Phenoxybenzamine
- I. Introduction to Phenoxybenzamine
- II. Composition of Phenoxybenzamine
- III. How Phenoxybenzamine Works
- Uses of Phenoxybenzamine
- Off-label Phenoxybenzamine Save Cancel
- VI. Dosage and Administration of Phenoxybenzamine
- VII. Special Considerations for Administration
- VIII. Phenoxybenzamine Interactions
- IX. Side Effects of Phenoxybenzamine
- X. Important Precautions When Using Phenoxybenzamine
- XI. Warnings and Contraindications of Phenoxybenzamine Use
- XII. Storage Recommendations for Phenoxybenzamine
- XIII. Careful Administration of Phenoxybenzamine
I. Introduction to Phenoxybenzamine
A. Brief Overview of Phenoxybenzamine
Phenoxybenzamine is a medication that is mainly used in the treatment of pheochromocytoma, which's a rare tumor found in the adrenal glands. This drug acts as an alpha antagonist blocking alpha receptors in the body and causing various positive physiological effects that are helpful for specific medical conditions.
B. Historical Context and Development
The development and production of Phenoxybenzamine can be traced back to the mid-20th century. Wellcome Research Laboratories filed the initial patent for this compound in the 1950s. Initially created as a medication to lower blood pressure, it has since been discovered to have other medical applications showcasing its versatility in clinical settings.
II. Composition of Phenoxybenzamine
A. Key Active and Inactive Ingredients
Phenoxybenzamine's main active component is Phenoxybenzamine Hydrochloride. This influential substance works by interfering with the functioning of alpha-adrenergic receptors in the body. The medication also includes inactive ingredients like magnesium stearate, sodium starch glycolate, and talc, which aid in the effective delivery and absorption of the drug.
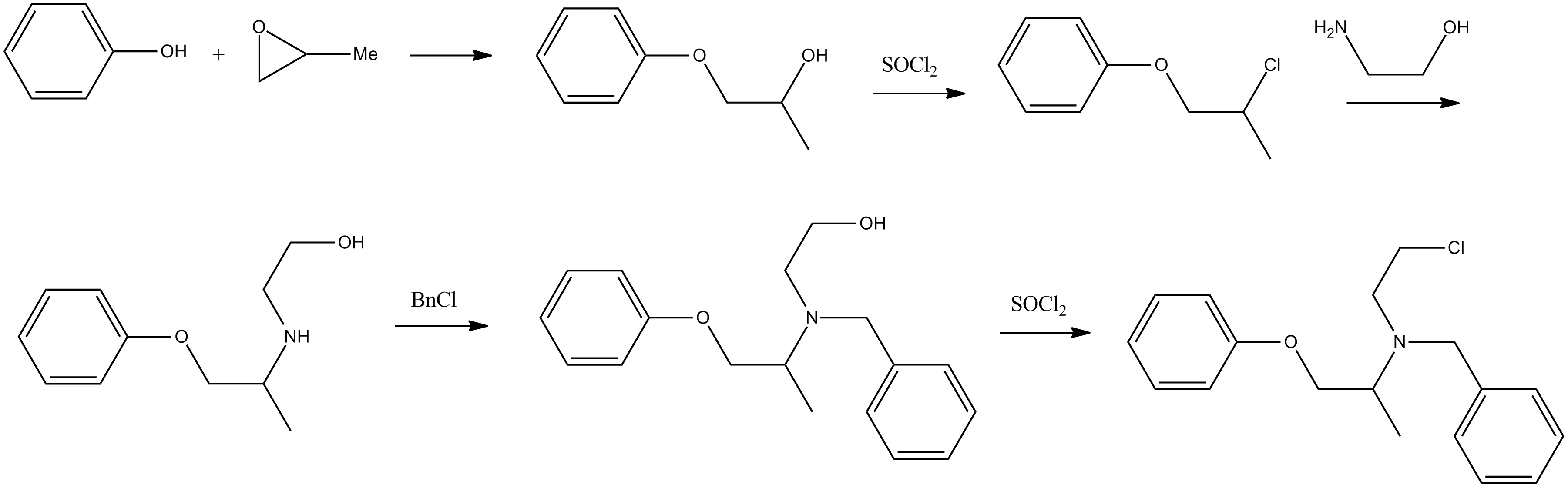
B. Chemical Structure and Properties
Phenoxybenzamine Hydrochloride is a compound known as N (2 chloroethyl) N (1 methyl 2 phenoxyethyl) benzylamine hydrochloride. It appears as a powder that can be white or off-white, in color and can dissolve in both water and alcohol. With a weight of 340.30 and a pKa value of 8.93, it influences how it behaves within the body and interacts with its physiological surroundings.
III. How Phenoxybenzamine Works
A. Mechanism of Action within the Body
Phenoxybenzamine blocks alpha receptors, making it different from other drugs. It forms a bond with the receptor preventing it from functioning correctly. This means that norepinephrine and epinephrine can't bind to the receptor resulting in a decreased heart rate, relaxed blood vessels, and lowered blood pressure. These effects are why it's used for purposes.
B. Effect on Various Bodily Systems
Phenoxybenzamine has an impact on various systems in the body. It helps lower blood pressure. Reduce the strain on the heart by causing blood vessels to dilate, which is beneficial for people with hypertension and pheochromocytoma. Additionally, it can help relieve symptoms by relaxing muscles in the prostate and bladder neck. It may also affect supporting respiratory function in some cases, although this is less common.
Uses of Phenoxybenzamine
Approved Uses in Medical Practice
Phenoxybenzamine is an alpha-adrenergic antagonist primarily used to manage symptoms of pheochromocytoma, a rare adrenal gland tumor. The drug helps alleviate symptoms such as hypertension, excessive sweating, and palpitations by blocking the activity of certain chemicals in the body that constrict blood vessels and stimulate heart rate. It is also utilized as a preoperative management tool to control blood pressure surges during the surgical removal of pheochromocytomas123.
Here are some references that you can use for your content:
Proven Benefits in Various Health Conditions
A plethora of case studies emphasize the effectiveness of Phenoxybenzamine in managing pheochromocytoma symptoms. One study involving a cohort of pheochromocytoma patients revealed that the drug significantly decreased episodes of hypertensive crises and improved quality of life. Another retrospective analysis confirmed the efficacy of Phenoxybenzamine in reducing intraoperative hemodynamic instability during adrenalectomy12.
Here are some references that you can use for your content:
Off-label Phenoxybenzamine Save Cancel
Exploration of Potential Applications
While Phenoxybenzamine is primarily indicated for pheochromocytoma, it has been used off-label for a range of conditions. Some common off-label applications include:
- Raynaud’s phenomenon: By promoting blood flow to the hands and feet, Phenoxybenzamine helps alleviate symptoms associated with this condition.
- Autonomic hyperreflexia: Phenoxybenzamine can be employed in managing this severe condition often seen in spinal cord injury patients.
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): Some studies suggest that Phenoxybenzamine may help alleviate symptoms of BPH, such as frequent urination and difficulty starting urination12.
Here are some references that you can use for your content:
VI. Dosage and Administration of Phenoxybenzamine
A. Standard Dosage Guidelines
The recommended amount of Phenoxybenzamine can vary based on the patient's age, weight, medical condition, and overall health. In adults, it is typically suggested to start with a dosage of 10mg taken twice a day. This amount can be adjusted gradually to a maintenance dose of 20 to 40mg twice daily. It's essential to tailor the dosage for each individual to find the balance between desired therapeutic effects and any potential adverse reactions.
B. Variations in Dosage Based on Specific Conditions
It's essential to customize the dosage of Phenoxybenzamine based on each patient's requirements. When treating pheochromocytoma, the dosage can be gradually increased 10 to 15 days before surgery. Modifying the dosage in response to the patient's reaction is crucial to manage hypertension effectively. Similarly, when dealing with the Raynaud phenomenon, the doses are adjusted depending on the symptoms' severity.
VII. Special Considerations for Administration
A. Administration to the Elderly
It is essential to be cautious when administering Phenoxybenzamine to patients. The aging process can bring about physiological changes, including decreased renal and hepatic function, which may affect how the drug is metabolized and eliminated from the body. As a result, dosage adjustments might be required. Additionally, elderly patients may have a likelihood of experiencing certain adverse effects, so it is crucial to monitor them carefully throughout their treatment.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Considering the limited clinical data available, it is advisable to administer Phenoxybenzamine to pregnant women if the potential benefits outweigh any potential risks. Similarly, it is not known whether Phenoxybenzamine is excreted in breast milk, so nursing mothers should be cautious. If it becomes necessary to take the medication, one way to minimize infant exposure is to avoid breastfeeding during treatment.
C. Administration to Children
The use of Phenoxybenzamine in children has not been definitively proven to be safe and effective. Therefore it is essential to have a specialist oversee its administration. The patient dosage should be carefully determined based on the child's weight and response to treatment, with adjustments made as needed.
VIII. Phenoxybenzamine Interactions
A. Potential Drug Interactions
Phenoxybenzamine has the potential to interact with medications, which could potentially impact their effectiveness or lead to an increase in side effects. In particular, there may be interactions with beta-blockers, epinephrine, and other alpha-blockers. These interactions can enhance the products or even result in paradoxical hypertension, so careful management is necessary.
B. Effects of Lifestyle Factors on Efficacy
Factors related to one's lifestyle, such as smoking, alcohol intake, and diet, can influence how well Phenoxybenzamine works. It is possible that consuming alcohol alongside Phenoxybenzamine could result in an added drop in blood pressure. On the other hand, smoking may diminish the drug's effectiveness because it tends to constrict blood vessels. To achieve optimal treatment results, it is advisable to maintain a diet and engage in regular exercise while undergoing drug therapy.
IX. Side Effects of Phenoxybenzamine
A. Common Side Effects and Their Management
Although Phenoxybenzamine is effective, it can cause a range of side effects. Some common ones include feeling dizzy when changing positions, having a nose, and experiencing discomfort in the stomach. To minimize these effects, it's important to move when changing jobs to avoid falls caused by dizziness, use decongestants to relieve nasal congestion, and have meals before taking the medication to ease gastrointestinal problems. It's always recommended to consult with your doctor and undergo monitoring to ensure proper management of these side effects.

B. Less Common but Serious Side Effects
There are uncommon but essential side effects of Phenoxybenzamine that should be taken seriously. These may include a heartbeat, trouble urinating, and blurry vision. If you experience any of these symptoms, you must reach out to your healthcare provider as soon as possible. Some patients may also have severe allergic reactions, like skin rashes, itching, or difficulty breathing. If you notice any of these reactions, seeking medical attention is crucial.
X. Important Precautions When Using Phenoxybenzamine
A. Identifying and Responding to Overdosage
Taking much Phenoxybenzamine can cause a significant drop in blood pressure and potentially dangerous complications. You may experience symptoms like feeling sick, throwing up, fatigue, or even going into a coma. In some cases, it's essential to provide support by increasing plasma volume by lying down flat and, if necessary, using medications that constrict blood vessels to raise blood pressure.
B. Handling Precautions for Patient Safety
Individuals taking Phenoxybenzamine should refrain from engaging in activities that demand focus, like driving or operating machinery, as it may lead to dizziness or fainting. Regularly checking blood pressure is crucial for those with existing cardiovascular issues, as significant changes can have adverse effects.
XI. Warnings and Contraindications of Phenoxybenzamine Use
A. Specific Health Conditions and Phenoxybenzamine
Individuals allergic to phenoxybenzamine and have artery or kidney disease should avoid taking this medication. It's also essential for patients with a heart attack or stroke to be cautious. Before starting this treatment, make sure to provide your healthcare provider with your medical history.
B. Contraindications Based on Other Medications
It is essential to avoid using Phenoxybenzamine with certain other medications because they can potentially interact in harmful ways. For example, combining it with beta-blockers may cause a decrease in heart rate and blood pressure. Similarly, using it alongside erectile dysfunction drugs can result in hypotension. It is crucial to inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter medicines, to prevent any adverse effects caused by drug interactions.
XII. Storage Recommendations for Phenoxybenzamine
A. Proper Storage Conditions
It is advisable to store Phenoxybenzamine in a dry location away from direct sunlight and heat. The ideal temperature range would typically be around 15-30 degrees Celsius (59 86 degrees Fahrenheit). Remember to keep the medication in its packaging until you need to use it, as this will help safeguard it against any moisture.
B. Safeguarding against Improper Storage
Improperly storing Phenoxybenzamine may result in decreased effectiveness or an increased chance of effects. Here are a few essential things to remember: Avoid storing it in the bathroom or near a sink, as moisture can potentially damage the medication. Do not expose it to temperatures beyond the recommended range, as extreme heat or cold could affect its potency. Always keep it out of reach and sight of children to prevent ingestion. Lastly, refrain from using the medicine after the expiration date mentioned on the packaging.
XIII. Careful Administration of Phenoxybenzamine
A. Understanding the Importance of Compliance
Following the recommended Phenoxybenzamine treatment plan is essential to get the most out of its benefits and reduce any potential adverse effects. Not sticking to the schedule or taking it irregularly can result in inadequate symptom control or severe health problems. Always remember that consistent and accurate medication administration plays a role, in achieving the desired health outcomes.
B. Strategies for Ensuring Correct Administration
To ensure the use of Phenoxybenzamine it's essential to follow a few strategic steps; 1. Take the medication consistently at the time of every day. 2. Use reminders on your phone. Pillboxes to help you remember when to take your doses. 3. Follow all instructions provided by your healthcare provider carefully and diligently. 4. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. However, if it's almost time for your dose, skip the missed one and continue with your regular schedule. 5. Avoid doubling doses to make up for a missed one. 6. Always remember that Phenoxybenzamine is a prescription medication that your healthcare provider should take exactly as directed. Please note that these measures are essential for ensuring the administration of Phenoxybenzamine and maintaining its effectiveness.

















