Nifedipine
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition of Nifedipine
- III. How Nifedipine Works
- IV. Approved Uses of Nifedipine
- V. Off-label Uses of Nifedipine
- VI. Dosage and Administration of Nifedipine
- VII. Interactions with Nifedipine
- VIII. Side Effects and Warnings of Nifedipine Use
- IX. Contraindications and Careful Administration of Nifedipine
- X. Overdose and Handling Precactions of Nifedipine
- XI. Conclusion
I. Introduction
A. Overview of Nifedipine: What is Nifedipine?
Nifedipine is a powerful calcium channel blocker commonly prescribed for treating high blood pressure and angina conditions that are part of a broader range of heart and circulatory diseases. This medication belongs to the dihydropyridine subclass of calcium channel blockers and is characterized by its distinctive chemical composition.
B. Purpose of the Article
The purpose of this article is to offer a thorough examination of Nifedipine. With an emphasis on its chemical makeup, mechanism of action and impact on cardiovascular health. By providing this in-depth information, we aim to encourage informed discussions between healthcare professionals and patients regarding this medication.
C. The Importance of Understanding Nifedipine Usage and Precautions
It is of utmost importance to comprehend the complexities of Nifedipine, encompassing its chemical properties and interaction with the human body. Such comprehension serves as a catalyst for achieving optimum utilization and managing potential side effects and interactions effectively. Consequently, this leads to enhanced treatment efficacy and ensures the safety of patients. Additionally, knowledge about Nifedipine empowers patients to make well-informed decisions and actively engage in their health management.
II. Composition of Nifedipine
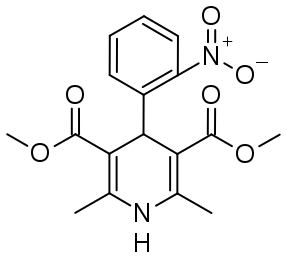
A. Chemical Structure and Properties
Nifedipine possesses a unique dihydropyridine structure. Underscoring its distinctiveness, the chemical formula for this compound is C17H18N2O6, which displays hydrophilicity and lipophilicity traits. The amphiphilic nature of Nifedipine empowers it to easily traverse cell membranes, which plays a crucial role in its bioavailability and effectiveness.
B. Active and Inactive Ingredients
Nifedipine contains Nifedipine as its primary active ingredient. However, pharmaceutical formulations typically encompass supplementary non-active constituents called excipients to boost stability levels alongside absorption rates while ensuring patient satisfaction. Such excipients can span across a spectrum of elements, including colorants, binders, disintegrants, fillers, and coating agents that mirror the specific dosage form employed (be it tablets or capsules). Thus it is essential to acknowledge that disparities exist among manufacturers about these compositions.
C. Manufacturing Process and Quality Control
The production of Nifedipine is a careful and precise procedure that guarantees both its effectiveness and safety. The process starts by synthesizing the active ingredient. Then proceeds to formulate it alongside the excipients. Quality control measures play a vital role in this manufacturing process as they involve checking the purity of the active ingredient and examining the stability and dissolution characteristics of the final product.
III. How Nifedipine Works
A. Mechanism of Action: Nifedipine's Role in the Body
To inhibit calcium ions from permeating into both the smooth muscle cells situated within both cardiac and arterial structures, Nifedipine comes into play. Its targeted sites for action solely revolve around L-type calcium channels. The outcome is reflected as reduced contractility within cardiac muscles alongside arterial dilation (widening), ultimately causing blood pressure levels to plummet while oxygen demand by our vital organs diminishes.
B. Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics
Nifedipine's pharmacodynamics revolve around its ability to dilate blood vessels. By preventing calcium from entering cells, it reduces the strength of contractions in the heart and blood vessels. This leads to a decrease in peripheral vascular resistance and blood pressure. In terms of pharmacokinetics. Nifedipine is readily absorbed when taken orally and undergoes significant metabolism in the liver before being excreted primarily through the kidneys. Its half-life is estimated to be around two to five hours.
C. Impact on Cardiovascular Health
Nifedipine, a potent vasodilator. Plays a crucial role in the management of cardiovascular health. It offers excellent benefits in lowering high blood pressure, a significant risk factor for heart disease and stroke. Moreover, by decreasing the workload and oxygen demand on the heart, Nifedipine can effectively relieve angina symptoms and prevent additional damage to the heart muscle in individuals with coronary artery disease. Therefore Nifedipine stands as a vital medication within the field of cardiovascular therapeutics.
IV. Approved Uses of Nifedipine
A. Hypertension: Treating High Blood Pressure with Nifedipine
Nifedipine is used to lower blood pressure in people with hypertension. It’s also used to treat vasospastic angina (chest pain due to a spasm in arteries around the heart) or chronic stable angina (chest pain that occurs with activity or stress)1. Nifedipine is in a group of drugs called calcium channel blockers. It works by relaxing the muscles of your heart and blood vessels. Nifedipine is used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure) and angina (chest pain)2.
Here are some references that you can use:
B. Angina Pectoris: The Role of Nifedipine in Chest Pain Management
Nifedipine is used to treat vasospastic angina (chest pain due to a spasm in arteries around the heart) or chronic stable angina (chest pain that occurs with activity or stress)1. Nifedipine is in a group of drugs called calcium channel blockers. It works by relaxing the muscles of your heart and blood vessels. Nifedipine is used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure) and angina (chest pain)2.
Here are some references that you can use:
- Nifedipine - Wikipedia
- Nifedipine: Side Effects, Dosage, Uses, and More - Healthline
- Nifedipine Uses, Dosage & Side Effects - Drugs.com
- Nifedipine (Oral Route) Description and Brand Names - Mayo Clinic
- Treatment of angina pectoris with nifedipine and atenolol … - Heart
- Nifedipine therapy for stable angina pectoris: Preliminary results of …
- Nifedipine in Angina Pectoris: A Multicentric Clinical Trial
C. Other FDA-Approved Uses
Nifedipine is a drug that belongs to a group of drugs called tocolytics, which work by preventing calcium from moving into the muscle cells of the uterus, making it less able to contract. One study shows that nifedipine is the most effective CCB for postponing preterm labor and is more effective than other tocolytics. Nifedipine and other tocolytic drugs might stop preterm labor for two to seven days, providing time to use corticosteroids to help reduce complications in the fetus associated with preterm delivery and to transport the mother to a hospital with a NICU. However, nifedipine does not prevent or delay preterm delivery for a significant period1.
Here are some references that you can use:
- Nifedipine In Pregnancy: Safety, Usage, Dosage And Side Effects - MomJunction
- Study to Determine the Efficacy of Nifedipine in Inhibiting Preterm Labor - Pakistan Journal of Medical and Health Sciences
- Nifedipine - Wikipedia
- Inhibition of acute preterm labor - UpToDate
- Treatment of Preterm Labor: Calcium Channel Blockers - Healthline
V. Off-label Uses of Nifedipine
A. Raynaud's Phenomenon: Nifedipine's Role
Nifedipine is a calcium channel blocker medication used to manage angina, high blood pressure, Raynaud’s phenomenon, and premature labor. While hypertension and angina pectoris are the primary conditions for which Nifedipine is FDA-approved, healthcare professionals often resort to off-label utilization of Nifedipine when addressing Raynaud’s Phenomenon.
Here are some references that you can use:
- Nifedipine - Wikipedia
- Raynaud’s Phenomenon - Mayo Clinic
- Raynaud’s Phenomenon - American College of Rheumatology
B. Other Unofficial yet Common Uses
Nifedipine is a calcium channel blocker medication used to manage angina, high blood pressure, Raynaud’s phenomenon, and premature labor. In addition to these primary uses, Nifedipine has been found to have other beneficial uses, such as anal fissures and esophageal spasms.
Here are some references that you can use:
- Nifedipine - Wikipedia
- Anal Fissure - American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons
- Esophageal Spasms - Mayo Clinic
C. The Scientific Evidence behind Off-Label Usage
The off-label use of Nifedipine is not without scientific basis. Several studies provide solid evidence supporting this usage. For example, several randomized trials have shown the effectiveness of Nifedipine in managing Raynaud’s Phenomenon. However, it is essential for physicians to use their clinical judgment and carefully consider the potential benefits and risks before prescribing Nifedipine off-label.
Here are some references that you can use:
- Nifedipine - Wikipedia
- Raynaud’s Phenomenon - Mayo Clinic
- Raynaud’s Phenomenon - American College of Rheumatology
VI. Dosage and Administration of Nifedipine
A. Standard Dosage Guidelines for Different Conditions
The nifedipine dosage should be tailored to the patient's specific condition and how they respond to the treatment. When it comes to treating hypertension, a typical starting dose would be 30 mg to 60 mg, taken once a day. However, the doctor may need to adjust this dosage depending on how the patient reacts to the medication. On the other hand, if treating angina pectoris, it is usually recommended to start with an initial dose ranging from 10 mg to 20 mg taken three times a day. It is essential to remember that these are general guidelines, and actual dosages can differ. Always make sure to follow the instructions given by your healthcare provider carefully.
B. Adjustments for Individual Patient Needs
Dosage adjustments may be necessary due to age, liver function, and concurrent medical conditions. For example, Elderly patients or those with impaired liver function might need a lower initial dose. In order to determine the dose that is most beneficial and carries the least risk, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional.
C. Instructions for Safe and Effective Use
To ensure the safe and effective use of Nifedipine, It is essential to follow these guidelines: Adhere strictly to the prescribed dosage as directed by your healthcare provider. It is crucial not to modify the dosage without consulting your healthcare provider and receiving their approval. Moreover, it is essential to discuss with your healthcare provider before abruptly discontinuing the medication.
VII. Interactions with Nifedipine
A. Drug-Drug Interactions: Which Medications to Avoid
It is essential to be aware of potential interactions between Nifedipine and other drugs, as these can impact the effectiveness of the medication and raise the likelihood of experiencing side effects. Notable interactions include certain beta blockers, which can increase the risk of low blood pressure: slow heart rate, and heart failure. Specific antifungal agents can elevate Nifedipine levels. It results in heightened side effects. To minimize any risks associated with drug interactions. You must always discuss your medication list with your healthcare provider.
B. Drug-Food Interactions: Dietary Considerations
Nifedipine can interact with specific foods. With grapefruit and grapefruit juice being particularly significant in this regard. These foods can potentially intensify the concentration of Nifedipine in the bloodstream. Consequently increasing the likelihood of experiencing side effects. You are advised to refrain from consuming these foods unless your healthcare provider advises otherwise.
C. Nifedipine and Alcohol: The Risks
Avoid potential complications such as dizziness, lightheadedness, and a higher likelihood of falls. It is advisable for patients taking Nifedipine to restrict their alcohol consumption. Combining alcohol with this medication can enhance its blood pressure-lowering effect necessitating careful consideration to maintain safety.
VIII. Side Effects and Warnings of Nifedipine Use

A. Common Side Effects: What to Expect
Nifedipine can produce some common side effects, including dizziness or lightheadedness, flushing (a sensation of warmth), and headaches. It is worth noting that these side effects are generally mild and tend to decrease as the body becomes accustomed to the medication.
B. Serious Side Effects: Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Although uncommon, there is a possibility of experiencing specific serious side effects. It is important to promptly seek medical assistance if any of the following symptoms occur: new or worsened angina resulting in chest pain: an irregular heartbeat, or severe dizziness leading to fainting.
C. General Warnings and Precautions: When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant or nursing, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional. Additionally, it is essential to seek medical advice before undergoing any type of surgery, including dental surgery. Furthermore, if your symptoms do not improve or worsen after taking Nifedipine, it is recommended that you reach out to a healthcare professional. Taking proactive measures for your health can significantly enhance the positive results of using Nifedipine.
IX. Contraindications and Careful Administration of Nifedipine
A. Individuals Who Should Avoid Nifedipine
While Nifedipine is generally safe for most individuals, specific individuals must exercise caution or avoid its use altogether. These include individuals who have a known hypersensitivity to Nifedipine or other dihydropyridines, individuals with severe aortic stenosis (a heart condition), and those experiencing cardiogenic shock (a critical condition caused by the heart's inability to pump enough blood). To ensure your safety. Always disclose your complete medical history to your healthcare provider to avoid any potential contraindications.
B. Administering to Elderly Patients: Special Considerations
Given the potential diminished organ function in elderly patients, caution should be exercised when administering Nifedipine due to possible alterations in its processing within their bodies. This renders this demographic at higher risk for encountering side effects. Henceforth, commencing treatment with lower initial doses and closely monitoring these individuals is strongly recommended.
C. Administering to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Risks and Recommendations
It is recommended to use Nifedipine during pregnancy only if the potential benefits outweigh the possible risks. Moreover, nursing mothers should exercise caution as Nifedipine is excreted in human milk. Therefore, consult with your healthcare provider if you are pregnant, planning to conceive, or currently breastfeeding.
D. Administering to Children: Age Restrictions and Dosing Guidelines
It is important to note that the safety and efficacy of Nifedipine in children has not been firmly established. Therefore. It is generally not advised to use this medication in pediatric patients. Unless there are specific circumstances and it is done under the supervision of a healthcare provider who exercises caution.
X. Overdose and Handling Precactions of Nifedipine
A. Identifying Signs of Nifedipine Overdose
Regarding Nifedipine overdose, one must be cautious as it can have serious repercussions. Some signs indicating such an overdose could entail severe dizziness, episodes of fainting, and either a significantly slowed or accelerated heartbeat.
B. Steps to Take in Case of Overdose
In case of an overdose making immediate contact with a healthcare provider or your local poison control center is imperative. The timeliness of the response holds great significance as it directly impacts the effectiveness of treatment and the overall recovery process.
C. Safe Handling and Storage of Nifedipine
Please store Nifedipine at room temperature making sure to keep it away from light and moisture. It is important to note that this medication should not be stored in the bathroom. Additionally, it is essential to keep all medications out of reach of children and pets. Under no circumstances should you flush medications down the toilet or pour them into a drain unless explicitly instructed.
XI. Conclusion
A. Recap of the Essential Facts about Nifedipine
Holding utmost importance in managing high blood pressure and chest pain conditions, nifedipine stands as a vital calcium channel blocker medication. Through its intricate mechanism involving muscle relaxation in both heart and blood vessels, it serves as an invaluable therapeutic option for patients. However, no medical intervention comes without trade-offs; therefore, assessing the benefits against potential risks becomes paramount when contemplating nifedipine administration. To ensure informed decision-making throughout this process guidance from healthcare professionals proves essential
B. The Significance of Responsible Nifedipine Use in Healthcare
Utilizing Nifedipine responsibly can significantly assist in controlling blood pressure and averting heart attacks. Yet it is imperative to fully grasp its mechanism of action, potential side effects, interactions, and contraindications to guarantee the utmost effectiveness and safety of this treatment.
C. Encouraging Further Reading and Patient-Doctor Communication
This article offers a thorough introduction to Nifedipine although it does not cover every aspect. Maintaining open and effective communication with your healthcare provider for successful treatment is crucial. Keep reading and inquiring to participate in your healthcare journey actively.