Losartan
- I. Introduction to Losartan
- II. Composition and Characteristics of Losartan
- III. The Mechanism: How Losartan Works
- IV. Approved Uses of Losartan
- V. Off-label Uses of Losartan
- VI. Dosage and Administration of Losartan
- VII. Potential Side Effects of Losartan
- VIII. Drug Interactions with Losartan
- IX. Contraindications and Warnings associated with Losartan
- X. Administration of Losartan in Special Populations
- XI. Handling an Overdose of Losartan
- XII. Important Precautions When Using Losartan
- XIII. Proper Storage of Losartan
- XIV. The Careful Administration of Losartan
I. Introduction to Losartan
A. What is Losartan?
A vital asset in the treatment and management of different cardiovascular ailments. Losartan is an antihypertensive drug categorized under angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). Its outstanding efficacy and safety track record have solidified its place as a staple medication globally. It is gaining widespread recognition within the medical community.
B. Brief History and Development of Losartan
During the late 20th century, Losartan's journey toward development took shape through a dedicated research initiative centered on improving cardiovascular health. After being subjected to rigorous clinical trials spanning several years, it gained FDA approval in 1995 as the inaugural ARB authorized for public use. This marked a significant milestone within the realm of cardiovascular therapeutics.
C. Purpose and Significance of Losartan in Medical Practice
Losartan's primary utility stems from its capacity to successfully manage hypertension, representing an alarming global health crisis affecting a significant segment of adults globally. Additionally, it plays an instrumental role in mitigating diabetic nephropathy while also reducing stroke risk among patients with left ventricular hypertrophy. This exceptional versatility greatly enhances Losartan's widespread application and paramount clinical importance.
II. Composition and Characteristics of Losartan
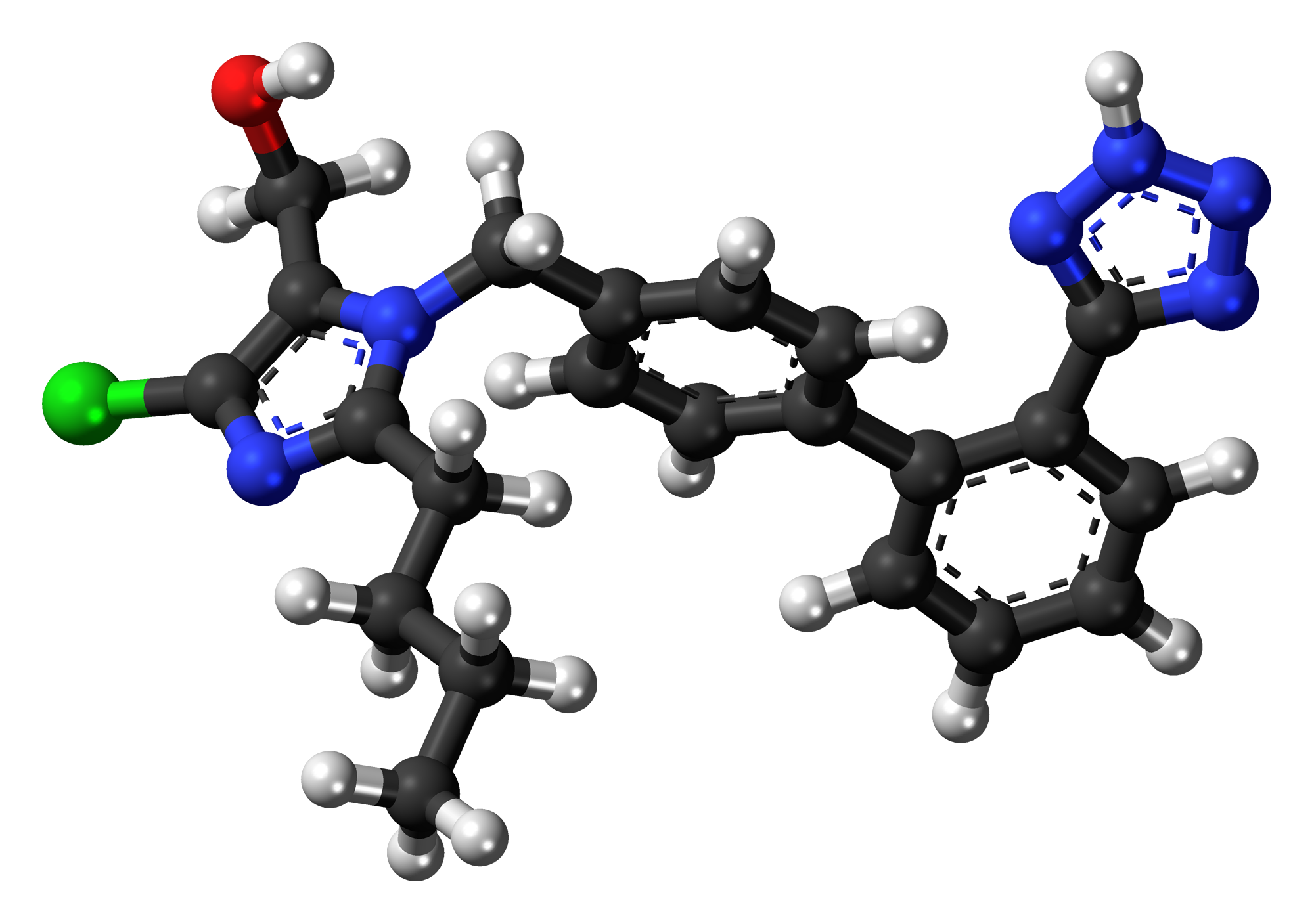
A. Chemical Structure and Properties
Losartan, with its active ingredient being losartan potassium, is a nonpeptide molecule containing a carboxylic acid functional group. Unlike other ARBs, this molecular structure gives it distinct pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties, which ultimately contribute to its therapeutic benefits.
B. Pharmaceutical Formulations
Losartan is readily available as oral tablets, which come in various strengths. Ranging from 25 mg to 100 mg. It is important to note that these dosage options are determined by the amount of losartan potassium, the active ingredient, in the medication.
C. Different Brand Names
Although Losartan is the medication's generic name, it is widely available under different brand names worldwide. Some examples of these brand names include Cozaar, Losacar, and Repace. These variations provide patients with various options to obtain this valuable drug.
III. The Mechanism: How Losartan Works
A. General Mechanism of Action
As an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB), Losartan works by preventing the attachment of angiotensin II to its receptor (AT1) found on the surface of different cells in the body. This disruption interferes with a chain of biochemical processes. It leads to a decrease in blood pressure and provides several positive effects on the cardiovascular system.
B. Impact on Renin-Angiotensin System
The Renin Angiotensin System (RAS) acts as an intricate hormone system that holds significant influence over blood pressure regulation and fluid balance. By inhibiting angiotensin II losartan skillfully interferes with the normal functioning of the RAS, resulting in vasodilation and decreased circulating blood volume.
C. Role in Vasodilation and Blood Pressure Regulation
Losartan works by blocking the angiotensin II receptors, which helps to prevent the vasoconstrictive effects of angiotensin II. This, in turn, leads to vasodilation or the widening of blood vessels. The result is a reduction in blood pressure and a decrease in the workload on the heart, ultimately promoting cardiovascular health.
IV. Approved Uses of Losartan
A. Losartan for Hypertension
Losartan is an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) used to treat hypertension. It works by blocking a substance in the body that causes blood vessels to tighten. Lowering blood pressure may reduce the risk of strokes and heart attacks1. Losartan is also used to decrease the risk of stroke in patients with high blood pressure and enlargement of the heart1. It is also used to treat kidney problems in patients with type 2 diabetes and a history of hypertension1.
The efficacy of Losartan in managing hypertension is well established. Its primary role is to inhibit the angiotensin II receptor, which prevents the constriction of blood vessels and ultimately decreases systemic blood pressure. By doing so, Losartan helps reduce the risk of stroke and heart attack, commonly associated with sustained hypertension. Consequently, individuals who take Losartan can expect an enhanced quality of life1.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Losartan:
B. Use in Heart Failure
Losartan is used alone or with other medicines to treat high blood pressure (hypertension). High blood pressure adds to the workload of the heart and arteries. If it continues long, the heart and arteries may not function properly1. Losartan is effective in treating patients with heart failure. This medication helps to decrease the stress on the heart during pumping, ultimately leading to a decrease in the overall workload of the heart. As a result, it plays a vital role in ensuring that the heart can maintain an optimal output and effectively manage symptoms associated with heart failure. Moreover, Losartan has also positively impacted life expectancy for individuals suffering from this condition23.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Losartan:
C. Losartan in Protecting Kidney from Diabetes Complications
Nephropathy is a debilitating complication often encountered by individuals living with diabetes. This complication targets explicitly and damages the vital filtering units within the kidneys. Thankfully, there is hope through Losartan as it serves a vital role against this condition. By mitigating proteinuria, which acts as a significant risk factor for causing renal damage, Losartan helps slow down the progression of nephropathy. Ultimately, its usage holds the potential for preserving renal function among those with diabetes12.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Losartan:
V. Off-label Uses of Losartan
A. Losartan in Migraine Management
Though not its primary application, Losartan has shown promise in managing migraines effectively1. However, the exact scientific mechanisms at play are still not fully graspable; nonetheless, there exists a belief that this medication's ability to dilate blood vessels could potentially alleviate migraine symptoms2. Ongoing research endeavors aim at uncovering and utilizing the full therapeutic potential of Losartan within this domain3.
References
- Losartan for the treatment of migraine in hypertensive subjects - PubMed
- Potential role of angiotensin receptor blockers in the treatment of migraine - PubMed
- The role of angiotensin II in migraine: pre-clinical and clinical studies - PubMed
B. Role in Marfan Syndrome
The presence of Marfan Syndrome entails structural deviations in connective tissue and often results in the development of aortic dilation and dissection. Within this realm, Losartan has emerged as an essential therapeutic intervention option. Its ability to inhibit TGF beta—a substance that contributes to weakened blood vessels—may significantly reduce the risk of severe consequences for individuals affected by Marfan syndrome12.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Losartan:
C. Emerging Off-label Uses: Current Research and Perspectives
Losartan’s therapeutic potential goes beyond its traditional uses and off-label indications. Preliminary studies indicate potential advantages in conditions such as fibrosis and specific forms of cancer. Additionally, researchers are investigating Losartan’s role in addressing lung damage associated with COVID-19123.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Losartan:
VI. Dosage and Administration of Losartan
A. Standard Dosage Guidelines
Oral administration remains customary for Losartan usage. To cater specially for hypertensive conditions occurring within adult patients specifically requires initiating treatment with an initial once-a-day dosage amounting to approximately 50 mg initially prescribed within this context of hypertension management indications mandated as such within medical advisories. Dosage adjustments may be made progressively based on observed patient blood pressure responses up to a systemic maximal daily dosage of 100 mg. However, when patients present with comorbid diabetic kidney disease, medical recommendations maintain an ordered treatment plan involving unchanged standardized daily Losartan doses of 100mg, which only deviate following professional practitioners' discretion upon carefully appraising and assessing individually characteristic patient therapeutic responses engendered by the imposed treatment courses rendered.
B. Dose Adjustments in Special Situations
Dosage adjustments may be necessary for special situations. It is advisable to prescribe an initial lower dose for patients with hepatic impairment due to changes in drug metabolism. Likewise, In elderly patients and individuals with renal impairment. Adjusting the dosage to avoid any potential adverse effects cautiously is essential.
C. Administration Instructions for Optimal Absorption
You may take Losartan with or without food. To maintain stable plasma levels, taking the medication consistently, typically in the morning or evening, is recommended. However, for the best effect, it should be taken as instructed by your healthcare provider.
VII. Potential Side Effects of Losartan

A. Common Side Effects: Identification and Management
Commonly experienced Losartan side effects may include dizziness, fatigue, and nasal congestion. It is important to note that these effects are temporary and typically fade as the body becomes accustomed to the medication. However, in cases where these side effects persist or result in discomfort, it is advisable to seek medical guidance.
B. Less Common but Serious Side Effects
Serious side effects, although less frequent, are worth mentioning. They encompass a decrease in the blood cell count, kidney issues, and severe allergic reactions. If any indications of these arise such as unexplained fatigue, alterations in urine output or swelling of the face or throat seeking immediate medical attention is imperative.
C. Recognizing Allergic Reactions
Although uncommonly reported, it should be acknowledged that there exists a possibility of developing allergic reactions toward Losartan. Such reactions may include symptoms like rash, itching, severe dizziness, and respiratory distress. If you suspect an allergic reaction transpiring while consuming this medication, it is crucial to cease its usage immediately and ensure that urgent medical assistance is sought without delay.
VIII. Drug Interactions with Losartan
A. Commonly Interacting Drugs and Substances
There are several medications, such as potassium-sparing diuretics, lithium, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). And certain antiviral drugs, which can interact with losartan. It is important to note that alcohol and tobacco can also hurt the efficacy of this medication.
B. Potential Impact of Interactions
Interactions with other substances can either strengthen or weaken the effectiveness of Losartan. They result in uncontrolled blood pressure or heightened side effects. There have been instances where these interactions have caused severe clinical conditions, including renal impairment.
C. Proactive Measures to Avoid Harmful Interactions
To avoid any harmful interactions, it is crucial to provide the healthcare provider with all details about your current medications, over-the-counter products, and lifestyle habits by regularly monitoring and conducting laboratory tests. We can effectively track the drug's effectiveness and identify any complications that may arise from interactions in their early stages.
IX. Contraindications and Warnings associated with Losartan
A. Absolute Contraindications
Patients with a confirmed sensitivity to Losartan or any of its ingredients should not use this drug. It is also essential for individuals with severe liver dysfunction to avoid taking this medication, as increased plasma concentrations may intensify undesirable side effects.
B. Relative Contraindications and Precautionary Measures
To ensure patient safety and well-being, it is advisable to exercise caution when prescribing Losartan for individuals with relative contraindications like renal dysfunction and heart failure or those undergoing renal dialysis. Likewise, patients suffering from bilateral renal artery stenosis or stenosis of the artery leading to a solitary functioning kidney should also approach the use of Losartan attentively. Close monitoring of their renal function is strongly advised in such scenarios.
C. Understanding the Black Box Warning
The use of Losartan is accompanied by a severe warning called a black box warning due to its potential harm to unborn babies. This warning states explicitly that drugs that affect the renin-angiotensin system, such as Losartan, have the potential to cause harm and even death to developing fetuses when used during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. Therefore it is highly recommended that Losartan be immediately stopped upon pregnancy detection.
X. Administration of Losartan in Special Populations
A. Usage in Elderly Patients
It is safe and prudent to prescribe Losartan to elderly patients. Though, starting with a lower dose is recommended due to their increased vulnerability to its hypotensive effects. To ensure the utmost care close monitoring of renal function and electrolyte balance should be diligently carried out for this demographic.
B. Losartan in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Risks and Recommendations
As previously indicated, there is potential fetal harm with Losartan, which should be discontinued if pregnancy is detected. However, whether Losartan passes into human milk for nursing mothers is uncertain. Careful consideration must be given to the possible adverse effects on the nursing infant. This necessitates deciding between discontinuing breastfeeding or discontinuing the medicine.
C. Pediatric Use: Safety and Dosing
Losartan has been approved to address hypertension in pediatric patients aged six years and older. It is essential to exercise caution when considering its administration in children with a glomerular filtration rate below 30 ml/min/1.73 m2, as it is not advised. Furthermore, individualized dosage adjustments should be made based on the child's weight and response to therapy.
XI. Handling an Overdose of Losartan
A. Identifying Signs of Overdosage
Symptoms of an overdose might encompass hypotension, tachycardia, and palpitations. In more severe cases, one might experience acute renal failure and lethargy.
B. Immediate Steps and Treatment Approaches
If an overdose occurs, it is crucial to closely monitor the patient and offer symptomatic and supportive treatment. During the initial period after ingestion. Procedures such as gastric lavage and the use of activated charcoal may be helpful.
C. Preventing Future Overdose Events
Educating patients about adhering diligently to prescribed dosages and acknowledging the potential perils related to overdose is a necessary measure in preventing future instances of this nature. Additionally, conducting regular follow-up visits and providing attentive surveillance further fortify efforts to prevent these unfortunate occurrences.
XII. Important Precautions When Using Losartan
A. Monitoring Blood Pressure and Kidney Function
Regular blood pressure and kidney function monitoring is of utmost importance when utilizing Losartan. In certain instances, the medication can excessively reduce blood pressure. It results in hypotension. Additionally, it is advisable to conduct regular blood tests to assess kidney function, especially in individuals with pre-existing renal conditions.
B. Lifestyle Changes to Enhance Treatment Efficacy
Making healthy lifestyle choices can significantly enhance the benefits of taking Losartan. These choices encompass maintaining a well-balanced diet low in salt—engaging in regular physical activity. Avoiding smoking. Limiting alcohol consumption and and utilizing stress management techniques. Incorporating these changes into your daily routine can effectively regulate your blood pressure and enhance your overall cardiovascular health.
C. Adherence to Medication and Regular Checkups
It is imperative to follow the recommended Losartan dosage and attend regular checkups to ensure that the drug works effectively and to monitor any potential side effects. Stopping the medication abruptly or missing doses can result in uncontrolled blood pressure and possible complications.
XIII. Proper Storage of Losartan
A. Ideal Storage Conditions
To ensure the optimal storage conditions for Losartan, keeping it in a location with room temperature is advisable. It is essential to protect the medication from both light and moisture. Therefore, storing it away from areas with high humidity, like bathrooms is recommended. Additionally, maintaining the medication in its original packaging until the time comes to consume it will aid in safeguarding it from any potential harm caused by light and moisture.
B. Guidelines for Disposal of Expired Medication
It is essential to dispose of expired or no longer properly needed Losartan. Flushing it down the toilet or pouring it into a drain is not recommended. To ensure safe disposal, it is advised to consult a pharmacist or local waste disposal company for guidance on appropriate disposal methods.
C. Ensuring Safety and Potency of Stored Medicine
It is important to store Losartan where it cannot be accessed by children and pets. Additionally, it is crucial to refrain from using the medication after its expiry date, as this can lead to decreased effectiveness and potential harm. Before administering the medication, it is advisable to always examine its appearance, including color, shape, and size. Any noticeable alterations in these aspects may indicate an issue that should be addressed.
XIV. The Careful Administration of Losartan
A. Patient Education for Safe Administration
It is crucial to provide patients with adequate education regarding the significance of adhering to the prescribed dosage of Losartan and informing them about potential side effects, appropriate actions in case of an overdose, and the indispensability of regular monitoring. Additionally, it is imperative to encourage patients to openly discuss any concerns or inquiries they may have with their healthcare provider.
B. The Role of Healthcare Providers in Ensuring Proper Use
It is of utmost importance that healthcare providers contribute significantly to promoting the safe utilization of Losartan. To accomplish this, they should provide thorough education, regularly evaluate treatment effectiveness, make necessary adjustments to dosages, and promptly and effectively address any patient concerns or queries.
Healthcare providers should address difficulties in medication administration, such as swallowing tablets. Alternatives or solutions like splitting the tablets or using a pill dispenser can be discussed. It is important to remember that Losartan should not be taken with meals high in potassium to avoid increasing the risk of hyperkalemia.