse effects on lactation or the infant.
12. Overdose of Gardasil Pre-filled Injection
Symptoms of Overdose
In instances when an overdose occurs, symptoms may include pain or swelling at the injection site as well as general signs, like fever or feeling unwell.
Recommended Management and Treatment
Dealing with an overdose requires providing care for symptoms and closely monitoring the individual's condition to ensure their well-being is maintained properly by healthcare providers, who should notify vaccine safety monitoring systems about incidents for assessment.
13. Handling Precautions for Healthcare Professionals
Proper Technique for Vaccine Preparation
Maintaining an environment is crucial when preparing Gardasil for use. Making sure the vaccine is well mixed and devoid of any particles before it is administered is essential for its effectiveness.
Avoiding Cross-contamination in Clinical Settings
To avoid spreading infections it's important to use syringes and needles each time and properly dispose of them after use to reduce the risk of hospital acquired infections.
Documentation and Reporting of Adverse Events
Thoroughly documenting the administration of vaccines, with details such as batch numbers and injection locations is crucial, for monitoring and addressing any reactions that may occur after vaccination.
14. Off-label Uses and Emerging Applications
Research on Broader HPV Type Coverage
Cutting edge research is delving into the possibility of Gardasil being effective, against more HPV strains that are not currently included in existing vaccines potentially broadening its range.
Investigational Uses for Non-cancerous HPV-Related Conditions
New uses are being explored, such as stopping recurring papillomatosis and other harmless HPV related issues with results showing positive prospects.
Global Impact and Expanded Recommendations
Gardasil's integration into global immunization programs has significantly reduced HPV prevalence. Expanding access in low-resource settings remains a critical goal to ensure equitable healthcare outcomes worldwide.
Gardasil Pre-filled Injection FAQ
- Where to give gardasil injection?
- What is gardasil 9 injection?
- What is gardasil injection used for?
- What is gardasil injection?
- How to give gardasil injection?
- What is the protocol for Gardasil injections?
- How many shots of Gardasil are needed?
- What is the route of injection for Gardasil?
- Where does the Gardasil shot go?
- Do I need 3 doses of Gardasil?
- Does Gardasil need to be refrigerated?
- Can I eat before the HPV vaccine?
- How long does Gardasil last?
- Where to give gardasil injection?
- What is gardasil 9 injection?
- What is gardasil injection used for?
- What is gardasil injection?
- How to give gardasil injection?
- What is the protocol for Gardasil injections?
- How many shots of Gardasil are needed?
- What is the route of injection for Gardasil?
- Where does the Gardasil shot go?
- Do I need 3 doses of Gardasil?
- Does Gardasil need to be refrigerated?
- Can I eat before the HPV vaccine?
- How long does Gardasil last?
Where to give gardasil injection?
The HPV vaccines are typically given as shots in either the arm or thigh area, specifically the outer part of the thigh or the deltoid muscle in the upper arm.
What is gardasil 9 injection?
The GARDASIL 9 vaccine offers protection to people aged 9 to 45 from illnesses caused by nine strains of HPV, including cancer and genital warts, in both men and women, as well as anal cancer and specific head and neck cancers, like throat and mouth cancers in females.
What is gardasil injection used for?
To reduce the risk of cancers, like cancer and others caused by HPV infection that affects various body parts including the head and neck region as well as anal and vaginal areas
What is gardasil injection?
The Gardasil vaccine helps prevent illnesses caused by the papillomavirus (HPB).
How to give gardasil injection?
Administer GARDASIL by injecting it into the area of the arm or the outer part of the thigh, slightly higher up.
What is the protocol for Gardasil injections?
The HPV vaccine is given in two doses (first dose followed by a dose 6 to 12 months later) for individuals starting the vaccination between the ages of 9 and 14 years old. For individuals starting the vaccination between the ages of 15 and 45 years old, as for those with weakened immune systems, the HPV vaccine is administered in three doses (first dose followed by a second dose 1 to 2 months later and a third dose 6 months after the first).
How many shots of Gardasil are needed?
Teens and young adults aged 15 to 26 who begin the HPV vaccine series are advised to get three doses over a schedule of 0 months followed by 1–2 months. Then, at 6 months, the same recommendation applies to those who are immunocompromised.
What is the route of injection for Gardasil?
Intramuscular injection
Where does the Gardasil shot go?
Administer the injection either in the muscle of the arm or in the outer area of the thigh.
Do I need 3 doses of Gardasil?
Your healthcare provider or pharmacist may suggest a regimen of three shots for individuals between the ages of 15 and 45.
Does Gardasil need to be refrigerated?
Correct storage and handling of vaccines are crucial for safeguarding individuals and communities against diseases that can be prevented by vaccines. Store them in the fridge at temperatures between 2 and 8 degrees Celsius (36 to 46 degrees Fahrenheit). Avoid freezing them, and dispose of any vaccine that has been frozen.
Can I eat before the HPV vaccine?
You're free to consume anything you desire without any limitations, including alcohol.
How long does Gardasil last?
Gardasil has been shown to protect against HPV strains for a minimum of 10 years (18). Cervarix offers protection for up to 11 years (17), while Gardasil 9 provides protection for 6 years (19).
Where to give gardasil injection?
The HPV vaccines are typically given through a shot into the muscle, in the arm or the front area of the thigh.
What is gardasil 9 injection?
The GARDASIL 9 vaccine protects people aged 9 to 45 against diseases caused by nine types of HPV, including cancer in women. Also, it helps prevent vaginal and vulvar cancers in females and anal cancer as well as certain head and neck cancers like throat and mouth cancers in addition to genital warts, in both men and women.
What is gardasil injection used for?
To reduce the risk of developing cancers linked to HPV, like cancer and others in the genital and head or neck areas, it is advisable to consider getting the Gardasil 9 vaccine.
What is gardasil injection?
The Gardasil vaccine shields against illnesses triggered by the papillomavirus (HP V).
How to give gardasil injection?
Administer the Gardasil vaccine into the muscle in the arm or the front of the thigh for effectiveness.
What is the protocol for Gardasil injections?
The HPV vaccine is given in two doses over a period of 6 to 12 months for individuals starting the vaccination between ages 9 and 14 or in three doses over a period of 1 to 6 months for those starting between ages 15 and 45 or who are immunocompromised.
How many shots of Gardasil are needed?
It is advisable for teenagers and young adults aged 15 to 26 who begin the HPV vaccination series and individuals with compromised systems to receive three doses of the vaccine at intervals of 0 months for the first dose and 1–6 months for the subsequent doses.
What is the route of injection for Gardasil?
Intramuscular injection
Where does the Gardasil shot go?
Administer the injection into the muscle of the shoulder or the front outer area of the thigh.
Do I need 3 doses of Gardasil?
Three doses are recommended by your healthcare provider or pharmacist for individuals between the ages of 15 and 45.
Does Gardasil need to be refrigerated?
Ensuring that vaccines are stored and handled correctly is crucial for safeguarding the health of individuals and communities against diseases.The recommended storage temperature is between 2 and 8°C (36 to 46°F), with a caution against freezing the vaccine and a reminder to discard it in case of freezing.
Can I eat before the HPV vaccine?
There are no dietary restrictions.
How long does Gardasil last?
As of now, Gardasil has been shown to provide protection against infections caused by HPV types for a minimum of 10 years (18), while Cervarix offers protection for up to 11 years (17), and Gardasil 9 provides at least 6 years of protection (19).