Isoprenaline is a medication used to treat heart block, Adams-Stokes attacks, bronchospasm in anesthesia, cardiac arrest, hypovolemic shocks, septic shock, hypoperfusion, congestive heart failure, and cardiogenic shock 12. It is a non-selective beta-adrenergic receptor agonist that activates the myocardium, elevating both heart rate and contractility 12. This property makes it a significant medication for reviving individuals experiencing cardiac arrest situations 12.
Isoprenaline
- I. Introduction
- II. What is Isoprenaline? How Does It Work?
- III. Approved Uses of Isoprenaline
- IV. Off-Label Uses of Isoprenaline
- V. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- VI. Composition and Chemical Properties
- VII. Storage Recommendations for Isoprenaline
- VIII. Drug Interactions with Isoprenaline
- IX. Side Effects and Warnings
- X. Contraindications: Who Should Not Use Isoprenaline
- XI. Special Precautions and Careful Administration
- XII. Overdose Management and Handling Precautions
- XIII. Conclusion
I. Introduction
Isoprenaline, which is also referred to as isoproterenol, is a medication that has a variety of applications. It is used to treat disorders as well as respiratory problems. Knowing its uses, potential side effects, and precautions is crucial for healthcare professionals and patients. This article aims to provide a guide on Isoprenaline, including information about its chemical structure, approved uses, off-label applications, interactions with other medications, and additional relevant details.
II. What is Isoprenaline? How Does It Work?
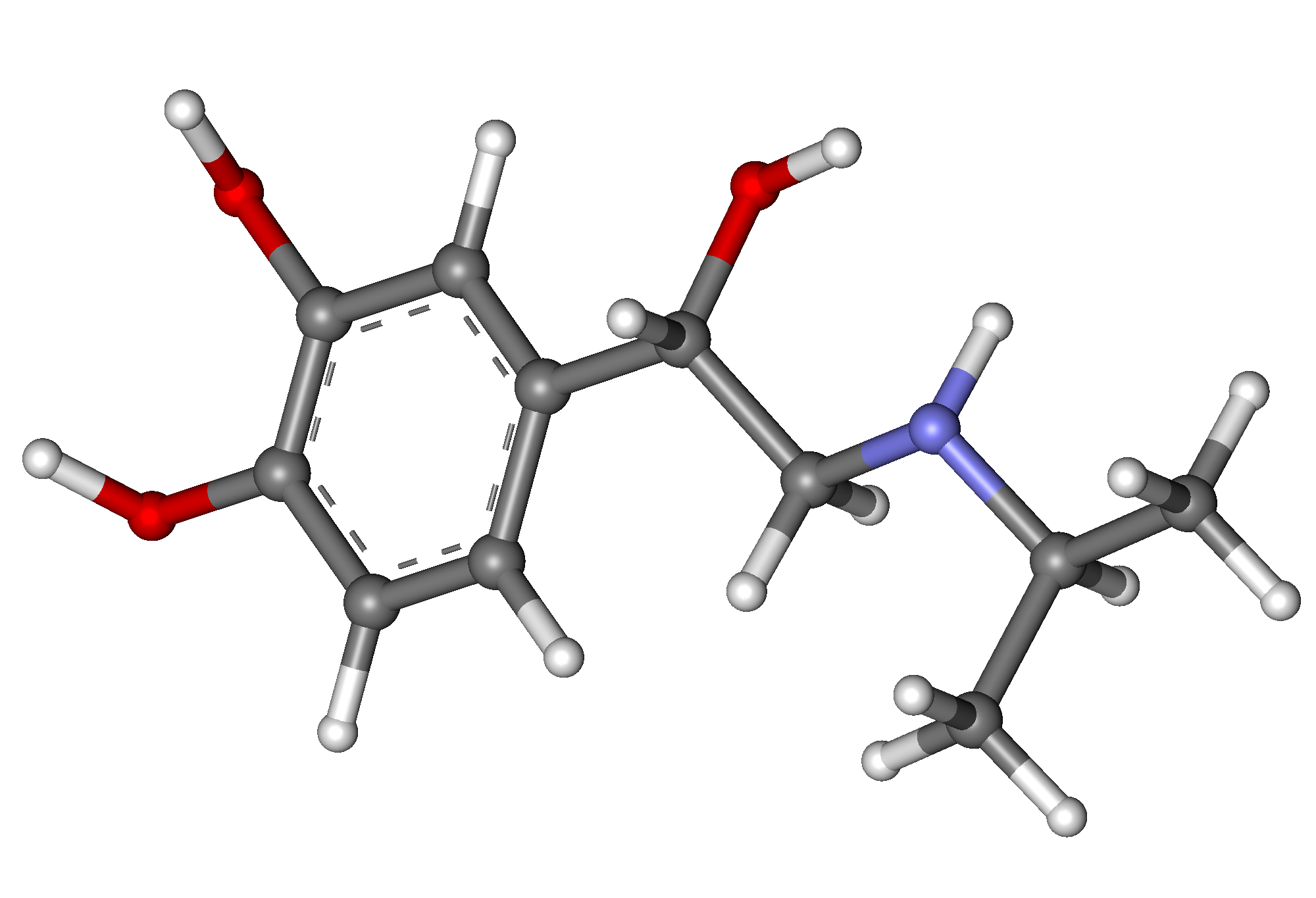
Chemical Structure and Classification
Isoprenaline falls into the category of beta-agonists. Its chemical makeup consists of a benzene ring with hydroxyl—Isopropylamine substituents, indicating that it is derived from catecholamine.
Mechanism of Action: How Isoprenaline Affects the Body
The medication mainly affects the beta one and two receptors, increasing cyclic AMP. As a result, it boosts the heart's pumping capacity. Helps relax the muscles in the bronchial tubes.
Comparison with Other Similar Drugs
Epinephrine is known to be more efficient in narrowing blood vessels while also having the effects of opening up the airways. On the other hand, Albuterol is mainly used to treat bronchospasm, but it doesn't show effectiveness in cardiac conditions. Conversely, Dobutamine primarily targets beta-1 receptors and is commonly used for treating heart failure.
III. Approved Uses of Isoprenaline
Cardiac Arrest: How Isoprenaline Can Regulate Heart Rate
Bradycardia: Stabilizing Low Heart Rates
Isoprenaline is a non-selective beta-adrenergic receptor agonist that has the ability to increase heart rates that are dangerously low, which is referred to as bradycardia, through its impact on beta-1 adrenergic receptors 123.
Beta-1 adrenergic receptors are expressed predominantly in cardiac tissue and are associated with the Gs heterotrimeric G-protein. Activation of these receptors by isoprenaline leads to an increase in cyclic AMP levels, activating protein kinase A (PKA). PKA phosphorylates cardiac L-type calcium channels such as Ca v 1.2, depolarizing cells by inward active transport of calcium ions. This results in an increase in heart rate and cardiac contractility 13.
Learn more:
Medicine LibreTexts. (2022). Adrenergic Neurons and Receptors.
Asthma and Bronchospasm: Respiratory Benefits
Isoprenaline is a bronchodilator used to manage asthma and bronchospasm due to its bronchodilatory properties 1. However, it is generally regarded as a second choice due to its potential cardiac side effects 12.
Here are the references for the above content:
1: Pharmacology and Therapeutics of Bronchodilators Revisited 2: Isoprenaline: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action - DrugBank Online
Heart Block: Ensuring Adequate Blood Flow
Isoprenaline can potentially improve heart block conditions by increasing the conductivity and automaticity of the heart tissue 123.
Here are the references for the above content:
1: Isoprenaline: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action - DrugBank Online 2: Cardiac excitability, mechanisms of arrhythmia, and action of antiarrhythmic drugs - UpToDate 3: Cellular Pharmacology of Cardiac Automaticity and Conduction - SpringerLink
IV. Off-Label Uses of Isoprenaline
Management of Hypotension: What Studies Say
Studies have indicated that Isoprenaline may have potential to manage blood pressure situations, although this particular application is not widely acknowledged 12.
Here are the references for the above content:
1: Isoprenaline: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action - DrugBank Online 2: New Guidance on Blood Pressure Management in Low-Risk Adults with Stage 1 Hypertension - American College of Cardiology
Anaphylaxis: Emergency Uses
Isoprenaline is a non-selective beta-adrenergic receptor agonist that is typically used to treat heart block, Adams-Stokes attacks, bronchospasm in anesthesia, cardiac arrest, hypovolemic shocks, septic shock, hypoperfusion, congestive heart failure, and cardiogenic shock 1. Although it is not typically the initial treatment choice for anaphylactic reactions, it has been utilized in some cases to help sustain the heart’s pumping capacity 1.
Here are the references for the above content:
DrugBank. Isoprenaline: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action.
Other Potential Off-Label Applications: Research and Case Studies
Isoprenaline is a non-selective beta-adrenergic receptor agonist that is typically used to treat heart block, Adams-Stokes attacks, bronchospasm in anesthesia, cardiac arrest, hypovolemic shocks, septic shock, hypoperfusion, congestive heart failure, and cardiogenic shock 1. Although it is not typically the initial choice of treatment for anaphylactic reactions, it has been utilized in some cases to help sustain the heart’s pumping capacity 1.
There is limited information available on the use of Isoprenaline for Hyperkalemia. However, it has been suggested that Isoprenaline may relieve symptoms of Hyperkalemia 2.
Studies have suggested that Isoprenaline may have potential benefits in treating Obstructive Cardiomyopathy 34.
Here are the references for the above content:
DrugBank. Isoprenaline: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action.
V. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Standard Dosage for Different Conditions
The recommended dosage may differ based on the addressed condition, with a range of 2 to 25 micrograms per minute administered intravenously.
Administration Routes: Intravenous, Subcutaneous, etc.
Isoprenaline can be given using methods such as intravenous infusion or subcutaneous injection.
Titration and Dosage Adjustment
It is recommended to monitor the titration process, adjusting the dosages based on hemodynamic responses and potential side effects.
VI. Composition and Chemical Properties
Active Ingredients
The main component used is Isoprenaline hydrochloride, which is, in a salt form to increase its solubility.
Inactive Ingredients
Some inactive ingredients include sodium chloride and sterile water for injection.
Stability and Shelf-life
When stored in conditions, isoprenaline can last up to 24 months.
VII. Storage Recommendations for Isoprenaline
Optimal Storage Conditions
It's important to store Isoprenaline in a dry location away from any exposure to light or moisture.
What Happens When the Drug is Improperly Stored
Storing medication incorrectly can cause the active compound to deteriorate, making the medicine less effective or potentially dangerous.
VIII. Drug Interactions with Isoprenaline
Common Drugs that Interact with Isoprenaline
Beta-blockers may have a reduced effect, while diuretics can potentially increase the risk of hypokalemia.
Risk of Combining with Blood Pressure Medication
Combining Isoprenaline with medications used to treat blood pressure might reduce the effectiveness of the antihypertensive drugs.
Interactions with OTC Drugs and Herbal Supplements
It is essential to be cautious when mixing prescription drugs such as natural supplements like ginseng as they could enhance the potential for adverse effects, on the heart.
IX. Side Effects and Warnings
Common Side Effects: What to Expect
Typically, people may experience palpitations, headaches, or tremors as side effects. While these effects are generally not serious, it's important to watch them.
Rare but Serious Side Effects: When to Seek Medical Attention
Serious but infrequent adverse effects, such as discomfort, in the chest, irregular heartbeat, or low blood pressure, need medical attention.
General Warnings: Who Should Avoid This Drug
People with conditions such as cardiomyopathy, tachyarrhythmia, or hyperthyroidism should be careful and seek advice from a healthcare professional before using Isoprenaline.
X. Contraindications: Who Should Not Use Isoprenaline
Cardiac Conditions that Prevent Use
Individuals with heart conditions, such as tachyarrhythmia, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and myocardial ischemia, should avoid Isoprenaline. The drug's tendency to increase excitability could worsen these conditions.
Drug Allergies and Other Medical Histories
People who have experienced sensitivity, to Isoprenaline or its ingredients should avoid using it. It is essential to gather a medical history to identify any potential issues related to previous drug interactions or allergies.
Pregnancy and Nursing: A Closer Look
Isoprenaline is classified as pregnancy category C, meaning no data can determine its safety during pregnancy. Similarly, it is unclear if the drug passes into breast milk. As a result, it is advised to exercise caution when using it while pregnant or breastfeeding.
XI. Special Precautions and Careful Administration
How to Administer Safely in Elderly Patients
Begin by gradually adjusting the dosage to find the lowest adequate amount. It's essential to watch for any effects like irregular heart rhythms or low blood pressure. Regularly assessing the state of your body's blood flow is crucial in this process.
Precautions for Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Considering the amount of conclusive research available regarding the impact of Isoprenaline on pregnancy and breastfeeding, it is advisable to use this medication in those situations only if the potential advantages outweigh any hypothetical risks.
Considerations for Children: Dosage and Safety
In children, doctors usually prescribe medication based on their weight. It's essential to watch out for any side effects, like rapid heartbeats or feeling anxious.
XII. Overdose Management and Handling Precautions
Symptoms of Isoprenaline Overdose
Signs of a dose can include but are not restricted to, feelings of a racing heartbeat, rapid heart rate, high blood pressure, and intense shaking. It's also possible to experience difficulty in breathing.

Immediate Actions: What to Do in Case of Overdose
Taking medical action is crucial. The treatment focuses on addressing the symptoms. This may involve stopping the medication using beta blockers and providing supportive care such as oxygen therapy.
Preventing Overdose: Measures to Take
To ensure protection, it's essential to follow the recommended dosage regularly, undergo medical check-ups, and avoid self-administering without proper guidance from a healthcare professional.
XIII. Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Isoprenaline is a purposeful medication with different uses in medical practice, but it's essential to be aware of potential risks and contraindications. Precise dosage and careful administration are essential for maximizing the effectiveness of treatment while minimizing any effects.
Importance of Consulting a Healthcare Provider
The complexities linked to Isoprenaline highlight the importance of seeking medical guidance. It is crucial to receive medical advice to ensure safe and effective treatment.