Lamivudine
- I. Introduction to Lamivudine
- II. The Pharmacology of Lamivudine: How it Works
- III. The Clinical Uses of Lamivudine
- IV. Off-Label Uses of Lamivudine
- V. Dosage and Administration of Lamivudine
- VI. Special Considerations for Administration
- VII. Potential Side Effects of Lamivudine
- VIII. Understanding Drug Interactions with Lamivudine
- IX. Warnings and Contraindications for Lamivudine Use
- X. Overdose: Risks and Management
- XI. Proper Storage and Handling Precautions for Lamivudine
- XII. Important Precautions when Using Lamivudine
- XIII. Conclusion: The Careful Use of Lamivudine
I. Introduction to Lamivudine
A. Overview of Lamivudine and its Therapeutic Purpose
In medical treatment for Hepatitis B and HIV/AIDS patients, Lamivudine emerges as a prominent synthetic nucleoside analog drug type known as a reverse transcriptase inhibitor. By intervening with the viral DNA replication process, it effectively curtails virus growth inside human bodies. This significantly contributes towards the reduction of disease manifestations and arrest of further deterioration.1.
B. The Importance of Understanding Medications
Recognizing their mechanisms and effects is a key factor in utilizing medications like Lamivudine safely and effectively. Comprehensive comprehension regarding dosage requirements, potential adverse reactions, or drug interactions empowers those involved in medical care - whether patients or healthcare providers - by providing them with valuable knowledge that enables them to make informed decisions concerning available treatments options without complications or risks involved in managing the medicinal routine involved for a successful therapy outcome.
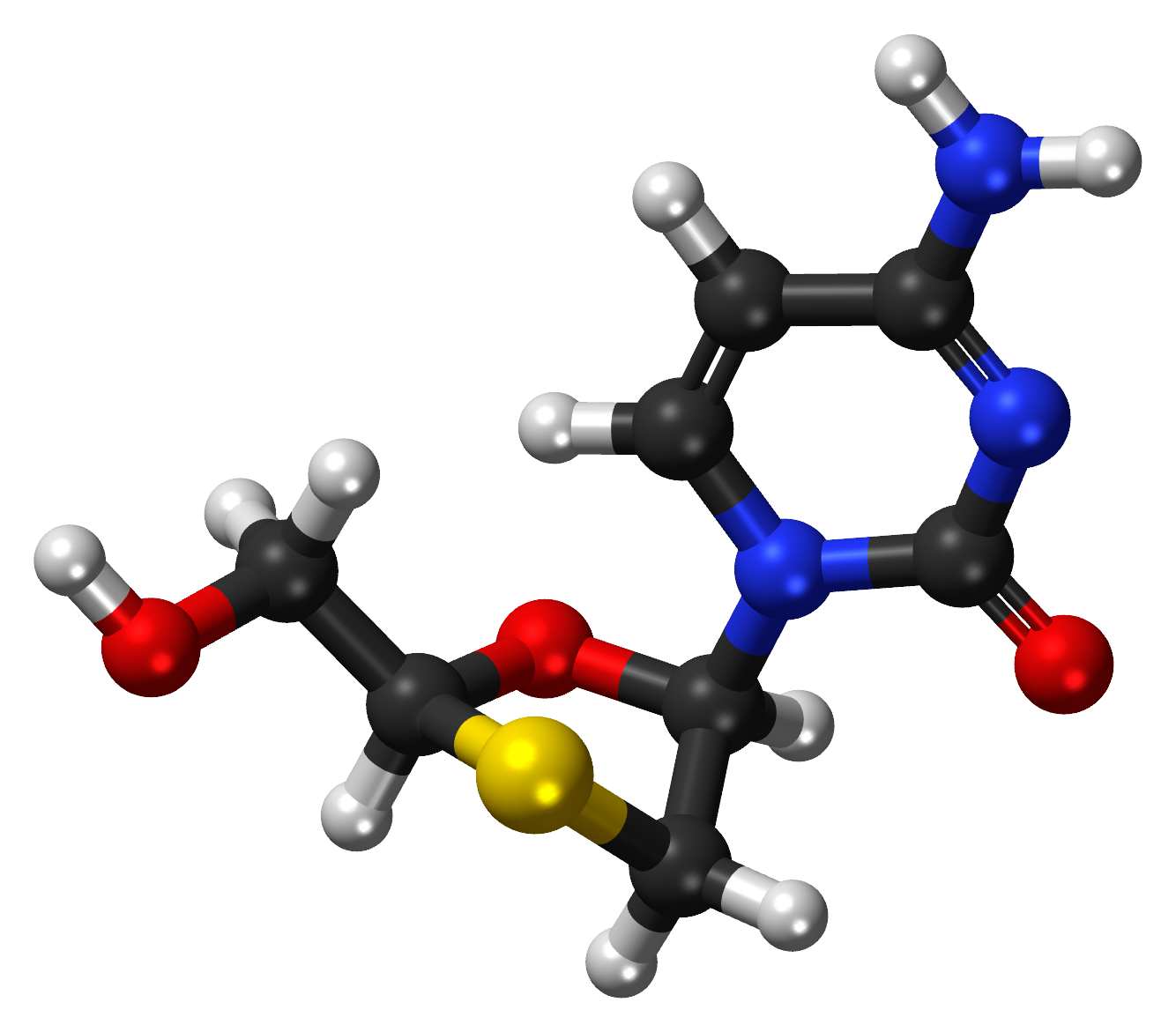
C. Brief on the Composition of Lamivudine
When prescribed as an antiviral medication, the chemical compound lamivudine takes the form of oral tablets and solutions. Additional substances known as excipients are added to these medications to help enhance drug disposition while the active ingredient remains constant -namely, lamivudine. Given its powdery consistency being classified from white-to-off-white in appearance, lamivudine white eventually dissolves within the body after being ingested into whichever form is preferred by patients and doctors alike2.
II. The Pharmacology of Lamivudine: How it Works
A. Mechanism of Action in the Body
An essential aspect of Lamivudine's mechanism is its ability to hinder reverse transcriptase- a fundamentally pivotal enzyme in HIV and Hepatitis B virus propagation. It combines with the viral DNA chain during reproduction, leading to untimely termination. Consequently, this medication curtails the growth rate of viruses while limiting their adverse impact on body cells.3.
B. Pharmacokinetics: Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion
Lamivudine gets absorbed into our system from the gastrointestinal tract quicker than most medications, boasting over 80% of bioavailability. Funneling itself into body tissues and fluids beyond plasma makes its distribution more prodigious. Its metabolism distinguishes it from other drugs as it doesn't undergo extensive phase I biotransformation. Instead, it gets excreted mostly unchanged as organic cationic secretion is present within urination cycles. The processing time duration lingers roughly 5-7 hours in adult bodies and dips to around two hours in neonates and infants4. Adhering to a profound comprehension of Lamivudine's pharmacokinetic traits becomes crucial when aiming for maximal therapeutic potential without negative impacts arising.
III. The Clinical Uses of Lamivudine
A. Approved Indications for Lamivudine
For individuals afflicted with two prevalent viral infections, Lamivudine represents a critical treatment option that can make a significant difference in the progression of their disease. Specifically, this medication is an essential component of antiretroviral therapy (ART) regimens for HIV/AIDS patients and acts in association with other drugs to suppress the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). 1. As a result, it has proven highly useful in reducing morbidity and mortality rates. Furthermore, for those diagnosed with chronic Hepatitis B - another viral infection notorious for impacting liver function - Lamivudine is highly effective. Essentially reducing viral load in afflicted individuals and helping mitigate the risk of potential liver-related complications. 2.
B. Clinical Studies Supporting its Uses
In managing both HIV/AIDS and chronic Hepatitis B, healthcare professionals can confidently rely on Lamivudine based on solid evidence from clinical trials and studies. One influential trial - the CAESAR study - found that combining Lamivudine with other antiretroviral agents reduced mortality rates and morbidity associated with HIV3. Another notable research report published by The Lancet demonstrated substantially improved liver histology among patients treated with this medication compared to those who received a placebo4. The results from such comprehensive studies attest to the importance of using Lamividune as part of an effective treatment strategy.
IV. Off-Label Uses of Lamivudine
A. Exploration of Common Off-Label Uses
Lamivudine is a widely prescribed medication in the healthcare sector known for its commendable competence in tackling HIV/AIDS and Hepatitis B patients globally. Nevertheless, research studies have explored this drug and suggested possible clinical benefits for various causes beyond its approved indications1. Let's look at these off-label applications dermatologists have been using with success! In unique scenarios where hepatitis D is present, health professionals may combine interferon with Lamivudine as an effective management plan to counter significant symptoms. Additionally, post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) regimes include LAM due to its innate antiviral properties combating infection and reducing viral load after potential exposure to HIV through sex or shared needles encounters2.
B. Clinical Research on Off-Label Applications
Although clinical research examining off-label applications cannot produce results as substantial as those focused on primary aims, credible information supports some Lamivudine uses. Patients suffering from the Hepatitis D virus have benefited from this medication when combined with interferon, according to a study published in the Journal of Hepatology; this method led to an extended and desired virological response3. Similarly encouraging is an investigation reported by the Journal of Clinical Virology revealing decreased seroconversion risk when patients undergoing Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) were treated with Lamivudine. These studies suggest lamivudine potential benefits in a broader range of situations. But as usual, careful medical supervision must accompany the use of this drug off-label. 4.
V. Dosage and Administration of Lamivudine
A. Standard Dosage Guidelines for Adults
Individuals receiving treatment with Lamivudine are prescribed varied dosages dependent upon unique medical requirements and the respective conditions being treated. For those managing HIV/AIDS symptoms and illness, typical recommendations involve taking approximately3--0 mg/day that can either be taken all at once as one solo dose or divided into two equal50% doses -each totaling approximately150 mg—for more even ingestion across each day1. When treating chronic Hepatitis B symptoms in adulthood patients, though-—and by comparison-—the suggested regimen amounts to around 100 mg/day instead2.
B. Dosage Adjustments for Specific Populations
Diverse factors can impact how our bodies handle medications, highlighting the need for specific dosage adjustments in certain populations. Renal impairment, which reduces drug clearance capacity, calls for close attention when prescribing medicines as it may require tailored dosages for afflicted individuals. Timely monitoring of renal function remains essential3.
C. The Correct Way to Administer Lamivudine
There are distinct options of both tablet and liquid forms for Lamivudine medication. It is good to note that it can be consumed with or without meals. Nonetheless, preserving drug efficiency will demand daily consistency when taking it as well as timely remembrance of any missed doses4.
VI. Special Considerations for Administration
A. Administration to Elderly Patients
It's necessary to exercise caution when administering Lamivudine to elderly patients, just as with any medication. This demographic frequently encounters renal function changes that could necessitate modifying the dosage. It is recommended to conduct regular checkups for possible adverse reactions5.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
If considering administering Lamivudine during pregnancy or lactation, individuals should carefully evaluate whether its potential benefits justify any associated risks. Although this medication does pass into breast milk and may have some unknown effects on newborns as a result of ingestion via breastfeeding, its' necessary that people discuss their options with a healthcare professional before proceeding6.
C. Administration to Pediatric Patients
When prescribed to children, Lamivudine is safe for use upon approval, with dosage adjusted according to their weight. Monitoring the child's response and detecting unfavorable reactions are crucial for ensuring effectiveness7.
VII. Potential Side Effects of Lamivudine
A. Commonly Encountered Side Effects
Side effects are possible with any medication - and Lamivudine is no exception. The commonly experienced adverse reactions associated with it include headache, fatigue, nausea, and diarrhea. These symptoms typically do not pose a severe threat and diminish over time as your system builds tolerance for Lamivudine1.
B. Less Frequent, but Serious Side Effects
Despite being rare occurrences with Lamivudine use in people living with HIV/AIDS, Hepatic steatosis, Lactic acidosis, and Immune reconstitution syndrome are some potentially severe side effects that should be immediately reported to physicians upon recognizing symptoms such as constant PAIN in the abdomen region, RAPID BREATHING -shortness of breath, and nonstop feeling of NAUSEA. If any such condition arises, the advice would be to seek prompt medical attention from a licensed healthcare provider for appropriate management and monitoring2.
VIII. Understanding Drug Interactions with Lamivudine
A. Interactions with Other Prescription Medications
Lamivudine may interact negatively with certain prescription drugs, for instance. Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole - commonly prescribed for bacterial infections - has been shown to diminish the effectiveness of Lamivudine3. It is vital for those taking this medication to inform their healthcare provider about all their current prescriptions and medical history to minimize any potential adverse effects.
B. Interactions with Over-the-Counter Drugs and Supplements
In addition to medication prescribed by a doctor, some individuals use nonprescription drugs and supplements to address health concerns—including those related to depression—in tandem with Lamivudine treatment. One such option is St. Johns's's wort. But it's important to understand that this popular herbal supplement has been demonstrated to impact how effective Lamivudine may be4.
C. How to Manage Potential Interactions
Effective management of potential interactions requires thorough communication with healthcare providers regarding any prescription medications over the counter drugs, or supplements currently in use. Consistent and diligent monitoring along with appropriate medication adjustments can play a significant role in mitigating the risk of drug interactions 5.
IX. Warnings and Contraindications for Lamivudine Use
A. Pre-existing Conditions that May Affect Lamivudine Use
Its worth knowing that several pre-existing medical conditions can impact the suitability of using Lamivudine. These include kidney disease, liver disease (including hepatitis B or C), and a history of pancreatitis. When considering whether or not this is a viable treatment option for you it's best to speak with your trusted healthcare provider6.
B. Contraindications to Avoid Serious Health Risks
While generally safe for use, Lamivudine has some exceptions that must be considered beforehand. One such exception occurs in those who have had an allergic reaction to the drug previously; they should avoid taking it altogether. Another instance arises in patients at an increased risk of heart disease where caution is warranted due to Lamivudines' potential ability to cause lactic acidosis and potentially worsen existing cardiac issues.7.
X. Overdose: Risks and Management
A. Signs and Symptoms of Overdose
Although rarely occurring, overindulging in Lamivudine medication can endanger one's well-being immensely. Typical signs pointing to an overdose would include relentless nausea and vomiting coupled with unexplained muscle aches and difficulty breathing. These indications could suggest a severe metabolic calamity named 'lactic acidosis.' Thus it is crucial always to adhere strictly to prescribed dosages during intaking this drug for optimal safety measures 1.
B. Necessary Steps for Managing an Overdose Situation
In case of an overdose, seeking immediate medical aid is essential. Typically, managing an overdose necessitates offering symptomatic and supportive care since there isn't a specified antidote for Lamivudine2.
XI. Proper Storage and Handling Precautions for Lamivudine
A. Recommendations for Safe Storage
Lamivudine retains its effectiveness when stored within average room temperatures under conditions that minimize exposure to light and moisture. Do not leave the drug around where kids or domesticated animals may access them, thus reducing unintended swallowing3.
B. Guidelines for Handling Lamivudine Responsibly
Proper handling of Lamivudine tablets involves swallowing them whole without breaking or chewing. It's crucial to observe good hand hygiene before and after administering this medication to decrease the likelihood of contamination4.
XII. Important Precautions when Using Lamivudine

A. Safeguarding Your Health: Do's and Don'ts
Lamivudine should be carefully used according to your healthcare provider's instructions for favorable outcomes. It is crucial not to miss dosages or halt medication without consulting a doctor because this could lead to unfavorable consequences, such as viral resistance, in case of any unwanted side effects. Ensure prompt reporting and follow all necessary precautions diligently 5.
B. When and How to Seek Medical Help
If any adverse effects arise, it is recommended to seek medical assistance promptly. Remarkably if they suggest severe conditions like lactic acidosis or immune reconstitution syndrome, consistent check-ins and laboratory examinations can also aid in overseeing the development and detecting any possible issues sooner6.
XIII. Conclusion: The Careful Use of Lamivudine
A. The Importance of Adherence to Prescribed Dosage
Consistency in taking Lamivudine as directed is fundamental in attaining the desired therapeutic benefits and avoiding the emergence of viral resistance. Therefore, it's crucial for individuals undergoing this treatment to comprehend that making modifications to their prescribed regimen can hinder its efficacy. 7.
B. Emphasis on Regular Checkups and Monitoring
For optimum results from Lamivudine treatment. Regular medical checkups are critical. These appointments provide opportunities for prompt detection and timely management of any unwanted side effects while maintaining drug effectiveness. 8. Ensuring success requires consistent communication with healthcare providers, faithful adherence to medication schedules, and active participation in personal healthcare management.
Lamivudine FAQ
- What is Lamivudine Abacavir?
- What is Lamivudine/Zidovudine?
- What is Lamivudine Zidovudine?
- What are Lamivudine side effects?
- What is the brand name of Lamivudine?
- What is Lamivudine and Abacavir?
- What is the drug class of Lamivudine?
- What is the mechanism of action of Lamivudine?
- What class is Lamivudine in?
- What is Lamivudine 3TC?
- What are the side effects of Lamivudine Zidovudine?
- What is Lamivudine Tenofovir Efavirenz?
- What is Lamivudine Efavirenz Tenofovir?
- What is the dosage of Lamivudine?
- What is the price of Lamivudine?
- What is Lamivudine and Zidovudine?
- What are the uses of Lamivudine?
- What is Abacavir and Lamivudine?
- What is Zidovudine and Lamivudine?
- What is the cost of Lamivudine?
- What is Lamivudine Tenofovir?
- What is Lamivudine for Hepatitis B?
- What is Lamivudine Efavirenz Tenofovir?
- What is the role of Lamivudine in Hepatitis B?
- How is Lamivudine used in Hepatitis B treatment?
- What is Lamivudine?
- What is the structure of Lamivudine?
- What is the price of Lamivudine Zidovudine?
- What does the Lamivudine package insert include?
- What is Lamivudine Emtricitabine?
- What is Lamivudine and Tenofovir?
- What is Lamivudine Dolutegravir?
- What is a Lamivudine tablet?
- What is the generic name for Lamivudine?
- What are the warnings associated with Lamivudine?
- What is the renal dosing for Lamivudine?
- What are the interactions of Lamivudine?
- What are the contraindications of Lamivudine?
- What is Lamivudine HBV?
- What is Lamivudine and Emtricitabine?
- What is Lamivudine solution?
- What does Lamivudine NRTI mean?
- What are the adverse effects of Lamivudine?
- What is the brand name of Lamivudine/Zidovudine?
- What is Lamivudine-Zidovudine tab 150-300 mg?
- What is Lamivudine Tenofovir Dolutegravir?
- What is Lamivudine Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate?
- What is the indication of Lamivudine?
- Is there copay assistance for Lamivudine?
- What is Lamivudine oral solution?
- What is Lamivudine resistance in Hepatitis B treatment?
- Can Lamivudine cure Hepatitis B?
- Why is Lamivudine called 3TC?
- Can Lamivudine be used as PEP?
- What is Lamivudine/Zidovudine used for?
- What is Lamivudine tablet used for?
- What is Lamivudine used to treat?
- What is Lamivudine used for?
- Is Lamivudine a protease inhibitor?
- Is Lamivudine used for HIV?
- What is the dosage of Lamivudine for Hepatitis B?
- What is Lamivudine used for?
- What is Lamivudine Abacavir?
- What is Lamivudine/Zidovudine?
- What is Lamivudine Zidovudine?
- What are Lamivudine side effects?
- What is the brand name of Lamivudine?
- What is Lamivudine and Abacavir?
- What is the drug class of Lamivudine?
- What is the mechanism of action of Lamivudine?
- What class is Lamivudine in?
- What is Lamivudine 3TC?
- What are the side effects of Lamivudine Zidovudine?
- What is Lamivudine Tenofovir Efavirenz?
- What is Lamivudine Efavirenz Tenofovir?
- What is the dosage of Lamivudine?
- What is the price of Lamivudine?
- What is Lamivudine and Zidovudine?
- What are the uses of Lamivudine?
- What is Abacavir and Lamivudine?
- What is Zidovudine and Lamivudine?
- What is the cost of Lamivudine?
- What is Lamivudine Tenofovir?
- What is Lamivudine for Hepatitis B?
- What is Lamivudine Efavirenz Tenofovir?
- What is the role of Lamivudine in Hepatitis B?
- How is Lamivudine used in Hepatitis B treatment?
- What is Lamivudine?
- What is the structure of Lamivudine?
- What is the price of Lamivudine Zidovudine?
- What does the Lamivudine package insert include?
- What is Lamivudine and Tenofovir?
- What is Lamivudine Dolutegravir?
- What is a Lamivudine tablet?
- What is the generic name for Lamivudine?
- What are the warnings associated with Lamivudine?
- What is the renal dosing for Lamivudine?
- What are the interactions of Lamivudine?
- What are the contraindications of Lamivudine?
- What is Lamivudine HBV?
- What is Lamivudine and Emtricitabine?
- What is Lamivudine solution?
- What does Lamivudine NRTI mean?
- What are the adverse effects of Lamivudine?
- What is the brand name of Lamivudine/Zidovudine?
- What is Lamivudine-Zidovudine tab 150-300 mg?
- What is Lamivudine Tenofovir Dolutegravir?
- What is Lamivudine Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate?
- What is the indication of Lamivudine?
- Is there copay assistance for Lamivudine?
- What is Lamivudine oral solution?
- What is Lamivudine resistance in Hepatitis B treatment?
- Can Lamivudine cure Hepatitis B?
- Why is Lamivudine called 3TC?
- Can Lamivudine be used as PEP?
- What is Lamivudine/Zidovudine used for?
- What is Lamivudine tablet used for?
- What is Lamivudine used to treat?
- What is Lamivudine used for?
- Is Lamivudine a protease inhibitor?
- Is Lamivudine used for HIV?
- What is the dosage of Lamivudine for Hepatitis B?
- What is Lamivudine used for?