Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride
- I. Introduction to Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride
- II. Composition and Properties of Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride
- III. Mechanism of Action: How Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride Works
- IV. Uses of Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride
- V. Off-Label Uses of Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride
- VI. Dosage and Administration of Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride
- VII. Side Effects of Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride
- VIII. Important Precautions and Warnings
- IX. Interactions with Other Medications
- X. Special Considerations in Administration
- Administration to Elderly Patients
- Adjustments in Dosage and Monitoring
- Risks and Benefits Analysis
- Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
- Safety Profile and FDA Pregnancy Category
- Recommendations and Alternatives
- Administration to Children
- Age-Specific Dosage and Safety Information
- Clinical Studies and Efficacy Data
- XI. Guidelines for Overdosage and Emergency Situations
- XII. Storage, Stability, and Handling of Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride
I. Introduction to Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride
Overview and Significance in Medical Treatments
Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride, a vasodilator, is crucial in treating circulatory issues. It helps improve blood circulation in peripheral regions, easing symptoms of vascular problems and supporting tissue well-being.
Historical Development and FDA Approval
Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride, which was created in the middle of the century, was first employed for addressing vascular conditions and was subsequently granted approval by the FDA for specific uses. Its widespread use has been shaped by studies showcasing its effectiveness and safety record.
II. Composition and Properties of Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride
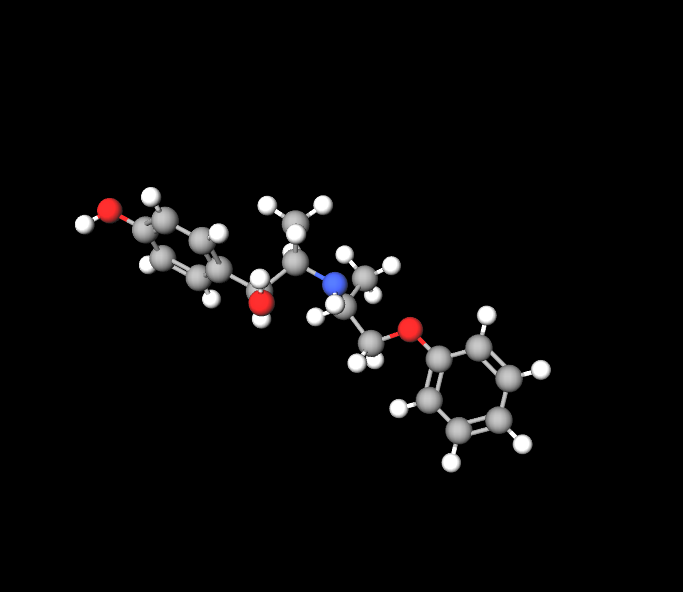
Chemical Structure and Classification
The molecular structure of Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride places it in the category of beta 2 agonists, which leads to its function as a muscle relaxant that effectively widens blood vessels.
Formulations Available
This medicine comes in forms, such as tablets to take by mouth and liquid injections, meeting a range of medical requirements and making it easier for patients to follow their treatment plans.
III. Mechanism of Action: How Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride Works
Pharmacodynamics: Vasodilatory Effects and Muscle Relaxation
The benefits of Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride involve relaxing the muscles in blood vessels, which helps enhance blood circulation and oxygen supply to tissues.
Impact on Blood Flow and Peripheral Circulation
Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride boosts circulation by widening blood vessels, crucial for managing peripheral arterial disease and vascular headaches.
IV. Uses of Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride
Primary Indications: Vascular Diseases and Peripheral Artery Disorders
-
Peripheral Vascular Disease and Cerebrovascular Insufficiency:
- Isoxsuprine is a vasodilator that relaxes veins and arteries, widening them and allowing blood to flow more easily. It is used to treat conditions such as cerebrovascular insufficiency (poor blood flow to the brain), arteriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), Raynaud’s phenomenon, and other conditions involving poor blood flow in veins and arteries123.
-
Peripheral Vascular Diseases:
- Isoxsuprine can be used to treat peripheral vascular diseases, including Buerger’s disease and Raynaud’s disease. It improves blood flow by opening up blood vessels2.
-
Symptomatic Treatment of Arterial Disorders:
- Isoxsuprine is indicated for the relief of symptoms associated with cerebrovascular insufficiency and peripheral vascular disease due to arteriosclerosis obliterans and thromboangiitis obliterans (Buerger’s disease). It is also used in the management of Raynaud’s disease3.
V. Off-Label Uses of Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride
Research on Neuroprotective Effects and Future Potential
-
Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Neurodegenerative Disorders:
- Oxidative stress plays a crucial role in the pathophysiology of neurodegenerative diseases. It results from an imbalance between pro-oxidant species (reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen species) and endogenous antioxidants. Recent studies emphasize the impact of oxidative stress and associated mitochondrial dysfunction in conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, and Huntington’s disease. Understanding these mechanisms may pave the way for therapeutic interventions to mitigate the progression of these disorders and yield clinical benefits1.
-
Identification of Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride as a Neuroprotectant in Ischemic Stroke:
- In a study, isoxsuprine hydrochloride was identified as a neuroprotectant in ischemic stroke. The research explored its potential through cell-based high-throughput screening. This finding suggests that isoxsuprine could have neuroprotective effects, which may be relevant to other neurodegenerative conditions as well2.
-
Exploring the Therapeutic Effect of Neurotrophins and Growth Factors:
- While not directly related to isoxsuprine, it’s worth noting that neurotrophic factors like GDNF (Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor) have been studied extensively for their potential therapeutic effects in neurodegenerative conditions. Non-clinical studies have investigated GDNF administration via gene therapy or direct brain injection as a potential avenue for treatment3.
VI. Dosage and Administration of Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride
Recommended Dosage for Different Conditions
Methods of Administration: Oral, Injectable Forms
VII. Side Effects of Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride
Overview of Common and Serious Side Effects
- Potential reactions that individuals may experience consist of heartbeat, heart palpitations and skin redness.
- Severe negative responses are uncommon; however, they could involve heartbeats and low blood pressure.
Managing Side Effects in Clinical Practice
To manage side effects effectively, it is essential to keep track of signs, educate patients, and make dose adjustments as needed to ensure the safety and well-being of the patient.
VIII. Important Precautions and Warnings
Contraindications for Use
Patients with arterial bleeding right after giving birth and those who are allergic to the medication should avoid using Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride.

Special Warnings for Specific Populations
Extra care should be taken when giving this treatment to groups like older individuals, expectant mothers, and people with existing heart issues. It's essential to monitor them and consider adjusting the treatment methods if needed.
IX. Interactions with Other Medications
Common Drug Interactions and Their Management
- Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride might interact with medications, such as beta blockers, antihypertensives and other vasodilators.
- When used together these medications can enhance the blood pressure lowering effect of isoxsuprine which may call for monitoring and adjustments, in dosage to prevent low blood pressure.
Effects of Food, Alcohol, and Supplements
The effectiveness of Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride may be affected by consuming substances:
- Alcohol; It could enhance the effects increasing the chances of experiencing side effects.
- Caffeine; It might counteract the intended effects of isoxsuprine potentially diminishing its effectiveness.
- Herbal supplements, Especially those with properties, should be approached with caution because of possible interactions.
X. Special Considerations in Administration
Administration to Elderly Patients
Elderly individuals frequently show heightened responsiveness to vasodilators such as Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride, which may require dosage modifications and closer monitoring for potential side effects.
Adjustments in Dosage and Monitoring
It's important to adjust the dosage for liver-impaired patients to prevent too much medicine in the body, which could lead to harmful heart events.
Risks and Benefits Analysis
Balancing the benefits of blood flow with the dangers of low blood pressure and its associated issues is essential in a comprehensive assessment.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
While Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride is utilized to handle labor, it is crucial to ensure that it is administered with close medical monitoring during pregnancy as it may pose risks to the unborn baby.
Safety Profile and FDA Pregnancy Category
Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride falls into FDA Pregnancy Category C. It is recommended to use it only if the advantages outweigh the possible risks to the unborn child.

Recommendations and Alternatives
When the potential dangers are greater than the advantages, it's advisable to explore treatment options that are known to be safer for pregnant women.
Administration to Children
The safety and efficacy of Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride in patients have not been confirmed, so its administration to children should be decided after a thorough evaluation of the risks and benefits.
Age-Specific Dosage and Safety Information
Considering the availability of detailed data, it is advisable to exercise caution when recommending isoxsuprine, for children, and healthcare providers should closely supervise its administration.
Clinical Studies and Efficacy Data
Recent research trials and studies could offer an understanding of how safe and effective Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride is for children in medical settings.
XI. Guidelines for Overdosage and Emergency Situations
Signs and Symptoms of Overdose
Signs of taking too much medication can lead to serious low blood pressure, feeling lightheaded, passing out, and a fast heart rate. It's crucial to seek help right away if experiencing these symptoms.
Immediate Interventions and Treatment Protocols
In case of an overdose, it is important to focus on keeping the airway breathing and circulation intact. Additionally, providing care and support, like fluid replenishment and monitoring, for heart irregularities are crucial interventions.
XII. Storage, Stability, and Handling of Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride
Proper Storage Conditions to Maintain Efficacy
Be sure to keep Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride from light and moisture at room temperature to preserve its effectiveness and extend its storage duration.
Handling Precautions for Safety
Working with isoxsuprine involves following safety protocols to avoid exposure, particularly in areas where nonpatients are present, to safeguard the drug's effectiveness and the well-being of individuals managing it.