Tolterodine
- I. Introduction to Tolterodine
- II. Understanding How Tolterodine Works
- III. Detailed Composition of Tolterodine
- IV. Comprehensive Uses of Tolterodine
- V. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- VI. Potential Interactions of Tolterodine
- VII. Recognizing and Managing Side Effects of Tolterodine
- VIII. Special Warnings and Contraindications
- IX. Special Considerations for Administering Tolterodine
- X. Overdose: Identifying and Responding
- XI. Proper Storage of Tolterodine
- XII. Precactions When Handling Tolterodine
I. Introduction to Tolterodine
Background and Classification of Tolterodine
Tolterodine belongs to a group of medications called antimuscarinics or urinary antispasmodics. It is commonly used to treat conditions. Approved by the FDA in 1998, doctors often prescribe it to alleviate symptoms of a bladder, such as frequent urination, urgency, and incontinence. The primary purpose of this medication is to reduce the contractions of muscles in the urinary bladder.
Importance and Prevalence of Use in the Medical Field
Tolterodine has gained popularity due to its effectiveness and manageable side effects. With the increasing number of adults dealing with overactive bladder symptoms, this medication offers much-needed relief. Its significance is further validated by its inclusion on the World Health Organizations Model List of Essential Medicines highlighting its role in healthcare systems worldwide.
II. Understanding How Tolterodine Works
The Biological Mechanism of Tolterodine
Tolterodine functions as an agent blocking the muscarinic receptors located in the detrusor muscle of the bladder. These receptors are usually stimulated by acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter, to trigger muscle contraction. However, Tolterodine inhibits this process by reducing the activity of acetylcholine. As a result, it helps relax the bladder muscle and alleviates the urge to urinate frequently.
Its Role in Treating Various Health Conditions
Tolterodine is mainly used to treat bladder (OAB) and its related symptoms. However, it can also be beneficial for health issues involving urinary tract function problems. For example, it can be used in addition to treatments for patients with neurogenic bladder disorders, which are urinary conditions that occur in individuals with nervous system damage.
III. Detailed Composition of Tolterodine
Main Active Ingredient and Its Properties
Tolterodine contains the active component called tolterodine tartrate, which is responsible, for its therapeutic effects. This compound has antimuscarinic properties that effectively reduce bladder muscle contractions offering relief from symptoms associated with overactive bladder.
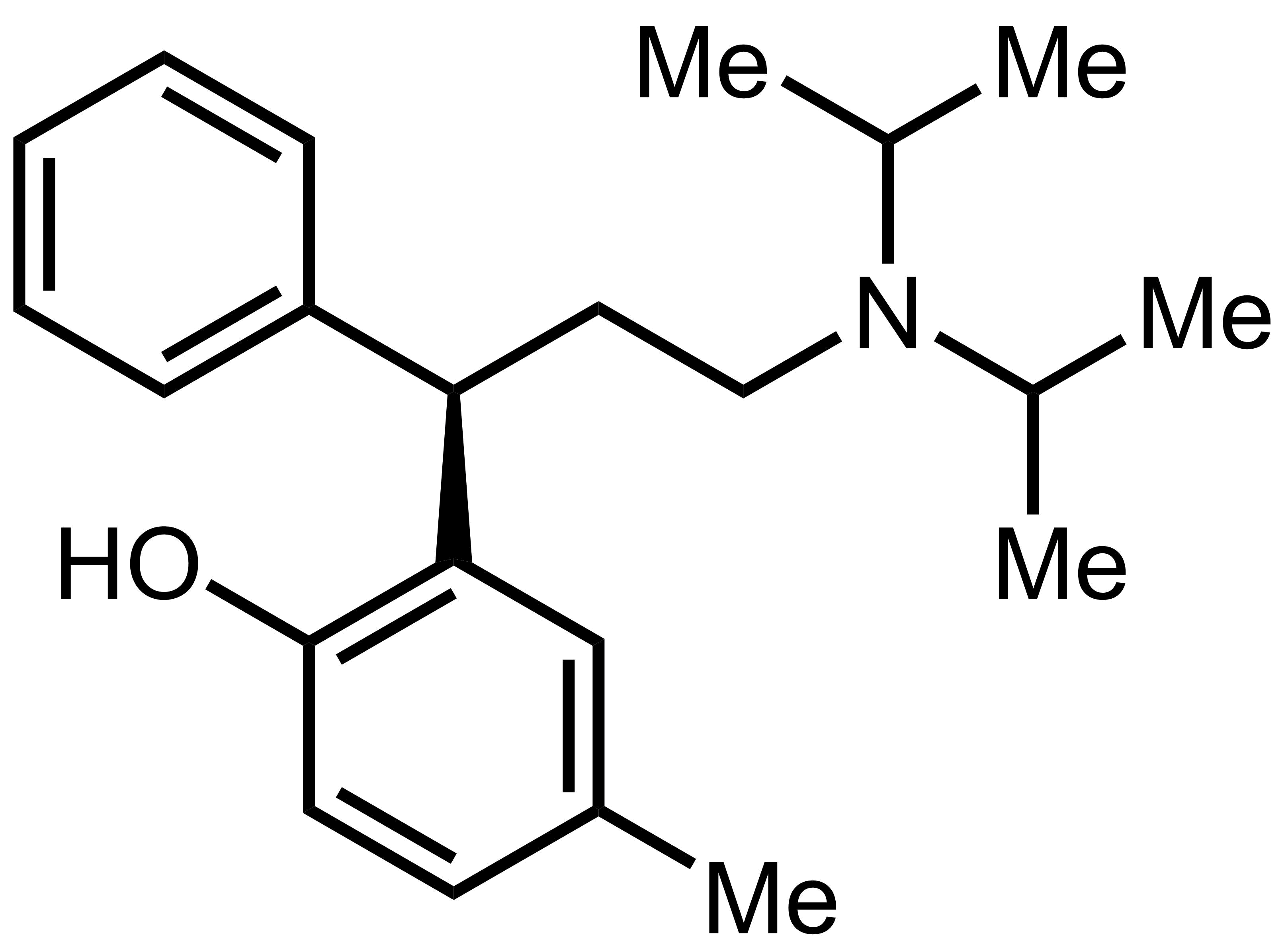
List of Inactive Components and Their Roles
Tolterodine is composed of more than the active ingredient. Other constituents that are not directly responsible for effects play a role in the medication formulation. These additional components contribute to the stability, bioavailability, and patient tolerance of the drug. For instance, Starch is included as a filler to give volume to the medication. Lactose acts as a diluent ensuring the distribution of the drug within the pill. Magnesium stearate is a lubricant to prevent ingredients from sticking to machinery during production.
IV. Comprehensive Uses of Tolterodine
Traditional Therapeutic Use of Tolterodine
Tolterodine is commonly used to treat the symptoms of an overactive bladder, which is characterized by frequent and uncontrollable urges to urinate. By acting as an antimuscarinic agent Tolterodine effectively prevents involuntary muscle contractions in the bladder, reducing urgency, incontinence and nighttime urination1.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information:
Less Common Uses of the Medication
Tolterodine is mainly used to treat bladder symptoms, but it can also be used to address other conditions. For example, some doctors use Tolterodine to manage incontinence caused by problems with the bladder muscles. It may also help reduce symptoms after specific surgeries, like radical prostatectomy123.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information:
Exploration of Off-label Uses of Tolterodine
Off-label use refers to when a medication is used for a purpose that it has not been officially approved for. In some situations, Tolterodine has been used off-label to treat pediatric enuresis, when children experience nighttime incontinence12. However, it is essential to conduct clinical studies to determine the safety and effectiveness of using Tolterodine for these unconventional purposes3.
Here are some references that you can check out for more information:
V. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Standard Dosage Instructions
The usual starting dose for adults taking Tolterodine is 2 mg twice daily. However, in cases where the patient's tolerance or symptom severity is a concern, the amount may be lowered to 1 mg twice a day. It doesn't matter if you take this medication with or without food. It's important to stick to a consistent dosing schedule for optimal effectiveness.
Procedures for Administering Tolterodine
Tolterodine is usually given to patients as tablets or capsules, which should be taken by mouth. It's important to swallow the medication whole with an amount of water. Avoid crushing, splitting, or chewing the drug, as it may affect how it is released into the body.
Factors Influencing Dosage: Age, Condition, and Others
There are reasons why dosage adjustments might be necessary, such as considering a person's age, liver, kidney function, and other existing medical conditions. For instance, in individuals or those with liver or kidney problems, it may be advisable to start with a lower dose. Moreover, interactions with other medications can also influence the appropriate dosage.
VI. Potential Interactions of Tolterodine
Interactions with Other Medications
Tolterodine can interact with medications, affecting their effectiveness or leading to increased side effects. These interactions can occur with drugs, macrolide antibiotics, and other medications that work similarly to tolterodine. Patients must inform their healthcare provider about all the medications they are currently taking, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medicines, and herbal supplements.
Interactions with Food and Dietary Supplements
While taking Tolterodine, it is generally not necessary to consider your meals. However, it is important to note that the absorption and effectiveness of Tolterodine may be affected by foods or dietary supplements. One example is the consumption of grapefruit juice, at the time which has the potential to increase Tolterodine levels and possibly enhance its side effects.
How to Prevent and Manage Potential Interactions
To avoid any interactions it is important to fully disclose all the medications you are currently taking and your dietary habits to your healthcare provider. Additionally, it is advisable to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any medicine. If there is a suspicion of an interaction your healthcare provider may need to adjust the dosage of Tolterodine or the other medication involved. They may suggest an alternative medicine.
VII. Recognizing and Managing Side Effects of Tolterodine
Common Side Effects and Their Management
Like any medication, Tolterodine can cause side effects, although not everyone will experience them. Some common side effects may include the mouth, difficulty passing stools, and blurred vision. To help alleviate these symptoms you can try drinking fluids incorporating fiber-rich foods into your diet and using lubricating eye drops. If these side effects continue or worsen, it would be advisable to seek advice.
Serious Side Effects: Indications and Emergency Responses
Sometimes Tolterodine can have some side effects. These could include a heartbeat, trouble urinating, and intense stomach pain. If you notice any of these symptoms, it's essential to seek medical help. You should stop taking the medication and get in touch with your healthcare provider away.
VIII. Special Warnings and Contraindications
Medical Conditions that Prohibit Use
There are medical conditions in which it is essential to be cautious or avoid using Tolterodine. These conditions include retention, uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma and urinary retention. It is also advisable for individuals with bladder outflow obstruction or those who are hypersensitive, to Tolterodine to refrain from taking this medication.
Drug Allergies and Cross-reactivity
If you have a known sensitivity to Tolterodine or its ingredients, it's best to avoid using it. Additionally, if you've had reactions in the past, to similar antimuscarinic medications it's important to be cautious as there is a possibility of cross-reactivity.
Other Contraindications and Precautions
Tolterodine should not be given to individuals with kidney problems, myasthenia gravis, or severe liver problems. Moreover, it should not be used together with CYP3A4 inhibitors.
IX. Special Considerations for Administering Tolterodine
Administration to Elderly Patients
Caution should be exercised when administering Tolterodine to patients as their liver, kidney, or heart function may be compromised. It is essential to monitor them and consider adjusting the dosage if necessary.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Considering the possible risks and benefits, tolterodine should only be given to women if necessary. Likewise, if there is a chance of adverse reactions in breastfeeding infants, a choice should be made to stop breastfeeding or stop using the medication.
Administration to Children: Safety and Dosage Guidelines
The use of Tolterodine in children is not recommended as its safety and effectiveness in patients have not been established. However, if it is deemed necessary, it should be administered under the supervision of a healthcare provider.
X. Overdose: Identifying and Responding
Symptoms and Signs of Overdose
Signs of taking much Tolterodine may include experiencing trouble with breathing, intense feelings of dizziness, an irregular heartbeat, and episodes of fainting. An overdose can also manifest as amplified versions of the side effects associated with the medication.
Essential First Aid Steps and Medical Interventions
If someone overdoses on a substance and you think it's serious, getting help right away is important. While waiting for the professionals, you should keep their airway clear. Help them breathe. It may be worth considering lavage, and giving them activated charcoal could be helpful. It is essential to provide ongoing support and treatment based on their specific symptoms and how they're doing overall.
XI. Proper Storage of Tolterodine
Ideal Conditions for Storage
Tolterodine should be stored in a dry place, preferably at room temperature, between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). It is essential to keep it out of the reach and sight of children to prevent ingestion or misuse. Additionally, store the medication in its packaging to protect it from moisture and light until you need to use it.

Guidelines for Disposal of Expired Medication
It is not recommended to throw expired or unused Tolterodine in the regular trash or flush it down the drain. The appropriate method of disposal is through a medicine take-back program. If that is not possible, it is advisable to follow the guidelines provided by the FDA or consult a pharmacist for disposal instructions. We can minimize any potential environmental harm and reduce the risk of accidental exposure to animals and people.
XII. Precactions When Handling Tolterodine
Safe Handling Practices
Make sure to wash your hands both after handling Tolterodine. It's important not to break or crush the tablets or capsules. If you accidentally do so, avoid touching your skin or eyes directly. In case of contact, thoroughly rinse with water. Seek medical help if any irritation persists.
Protection Measures to Minimize Exposure Risk
To reduce the chances of exposure, it is essential to handle Tolterodine in a space with ventilation and away from any food or beverages. It is advised not to eat, drink, or smoke while dealing with this medication. Additionally, if you are pregnant, nursing, or have hypersensitivity, it is best to avoid handling this medication whenever possible. If there is a need to take it in situations, make sure to wear proper protective gear, like gloves and eye protection.