Labetolol Injection
- Introduction
- Uses of Labetolol Injection
- How Labetolol Works
- Dosage and Administration
- Composition of Labetolol Injection
- Storage Conditions for Labetolol Injection
- Drug Interactions
- Warnings and Contraindications
- Careful Administration and Important Precautions
- Special Populations: Dosage and Precautions
- Side Effects of Labetolol
- Overdose and Handling Precautions
- Conclusion
Introduction
Labetalol1, a medication used to treat blood pressure, has a long-standing medical history. It was first introduced in the 1970s. It quickly became widely accepted as an essential treatment for hypertension and heart-related conditions. The significance of controlling blood pressure cannot be emphasized enough, as uncontrolled hypertension can lead to serious health complications like strokes, heart failure, and kidney problems. This article explores the uses of Labetalol with a specific focus on its intravenous administration, highlighting its crucial role in managing a wide range of clinical situations.
Uses of Labetolol Injection
Primary Use: Hypertension Management
Labetalol plays a role in healthcare by effectively managing hypertension. This medication works as a receptor antagonist, helping widen blood vessels and lower heart rate, significantly decreasing blood pressure. When given intravenously, Labetalol provides therapeutic benefits, particularly beneficial in urgent situations.
- It has an onset of action.
- Minimal side effects compared to other drugs used for hypertension
- Highly effective in treating emergency hypertensive crises.
Controlling High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is commonly known as the " killer," silently increasing the chances of developing heart-related issues. Labetalol injection reduces these risks, providing both immediate relief and a long-term management approach when oral medication is not possible. It proves explicitly to be highly advantageous in cases of hypertension, where prompt action is essential.
Role in Emergency Cases
In situations, Labetalol plays a crucial role in achieving swift stabilization. Its ability to function as both an alpha and beta blocker has a synergistic effect on the cardiovascular system. Emergency departments often rely on Labetalol for hemodynamic stabilization, especially in acute heart attack or hypertensive emergencies.
Secondary Uses: Off-label and Other Clinical Scenarios
Labetalol, primarily used for treating hypertension, has other applications and specific uses in clinical settings. These include being used as a treatment for heart failure and to alleviate symptoms of tachycardia caused by anxiety. It's important to note that despite growing evidence supporting these secondary uses, they are not universally accepted or endorsed.
- Treating angina pectoris
- Postoperative hypertension
- Managing anxiety-induced tachycardia.
Use in Pheochromocytoma
Pheochromocytoma is a tumor found in the adrenal gland. It can cause increases in blood pressure due to the overproduction of catecholamines. With its pharmacological characteristics, Labetalol is an excellent choice for reducing these high blood pressure episodes and helps minimize the risks of irregular heart rhythms and reduced blood flow to the heart that often accompanies this condition.
Use in Pregnancy-Induced Hypertension
Labetalol has become widely acknowledged for its safety and effectiveness in treating hypertension during pregnancy. High blood pressure caused by pregnancy can pose risks to both the mother and the baby, making it crucial to act promptly and effectively. Healthcare professionals favor Labetalol due to its documented safety record and ability to cross the placental barrier without causing significant harm to the fetus.
How Labetolol Works
Mechanism of Action
Labetalol blocks alpha and beta receptors in the nervous system, leading to various physiological changes. These changes include widening blood vessels (vasodilation) and decreased heart rate. As a result, it effectively lowers blood pressure, which is the main goal in managing hypertension.
- Vasodilation causes the expansion of blood vessels
- The reduction in heart rate reduces the demand for oxygen by the heart muscle
- Consistently controlling blood pressure.
Alpha and Beta Receptor Blocking
Labetalol works by reducing the function of alpha and beta receptors. By blocking alpha receptors, it helps widen arteries and decrease resistance. At the time, it blocks beta receptors, slowing heart rate and lowering cardiac output. Therefore, this medication acts synergistically to optimize parameters.
Comparative Efficacy: How Does Labetolol Stand Against Other Antihypertensive Drugs?
Compared to medications used to treat high blood pressure, Labetalol has several distinct advantages. Its ability to block two receptors makes it a comprehensive and effective treatment option, eliminating the need for multiple medications in some cases. Additionally, it has side effects and starts working quickly, making it especially useful in urgent medical situations. It also risks causing dizziness upon standing and metabolic disturbances while helping normalize blood pressure promptly.
Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosages for Adult Patients
Typically, adult patients start with a dose of 100 mg taken twice a day to treat hypertension. However, the dosage may need to be adjusted depending on the response to the treatment. An initial dose of 20 mg can be used in administration, and further adjustments can be made based on the clinical situation.
Adjustments for Specific Medical Conditions
Considering the range of medical conditions people have, it may be necessary to make adjustments in the dosage. For example, individuals with existing problems might require lower initial doses to reduce the potential risks of low blood pressure or a slow heart rate.
Renal Impairment
Patients who have insufficiency often require adjustments to their medication dosage. Due to the metabolites eliminated through the kidneys, it is essential to monitor and adjust the dosage to prevent any potential complications caused by medications, such as drug toxicity or worsened low blood pressure.
Hepatic Impairment
Likewise, when the liver is not functioning correctly, it can significantly affect how Labetalol is processed. To ensure safety and effectiveness, following a dosage plan often involves lower doses, and close monitoring of patients with liver problems is essential.
How to Administer Labetolol Injection: Step-by-Step Guidelines
When administering Labetalol intravenously, following the established guidelines is crucial to ensure maximum effectiveness and minimize any potential adverse effects. The usual procedure involves using techniques and following these steps:
- Prepare the syringe with the dosage.
- Verify the patient's identity. Review their medical history.
- Confirm that the IV line is open and functioning correctly.
- Administer the injection slowly over two minutes.
- Continuously monitor the patient's hemodynamics after administration.
By adhering to these steps, we can ensure the administration of Labetalol while prioritizing safety and efficacy.
Composition of Labetolol Injection
Active Ingredients
The main ingredient in Labetolol injection is Labetalol hydrochloride, which is unsurprising. This active component acts as a selective adrenergic receptor antagonist and plays a significant role in producing the well-known antihypertensive effects of the medication. Labetalol hydrochloride is primarily responsible for achieving results. Additionally, it's worth noting that the enantiomeric mixture of this compound contains both R and S enantiomers.
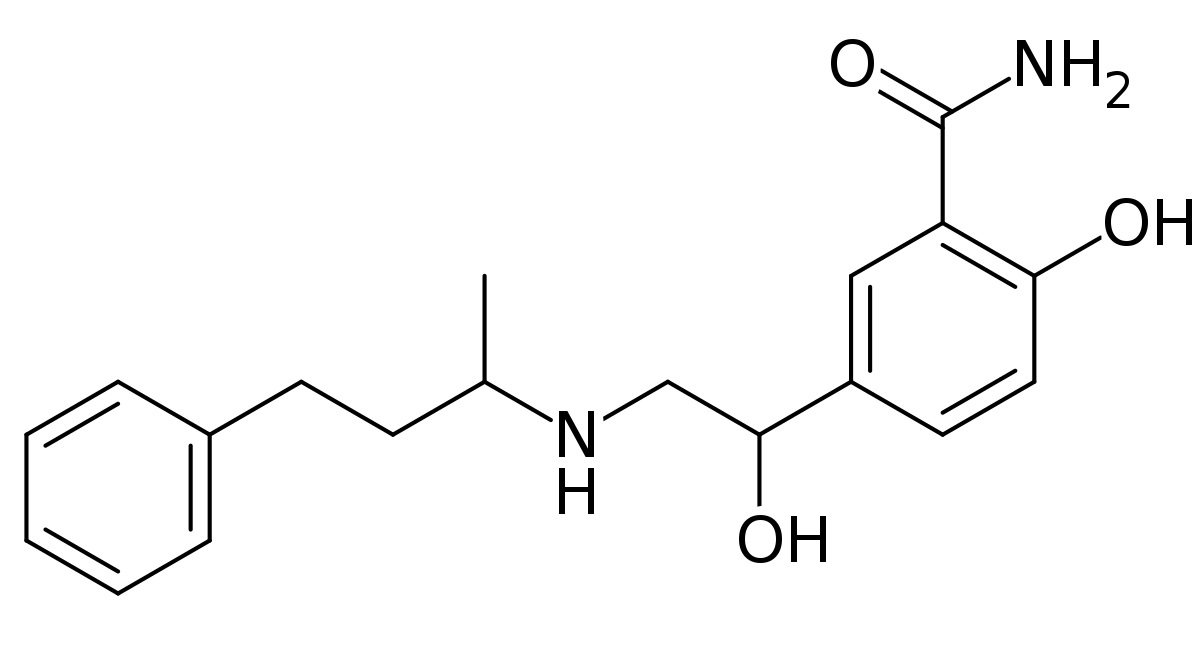
Inactive Ingredients
Apart from the components, Labetolol injection also includes a range of inactive ingredients that act as stabilizers, solubilizers, or preservatives. These may consist of water for injection, citric acid for pH adjustment, and sodium chloride for solubility.
- Water for injection serves as the solvent
- Citric acid helps regulate the pH levels
- Sodium chloride acts as an osmolarity regulator.
Available Concentrations
Labetolol injection is readily available in varying concentrations, typically ranging from 5 mg/mL to 20 mg/mL. These different concentrations allow for dosage adjustments, making it suitable for various clinical situations and each patient's needs.
Storage Conditions for Labetolol Injection
Temperature Guidelines
It's crucial to follow temperature guidelines to maintain the quality of Labetolol injection. It would be best if you stored the infusion at a controlled room temperature, typically ranging from 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F).
Light and Moisture Sensitivity
Labetolol can degrade if it is exposed to much light and moisture. Therefore, storing the vials in their carton is essential to protect them from these harmful environmental conditions.
Shelf Life and Expiry
The usual duration for which Labetolol injection remains effective is 24 months from the time it is manufactured. However, discarding any product that has exceeded its expiry date or displays any signs of discoloration is essential.
Drug Interactions
Commonly Interacting Medications
Like pharmaceutical drugs, Labetolol doesn't work within the clinical realm in isolation. It has been observed to interact with medications, including but not limited to antipsychotics, antiarrhythmic, and certain anesthetics. These interactions can influence how the drug affects the body in terms of its pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics.
- Antipsychotics: Enhancing the hypotensive effects
- Antiarrhythmics: Modifying responses
Antidiabetic Medications
When taking medications simultaneously, monitoring your blood sugar levels closely is essential. Labetolol can make it difficult for doctors to detect a heartbeat caused by low blood sugar, a common symptom they rely on for diagnosis.
Other Antihypertensive Agents
When taken together with medications for high blood pressure, there can be a combined effect that lowers blood pressure. In some cases, it may be necessary to adjust the dosage to prevent shallow blood pressure that could lead to a sudden drop in circulation.
Herbal and Supplement Interactions
Interactions go beyond pharmaceutical drugs. Even herbal supplements like St. John wort or ginseng can impact the effects of Labetolol, either reducing or intensifying them. Therefore, it is essential to have a patient history that includes all supplements to achieve the best clinical outcomes.
Warnings and Contraindications
Medical Conditions that Prohibit Labetolol Use
Although Labetolol has been widely used as a medication for hypertension, it is not suitable for everyone. There are medical conditions where its usage is contraindicated. For instance, patients with heart failure or severe bradycardia should avoid taking this medication.
- Uncontrolled heart failure can worsen symptoms. Reduce the effectiveness of the heart-pumping ability.
- Severe bradycardia has the potential to cause life-threatening cardiac events.
Heart Failure
Labetolol may not be suitable for patients with controlled heart failure. While its beta-blocking effect is beneficial for treating hypertension, it can potentially worsen function in such individuals, exacerbating heart failure symptoms.
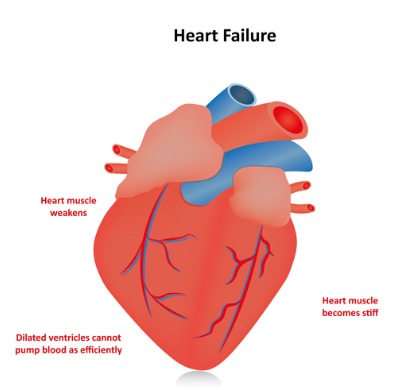
Severe Bradycardia
Bradycardia, which refers to a low heart rate, presents another significant concern. The blocking effect of labetolol on the nervous system may further decrease the heart rate, potentially leading to a dangerous disruption in blood flow.
Drug Allergies and Cross-Reactivity
Patients who experience responses to Labetolol or any of its inactive components should avoid using it. Additionally, it is important to examine potential cross-reactivity with other beta-blockers or alpha-blockers before starting treatment.
Careful Administration and Important Precautions
Monitoring Vital Signs
It is crucial to monitor vital signs while administering Labetolol. Monitoring blood pressure and heart rate provides information about the effects of the medication on the body's hemodynamics. First, it is essential to establish vital signs before starting the administration. This initial assessment helps select a reference point for comparison. Regular monitoring should be conducted throughout the administration process to ensure the medication is working effectively. We can determine if the treatment achieves its intended therapeutic effects by reassessing vital signs.
Role of Healthcare Provider in Supervising Administration
Healthcare providers play a role in responsibly administering Labetolol. Their duties include adjusting the dosage based on monitored factors, promptly addressing reactions, and educating patients about possible side effects.
Signs to Watch Out for During Treatment
Both healthcare providers and patients need to remain vigilant in identifying signs of adverse drug interactions or side effects. These can manifest in ways including but not limited to symptoms like feeling lightheaded, experiencing low blood pressure, or encountering respiratory problems such as difficulty breathing. Feeling lightheaded could suggest a decrease in blood pressure, while low blood pressure may require immediate intervention. It's important to note that bronchospasm, although rare, is a respiratory complication that should be taken seriously.
Special Populations: Dosage and Precautions
Administration to the Elderly
The elderly population presents a challenge regarding treatment because their body processes drugs differently. When using Labetolol3, it is crucial to adjust the dosage to avoid giving too much medication, which can cause low blood pressure and other adverse effects. It is recommended to start with a dose due to their slower metabolism. Additionally, regularly monitoring their parameters is essential for proper evaluation.

Age-Related Dosage Adjustments
In cases where patients are older, adjustments to the usual dosage may be needed to consider any potential kidney or liver function issues. We can minimize the chances of effects accumulating over time by reducing the dosage or extending the time between doses.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Labetolol has been prescribed for cases of hypertension during pregnancy. However, assessing the balance between risks and benefits is crucial since there is limited conclusive research on its impact on the fetus. Nursing mothers should be cautious as the medication can pass into breast milk.

Safety Profile and Guidelines
The safety of Labetolol in women and nursing mothers is still being studied. While animal studies have not shown any effects, it is essential to exercise caution and seek medical supervision on the developing fetus.
Administration to Children
Although there is research on using Labetolol in children, it can be considered in specific situations, particularly for hypertensive emergencies. However, it is essential to exercise increased caution when using this medication in patients. It is crucial to follow pediatric protocols and make necessary adjustments based on age and weight for accurate dosing.

Pediatric Dosage and Safety
Adjusting the dosage according to a child's body weight is often advised. Monitoring and promptly recognizing any possible adverse effects is essential to make necessary treatment adjustments.
Side Effects of Labetolol
Common Side Effects
Like any medication, Labetolol has its share of side effects2. Fatigue and dizziness are among the frequently reported adverse reactions, typically of a mild and temporary nature.

Fatigue
Fatigue is a side effect that can occur due to the drug's impact on the sympathetic nervous system. Although it is usually mild, it might require adjusting the dosage or further assessment.
Dizziness
Patients may feel lightheaded, mainly from sitting or lying down to standing. When changing positions, this blood pressure drop requires consideration of the initial dosage and continuous monitoring.
Serious Side Effects
Sometimes, although it's not common, Labetolol can cause side effects that need immediate medical attention. These can include blood pressure and irregular heart rhythms.
Hypotension
Sudden and significant decreases in blood pressure can happen, especially when starting the treatment. If such episodes of blood pressure occur, immediate adjustments in the treatment are needed, and in severe situations, the medicine may need to be stopped.
Heart Arrhythmias
Although Labetolol usually helps stabilize heart rhythms, it can unexpectedly trigger arrhythmias in some vulnerable people. These incidents are typically uncommon. Require immediate medical attention.
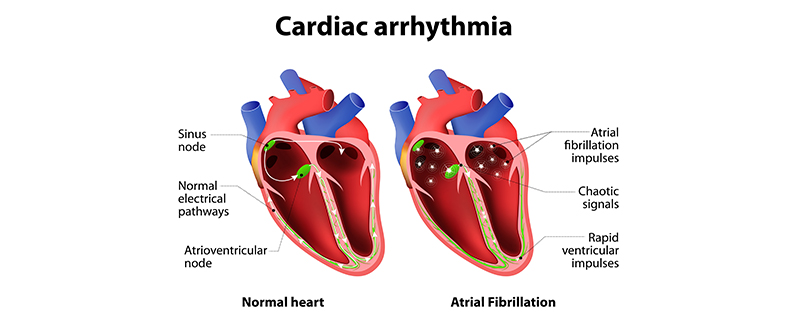
Overdose and Handling Precautions
Symptoms of Labetolol Overdose
Taking an amount of Labetolol requires prompt identification and intervention. Although it usually has a therapeutic range, exceeding the recommended dosage can lead to harmful consequences. Signs of an overdose include:
- Profound Hypotension: A significant decrease in blood pressure.
- Bradycardia: low heart rate.
- Respiratory Distress: Symptoms indicating lung function.
Recognizing these symptoms and taking appropriate action to address the situation effectively is crucial.

Emergency Protocols for Overdose
In the event of an overdose, promptly providing symptomatic and supportive treatment is crucial. Medical professionals should focus on stabilizing the cardiovascular systems as a top priority. While specific antidotes may not be accessible, supportive care remains the foundation of managing cases.
Safety Measures to Prevent Overdose
It is essential to implement various precautionary measures to prevent the dangers of taking too much medication. These measures are not restricted to:
- Strictly following the prescribed dosage as instructed
- Ensuring the drug is stored in a secure and out-of-reach place
- Educating patients about the warning signs of an overdose
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
The various uses and possible consequences of Labetolol and its use among different groups of people make it a complex but precious medication. Its unique ways of working in the body and how it affects drugs require administration and close monitoring.
Recommendations for Patients and Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers understand the importance of considering a patient's medical history, medications they are taking, and any unique metabolic characteristics they may have. This attention to detail is essential for achieving the possible treatment results. Patients are encouraged to work with their healthcare providers and promptly report any symptoms or adverse events they experience.
- Continual Monitoring: Regularly checking for and addressing any side effects to maximize the treatment's effectiveness.
- Collaborative Care: A collaborative approach involving patients and healthcare providers working together towards a goal.
Further Resources and References
To understand the pharmacology, proper dosing, and evidence-based recommendations for Labetolol, individuals must consult reliable sources such as peer-reviewed medical journals and treatment guidelines provided by reputable healthcare organizations.











