Trospium Chloride
- What is Trospium Chloride
- Uses of Trospium Chloride
- How Trospium Chloride Works
- Composition of Trospium Chloride
- Dosage and Administration
- Side Effects of Trospium Chloride
- Interactions with Other Medications
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Administration to Special Populations
- Trospium Chloride Alternatives
- Overdosage
- Storage and Handling Precautions
- Discontinuation Effects
- Conclusion
What is Trospium Chloride
Overview of Trospium Chloride
Trospium Chloride, a type of ammonium compound, is well known for its effectiveness in treating overactive bladder (OAB). This medication works as an antimuscarinic, targeting receptors to ease detrusor muscle contractions. Individuals with symptoms like urination, urgency, and involuntary leakage benefit significantly from taking this medication. The treatment plan typically involves administration with carefully adjusted dosages to improve bladder control while minimizing adverse effects. Trospium chloride stands out for its lipophilicity, which limits its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and reduces the risk of side effects on the central nervous system commonly seen with anticholinergic medications.
History and Development
Trospium chloride origins can be traced back to the mid-20th century when there was a growing interest in creating targeted treatments for bladder issues. Pharmacologists led the research to find alternatives to atropine derivatives to reduce the side effects of existing therapies. After conducting a series of experiments and making chemical modifications, Trospium Chloride emerged as a promising option. Its development process included preclinical studies focusing on its effects and how it moves through the body. Clinical trials began in the 1980s, showcasing their effectiveness and safety. These collective efforts established Trospium Chloride as a player in treating overactive bladder conditions.
Trospium Chloride Drug Class
Trospium Chloride, a medication classified as an anticholinergic with properties, acts by blocking parasympathetic nerve signals to control smooth muscle movements in different body areas. Its unique feature is its effect on muscarinic receptors, especially in the bladder. Anticholinergics such as Trospium Chloride play a role in managing symptoms of an overactive bladder, like frequent urination, urgency, and leakage, by counteracting acetylcholine muscle contracting effects and easing bladder spasms.
One of its advantages is its limited ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, reducing the likelihood of central nervous system side effects often associated with similar medications. This makes it a preferred option for patients with such effects. Trospium Chloride is taken orally with consistent dosing for optimal therapeutic levels and can be affected by food intake; hence, it is best taken on an empty stomach.
Metabolism mainly occurs in the liver, and excretion through the kidneys underscores the importance of adjusting doses for patients with issues. Trospium Chloride is unique among medications because it explicitly targets bladder receptors, has a favorable side effect profile, and is effective in treating symptoms of overactive bladder. It is taken orally, affected by food intake, metabolized in the liver, and eliminated through the kidneys.
Uses of Trospium Chloride
Primary Uses
Trospium chloride is vital as a treatment option and is mainly recommended for its antimuscarinic effects. It is utilized to ease symptoms linked to bladder issues. This drug plays a role in managing conditions characterized by uncontrolled contractions of the bladder muscle, resulting in frequent and urgent urination. It proves helpful for people experiencing disruptions in normal urinary function, offering significant relief by targeting muscarinic receptors.
Treatment of Overactive Bladder (OAB)
OAB or Overactive Bladder is an issue where the bladder muscle contracts suddenly and involuntarily, causing a solid urge to urinate. Trospium Chloride is quite effective in treating OAB by preventing these contractions. Patients often notice a decrease in the frequency and severity of their symptoms, which helps them regain control over their bladder functions. This medication works by blocking the impact of acetylcholine on receptors, which helps relax the detrusor muscle and lessen spasms.
Reduction of Urinary Frequency and Urgency
A key indicator of OAB is the urgent urge to urinate, which can significantly disrupt a person's everyday routine. Trospium Chloride tackles these signs by regulating bladder muscle function and decreasing activity. As a result, patients' urination frequency decreases during both daytime and nighttime. This outcome enhances quality of life as patients experience fewer disruptions to their daily tasks and sleep patterns.
Management of Urge Incontinence
A sudden urge to urinate, known as urge incontinence, can be quite bothersome for those with bladder (OAB). Problems Trospium Chloride effectively treats this issue by stabilizing the bladder muscles and stopping contractions. This medication helps patients stay dry, minimizing the discomfort and disruption caused by leaks. Its capacity to improve bladder function makes it a beneficial choice for people dealing with this symptom.
Off-label Uses
Trospium Chloride is sometimes used for purposes not approved by the authorities, such as treating urological and non-urological conditions. Doctors consider using it in these cases based on their experience and new studies showing possible advantages in addressing bladder issues beyond its standard uses.
Potential Benefits in Spastic Bladder
People with conditions like spinal cord injury or multiple sclerosis often experience bladder, which can be alleviated with Trospium Chloride. This medication works by relaxing the bladder muscle, reducing spasms, and enhancing its storage capacity. Using Trospium Chloride for this purpose, though not its primary use offers a treatment option for individuals whose spastic bladder severely affects their life and overall well-being.
Use in Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity
Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity (NDO) is a condition where the bladder contracts involuntarily due to issues. Trospium chloride effectively treats NDO by reducing the frequency and intensity of these contractions. This treatment is especially beneficial for individuals with cord injuries or multiple sclerosis, as it helps enhance bladder control. By promoting bladder stability, Trospium Chloride aids in improving continence and lowering the chances of urinary tract infections, which are common among NDO patients.
How Trospium Chloride Works
Mechanism of Action
Trospium chloride works mainly by affecting muscarinic receptors. These receptors in the bladder are vital in controlling detrusor muscle movements. By blocking the M3 muscarinic receptors, Trospium Chloride hinders the function of acetylcholine, a key neurotransmitter, for activating bladder muscles. This blockage causes the detrusor muscle to relax, easing contractions that result in symptoms of overactive bladder (OAB) like urgency, frequency, and incontinence.
Pharmacodynamics
Trospium chloride pharmacodynamics showcase its effectiveness in treating bladder issues. Acting as an agent, it precisely targets muscarinic receptors, steering clear of nicotinic receptors to ensure focused therapeutic benefits. Its low lipophilicity restricts its passage through the blood-brain barrier, thus reducing the risk of central nervous system side effects commonly associated with other similar medications. This distinctive feature allows Trospium Chloride to offer a solution for managing bladder function, enhancing treatment effectiveness while upholding a favorable safety profile.
Pharmacokinetics
Trospium chloride's pharmacokinetic characteristics highlight its practicality and ease of use in settings. When taken orally, the medication has a bioavailability of around 10%, which, while relatively low, is adequate for its intended therapeutic purposes. It reaches peak levels in the bloodstream within 5 to 6 hours after being taken, providing symptom relief. The absorption of Trospium Chloride may be affected by food consumption and high-fat meals that can lower its bioavailability. As a result, it is generally recommended to take it on a stomach or at least one hour before eating. The drug is mainly eliminated unchanged through urine, with renal clearance playing a role in its removal from the body. This pharmacokinetic pattern requires dosage adjustments for individuals with kidney issues to prevent buildup and adverse effects.
Trospium Blood Brain Barrier
Trospium Chloride works by interacting with receptors, especially in the bladder. Unlike other anticholinergic medications, It cannot cross the blood-brain barrier. This feature helps decrease the chances of experiencing side effects of the nervous system (CNS), such as cognitive impairment, commonly seen with similar drugs. The hydrophilic nature of Trospium Chloride is a factor in its restricted penetration into the CNS, ensuring that its effects mainly target peripheral areas. This quality makes Trospium Chloride a preferred choice for patients at risk of CNS disturbances.
Trospium vs Oxybutynin
We can see some significant differences when we look at Trospium Chloride compared to Oxybutynin, another anticholinergic medication. Both drugs are designed to help with symptoms of bladder, but they vary in their side effects and how they work in the body. Oxybutynin is effective. It has a higher chance of causing side effects related to the central nervous system, like dizziness, confusion, and memory problems, because it can easily cross into the brain. Trospium Chloride doesn't penetrate the nervous system as much, so it tends to have fewer side effects, which is especially beneficial for older patients or those sensitive to such issues. While Oxybutynin comes in forms like immediate-release pills, extended-release tablets, and patches you put on your skin for different ways of taking it, Trospium Chloride stands out for its reliable effectiveness and lower risk of central side effects. This makes it an attractive option for people looking to balance efficacy and tolerability.
Trospium vs Myrbetriq
Trospium Chloride and Myrbetriq (mirabegron) offer two ways to treat overactive bladder. Myrbetriq relaxes the detrusor muscle during the bladder's storage phase, while Trospium Chloride acts as an agent. Myrbetriq has a side effect profile that avoids common issues like dry mouth and constipation associated with Trospium Chloride. However, it may raise blood pressure, so it might not be ideal for patients with hypertension. Trospium Chloride targets receptors with minimal impact on the central nervous system, making it a dependable option for those looking to reduce traditional anticholinergic side effects. The decision between these medications should consider the patient's health and specific symptoms, considering factors like different mechanisms of action and potential side effects based on individual health profiles.
Composition of Trospium Chloride
Active Ingredients
Trospium Chloride is a quaternary ammonium compound containing chloride as its primary active component. This compound is formulated to target the receptors in the bladder for its therapeutic effects. By binding to these receptors, trospium chloride hinders the action of acetylcholine, leading to a decrease in involuntary bladder contractions. The dosage forms are meticulously adjusted to balance effectiveness and minimize any side effects.
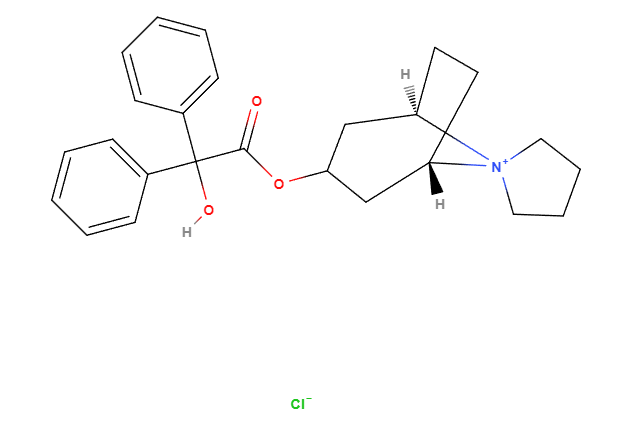
Inactive Ingredients
Trospium Chloride formulation also contains inactive ingredients crucial for maintaining the medication's stability, effectiveness, and patient friendliness. These additional components typically consist of:
- Cellulose: Used to fill and give strength to the tablet structure.
- Lactose monohydrate: Functions as a filler and aids in the tablet production process.
- Magnesium stearate: Acts as a lubricant to prevent components from sticking during manufacturing.
- Sodium starch glycolate: Works as a disintegrant, aiding in the tablet's breakdown for absorption in the gut.
- Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose: Employed in coating to enhance appearance and ease of swallowing.
- Gglycol: Improves solubility and dissolution speed of the active ingredient.
- Titanium dioxide: Imparts a white color to the tablet and is used in coating.
These inactive ingredients are thoughtfully selected to ensure that the medication is effective and well tolerated by patients.
Available Formulations
Trospium chloride comes in various types to meet patients' different preferences and requirements. The main options include:
- Immediate-release tablets: These are 20 mg in strength and are meant for quick absorption and fast action. They are typically taken twice a day.
- Extended-release capsules: Available in 60 mg strength, these capsules release the ingredient gradually, allowing for once-daily dosing. This type is convenient for patients looking for simplicity in their treatment routine.
- Liquid solution: This solution is suitable for patients who struggle with swallowing tablets or capsules. It offers flexibility in dosing and easy administration.
Each type aims to ensure that trospium chloride is delivered effectively for symptom relief. With these choices healthcare providers can customize treatment plans based on individual patient needs to improve overall therapeutic results.
Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosage for Adults
The usual suggested Trospium Chloride for grown-ups is 20 mg twice daily. This dosing schedule aims to uphold the therapeutic level of the medication in the blood, guaranteeing successful control of symptoms related to overactive bladder (OAB). In the case of extended-release versions, a popular dose is 60 mg consumed daily, ideally in the morning. This single daily intake enhances adherence and delivers consistent symptom relief all day.

Dosage Adjustments for Specific Populations
Adjusting the dosage of Trospium Chloride might be necessary for specific groups to ensure its effectiveness and safety. Customizing the dosage according to each patient's requirements is essential for maximizing treatment benefits while reducing side effects.
Elderly Patients
Elderly individuals may experience changes in how Trospium Chloride is processed in their bodies due to age-related adjustments. These alterations could involve reduced kidney function and changes in metabolizing the drug. As a result, it is advisable to take a careful approach, typically beginning treatment with lower doses. Regular monitoring is crucial to tune the dosage according to the patient's reaction and tolerance levels.
Patients with Renal Impairment
The removal of Trospium Chloride from the body dramatically affects kidney function. In individuals with kidney problems those with severe dysfunction (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min) the dosage should be modified to avoid excessive drug buildup and potential harm. For these patients, it is suggested that the dosage be decreased to 20 mg daily or even less based on the extent of the impairment. It is recommended that tests on kidney function be conducted to help determine any needed adjustments in dosage.
Administration Guidelines
Trospium Chloride is best taken when your stomach is empty one hour before eating or two hours after a meal. This recommendation helps the body absorb the medication effectively and ensures its availability. If you use the extended-release version, swallow the capsule whole without crushing, chewing, or splitting it to preserve its extended-release function.
Missed Dose Instructions
If someone forgets to take a dose of Trospium Chloride, they should take it as soon as they remember unless it's close to the time for the next dose. In that case, they should skip the missed dose and continue with their usual dosing routine. It's best not to take two doses to compensate for a missed one, as this could raise the chances of experiencing adverse reactions. Handling missed doses can ensure treatment consistency and reduce the likelihood of problems arising.
How Long Should Take Trospium Chloride
Following the schedule when taking Trospium Chloride is essential to achieving the best results. Typically, you'll need to take one tablet in the morning and one in the evening on an empty stomach. This helps ensure that the medication is absorbed effectively and works well. The length of time a person should use Trospium Chloride can vary based on how they respond to treatment and their specific health condition. For issues like overactive bladder, long-term use might be required.
- Patients should always follow their healthcare provider's guidance.
- Avoid stopping the medication suddenly without consulting a doctor.
- Regular checkups are necessary to assess the effectiveness of the treatment and adjust as needed.
How Long Does It Take for Trospium Chloride to Work
Trospium chloride may show varying onsets of action among individuals, with some patients noticing improvements in their symptoms within the initial week of treatment. However, the full therapeutic effects might take four to six weeks to become evident. This delay is attributed to the time needed for the medication to reach a concentration in the body and for physiological changes to occur. Initial improvements could be seen within a week. Full effects may take four to six weeks. Patients are advised to adhere to their treatment regimen even if immediate enhancements are not made.
Patience and consistency play roles in managing conditions like an overactive bladder. Sometimes, dosage adjustments might be required to enhance the therapeutic response. Healthcare providers might initiate treatment with a dose and gradually adjust it based on individual tolerance levels and clinical response. Trospium Chloride has been well-documented for its effectiveness in alleviating bladder symptoms; however, individual reactions can differ. Patients and healthcare providers must work closely together to customize the treatment plan according to each patient's needs, ensuring outcomes.
Side Effects of Trospium Chloride
Overview of Potential Side Effects
Although effective for treating the bladder, trospium chloride has various side effects that differ in intensity. Patients and healthcare providers must be aware of these adverse reactions to ensure the medication is used safely and effectively. The side effects may include commonly encountered symptoms and severe but rare conditions that demand prompt medical intervention.

Common Side Effects
Some common side effects of Trospium Chloride include:
- Feeling parched in the mouth
- Difficulty with bowel movements
- Head pain
These effects are usually not severe. They tend to lessen as the body gets used to the medicine. To ease these signs, patients are recommended to drink plenty of fluids and make changes to their diet.
Dry Mouth
One of the side effects that patients may experience when using Trospium Chloride is dry mouth, also known as xerostomia. This occurs due to the medication's effects, which can decrease saliva production. Although typically not dry, severe mouth can cause discomfort. Potentially lead to dental problems if it persists. To help manage this symptom, patients can try the following;
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water
- Chewing sugar gum
- Using artificial saliva products
Constipation
Constipation is a side effect linked to Trospium Chloride. The drug's antimuscarinic action can slow down motility, making it hard to have regular bowel movements. To deal with this issue, patients are advised to include
- Fiber in their diet,
- Drink plenty of water
- Stay active with regular exercise
In certain situations, over-the-counter laxatives might be suggested to ease the discomfort.
Headache
Using Trospium Chloride can lead to headaches as a side effect. The severity of these headaches may vary from mild to moderate and is usually temporary. If patients experience headaches, it is important for them to stay hydrated and consider using over-the-counter pain relievers after consulting with their healthcare provider.

Serious Side Effects
Sometimes, Trospium Chloride may lead to severe side effects requiring prompt medical care. These can include Swelling under the skin, allergic responses
Angioedema
Angioedema is marked by profound swelling under the skin, typically near the eyes and mouth and occasionally in the throat. This response can hinder breathing. It is viewed as a medical crisis. Individuals showing symptoms of angioedema should promptly seek assistance. Signs to be vigilant for consist of:
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue or throat
- Trouble breathin
- Swallowing
- Skin hives or rash
Severe Allergic Reactions
Serious allergic reactions, while rare, can happen with Trospium Chloride. Signs may involve:
- Skin rash Itchy
- Swollen skin ( on the face, tongue, or throat)
- Intense dizziness
- Difficulty breathing
Individuals experiencing any of these signs should stop taking the medication and promptly seek medical help. Recognizing these symptoms early and getting treatment for severe allergic reactions is important to avoid possible life-threatening issues.

Does Trospium Cause Weight Gain
While Trospium Chloride effectively treats bladder symptoms, it may lead to various side effects, but weight gain is not commonly reported. Most patients do not notice changes in their weight when taking this medication. However, it's essential to watch for any shifts in body weight and talk to your healthcare provider about them. Weight gain isn't a side effect. Stay vigilant for any surprising changes. Any fluctuations in weight that you observe could be due to lifestyle changes or other medications you are taking than Trospium Chloride itself. Maintaining a diet and regular exercise routine is recommended to help counteract any indirect impacts on your weight.

Does Trospium Cause Dementia
Anticholinergic medications like Trospium Chloride have been extensively studied for their impact on cognitive function. Unlike some anticholinergics, Trospium Chlorides' limited ability to cross the blood-brain barrier suggests a lower likelihood of causing central nervous system side effects such as dementia. Though concerns exist about the long-term use of anticholinergics and cognitive decline, current research does not definitively establish a link between Trospium Chloride and an elevated risk of dementia. It is advisable for patients and older individuals to openly discuss any worries and medical background with their healthcare provider. Regular cognitive evaluations can aid in identifying and addressing cognitive challenges early on. In summary, while the Trospium chloride side effect profile appears milder when compared to anticholinergic drugs, maintaining ongoing awareness and open communication with healthcare professionals is crucial for ensuring its safe and effective utilization.

Interactions with Other Medications
Drug-Drug Interactions
Trospium Chloride, like other medications, can interact with different drugs that might change how well it works or raise the chances of adverse effects. Knowing about these interactions is essential for getting the treatment results and keeping patients safe. Some meaningful drug interactions to watch out for are anticholinergic drugs, antihistamines, and various types of medications that could make side effects worse or reduce how well the treatment works.

Interaction with Anticholinergic Drugs
When Trospium Chloride is used with anticholinergic medications, the combined impact of anticholinergic effects can be significant. These interactions can increase the likelihood of experiencing side effects like mouth constipation, blurry vision, and difficulty urinating. Some common anticholinergic drugs that could lead to interactions include Atropine, Scopolamine, and oxybutynin. Healthcare providers must monitor patients closely for any heightened effects and consider adjusting dosages to manage potential risks.
Interaction with Antihistamines
First-generation antihistamines, like Diphenhydramine, Chlorpheniramine, and Promethazin, also have properties. When taken together with Trospium Chloride, there is a risk of experiencing additional side effects. This combination can worsen drowsiness, dry mouth, and other anticholinergic effects. It's important to caution patients against operating machinery or driving while using these medications in combination.
Food and Alcohol Interactions
Trospium Chloride absorption can be affected by food intake. High-fat meals, especially, reduce the drug's bioavailability. To enhance absorption, it's best to take Trospium Chloride on an empty stomach either an hour before or two hours after eating. This helps ensure drug absorption while maintaining its therapeutic benefits. Alcohol can worsen the nervous system side effects of Trospium Chloride, like drowsiness and dizziness. Patients are advised to limit or avoid alcohol while using this medication to prevent these effects.
Moreover, alcohol can heighten the risk of retention, potentially counteracting the advantages of Trospium Chloride in managing symptoms of an overactive bladder. In conclusion, though Trospium Chloride is effective for treating bladder issues, it's crucial to consider its interactions with other drugs and substances. By understanding these interactions, healthcare providers can make informed choices to optimize treatment and ensure patient safety.
Contraindications
Absolute Contraindications
Trospium Chloride should not be used in situations that could seriously harm your health. It's crucial to follow guidelines to avoid severe side effects or complications. These situations include an allergic reaction to Trospium Chloride and severe kidney problems.
Hypersensitivity to Trospium Chloride
People who are sensitive to Trospium Chloride or any of its ingredients should avoid taking this medication. Sensitivity reactions may appear as
- Skin rashes
- Persistent itching
- Allergic responses.
In case of such reactions, Immediate cessation of the medication and quick medical attention are required.
Severe Renal Impairment
Kidney problems are a major red flag when using Trospium Chloride. This medication mainly leaves the body through the kidneys. If your kidney function isn't working well, it can cause the drug to build up in your system, raising the chances of harmful effects. Signs of these effects could be feeling thirsty, Having trouble seeing clearly, or Feeling confused. If someone has a creatinine clearance below 30 mL/min, it's best to think about trying other treatment options.
Relative Contraindications
Certain conditions that are not contraindications may call for cautious evaluation and clinical assessment. While these situations do not completely forbid the utilization of Trospium Chloride they may require supervision and potential adjustments, to the dosage.
Pre-existing Gastrointestinal Conditions
Patients who have preexisting gastrointestinal conditions like severe ulcerative colitis, toxic megacolon, or obstructive gastrointestinal disorders need to be cautious when using Trospium Chloride. The anticholinergic effects of this medication can worsen these conditions, potentially leading to the following:
- Increased bowel obstruction
- Risk of paralytic ileus
- Aggravation of toxic megacolon
In such situations, it's crucial to carefully consider the benefits versus the risks of treatment and explore alternative therapies when appropriate. Understanding the contraindications associated with Trospium Chloride is vital for ensuring patient safety and optimizing treatment outcomes. Healthcare providers can make informed decisions by acknowledging absolute and relative contraindications to effectively manage risks and deliver quality care.
Warnings and Precautions
Important Precautions
When recommending Trospium Chloride, precautions must be taken to guarantee patient safety and treatment effectiveness. These measures help reduce dangers and improve the overall therapy process. Essential factors to consider include the chance of retention, the risk of heat-related issues in hot environments, and the necessity for cautious dosing in specific patient groups.

Risk of Urinary Retention
Although helpful in treating overactive bladder, trospium chloride's properties as an agent may also result in urinary retention. This condition, which is characterized by the inability to empty the bladder fully, can lead to discomfort and an increased risk of tract infections. Individuals at risk are those with existing bladder outflow issues or a tendency toward urinary retention. Signs to watch for include:
- Difficulty starting urination
- Urine Flow Feeling of not completely
- Emptying the bladder
Seeking prompt medical attention is crucial if there are concerns about urinary retention.
Heat Prostration in High-Temperature Environments
Patients prescribed Trospium Chloride must know the potential danger of heat prostration, especially in hot weather. This medication can reduce sweating, which raises the risk of heat-related conditions like heat exhaustion and heat stroke. Signs of heat prostration to watch out for include:
- Body temperature
- Heavy sweating followed by a sudden stop in sweating
- Feeling lightheaded and weak
Patients need to drink water avoid prolonged exposure, to extreme heat and seek immediate medical help if they notice any symptoms of heat prostration.
Careful Administration
Some patients must be given Trospium Chloride to prevent their health issues from worsening. This applies to individuals with neuropathy and those with liver problems.
Patients with Autonomic Neuropathy
Autonomic neuropathy has the potential to impact the nervous system, causing issues with different bodily functions. Individuals with this condition might experience changes in how they respond to Trospium Chloride, requiring observation and adjustments in dosage. Signs of neuropathy may consist of:
- Dizziness upon standing
- Delayed stomach emptying
- Problems with bladder control
It is crucial for healthcare professionals to closely monitor and adjust medication usage among individuals with this condition to ensure its safety and efficacy.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Trospium Chloride is mainly eliminated through the kidneys. Liver issues can affect how it is processed and removed from the body. It's essential to monitor patients with liver problems and make necessary changes to their dosage to avoid potential drug buildup and harmful effects. Symptoms of liver impairment may include:
- Jaundice
- High levels of liver enzymes
- Fatigue
- Weakness
It's advised that tests be conducted to monitor liver function for better treatment guidance and patient well-being.
Administration to Special Populations
Administration to Elderly
When giving Trospium Chloride to patients, it's essential to be cautious because their bodies change as they age. These changes can impact how their bodies process and get rid of the medication, making them more likely to experience effects. It's crucial to watch them and adjust the dosage based on their needs to make sure the treatment works well without causing harm.

Considerations for Age-Related Sensitivity
Elderly individuals frequently show heightened sensitivity to the effects, like experiencing dry mouth, constipation, and urinary retention. Furthermore, the decline in kidney function associated with aging can increase exposure to the medication throughout the body. To address these concerns:
- Begin treatment with the effective dose.
- Regularly monitor kidney function.
- Modify the dosage based on how well it is tolerated and the patient's response.
Healthcare professionals should also stay alert for any indications of decline since older patients are more prone to experiencing side effects that affect the central nervous system.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
The safety and effectiveness of Trospium Chloride when used during pregnancy and breastfeeding are factors to consider. Women and nursing mothers must thoroughly evaluate the risks and benefits before starting treatment.

Safety and Efficacy During Pregnancy
Trospium Chloride is classified as Pregnancy Category C. While animal studies have indicated impacts on the fetus, there is a lack of sufficient well-controlled research involving pregnant women. Hence, only utilize it if the expected advantages outweigh the risks to the fetus. Watch for any indications of fetal distress or developmental concerns. Expectant mothers should be educated about the risks and encouraged to promptly report any unusual symptoms they may experience.
Excretion in Breast Milk
It is unclear if Trospium Chloride is passed into breast milk. To safeguard nursing infants from harm, a choice must be made whether to halt breastfeeding or discontinue the medication, considering its significance to the mother. Suggestions involve having conversations with breastfeeding mothers about risks and keeping an eye on infants for any signs of effects if the medication is continued.
Administration to Children
The safety and effectiveness of Trospium Chloride in children is not firmly established. It is advised to use caution when considering its use in patients only if the advantages outweigh the potential risks.

Safety and Dosage Recommendations
In cases where information on how Trospium Chloride affects children is scarce, there are no set guidelines for the appropriate dosage. If considering the use of Trospium Chloride in patients:
- Begin with the smallest feasible dose.
- Modify the dosage according to how the patient responds to treatment and their ability to tolerate it.
- Watch for any adverse effects, especially those associated with anticholinergic activity.
Trospium Chloride Alternatives
Overview of Alternatives
Trospium Chloride is commonly prescribed to treat the bladder. Still, other options might better suit individual patients depending on their medical history, tolerance to side effects, and personal preferences. These alternatives encompass medications like anticholinergic agents, beta-3 adrenergic agonists, and nonpharmacological approaches.
Other Anticholinergic Agents
Other medications with anticholinergic properties can be used to manage an overactive bladder. Each medication has its benefits, side effects, and tolerance levels.
- Oxybutynin comes in forms such as tablets, extended-release tablets, and patches that are applied to the skin. While effective, it often causes dry mouth and constipation.
- Tolterodine is known for causing dry mouth compared to oxybutynin and is available in immediate and extended versions.
- Solifenacin allows for daily dosing and is usually better tolerated for dry mouth and constipation.
- Darifenacin targets the M3 receptor specifically, which might reduce the risk of side effects on the nervous system. These medications offer flexibility in treatment plans, enabling healthcare providers to customize approaches based on how patients respond to them and their ability to tolerate them.
Beta-3 Adrenergic Agonists
A new category of drugs called beta-3 agonists presents a different way to treat symptoms of an overactive bladder. Mirabegron, the widely recognized beta 3 adrenergic agonist, works by easing the detrusor muscle tension during the bladder's storage phase. It is especially helpful for individuals who cannot handle the side effects of anticholinergics. Typical adverse effects include high blood pressure and nasopharyngitis. These medications offer an alternative for patients who do not respond positively to anticholinergics or encounter side effects.
Non-Pharmacological Interventions
For individuals looking for alternatives to medication or those who face reactions from drug treatments, non-pharmacological methods may be explored.
- Behavioral therapies, such as bladder training, pelvic floor muscle exercises, and scheduled voiding, have shown effectiveness in managing bladder symptoms.
- Lifestyle adjustments, such as reducing fluid intake, eliminating bladder irritants (like caffeine and alcohol), and maintaining weight, can also help ease symptoms.
- Additionally, neuromodulation interventions such as nerve stimulation and percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation offer choices for patients with persistent symptoms. These approaches present integrated options that complement or even substitute pharmacological treatments in specific scenarios.
Combination Therapy
Sometimes a mix of medications and non medical treatments can be the best approach. Pairing anticholinergics with beta 3 agonists can work together to improve symptom management while reducing the need for high doses and potential side effects of each medication. Although Trospium Chloride is an option, other choices are available for treating overactive bladder. These options include anticholinergic drugs, beta-3 adrenergic agonists, and nonmedical interventions. This allows for customized treatment plans that cater to the needs and preferences of each patient.
Overdosage
Symptoms of Overdosage
An excessive intake of Trospium Chloride can lead to a range of symptoms mainly caused by its properties. It is vital to identify these symptoms for timely and efficient treatment. Some of the frequently noted signs include:
- Extreme dryness in the mouth
- Vision blurriness
- Rapid heartbeat, along with other noticeable effects.

Severe Dry Mouth
Experiencing dry mouth, known as xerostomia, is a crucial indicator of taking too much Trospium Chloride. Individuals may feel discomfort because of the notable decrease in saliva production. This could result in challenges with talking and eating and a higher likelihood of issues like cavities and gum disease.
Blurred Vision
Blurred eyesight occurs due to the impact of effects on the eye's ciliary muscles, causing difficulty in focusing accurately. This issue can significantly hinder a person's capacity to carry out tasks, like reading or driving, thereby raising the chances of accidents.

Tachycardia
When someone takes a lot of medication, they might experience tachycardia, which is when the heart beats too fast. This can lead to feelings of fluttering in the chest and lightheadedness, and, in some situations, it could result in severe heart problems. It's crucial to seek help immediately to deal with this dangerous situation.
Management of Overdosage
Managing an overdose of Trospium Chloride requires action and specific medical care to lessen symptoms and avoid additional issues. Swift intervention is crucial in reducing the impact of symptoms and avoiding problems.
Immediate Steps to Take
If you suspect or confirm an overdose, here's what you should do away:
- Stop the Medication: Immediately halt the use of Trospium Chloride to prevent further intake.
- Check Vital Signs: Monitor the patient's vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing rate, to evaluate the seriousness of the overdose.
- Decontaminate the Digestive System: In case of an overdose, giving activated charcoal can help limit drug absorption in the stomach. Gastric lavage might be considered for situations.
Medical Treatments and Antidotes
Specific medical care and remedies might be necessary depending on how severe the symptom is:
- IV Fluids: Give IV fluids to keep the body hydrated and support heart function.
- Treatment for Symptoms: Offer medications to ease symptoms, such as anti-nausea drugs for nausea or beta blockers for fast heart rate.
- Antidotes: Although there isn't an antidote for Trospium Chloride, cholinergic agents such as physostigmine could be considered in severe situations to counteract the anticholinergic effects.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Storage Guidelines
Ensuring the storage of Trospium Chloride is crucial for maintaining its effectiveness and safety. The medication must be stored in a controlled environment to avoid degradation or contamination.

Optimal Temperature and Conditions
Trospium Chloride should be kept in a room with temperatures ranging from 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). It's important to store the medication away from high heat, moisture, and direct sunlight, as these factors can impact the drug's stability and effectiveness. It is advised to store it in a dry place, like a medicine cabinet, away from areas with high humidity, such as bathrooms and kitchens.
Shelf Life
Trospium Chloride usually has an expiration date printed on the packaging. Patients and healthcare providers should make sure they use the medication before this date to ensure it remains effective and safe. Using expired medication may not work as intended and could also be harmful to health.
Handling Precautions
Proper management of Trospium Chloride is crucial for ensuring the well-being of patients and healthcare professionals. This involves following disposal procedures and administering them with caution.
Safe Disposal of Medication
Make sure to dispose of any Trospium Chloride you don't use, or that has expired to avoid accidental ingestion or harming the environment. It's best to follow your rules for getting rid of medications, such as taking them back to a pharmacy or following the disposal instructions given by healthcare experts. Putting pencils in the toilet or throwing them in the trash is not advisable so that it can be risky for safety and the environment.
Instructions for Healthcare Providers
Healthcare professionals need to teach patients about how to store and handle Trspium Chloride. This involves guidance on keeping the medicine away from children and pets, Avoiding exposure to unfavorable environmental conditions, and Following correct disposal procedures. Furthermore, healthcare providers must make sure that patients grasp the significance of following the storage instructions to preserve the medication's efficacy.
Discontinuation Effects
Potential Withdrawal Symptoms
Stopping Trospium Chloride, like other medications, could result in a return of the symptoms it was initially prescribed to treat. Patients may experience a recurrence of bladder symptoms such as frequent urination, urgency, and incontinence. While Trospium Chloride is not typically linked to withdrawal effects, suddenly stopping the medication can lead to discomfort and a decline in quality of life. Reemergence of symptoms Severe withdrawal effects are not commonly seen. In certain instances, patients might notice mild rebound effects related to anticholinergic properties, such as dry mouth or constipation, previously masked by the medication. These effects are usually short-lived. It can be not very pleasant. Patients must inform their healthcare provider about any discomfort they experience to manage these symptoms effectively.

Strategies for Safe Discontinuation
Patients need to work closely with a healthcare provider when stopping Trospium Chloride. Gradually reducing the dosage under supervision is advised to minimize the chance of symptoms returning and allow the body to adapt to the change. Before discontinuing Trospium Chloride, patients should talk with their healthcare provider. This discussion should cover why they stop the medication, possible risks, and other treatment options.
In some situations, switching to a medication or trying nonpharmacological approaches may be recommended. Lifestyle changes like bladder training exercises, dietary adjustments, and pelvic floor therapy can also aid in discontinuing Trospium Chloride. These techniques can help manage symptoms, enhance bladder control, and lessen the need for medication. A planned and monitored approach to discontinuation can reduce the risk of withdrawal symptoms and ensure a smooth transition away from Trospium Chloride while maintaining patient comfort and symptom management.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Trospium chloride is a treatment for controlling an overactive bladder, and its effectiveness is tied to the correct storage and handling procedures. Important factors to keep in mind are:
- Keeping the medication at room temperature away from heat, moisture, and light
- Using it within the expiration date for safety and optimal results
- Properly disposing of it to avoid harm
Final Considerations for Patients and Healthcare Providers
Patients and healthcare providers have roles in ensuring the safe use of Trospium Chloride. Patients must understand how to store and handle the medication properly, while healthcare providers should provide education and assistance. When they collaborate effectively, they can achieve the treatment results, maintaining Trospium Chloride as a safe and reliable option for treating overactive bladder.