Milrinone
- I. Introduction
- II. Milrinone Composition: What Is It Made Of?
- III. How Milrinone Works: The Pharmacodynamics Explained
- IV. Approved Uses of Milrinone: FDA-Endorsed Applications
- V. Off-Label Uses of Milrinone: Beyond Standard Practice
- VI. Dosage and Administration: Guidelines for Safe Use
- VII. Drug Interactions: What to Be Cautious Of
- VIII. Common Side Effects of Milrinone: What to Expect
- IX. Rare but Serious Side Effects: Warnings and Precautions
- Conclusion
- X. Contraindications: When to Avoid Milrinone
- XI. Important Precautions: Minimizing Risks
- XII. Careful Administration: Recommended Best Practices
- XIII. Overdose: Symptoms and Treatment
- XIV. Storage Guidelines: Keeping Milrinone Safe and Effective
- Conclusion
I. Introduction
Brief History of Milrinone
Milrinone, a medication in cardiac medicine, was first developed in the late 20th century. This drug is a therapeutic option acting as a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, providing an effective alternative to conventional treatments such as digoxin.
Importance in Modern Medicine
Milrinone is widely used in medicine due to its strong ability to improve heart muscle contraction and widen blood vessels. It plays a role in the treatment of both sudden and long-term heart failure making it an irreplaceable therapy option.
Scope of the Article
In this article, we will delve into the aspects of Milrinone, such as its composition, approved and off-label uses, recommended dosage instructions, and possible side effects. This article aims to offer an understanding of this vital medication for both healthcare professionals and the general public.
II. Milrinone Composition: What Is It Made Of?
Active Ingredients
Milrinone Lactate is a component that has pharmacological activity.
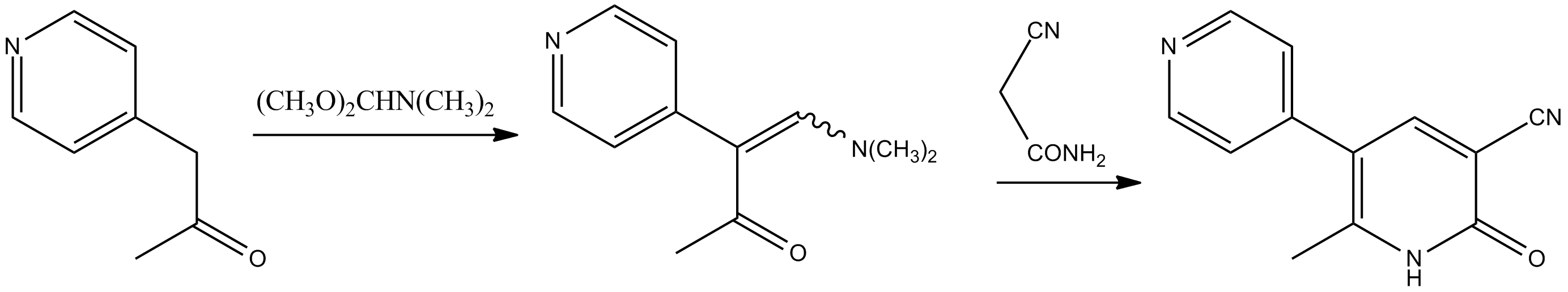
Inactive Ingredients
- Dextrose
- Water for Injection
III. How Milrinone Works: The Pharmacodynamics Explained
Mechanism of Action
Milrinone works by blocking the function of phosphodiesterase 3 (PDE3) in both heart and smooth muscle cells. This blockage results in increased levels of cyclic AMP, which boosts calcium flow and consequently improves the contractility of the heart muscle.
Pharmacokinetics
Once Milrinone is given through an IV, it starts working and reaches its highest levels in the bloodstream within a few minutes. The body primarily breaks down this medication in the liver. Eliminates it through the kidneys.
IV. Approved Uses of Milrinone: FDA-Endorsed Applications
Heart Failure
Milrinone is a positive inotropic agent used to treat heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) 1. It is mainly used to treat acute heart failure that has worsened suddenly 1. Milrinone helps improve the amount of blood pumped by the heart without causing an increase in the heart’s oxygen usage 1. This unique characteristic makes it suitable for cardiac conditions 1.
Here are some references that provide more information on Milrinone:
- Positive inotropic agents used to treat heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) include intravenous phosphodiesterase (PDE)-3 inhibitors (eg, milrinone), beta adrenergic receptor agonists (eg, dobutamine), intravenous calcium-sensitizing agents (eg, levosimendan, available in some countries outside the United States), and digoxin … 1
Post-Surgical Cardiac Management
Milrinone is a positive inotropic agent used to treat heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) 1. It is mainly used to treat acute heart failure that has worsened suddenly 1. Milrinone helps improve the amount of blood pumped by the heart without causing an increase in the heart’s oxygen usage 1. This unique characteristic makes it suitable for cardiac conditions 1.
Milrinone is commonly used in cardiac surgery to stabilize the hemodynamics of patients. It can avoid cardiopulmonary bypass, enhance cardiac contractility, prevent vasospasm, and ameliorate low output syndrome (LOS) 2.
Here are some references that provide more information on Milrinone:
- Positive inotropic agents used to treat heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) include intravenous phosphodiesterase (PDE)-3 inhibitors (eg, milrinone), beta adrenergic receptor agonists (eg, dobutamine), intravenous calcium-sensitizing agents (eg, levosimendan, available in some countries outside the United States), and digoxin … 1
- Milrinone, a PDE III inhibitor, is primarily used after open-heart surgery because it can avoid cardiopulmonary bypass, enhance cardiac contractility, prevent vasospasm, and ameliorate low output syndrome (LOS) 2.
V. Off-Label Uses of Milrinone: Beyond Standard Practice
Management of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
Milrinone is a positive inotropic agent used to treat heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) 1. It is mainly used to treat acute heart failure that has worsened suddenly 1. Milrinone helps improve the amount of blood pumped by the heart without causing an increase in the heart’s oxygen usage 1. This unique characteristic makes it suitable for cardiac conditions 1.
Milrinone has been used to improve pulmonary hypertension and enhance oxygenation in patients facing this condition 23.
Here are some references that provide more information on Milrinone:
- Positive inotropic agents used to treat heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) include intravenous phosphodiesterase (PDE)-3 inhibitors (eg, milrinone), beta adrenergic receptor agonists (eg, dobutamine), intravenous calcium-sensitizing agents (eg, levosimendan, available in some countries outside the United States), and digoxin … 1
- Milrinone has been shown to be effective in reducing pulmonary vascular resistance and pulmonary artery pressure in experimental models of pulmonary hypertension in adult humans and neonates 3.
- Inodilator milrinone is commonly used intravenously for patients with pulmonary hypertension and ventricular dysfunction in cardiac surgery 2.
Septic Shock
Milrinone is a phosphodiesterase III inhibitor used to treat septic shock as a secondary or tertiary option. It can widen blood vessels and increase cardiac output 1.
Here are some references that provide more information on the use of milrinone in the treatment of septic shock:
- The American Academy of Family Physicians provides a comprehensive overview of the diagnosis and management of sepsis. The article discusses the use of vasopressor therapy, including milrinone, in managing septic shock 2.
- UpToDate is a clinical decision support resource that provides evidence-based recommendations for the management of various medical conditions. Their article on glucocorticoid therapy in septic shock in adults discusses the use of milrinone as an adjunctive therapy in patients with septic shock 3.
- The EMCrit Project is a website that provides educational resources for critical care medicine. Their article on vasopressors discusses the mechanism of action and clinical use of milrinone in the management of septic shock 1.
Pediatric Heart Failure
Milrinone is a phosphodiesterase III inhibitor that has been used to treat septic shock as a secondary or tertiary option. It has the ability to widen blood vessels and increase cardiac output 1.
Milrinone has also been used off-label in pediatric patients with heart diseases. The frequent use of milrinone in pediatric patients undergoing heart surgery was supported by the findings of the Prophylactic Intravenous use of Milrinone After Cardiac Operation in Pediatrics (PRIMACORP) trial, which demonstrated that low cardiac output syndromes could be prevented by high-dose milrinone infusion after pediatric cardiac surgery 2. Milrinone has also been shown to be effective in preventing low cardiac output after cardiac surgery when combined with other inotropes, suggesting that milrinone could be safely employed in pediatric patients with heart diseases 3.
VI. Dosage and Administration: Guidelines for Safe Use
Standard Dosage for Approved Uses
To treat acute heart failure, it is recommended to start with an infusion rate of 50 micrograms per kilogram per minute.
Dosage Adjustments
Dosage should be tailored to the individual needs of groups of people.
For Elderly Patients
The recommended amount may need to be decreased because the liver or kidney function is not as effective in clearing it.
For Pediatric Patients
Exercise. Seek advice from a pediatric cardiologist due to the limited data availability.
Route of Administration
Usually, medical professionals would administer milrinone intravenously while closely monitoring the patient.
VII. Drug Interactions: What to Be Cautious Of
Interaction with Beta-Blockers
Using Milrinone at the time as a beta blocker might lessen its ability to increase heart contractions. It is essential to consider this when making decisions.
Interaction with Diuretics
Be cautious, as Milrinone can enhance the blood pressure-lowering effects of diuretics. Keep an eye on blood pressure levels.
Interaction with Other Inotropes and Vasodilators
Combining therapies might increase the chances of experiencing irregular heartbeats and low blood pressure. Monitoring the patient's cardiovascular status is essential to ensure their well-being.
VIII. Common Side Effects of Milrinone: What to Expect
Hypotension
Milrinone, a vasodilator, can cause low blood pressure, so it's essential to monitor for any changes closely.
Arrhythmias
Milrinone, due, to its ability to enhance the contractility of the heart muscle, has the potential to cause heart rhythms in both the atria and ventricles.
Headaches
One common side effect, although not too severe, is experiencing headaches that are usually brief.
IX. Rare but Serious Side Effects: Warnings and Precautions
Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions, like anaphylaxis, are not expected. They can be severe and require immediate medical attention.
Thrombocytopenia
Although it is uncommon, the use of Milrinone can potentially result in a decrease, in platelet count which could increase the risk of bleeding.
Liver Toxicity
It is recommended to be cautious when administering Milrinone to patients with liver problems as it may potentially worsen their liver dysfunction.
Conclusion
Milrinone is a cardiac medicine medication that has powerful effects on heart contractions and blood vessel dilation. It has a range of applications beyond just treating acute heart failure, although its use requires careful monitoring due to various precautions. To ensure the treatment outcomes, it is essential to administer Milrinone cautiously, considering potential drug interactions and possible side effects.
X. Contraindications: When to Avoid Milrinone
Severe Allergic Reactions
People who have experienced anaphylaxis or severe allergic reactions to Milrinone or its ingredients should avoid using it. Allergic sensitivity is a contraindication and should not be taken lightly.
End-stage Renal Disease
Due to its excretion through the kidneys, Milrinone should not be used in patients with kidney disease. Such usage may worsen kidney function. Cause severe complications related to medication.
Uncontrolled Hypertension
Patients with uncontrolled blood pressure should avoid using Milrinone as a treatment option. This is because Milrinone has effects that can cause dangerously high blood pressure levels.
XI. Important Precautions: Minimizing Risks
Monitoring Parameters
Monitoring electrolytes, cardiac rhythm, and liver function levels daily can help prevent various adverse effects.
Precautions for Special Populations
Elderly
The elderly population requires attention especially because their kidneys and liver may not function as efficiently. It is important to consider adjusting the dosage and monitoring them regularly.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
The transfer of Milrinone occurs through the placenta. It can also be found in breast milk. Therefore, it is recommended to consider using Milrinone in women and nursing mothers only if the potential advantages outweigh the possible risks involved.
Children
There is a lack of data regarding the use of this treatment in children. It is advisable to seek guidance from a specialist in cardiology.
XII. Careful Administration: Recommended Best Practices
Infusion Protocols
Milrinone should be administered through infusion and never given as a bolus. It is crucial to follow an infusion protocol to ensure maximum therapeutic effectiveness.
Emergency Situations
In situations such as a severe allergic reaction, it is crucial to stop the Milrinone infusion immediately. After that, it is essential to administer epinephrine and corticosteroids.
Clinician Supervision
The administration should be conducted by a clinician with extensive cardiac pharmacotherapy knowledge.
XIII. Overdose: Symptoms and Treatment
Signs of Overdose
- Hypotension
- Arrhythmias
- Unconsciousness
Emergency Management
The overdose requires stopping the Milrinone infusion stabilizing the patient's hemodynamics, and providing symptomatic relief.
XIV. Storage Guidelines: Keeping Milrinone Safe and Effective
Temperature Requirements
Milrinone should be kept in a room with a temperature. Any deviations from this standard could compromise the medication's quality and effectiveness.
Shelf Life
Make sure to be mindful of expiration dates. After the expiration date, the effectiveness of Milrinone significantly decreases, making it less effective and possibly even dangerous.
Handling Precautions
When preparing the infusion, it is essential to use the technique to prevent any microbial contamination. If you notice any particles or changes in color, in the solution, make sure to discard it.
Conclusion
Milrinone is a medication used in cardiovascular medicine that requires careful monitoring and judicious use. To prevent any effects and ensure the best treatment results, specific contraindications, precautions, and administration guidelines are in place. While it can provide a solution for heart conditions, clinicians need to understand its pharmacology to manage any potential risks effectively and thoroughly.











