Ketoconazole for Animals
- Introduction to Ketoconazole for Animals
- Composition and Properties of Ketoconazole
- Uses of Ketoconazole in Veterinary Medicine
- Off-Label Uses of Ketoconazole in Animals
- How Ketoconazole Works in Animals
- Dosage and Administration of Ketoconazole
- Storage and Handling of Ketoconazole
- Ketoconazole cream side effects
- Serious Side Effects and Risks of Ketoconazole
- Drug Interactions with Ketoconazole
- Warnings and Contraindications
- Precautions for Specific Populations
- Overdose Management in Animals
- Important Precautions When Using Ketoconazole
- Handling and Disposal Precautions for Ketoconazole
Introduction to Ketoconazole for Animals
Overview of Ketoconazole
In medicine, Ketoconazole is an antifungal drug commonly used to treat different kinds of fungal and yeast infections. With its effectiveness, in managing skin issues and internal fungal problems it has become an option among vets. The medication comes in forms that provide options for administration based on the animal's requirements.
Historical Background and Development
Initially launched in the 1970s era as an antifungal medication for humans, Ketoconazole found its way into veterinary medicine with improvements in formulation over the years to ensure better safety and efficacy in animal treatment.
Veterinary Applications and Relevance
Managing infections resistant to treatments is a function of Ketoconazole—particularly in small animal care settings where fungal and yeast infections are common among companion animals and exotic species alike.
Composition and Properties of Ketoconazole
Active Ingredients and Chemical Structure
Ketoconazole contains an imidazole derivative, as its component, which works by interfering with the cell membranes of fungi to stop their growth and reproduction effectively due to its chemical structure that targets a variety of fungal pathogens.
Mechanism of Action in Animals
The medication ketoconazole hinders the production of ergosterol in cell membranes, which weakens the cells and increases vulnerability to system attacks; it also has some anti-inflammatory effects that can help speed up recovery processes.
Available Formulations (Tablets, Topical Solutions, etc.)
Ketoconazole is available in various formulations, including: - Oral tablets for systemic infections - Topical creams and shampoos for localized skin conditions - Injectable forms for severe cases These options provide tailored treatments based on the severity and location of the infection.
Ketoconazole vs clotrimazole
Administering ketoconazole is required to address infections like candidiasis and blastomycosis. On the other hand, clotrimazole serves as a remedy for skin infections provoked by yeast, such as athletes' feet and ringworm. Additionally, it is suitable for administration to combat yeast infections.
Ketoconazole vs miconazole
You can use Ketoconazole to address infections such as candidiasis and blastomycosis. As for Miconazole, it is effective in treating ringworm jock itch and athlete's foot. It can also be used to treat fungal infections.
Selenium sulfide vs ketoconazole
Selenium sulfide includes selenium, a trace mineral known for its anti-inflammatory properties; it is commonly used as a shampoo to help manage oily skin conditions. Ketoconazole is a medication that can treat fungal infections, such as ringworm and skin infections, as well as more serious conditions, like cryptococcosis and Blastomyces.
Ciclopirox shampoo vs ketoconazole
Ciclopirox treats seborrheic dermatitis, a condition that causes dry, flaky, and itchy skin. Ketoconazole treats serious fungal or yeast infections, such as candidiasis (thrush), blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, chromoblastomycosis, or paracoccidioidomycosis.
Uses of Ketoconazole in Veterinary Medicine
Treatment of Fungal Infections
Pets commonly receive ketoconazole for infections caused by organisms like Candida and Aspergillosis, as well as Cryptococcus infections, due to its efficacy in treating both systemic and superficial fungal diseases.

Management of Dermatophytosis (Ringworm)
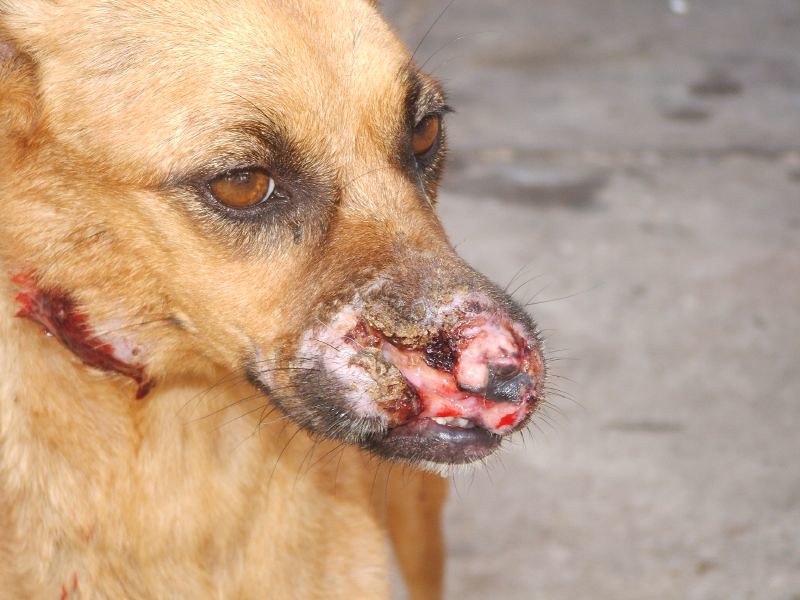
Ringworm is a skin infection found in animals that can be effectively treated with Ketoconazole therapy. The medication works by eradicating the fungal spores on the skin surface, thus reducing the spread of infection and providing relief from symptoms.
Treatment of Yeast Infections (Malassezia)
Dogs often receive Ketoconazole treatment to address Malassezia dermatitis—a yeast infection that impacts their skin and ears—with shampoos containing Ketoconazole for lasting effectiveness.
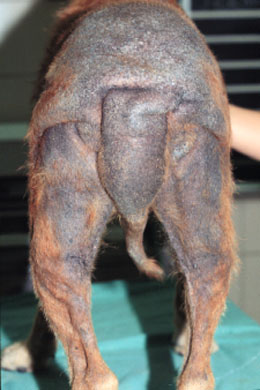
Ketoconazole for dogs
Using ketoconazole to manage Cushing's Disease in dogs is an off-label approach as it blocks steroid synthesis and helps control cortisol levels to enhance the dog well being.
Anti-inflammatory Applications in Veterinary Care
Ketoconazole not only acts against fungi but also provides relief from inflammation; thus, it is effective for ailments associated with prolonged inflammation.
Off-Label Uses of Ketoconazole in Animals
Potential Use in Parasitic Infections
Adjunct Therapy in Cancer Treatment
The inhibiting effect of Ketoconazole on steroid production makes it a valuable option for treating hormone tumors like carcinomas in dogs.
Off-Label Use for Systemic Fungal Infections in Exotic Pets
Exotic creatures, like birds and reptiles, could find Ketoconazole useful in treating infections due to its effectiveness across various species.

How Ketoconazole Works in Animals
Inhibition of Ergosterol Synthesis in Fungal Membranes
Ketoconazole works by affecting the production of ergosterol in cells, which then disrupts their structure and ability to reproduce effectively, resulting in their elimination over time.
Anti-inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Properties
Using ketoconazole helps control inflammation and lessen the swelling and discomfort caused by infections by regulating the bodys responses to improve the effectiveness of treatment overall.
Dosage and Administration of Ketoconazole
Standard Dosages for Dogs, Cats, and Other Animals
Dosages vary based on the animal's species, weight, and condition: - Dogs: Typically 5-10 mg/kg per day - Cats: Lower doses due to sensitivity - Exotic pets: Tailored based on veterinary recommendations
Factors Influencing Dosage (Weight, Age, Condition)
Changes need to be made for animals, as well as older ones and those with weakened immune systems, to make sure they get the right treatment benefits without any negative reactions occurring.
Methods of Administration (Oral, Topical)
Oral tablets are preferred for systemic infections, while topical solutions address localized issues. The method depends on the infection's location and severity.
Storage and Handling of Ketoconazole
Recommended Storage Conditions
Be sure to keep Ketoconazole in a dry spot that is shielded from direct sunlight exposure to ensure its effectiveness at its peak levels within the temperature range of 20 to 25 degrees Celsius.
Shelf Life and Expiry Considerations
Remember to look at the expiration date before using any medication and make sure to throw any expired medicine to prevent it from losing its effectiveness or becoming potentially harmful.
Safe Handling Practices
Remember to wear gloves when working with Ketoconazole products, like powders or creams to protect yourself from any harm such, as inhalation or skin contact that could occur if you don't take proper precautions.
Ketoconazole cream side effects
Gastrointestinal Upset (Vomiting, Diarrhea)
Gastrointestinal disturbances are among the most frequently observed side effects of Ketoconazole in animals. Symptoms such as vomiting and diarrhea may occur, particularly during the initial stages of treatment. These effects often subside as the animal's system adjusts to the medication.
- Vomiting may occur shortly after dosing.
- Loose stools or diarrhea might persist for a few days. To mitigate these effects, administering Ketoconazole with food is recommended.
Changes in Appetite
Ketoconazole may alter an animal's appetite, either increasing or decreasing food intake.
- Loss of appetite (anorexia) is more common in sensitive animals.
- Some animals may display heightened hunger due to metabolic changes. Close monitoring of eating habits is essential, especially during long-term therapy.
Lethargy and Behavioral Changes
Lethargy, characterized by unusual tiredness or reduced activity levels, can occur during treatment. Behavioral changes, such as irritability or withdrawal, might also be observed. These symptoms should be reported to the veterinarian if they persist or worsen.

Serious Side Effects and Risks of Ketoconazole
Liver Toxicity (Hepatotoxicity)
Liver toxicity is a significant concern associated with Ketoconazole use. Symptoms of hepatotoxicity include jaundice (yellowing of the eyes or skin), vomiting, and dark urine.
- Regular liver enzyme testing is crucial for early detection.
- Discontinuation of the drug is necessary in severe cases.
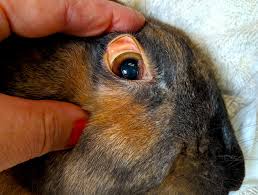
Hormonal Imbalance and Endocrine Effects
Ketoconazole can disrupt the endocrine system, potentially leading to hormonal imbalances. This is particularly relevant in animals with pre-existing conditions. Signs may include:
- Altered cortisol levels, causing symptoms similar to Addison's disease.
- Changes in reproductive cycles in female animals.
Potential Drug-Induced Allergic Reactions
Allergies to Ketoconazole are uncommon. It can show up as hives and swelling or make it hard to breathe in pets; seeking veterinary care is crucial if these signs appear.
Drug Interactions with Ketoconazole
Interaction with Other Antifungal Medications
The interaction, between ketoconazole and other antifungal medications might reduce their effectiveness. Raise the risk of toxicity levels escalating when used together necessitating dosage modifications.
Impact on Cytochrome P450 Enzyme System
Ketoconazole inhibits the cytochrome P450 enzyme system, which metabolizes many drugs.
- This can prolong the activity of certain medications.
- It necessitates dosage adjustments for co-administered drugs.
Risks of Concurrent Use with Steroids
Using ketoconazole can block the breakdown of steroids in the body cause higher levels of corticosteroids to build up which could make the side effects of steroid use.
Warnings and Contraindications
Absolute Contraindications in Animals
It's important not to administer Ketoconazole to animals who have shown sensitivity to the medication or have liver problems or existing liver dysfunction.

Conditions Requiring Special Caution
Animals with kidney function or chronic health issues need monitoring to catch any potential problems early through routine blood tests to detect adverse reactions promptly.
Warning Signs of Adverse Reactions
As an owner, it's important to stay alert for signs such as
- Experiencing prolonged bouts of vomiting or diarrhea, which can be quite distressing and uncomfortable.
- Feeling tired and sluggish
- Experiencing yellowing of the skin and eyes
- Unusual actions may be signs of a problem.
- It is recommended to seek advice if you notice these symptoms occurring.
Precautions for Specific Populations
Administration to Pregnant and Nursing Animals
It is important to be cautious when using ketoconazole in nursing animals due to its impact during fetal development or transmission through milk supply to the offsprings system; other treatment options are typically favored unless the benefits significantly outweigh the risks involved.

Considerations for Elderly Animals
Elderly animals may have reduced metabolic capacity, increasing the likelihood of adverse effects. - Lower starting doses are typically recommended. - Close monitoring of liver and kidney function is essential.
Use in Pediatric Veterinary Patients
Due to their developing organs, young animals are more sensitive to Ketoconazole's effects. Dosage adjustments and vigilant monitoring are critical in these cases.
Overdose Management in Animals
Signs and Symptoms of Ketoconazole Overdose
Signs of an overdose might manifest as vomiting or diarrhea along with skin and confusion; in severe instances, there could be seizures or loss of consciousness.
Immediate Interventions and Treatment Options
In case there is a suspicion of an overdose, Stop taking the medication. Only induce vomiting, with the guidance of a veterinarian. Give the person activated charcoal to lower absorption levels.
Long-Term Monitoring After Overdose
Following an overdose incident, routine checks on liver and kidney functions are essential for monitoring progress. To aid recovery, it's important to provide treatments, like IV fluids and medication, to safeguard the functioning of the organs.
Important Precautions When Using Ketoconazole
Monitoring Liver Function Regularly
Regular monitoring of liver enzymes is crucial when undergoing prolonged treatment to catch any signs of liver strain and prevent complications from arising.
Avoidance of Long-Term Use Without Veterinary Supervision
Consistent use raises the chances of experiencing overall side effects risk, while routine veterinary visits help maintain treatment safety and efficacy.
Educating Pet Owners on Proper Use
Pet owners can easily follow the treatment plan when they have guidance on how to give their furry friends and what to watch out for in terms of side effects.
Handling and Disposal Precautions for Ketoconazole
Guidelines for Safe Handling
- Always wear gloves when handling Ketoconazole tablets or topical solutions.
- Avoid direct contact with skin and mucous membranes.
Proper Disposal of Unused or Expired Medication
Environmental Considerations in Disposal
Improperly discarding waste can have an impact on animals and the natural environment in bodies of water, so it's important to follow the waste disposal rules in your area to protect the environment effectively.
Ketoconazole for Animals FAQ
- How long does it take for ketoconazole cream to work?
- Does ketoconazole shampoo cause hair loss?
- Can ketoconazole cause hair loss?
- How to use ketoconazole cream for toenail fungus?
- Does ketoconazole cause hair growth?
- Can I use ketoconazole and clotrimazole together?
- Will ketoconazole shampoo kill lice?
- What is ketoconazole used for in dogs?
- Does ketoconazole block dht?
- Can i use ketoconazole shampoo daily?
- Is ketoconazole safe for dogs?
- Can you get ketoconazole over the counter?
- Can you use mupirocin and ketoconazole together?
- Does head and shoulders have ketoconazole?
- Is ketoconazole stronger than clotrimazole?
- Can you use triamcinolone and ketoconazole together?
- How long does it take for ketoconazole to work in dogs?
- Does ketoconazole work on toenail fungus?
- Can I use ketoconazole and salicylic acid together?
- Does ketoconazole shampoo strip hair color?
How long does it take for ketoconazole cream to work?
It typically takes 2 to 4 weeks for ketoconazole cream and shampoo to show results.
Does ketoconazole shampoo cause hair loss?
Yes
Can ketoconazole cause hair loss?
Yes
How to use ketoconazole cream for toenail fungus?
Remember to wash and dry the impacted region thoroughly. Apply a coating of cream to the affected site and the nearby skin. Massage the cream gently into the skin. Remember to wash your hands.
Does ketoconazole cause hair growth?
Yes
Can I use ketoconazole and clotrimazole together?
Yes
Will ketoconazole shampoo kill lice?
Ketoconazole shampoo is effective for addressing head lice infestations.
What is ketoconazole used for in dogs?
Dogs are prescribed ketoconazole, which is a type of antifungal medication used to combat fungal infections in pets.
Does ketoconazole block dht?
It is believed that Ketoconazole works by inhibiting the activity of an enzyme called ́alpha reductase (5AR), helping to reduce dihydrotestosterone ( DHT ) levels in the body.
Can i use ketoconazole shampoo daily?
No
Is ketoconazole safe for dogs?
Ketoconazole can cause liver toxicity in dogs.
Can you get ketoconazole over the counter?
Yes
Can you use mupirocin and ketoconazole together?
Yes
Does head and shoulders have ketoconazole?
No
Is ketoconazole stronger than clotrimazole?
In some cases, ketoconazole tends to be stronger than clotrimazole.
Can you use triamcinolone and ketoconazole together?
The presence of ketoconazole could lead to a rise in the levels of triamcinolone in the bloodstream.
How long does it take for ketoconazole to work in dogs?
When treating a fungal infection, ketoconazole medication might take around 10 to 14 days before seeing a clear clinical improvement.
Does ketoconazole work on toenail fungus?
No
Can I use ketoconazole and salicylic acid together?
Yes
Does ketoconazole shampoo strip hair color?
Yes