Nebivolol
- I. Introduction to Nebivolol
- II. Understanding How Nebivolol Works
- III. Primary Uses of Nebivolol
- IV. Off-Label Uses of Nebivolol
- V. Nebivolol Composition and Formulation
- VI. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- VII. Potential Drug Interactions with Nebivolol
- VIII. Side Effects Associated with Nebivolol
- IX. Warnings and Contraindications for Nebivolol Use
- X. Specific Precautions and Careful Administration
- XI. Administration to Specific Populations
- XII. Handling an Overdose of Nebivolol
- XIII. Important Precautions When Handling Nebivolol
I. Introduction to Nebivolol
A. Brief Overview of Nebivolol
Nebivolol, a member of the third-generation beta-blocker group of medications, has gained significant recognition in the field of medicine due to its unique characteristics. This powerful compound, primarily utilized for treating blood pressure and heart failure, shows exceptional selectivity for beta1 adrenergic receptors making it a preferred choice among healthcare professionals.
With its ability to dilate blood vessels and block receptors, nebivolol offers a distinct mechanism of action that expands its potential applications and enhances its reputation in cardiovascular medicine. The drug's effectiveness in mitigating the impacts of heart conditions has resulted in its widespread usage and acknowledgment.
Hypertension symptoms
B. Key Characteristics of the Drug
Nebivolol stands out among beta-blockers due to its distinct characteristics;
- Selectivity; Nebivolol has an affinity for beta1 adrenergic receptors, specifically targeting them. This means it mainly affects the heart's function while having an impact on other systems regulated by beta2 adrenergic receptors.
- Vasodilatory Properties; Unlike beta blockers, Nebivolol has an interesting effect of widening blood vessels, known as vasodilation. This unique feature is primarily attributed to its ability to stimulate the release of nitric oxide from the endothelium, which acts as a vasodilator.
- Effect; Beyond its primary role in lowering blood pressure, nebivolol is recognized for its ability to protect the heart. It reduces the workload on the heart. Enhances its efficiency making it an important agent in managing various heart conditions.
II. Understanding How Nebivolol Works
A. Mechanism of Action
Nebivolol is a medication that selectively blocks adrenergic receptors in the heart, lessening the impact of adrenaline and noradrenaline. This leads to a decrease in heart rate, myocardial contractility, and ultimately a reduction in output.
In addition, to these effects of beta-blockers, nebivolol also has an interesting mechanism of action. It activates the endothelium, which's the inner lining of blood vessels, to produce and release more nitric oxide. Nitric oxide then signals the muscle cells in the walls of blood vessels to relax, resulting in vasodilation.
B. The Role of Nebivolol in Regulating Blood Pressure
Nebivolol plays a role in controlling blood pressure. It achieves this by blocking the beta1 receptors in the heart, which leads to a reduction in the heart pumping strength and output. Additionally, it helps lower blood pressure by widening the blood vessels, thereby reducing vascular resistance. This combined effect results in a decrease in blood pressure levels.
Moreover, nebivolol's unique ability to enhance blood flow throughout the body through oxide-mediated vasodilation is particularly beneficial for managing hypertension, especially in patients with underlying conditions like diabetes or atherosclerosis, where optimal blood flow is essential.
III. Primary Uses of Nebivolol
A. Approved Uses in Hypertension
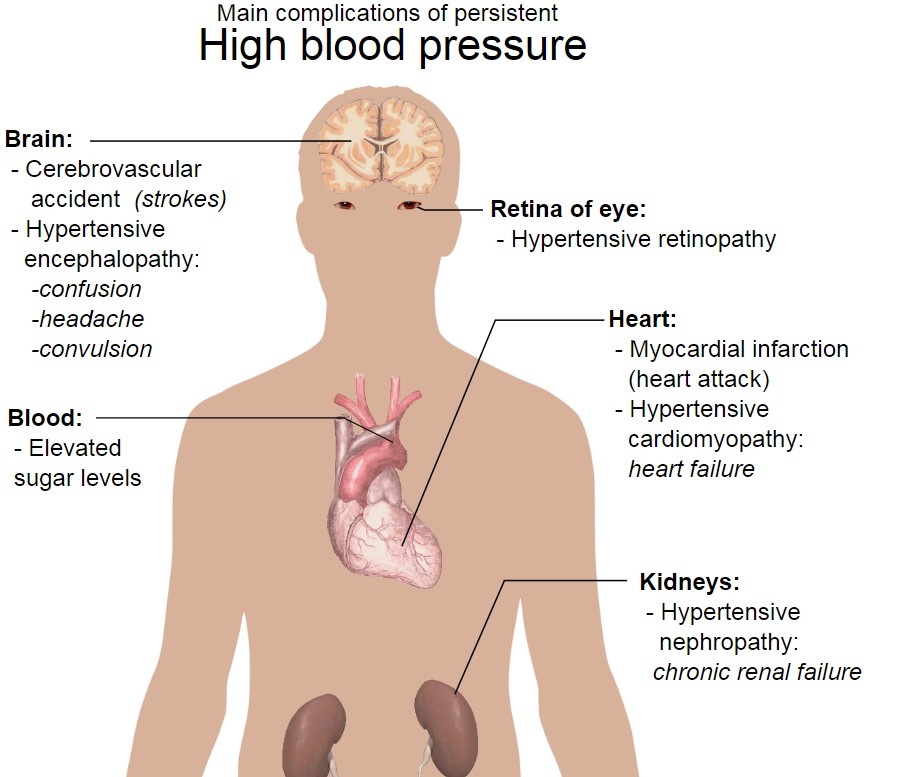
Nebivolol is mostly used for treating hypertension(1), which's a common condition in today's world. It has the ability to counteract the negative effects of excessive activation of the sympathetic nervous system effectively reducing both systolic and diastolic blood pressure in people with hypertension.(2)
The effectiveness of nebivolol in treating hypertension is based on its dual action mechanism; blocking beta1 receptors(3) and promoting vasodilation through nitric oxide. By doing it lowers cardiac output and decreases peripheral vascular resistance, which are key factors influencing blood pressure.
As a result, nebivolol helps bring these parameters to normal levels significantly reducing the risk of complications associated with high blood pressure such, as stroke or heart attack.(4)
1. GoodRx - What is Nebivolol (Bystolic)?
2. National Library of Medicine - Nebivolol in the management of essential hypertension: a review
3. PubMed Central - Nebivolol (Bystolic), a Novel Beta Blocker for Hypertension
4. PubMed Central - Efficacy and safety of nebivolol in hypertensive patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
B. Effects on Heart Failure
Heart failure is a condition where the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. Nebivolol, an effective medication, is commonly used in managing heart failure. It helps reduce symptoms and improves the quality of life for patients with this condition.
- One important benefit of nebivolol is that it eases the workload on the heart by slowing down its rate and reducing its contractility through its beta1-blocking properties. This is particularly helpful in cases of heart failure where the heart's ability to function optimally is already compromised.
- Nebivolol also has an effect on blood vessels, causing them to dilate. This vasodilation helps alleviate symptoms by lowering vascular resistance allowing the heart to pump blood more efficiently. As a result, it can potentially improve status and symptomatology in patients with heart failure.
- Additionally, nebivolol shows promise in protecting against damage caused by heart failure. While scientists are still investigating the mechanism behind this cardioprotective effect, it may involve positive effects on ventricular remodeling and endothelial function.
However, it's important to remember that proper guidance and supervision from a healthcare provider are crucial when using nebivolol for hypertension or heart failure treatment.
IV. Off-Label Uses of Nebivolol
A. Treatment of Anxiety Disorders
Nebivolol is primarily used in medicine but has potential applications beyond that. One emerging use of nebivolol, even though not officially approved, is in the treatment of anxiety disorders. Anxiety disorders involve fear and nervousness, often associated with an overactive sympathetic system. Nebivolol helps counter this overactivity by blocking adrenergic receptors, which help regulate the body's response to stress.(1)
By reducing symptoms like heartbeat and tremors that are commonly linked to anxiety, nebivolol may help alleviate the feeling of apprehension experienced by individuals with anxiety disorders. However, it's important to note that using nebivolol for off-label purposes should be done under medical supervision. Further research is still needed to understand the role of nebivolol in managing anxiety at this time.
1. PubMed Central - A Review of Nebivolol Pharmacology and Clinical Evidence

Anxiety-Disorders
B. Applications in Migraine Prophylaxis
Nebivolol has been studied for its potential to prevent migraines, a condition characterized by recurring episodes of severe headaches, often on one side. The cause of migraines is complex; it involves both vascular and neuronal dysfunction.
- Impact on Blood Vessels; Nebivolol's strong ability to widen blood vessels may explain its effectiveness in migraine prevention. Regulating the tone of blood vessels could potentially reduce the excessive reactivity observed in individuals experiencing migraines.
- Reducing Sympathetic Nervous System Activity; Migraines have also been linked to increased activity in the nervous system. As a blocker of beta1 receptors, nebivolol can help alleviate this heightened activity, which adds to its potential as a prophylactic treatment for managing migraines.
Although these findings offer promising insights into using nebivolol beyond its approved indications, it is important to interpret them. Further rigorous clinical trials are needed to establish the effectiveness and safety of nebivolol in treating anxiety disorders and preventing migraines.
V. Nebivolol Composition and Formulation
A. Active and Inactive Ingredients
The effectiveness relies on its main component, which is nebivolol hydrochloride. This substance gives the medication its properties by controlling the beta1 adrenergic receptor and promoting vasodilation through nitric oxide.
In addition to the ingredient, there are other components called excipients that are not medically active but are important for formulating the drug. Excipients in tablets can include microcrystalline cellulose, lactose monohydrate, starch, silica, magnesium stearate, and various colorants.
These excipients contribute to the stable absorption into the body and taste of the medication, effectively shaping how it works and how users experience it.
B. Available Forms and Strengths
Nebivolol is commonly found in the form of tablets, which are available in different strengths to suit various dosing needs. These tablets can be obtained in potencies like 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, and 20 mg, allowing for flexibility in dosage and making it easier to adjust the medication according to each patient's specific requirements.
VI. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
A. Standard Dosage Recommendations
The recommended dosage for nebivolol may differ depending on the condition being treated, how the patient responds to the medication, and their overall tolerance. Typically the initial dose for managing hypertension can be low as 5 mg taken once daily. Adjustments to the dosage are then made based on how the patient's blood pressure responds to the medication and their ability to tolerate it.
Hypertension
B. Dosage Adjustments and Special Considerations
Certain groups of patients might require adjustments in dosing or additional precautions. For example, individuals with kidney problems may need a lower starting dose, and their dosage should be carefully adjusted while being closely monitored. Similarly, it is important to exercise caution when prescribing nebivolol to patients or those with liver issues, as their ability to metabolize and eliminate the drug properly may be altered.
VII. Potential Drug Interactions with Nebivolol
A. Common Medications to Avoid
Like any medication, nebivolol can interact with drugs, which can result in unwanted effects. When taken alongside nebivolol, there are classes of medications that may influence its metabolism, effectiveness, or side effect characteristics. These classes encompass beta blockers, specific antiarrhythmics inhibitors of the cytochrome P450 enzyme system, and certain antidepressants.
B. Understanding the Risks of Drug Interactions
Interactions between drugs can affect how nebivolol works in our bodies, which may result in effective treatment or an increased risk of side effects. These interactions can potentially cause problems like a heartbeat, and low blood pressure, or worsen symptoms of heart failure.
That's why it's crucial to understand these interactions and ensure the safety and effectiveness of therapy. To avoid any drug interactions, it's important to openly discuss all medications you are taking with your healthcare provider, including over-the-counter drugs and dietary supplements.
It's also essential to follow your dosage carefully and seek immediate medical attention if you experience any negative reactions.
VIII. Side Effects Associated with Nebivolol
A. Common Side Effects to Anticipate
Although nebivolol is generally well tolerated, it can sometimes cause side effects. Fortunately, these side effects typically diminish as the body becomes accustomed to the medication. Some common adverse reactions linked to nebivolol include tiredness, lightheadedness, and headaches. Additionally, a few individuals may encounter a heart rate, feelings of nausea, or mild swelling, in their extremities.
B. Rare but Serious Side Effects
Though it is uncommon nebivolol can sometimes cause severe side effects. These can include bronchospasm, a decrease, in heart rate low blood pressure, and worsening of heart failure. Additionally, there have been reports of a serious skin reaction called Stevens-Johnson syndrome. If any of these side effects occur it is important to seek immediate medical attention.
IX. Warnings and Contraindications for Nebivolol Use
A. Situations When Nebivolol Should Be Avoided
In these circumstances, it is advisable to avoid the use of nebivolol. These situations include bradycardia, heart block beyond the first degree (without a pacemaker), cardiogenic shock, decompensated cardiac failure, sick sinus syndrome, and severe liver impairment. Moreover, patients with a hypersensitivity to the drug or any of its components should not be prescribed nebivolol.
B. Importance of Medical History in Prescribing Nebivolol
It is crucial for the clinician to have a knowledge of the patient's medical background when prescribing nebivolol. Conditions like asthma, bronchospastic diseases, diabetes, thyroid disorders, and peripheral vascular diseases should be taken into account as nebivolol may affect or worsen these conditions in cases.
X. Specific Precautions and Careful Administration
A. Monitoring Requirements during Treatment
It is essential to monitor patients undergoing nebivolol therapy. Regular checkups are necessary to assess their blood pressure, heart rate, kidney function, and any potential side effects. Patients should be advised to report any unusual symptoms or side effects they experience.
B. Adjustments for Liver and Kidney Disease
Patients who have liver or kidney diseases frequently experience changes in their ability to process and eliminate drugs. As a result, it is crucial to adjust the dosage of nebivolol and closely monitor these patients. When it comes to individuals with liver impairment, caution should be exercised when using this medication, and it may be necessary to start with a lower initial dose for those with severe renal impairment.
Healthcare providers need to educate patients about the risks and benefits associated with nebivolol therapy. Therefore any adjustments to medication should be supervised by a healthcare professional to ensure the safety of the patient.
XI. Administration to Specific Populations
A. Nebivolol in Elderly Patients
As people get older, their bodies go through changes that can affect how nebivolol works in their system. Because of this, it's important to start with a dose and gradually increase it in elderly patients to prevent a sudden drop in heart rate or blood pressure. It's also crucial to check their kidney function since it tends to decline as they age.
B. Use During Pregnancy and Nursing
Nebivolol should only be used during pregnancy if the benefits outweigh the risks to the baby. It is advisable to avoid taking nebivolol in the trimester and stop using it before the third trimester unless it is necessary to save the mother's life. Moreover, it is unclear whether nebivolol passes into breast milk. Therefore a decision should be made regarding whether to continue breastfeeding or discontinue taking the medication, considering its importance for the mother.
C. Considerations for Pediatric Patients
The use of nebivolol in patients is not recommended due to a lack of established safety and efficacy. Further comprehensive clinical studies are required to understand the potential benefits of using nebivolol in the pediatric context.
XII. Handling an Overdose of Nebivolol
A. Recognizing Symptoms of Overdosage
Taking much nebivolol can cause severe bradycardia, low blood pressure, bronchospasm, and heart failure. You may also experience symptoms such, as dizziness, difficulty breathing, and vomiting. It is important to recognize these signs in order to take prompt action and improve patient outcomes.
B. Immediate Steps and Treatment Approaches
If someone overdoses on nebivolol, it's crucial to stop taking the medication and provide the necessary support. For instance, healthcare professionals may consider using atropine, a beta2 agonist, or even a pacemaker to raise the heart rate.
Additionally, they may administer fluids and vasopressors to increase blood pressure. In some cases, cardiopulmonary resuscitation or mechanical ventilation might be necessary. It's unlikely that dialysis would effectively remove nebivolol from the body since the drug strongly binds to plasma proteins.
XIII. Important Precautions When Handling Nebivolol
A. Storage Conditions for Nebivolol
It is important to store Nebivolol tablets in a dry location preferably at room temperature. Avoid exposing the tablets to temperatures exceeding 30°C or storing them in areas with humidity like bathrooms or kitchens. Additionally, keep the medication out of the reach of children and pets to avoid ingestion.
B. Safe Handling and Disposal of Medication
When using tablets it's important not to crush or chew them. Instead, you should swallow the tablets with a good amount of water. It's also crucial to remember that if you have any expired medication it shouldn't be thrown in the regular trash or flushed down the toilet. The best course of action is to bring it to a pharmacy for proper disposal. This way we can prevent any harm to the environment. Avoid accidental ingestion, by people or animals.