Labetolol
- I. Introduction to Labetolol
- II. Composition of Labetolol
- III. How Labetolol Works
- IV. Indications and Uses of Labetolol
- V. Off-Label Uses of Labetolol
- VI. Dosage and Administration of Labetolol
- VII. Important Precautions while using Labetolol
- VIII. Side Effects of Labetolol
- IX. Contraindications and Warnings Associated with Labetolol
- X. Careful Administration of Labetolol
- XI. Drug Interactions with Labetolol
- XII. Labetolol Overdosage
- XIII. Storage Guidelines for Labetolol
- XIV. Handling Precautions for Labetolol
I. Introduction to Labetolol
A. Brief Overview and History of Labetolol
Labetalol, a used medication for treating high blood pressure and chest pain known as angina, was first introduced in the 1980s. It quickly became a game changer in the field of medicine because of its unique ability to work in two different ways. This dual mechanism of action has proven incredibly beneficial for patients who do not respond well to medications alone.
B. Importance and Significance in Medical Field
For over forty years, Labetalol has demonstrated its effectiveness as a fundamental component of cardiovascular pharmacology. It stands out from medications due to its ability to regulate high blood pressure, particularly during pregnancy. Additionally, it plays a role in treating hypertensive emergencies requiring immediate blood pressure control.
II. Composition of Labetolol
A. Chemical Composition and Structure
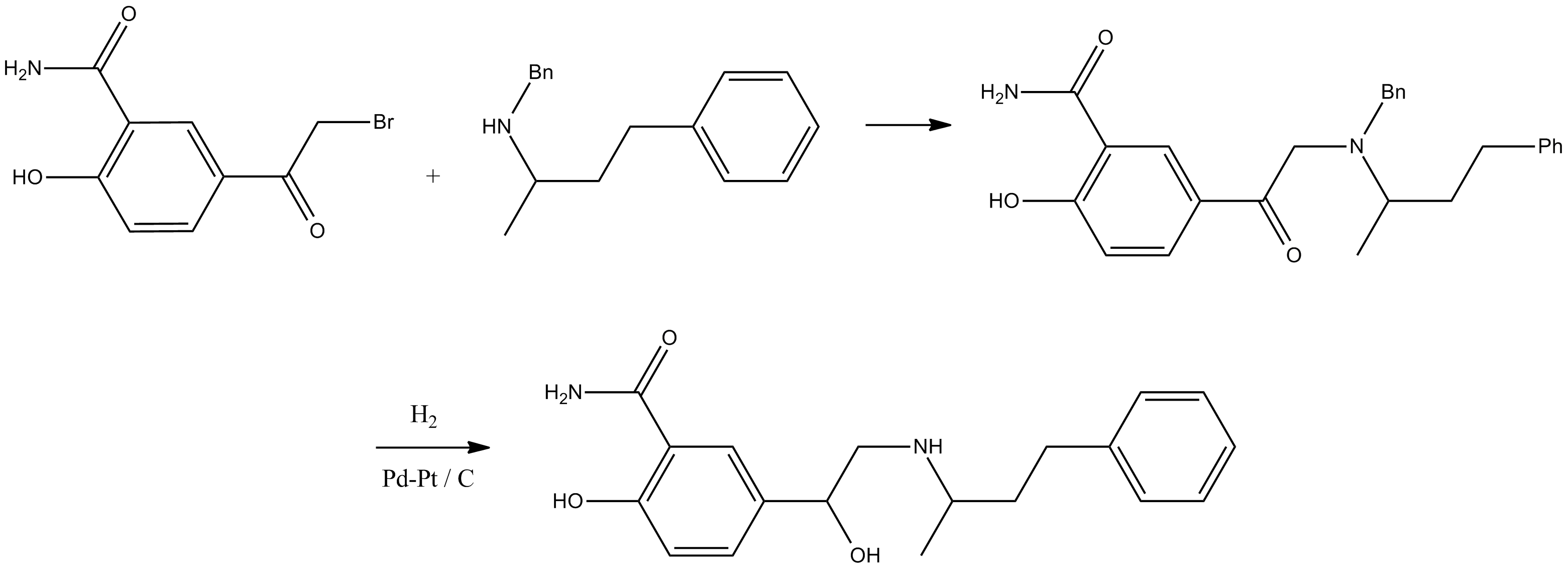
Labetalol, which functions, as an alpha and beta blocker has an intricate chemical structure. Its official chemical name is 2 hydroxy 5 [1 hydroxy 2 [(1 methyl 3 phenylpropyl)amino]ethyl] benzamide. This compound has the characteristic of being amphiphilic and contains two chiral carbon atoms leading to the presence of two pairs of enantiomers.
B. Variations in Formulation and Brand Differences
Labetalol is widely used due to its popularity. It comes in brand formulations that are designed for different clinical situations. For maintenance, there are oral tablets available while for acute cases injectable solutions are used. Some known brands, like Trandate and Normodyne, offer oral preparations whereas Labeta specializes in injectable formulations.
III. How Labetolol Works
A. Mechanism of Action in the Body
Labetalol demonstrates its effectiveness by working in two ways. It blocks both alpha and beta adrenergic receptors in the body reducing heart rate and myocardial contractility to lower output. At the time it causes peripheral vasodilation by blocking alpha 1 receptors, which helps to decrease systemic vascular resistance. This combination of actions is beneficial for controlling blood pressure.
B. Targeted Systems and Organs
Labetalol is a medication with uses in treating high blood pressure. Its primary focus is on the system, where it works to decrease the hearts output and widen the blood vessels. It also affects the system, particularly the juxtaglomerular cells, which helps regulate blood pressure by reducing the release of renin.
IV. Indications and Uses of Labetolol
A. Approved Therapeutic Uses
Labetalol is a medication that belongs to the class of beta blockers. It acts by blocking alpha and beta-adrenergic receptors. This decreases peripheral vascular resistance without significantly altering heart rate or cardiac output. Labetalol works by relaxing blood vessels and slowing heart rate to improve blood flow and decrease blood pressure1.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Labetalol:
- 1Labetalol - Wikipedia
- 2Labetalol: MedlinePlus Drug Information
- 3Labetalol: Indication, Dosage, Side Effect, Precaution - MIMS
- 4Labetalol: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action | DrugBank Online
B. Comparative Effectiveness with Other Medications
Labetalol is a medication that doctors prescribe to help manage blood pressure. It is used either alone or in combination with other medications. By reducing blood pressure it aids in preventing strokes, heart attacks, and kidney complications1.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Labetalol:
- 2Labetalol - Wikipedia
- 1Labetalol: MedlinePlus Drug Information
- 3Labetalol: Indication, Dosage, Side Effect, Precaution - MIMS
- 4Labetalol: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action | DrugBank Online
V. Off-Label Uses of Labetolol
A. Summary of Off-Label Uses
Labetalol is a medication that doctors prescribe to help manage blood pressure. It is used either alone or in combination with other medicines. Reducing blood pressure, it aids in preventing strokes, heart attacks, and kidney complications1.
Although it is not an officially approved use, Labetalol can also be prescribed for conditions like pheochromocytoma (a tumor that leads to high blood pressure), anxiety disorders, and migraine headaches2.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Labetalol:
- 2Preoperative Management of the Pheochromocytoma Patient | The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism | Oxford Academic
- 1Labetalol: MedlinePlus Drug Information
- 3Labetalol: Indication, Dosage, Side Effect, Precaution - MIMS
- Labetalol: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action | DrugBank Online
B. Evidence Supporting Off-Label Uses
Labetalol is not officially approved for treating anxiety disorders and migraine headaches. Further investigation is required to ascertain the efficacy of labetalol in addressing off-label ailments like anxiety disorders and migraine headaches. Nevertheless, there is evidence supporting the effectiveness of labetalol in treating pheochromocytoma.
Here are some references that you can check for more information about Labetalol:
- Preoperative Management of the Pheochromocytoma Patient | The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism | Oxford Academic
- Labetalol: MedlinePlus Drug Information
- Labetalol: Indication, Dosage, Side Effect, Precaution - MIMS
VI. Dosage and Administration of Labetolol
A. Recommended Dosage for Different Conditions
The dosage of Labetolol can vary depending on the severity of the condition and how the patient responds to the treatment. Typically for patients with blood pressure, it is recommended to start with an oral dose of 100 mg twice a day and then gradually increase it based on how their blood pressure responds. The usual maintenance dose is usually between 200 and 400 twice a day. In emergencies, it is suggested to begin with an initial dose of 20 mg, through intravenous administration followed by additional increments as necessary.
B. Adjustments for Specific Patient Populations
Administering Labetalol requires attention, especially when dealing with specific groups of patients. For example, older individuals may need an initial dose because their body processes the medication differently. Patients with kidney or liver issues might also require dosage adjustments due to reduced ability to metabolize and eliminate the drug. On the other hand, pregnant women with hypertension often find Labetolol a preferred option, and any necessary dosage changes are made based on blood pressure control.
VII. Important Precautions while using Labetolol
A. Prior Health Conditions to Consider
It is essential to be cautious when administering Labetalol to patients with pre-existing health conditions. These conditions include asthma or related bronchospastic conditions, as Labetolols beta-blocking activity can worsen these conditions. Individuals with overt heart failure or a history of heart failure should also be careful. Patients with bradycardia may also face risks due to further lowering their heart rate.
B. Lifestyle Factors and Labetolol Administration
Various aspects of one's lifestyle can impact how effectively and safely Labetalol works. For instance, if you consume alcohol, it can worsen the blood pressure-lowering effects of Labetolol, potentially resulting in hypotension. Likewise, those who engage in exercise should be aware of the heart rate-reducing effects that Labetalol may have.
VIII. Side Effects of Labetolol
A. Common Side Effects and Their Management
Like any medication, Labetalol may cause side effects. Some common ones include feeling dizzy, tired, or nauseous. Usually, these effects are mild and go away as your body gets used to the medicine. If they continue or bother you, it's an idea to consult with a healthcare professional. Moreover, staying well hydrated can often help alleviate these side effects.

B. Serious and Rare Side Effects
Sometimes, when using Labetolol, severe side effects may require immediate medical attention. These side effects include bradycardia, which's an abnormally slow heart rate. Another powerful side effect is heart failure, where symptoms like shortness of breath, swollen ankles or feet, unusual tiredness, and sudden weight gain may occur. Additionally, there is a risk of hepatotoxicity, which can present symptoms such as nausea or vomiting, severe stomach or abdominal pain, yellowing of the eyes or skin, and dark urine.
IX. Contraindications and Warnings Associated with Labetolol
A. Specific Medical Contraindications
Contraindications refer to health conditions or situations in which it is not advisable to use medication because of the possibility of adverse effects or the drug not working effectively. Some specific instances where Labetolol should be avoided include; Patients with asthma or a history of obstructive airway disease, as there is a potential risk of triggering bronchospasm. Individuals with third-degree heart block that is not controlled with a pacemaker. Patients who have a cardiac failure or cardiogenic shock. Individuals with severe bradycardia or heart rates below 45-50 beats per minute.
B. Situational Warnings and Precautions
It is crucial to provide warnings to prevent serious adverse events. Regarding Labetolol, it's essential to be cautious about stopping the therapy as it can worsen angina symptoms or even trigger a heart attack. Patients with hypersensitive reactions to Labetolol or related compounds should avoid using it.
X. Careful Administration of Labetolol
A. Administration to Elderly Patients
Due to the changes that come with aging, such as reduced kidney function and increased sensitivity to beta blockers, elderly individuals might have a varied responses to Labetolol. As a result, it is recommended to begin with dosage and adjust it carefully based on their response to the treatment and their ability to tolerate it.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Labetalol falls under pregnancy category C, which means it should only be used during pregnancy if the potential benefits are more significant than the risks. It's important to mention that Labetolol can pass through the barrier and be found in cord blood. Additionally, it is also excreted in breast milk, so nursing mothers should use it cautiously.
C. Administration to Children
The use of Labetolol in patients has not been proven to be safe and effective. As a result, it is not recommended for this age group.
XI. Drug Interactions with Labetolol
A. Common Drug-Drug Interactions
Labetalol has the potential to interact with medications, which can affect how the drugs work or increase the chances of experiencing side effects. Some examples of interactions include; When combined with other antihypertensive medications, it may result in intensified low blood pressure effects. If taken alongside drugs that deplete catecholamines, adjustments to the Labetolol dosage may be necessary. The combination of Labetalol, with insulin or oral hypoglycemic, can enhance their ability to lower blood glucose levels.
B. Drug-Food and Drug-Lifestyle Interactions
Labetolol can cause a drop in blood pressure. Drinking alcohol can make this effect even stronger, leading to orthostatic hypotension. It's worth noting that smoking can work against Labetolols ability to lower blood pressure. Additionally, if someone consumes amounts of caffeine, it may worsen their high blood pressure. To stay on the side patients should consult with their healthcare provider before making any significant changes, to their diet or lifestyle while taking Labetolol.
XII. Labetolol Overdosage
A. Signs and Symptoms of Overdose
Taking much Labetolol can result in an overdose, which shows various signs and symptoms. These can include low blood pressure, slow heart rate, heart failure, difficulty breathing, and low blood sugar levels. In addition, an overdose may lead to seizures, tiredness, pauses or stops in the heartbeat rhythm, and loss of consciousness.
B. Immediate Actions and Treatment Options
If you suspect an overdose, it's crucial to seek medical help. The focus of overdose treatment is addressing the symptoms and providing care to maintain essential bodily functions. After ingestion, the healthcare provider may consider performing gastric lavage or inducing vomiting. In cases with low blood pressure, intravenous fluids can be given to counteract it and for more critical situations vasopressors might be used. Furthermore, glucagon has proven effective in managing overdose symptoms in patients.
XIII. Storage Guidelines for Labetolol
A. Optimal Storage Conditions
Labetolol needs to be stored at room temperature, between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Make sure it's kept away from sunlight and moisture. Store it in a childproof place, ensuring that pets cannot access it to prevent accidental ingestion.
B. Shelf Life and Disposal
The packaging of Labetolol generally indicates its shelf life. It is crucial to refrain from using the drug once it has expired. Disposing of it should be done in compliance, with regulations. It is important to avoid flushing medications down the toilet or pouring them into drains unless specifically instructed. The recommended approach is to return any expired medications to a take back program or collection site.
XIV. Handling Precautions for Labetolol
A. Safety Measures during Handling and Administration
When dealing with Labetolol it is crucial to prioritize safety. It is essential to follow the dosage a healthcare professional provides and avoid sharing the medication with anyone else. Always practice hand hygiene before and after administering the drug, and make sure to store it in a secure place away from children and pets.
B. Accidental Exposure Scenarios and Corrective Measures
If someone accidentally comes into contact with this medication, like a child or pet swallowing it, it's crucial to seek help immediately. If the medicine gets in the eyes or on the skin, make sure to rinse it with plenty of water. Anyone who feels unwell or experiences any unusual symptoms after accidental exposure should promptly consult a healthcare provider.
Labetolol FAQ
- What are the side effects of Labetalol?
- What is the dose of Labetalol?
- What is the brand name of Labetalol?
- Can Labetalol be used during pregnancy?
- What are the uses of Labetalol?
- What is the significance of Labetalol 200 mg?
- What is the mechanism of action of Labetalol?
- What is Labetalol HCL?
- What is the intravenous (IV) dosage of Labetalol?
- Is Labetalol a beta blocker?
- What are other names for Labetalol?
- What are the side effects of Labetalol in pregnancy?
- How does Labetalol compare to Metoprolol?
- What is the maximum dose of Labetalol?
- What is the generic name of Labetalol?
- What are the drug interactions of Labetalol?
- What is the half-life of Labetalol?
- Is Labetalol safe for breastfeeding?
- What is the drug class of Labetalol?
- What are the contraindications of Labetalol?
- What is the class of Labetalol?
- Does Labetalol treat blood pressure?
- Is Labetalol used for anxiety?
- Is Labetalol used for preeclampsia?
- Can Labetalol be used while breastfeeding?
- What is Labetalol used for ("para que sirve")?
- Can Labetalol be used during pregnancy?
- What is the IV to PO conversion for Labetalol?
- Can Labetalol be taken with alcohol?
- How does Labetalol compare to Carvedilol?
- What is a Labetalol pill?
- How is Labetalol given as an IV push?
- What are the warnings associated with Labetalol?
- Labetalol side effects anxiety
- Labetalol duration of action
- Labetalol drip
- Labetalol brand
- Labetalol cost
- Labetalol with asthma
- Labetalol vs nifedipine
- Labetalol indication
- Labetalol IV half-life
- Labetalol hydrochloride injection
- Labetalol half-life IV
- Labetalol name
- Labetalol and heart rate
- Labetalol vs propranolol
- Labetalol overdose
- Can labetalol cause headaches?
- What is labetalol HCl used for?
- Labetalol and nifedipine?
- Labetalol selective or nonselective?
- Labetalol effect on heart rate?
- Labetalol patient teaching?
- Labetalol Trandate?
- Labetalol safe for pregnancy?
- Labetalol side effects heart rate?
- Labetalol false positive drug test?
- Labetalol beta 1 or 2?