Pitavastatin Calcium
- Introduction
- Background of Statins
- Discovery and Development of Pitavastatin Calcium
- How Pitavastatin Calcium Works
- Dosage and Administration
- Uses of Pitavastatin Calcium
- Off-label Use
- Composition
- Storage
- Interaction
- Warning
- Contraindication
- Careful Administration
- Important Precautions
- Administration to Elderly
- Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
- Administration to Children
- Overdosage
- Handling Precautions
- Side Effects
- Common Side Effects
- Conclusion
Introduction
Statins, which are highly effective at lowering lipids, have revolutionized the field of treatment. Their ability to significantly reduce cholesterol levels has provided patients with a new lease on life. Among the statins available, one particular compound that stands out is Pitavastatin Calcium. This article provides an exploration of Pitavastatin Calcium, shedding light on its origins, mechanism of action, and guidance for its therapeutic application.
Background of Statins
The journey of statins started in the half of the 20th century, driven by an unwavering quest to combat the widespread prevalence of cardiovascular diseases. These substances, mainly obtained from byproducts, left a lasting impact with their impressive ability to control cholesterol production.
Discovery and Development of Pitavastatin Calcium
Pitavastatin Calcium, a breakthrough in the field of lipid management, was first created in Japan. Unlike versions, Pitavastatin has a unique chemical structure that gives it a distinct pharmacokinetic profile. Its development involved clinical evaluations which confirmed both its effectiveness as a treatment and its safety record.
How Pitavastatin Calcium Works
Mechanism of Action
Pitavastatin Calcium works by blocking an enzyme called HMG CoA reductase, which plays a key role in the production of cholesterol. By inhibiting this enzyme, the medication effectively reduces the amount of cholesterol within cells, prompting liver cells to remove LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) from the bloodstream. As a result of these actions, there is a decrease in LDL levels in the blood.
Comparative Effectiveness with Other Statins
When compared to statin drugs, Pitavastatin demonstrates a balanced combination of effectiveness and tolerability.
- Notable characteristics include its ability to consistently lower LDL cholesterol levels across patient groups,
- Its lower likelihood of interacting with other medications
- Its impressive safety profile reduces the risk of muscle-related side effects.
These qualities highlight the potential of Pitavastatin as an option for managing cholesterol levels.
Dosage and Administration
Recommended Daily Dose
The key to therapy lies in finding the right dosage. In some cases, starting with a daily dose of 2 mg has proven to be effective for the majority of patients; depending on how the patient responds and their tolerance, this dosage can be gradually increased, with 4 mg being the highest recommended amount in most situations.
Adjustments in Special Populations
Certain specific groups of people, like elderly individuals with kidney problems or those taking medications at the same time, might require a reevaluation of their dosage. It is extremely important to keep track of their kidney function and make necessary adjustments to the doses. Taking an approach by making small changes gradually is often crucial for achieving positive outcomes in these particular groups.
Tips for Proper Medication Adherence
It is extremely important to make sure that people consistently follow their medication schedules. There are strategies that can help with this;
1. Creating a daily routine for taking medication.
2. Using pill organizers to avoid missing any doses.
3. Regularly checking in with healthcare professionals to discuss any concerns or side effects.
By sticking to these strategies, not only will the effectiveness of the medication be enhanced, but also the chances of experiencing any negative effects will be reduced.
Uses of Pitavastatin Calcium
Pitavastatin Calcium(1), an effective drug for reducing cholesterol levels, is widely praised for its ability to control high cholesterol. However, its uses extend beyond this area. Within the field of medicine, Pitavastatin Calcium plays multiple important roles.
1. WebMD - Pitavastatin Calcium
High cholesterol
Primary Indications
The main reasons why doctors usually prescribe Pitavastatin Calcium are its ability to modulate cholesterol and its impact on key indications.(1)
1. NCBI - Pleiotropic effects of pitavastatin
Lowering Bad Cholesterol (LDL)
LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein)(1) is commonly referred to as the 'culprit' in the network of lipoproteins. When its levels rise, it signals the onset of cardiovascular conditions. Pitavastatin Calcium effectively reduces the production of this lipid component, resulting in levels in the bloodstream and reducing associated risks.(2)
1. CDC - LDL and HDL Cholesterol and Triglycerides
2. PubMed Central - Pitavastatin for lowering lipids
Preventing Cardiovascular Diseases
Unfortunately, cardiovascular diseases are common in society and often occur due to abnormal lipid levels. Pitavastatin Calcium is a medication that helps regulate cholesterol levels and can greatly contribute to preventing these diseases.(1)
Its key advantages include reducing plaque formation in the arteries, decreasing inflammation in blood vessels, and improving endothelial function to promote overall vascular health.(2)
As a result, this remarkable pharmaceutical plays a role in preventing cardiovascular diseases.
1. AidsMap - Pitavastatin lowers risk of cardiovascular events in people living with HIV
Secondary Indications
Although Pitavastatin Calcium is primarily known for its ability to regulate lipids, its therapeutic range extends beyond that. The drug has shown effectiveness in additional areas. Some noteworthy examples include its ability to regulate markers, enhance insulin sensitivity, and even potentially benefit certain kidney conditions. These secondary uses, while less commonly known, demonstrate the drug's therapeutic potential.
Off-label Use
In the changing field of medicine, there are often situations where drugs, initially designed for specific purposes, show potential effectiveness in areas outside of their intended use. This is known as "off-label use." It highlights the adaptability and dynamic nature of pharmacotherapy. An example of this is when certain treatments are used off-label, which warrants an examination of their alternative therapeutic possibilities.
Efficacy in Other Medical Conditions
In the realm of exploring and using drugs, sometimes a molecule shows remarkable effectiveness in treating conditions that are unrelated to its original purpose. The reasons behind this could involve biochemical pathways, unexpected discoveries, or insightful observations from clinical practice. Some common examples of off-label uses include;
- Its inflammatory effects in autoimmune disorders
- Its ability to protect the nervous system in degenerative neurological diseases
- Its role in regulating metabolism in hormonal imbalances.
These unexplored therapeutic areas serve as evidence of the potential that can be found within a single molecule.
Research Findings and Clinical Trials
The foundation of using medications for purposes other than their approved indications is based on solid scientific evidence. Knowledge about a drug's alternate effectiveness usually comes from anecdotal experiences in clinical practice or initial laboratory research.
However, the ultimate test of credibility lies in clinical trials. At times, numerous treatments have undergone comprehensive trials to explore their off-label potential. These trials, which are carefully planned and executed, involve stages;
- Initial pilot studies to assess preliminary effectiveness and safety.
- Randomized controlled trials are considered the gold standard to establish clear therapeutic benefits.
- Meta-analyses and systematic reviews that combine data from different sources to provide stronger statistical power and reliability.
After completion of the trial, the gathered data undergoes examination to ensure the safety and effectiveness of using the treatment in new areas.
Composition
Active and Inactive Ingredients
Pitavastatin Calcium, like other pharmaceutical drugs, is a combination of active and inactive components. The active component, known as Pitavastatin, is the molecule that brings about the therapeutic effects of the drug. It works by inhibiting the HMG CoA reductase enzyme, leading to a reduction in LDL cholesterol levels.
Supporting this ingredient are inactive components called excipients. Although they don't have any effects, these ingredients play important roles, such as improving solubility, ensuring stability, and controlling drug release. Together these active and inactive components work together to create a formulation that's effective for patients while also being user-friendly.
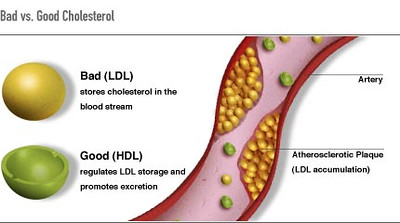
LDL HDL
Available Formulations and Strengths
Pitavastatin Calcium is a versatile medication that comes in various formulations and strengths. It is commonly prescribed as tablets with a range of options;
- 1 mg for patients who need minimal lipid adjustment
- 2 mg is a standard starting dose for many patients
- 4 mg for those requiring more aggressive cholesterol management.
Having these strengths allows doctors to adjust the dosage according to each patient's specific needs, ensuring personalized treatment plans.
Storage
Ideal Storage Conditions
To guarantee the effectiveness and safety of Pitavastatin Calcium, it is essential to store it under certain conditions. The tablets perform best when kept in a dry place away from direct sunlight. Excessive moisture or heat can jeopardize the quality of the medication, resulting in reduced effectiveness or possible negative consequences.
Shelf Life and Expiry Considerations
The time frame in which a drug remains effective, known as its shelf life, is extremely important. Generally, Pitavastatin Calcium maintains its effectiveness for a few years after it is manufactured. However, once it reaches its expiry date, its efficacy decreases, and safety becomes uncertain. Therefore it is crucial to check your supply of medication and avoid using expired tablets.
Interaction
Drugs that Affect Pitavastatin Metabolism
Pharmacokinetic ballets frequently include interactions with drugs. Pitavastatin metabolism can be affected by substances.
For example, rifampin, an enzyme inducer, can speed up the breakdown of pitavastatin, potentially reducing its effectiveness.
On the other hand, certain antifungals and macrolides act as enzyme inhibitors and may increase the levels of pitavastatin in the body, thereby increasing the likelihood of experiencing side effects.
Pitavastatin's Impact on Other Medications
On the other hand, Pitavastatin can also have an impact on how other medications work. For example, when taken together with blood thinners, it may increase their effectiveness, requiring careful adjustments to the dosage.
Food and Beverage Interactions
The food we choose to eat can affect how well a drug is absorbed by our bodies and how effective it is. While eating food doesn't seem to have an impact on the absorption of Pitavastatin Calcium, consuming grapefruit or its juice can increase the levels of the drug in our system, which can increase the chances of experiencing negative side effects.
Warning
Potential Risks with Long-Term Use
While Pitavastatin Calcium is effective, it's important to be aware that there are risks associated with long-term use. Continuous therapy may be connected to liver abnormalities, which would require monitoring of liver function through tests. Additionally, there is a possibility of experiencing muscle-related problems ranging from muscle pain to more severe cases of rhabdomyolysis.
Monitoring Parameters and Follow-up
To make sure that the drug remains safe over a period, it is important to have a well-organized monitoring plan. It's crucial to check lipid levels, liver functions, and muscle enzymes. Furthermore, periodic clinical evaluations can anticipate any problems and ensure that the treatment is both effective and safe.
Contraindication
Absolute Contraindications
In the field of drug administration, absolute contraindications refer to situations where using a drug can lead to sometimes irreversible consequences. These conditions are non-negotiable. Require immediate attention.
They include having a known allergy to the ingredients or other components of the drug situations where taking the drug could worsen existing medical conditions or cause harmful reactions, and cases where combining medications could result in dangerous interactions.
Relative Contraindications
Relative contraindications, when compared to contraindications, refer to situations where a medication could potentially be given with caution. In these cases, the benefits of the drug might outweigh any risks, but thorough evaluation is still necessary.
- This includes patients who have shown mild hypersensitivity reactions in the past.
- It also applies to individuals with existing conditions that may be slightly worsened by the drug but can be effectively managed through careful monitoring.
- Additionally, it involves considering medications that may interact with the drug but can be handled and controlled effectively.
Careful Administration
Patients with Liver Diseases
Liver diseases can affect the processing of medications, so it's important to be careful when administering them. The liver plays a role in breaking down and detoxifying many drugs.
Therefore drugs that are mainly processed in the liver may require doses or even avoidance altogether. It's essential to check liver enzymes to prevent any potential harm to the liver.
If there are prolonged abnormalities in blood clotting time or other coagulation factors, it could indicate that the liver function is compromised. Caution should be exercised.
Patients with Renal Impairments
The kidneys are organs responsible for filtering out waste and drugs from the body. When patients have kidney problems, it's important to adjust medication doses based on their filtration rate (GFR).
Drugs that are mainly eliminated through the kidneys can build up and cause harm, so it's crucial to monitor kidney function by checking parameters, like serum creatinine levels and urine output.
Important Precautions
Some medications, those designed to regulate cholesterol, have the potential to cause muscle-related issues. These can vary from muscle pain to more severe conditions, like rhabdomyolysis.
It's important for patients to be informed about the possibility of experiencing muscle pain or weakness as warning signs. Monitoring levels of serum creatine kinase (CK) can help predict any muscle injuries.
If severe symptoms occur, it is crucial to stop taking the medication and seek medical assistance.
Precautions in Diabetic Patients
Diabetic individuals commonly pose a challenge when it comes to administering medication. Their unique metabolic situation often requires consideration in pharmacotherapy.
It's crucial to monitor their blood glucose levels since certain medications can either increase or decrease it, leading to hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia respectively.
Furthermore, special attention must be given to medications that may affect insulin secretion or its effectiveness. Regularly assessing the levels can provide valuable insights into long-term glycemic control and how different drugs may influence it.
Administration to Elderly
As time passes, the human body goes through changes. Specifically, as people get older, their bodies experience subtle changes in how drugs are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted.
- There may be a decrease in the absorption of drugs in the stomach and intestines due to reduced blood flow and gastric acid secretion.
- Changes in body composition, such as a shift in distribution and alterations in protein binding and total body water content, can affect how drugs are distributed throughout the body.
- Metabolism might slow down due to a decrease in liver size and blood flow.
- The decline in kidney function, indicated by a glomerular filtration rate, can impact how drugs are eliminated from the body.
Adjusted Dosing Recommendations
Considering the changes in how drugs are processed within the body, it is important to adjust the dosages for older individuals carefully.
- It is often wise to begin treatment with doses and gradually increase them ("start low, go slow").
- Regular monitoring and evaluation help ensure that the treatment is effective while avoiding any side effects.
- Special attention should be given to any increased sensitivities to drugs that affect the nervous system.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Potential Risks to the Fetus
Pregnancy brings about a series of changes that have implications for medication. One major concern is the possibility of causing abnormalities, known as teratogenicity.
- Drugs can cross the barrier and potentially harm the developing fetus.
- It is crucial to be aware that certain pharmaceutical agents can pose risks during the stages of embryo and fetal development.
- Regular prenatal screening helps monitor any adverse effects on the fetus.
Excretion in Breast Milk and Impacts
Breastfeeding mothers who have recently given birth often face the dilemma of whether drugs they take can pass into their breast milk, which could potentially affect the health of their newborns.
- Certain drugs, based on their chemical properties, have the ability to enter breast milk.
- Since a newborn's metabolic and excretory systems are not fully developed, there is a risk of drug accumulation and potential harm.
- It is important for breastfeeding mothers to receive guidance on when to take medications in relation to their breastfeeding schedules in order to minimize any exposure for their newborns.
Administration to Children
Safety and Efficacy Data
Children, who encompass a range of developmental stages, need personalized approaches to pharmacotherapy. Unfortunately, there is a lack of clinical trials conducted specifically on pediatric populations, leading to limited availability of reliable safety and effectiveness data.
- It is not uncommon for drugs to be used off-label in children, which emphasizes the importance of monitoring.
- Children have metabolic profiles, organ system development, and responses to medications that can significantly differ from those of adults.
- It is crucial to identify and address any expected or unexpected adverse reactions to drugs in this population.
Pediatric Dosing Recommendations
The saying "kids are not just adults" is absolutely true, especially when it comes to determining the right dosage for medications.
Pediatric dosing involves a combination of weight-based calculations considering their development and relying on expertise. Weight-based dosing, usually measured in mg/kg, is crucial. Requires regular updates as children grow. It's essential to take into account the maturity of organ systems, the liver and kidneys.
Dosing decisions also need to consider factors like how sensitive certain receptors are and how drugs interact with them.
Overdosage
Symptoms of Overdose
When it comes to using medications, taking too much can have both positive and negative effects. While the right dosage can provide benefits, accidentally taking too much can lead to a range of symptoms.
Symptoms of an overdose may include issues like a fast or slow heart rate, neurological problems such as feeling dizzy, fainting, or even having seizures, gastrointestinal disturbances like feeling nauseous, vomiting, or experiencing stomach cramps and respiratory difficulties ranging from shortness of breath to slowed breathing.
Management and Antidotes
The immediate and effective management of an overdose is crucial. Key steps involve stabilizing the patient's signs, such as heart rate, breathing, and brain function.
To prevent absorption of the drug, gastric lavage or activated charcoal may be administered. If specific antidotes are available, they can be used to counteract the effects of the drug.
Continuous monitoring and supportive care are provided to ensure the patient's recovery.
Handling Precautions
Safe Handling and Disposal
Pharmaceutical substances, due to their makeup, require careful handling to prevent accidental exposure and negative environmental impacts. Important guidelines for handling include;
- Use personal protective equipment like gloves and masks to avoid direct contact with the skin or inhalation.
- Storing them in sealed containers away, from sunlight and extreme temperatures.
- Following local Guidelines when disposing of expired or unused medications to protect the environment.
Steps in Case of Spillage or Exposure
Unforeseen emergencies, such as spills or direct contact, require addressing them effectively. Here are the recommended steps to take;
1. Quickly evacuate the area affected by the spill, minimizing personnel exposure.
2. Immediately cleanse any exposed skin with plenty of water and mild soap.
3. Use spill. Absorbent materials to contain and neutralize the spill.
4. Seek evaluation after exposure to determine any potential health effects.
Side Effects
Overview of Side Effect Profile
Every medication, like a tapestry, combines therapeutic advantages with possible side effects. It is crucial for healthcare providers to be knowledgeable about these consequences in order to prioritize patient safety.
Distinguishing Common vs. Rare Side Effects
Side effects come in forms and can be categorized based on how often they occur.
- We have side effects, which are relatively common and usually mild, and they tend to improve over time with continued treatment.
- On the other hand, there are rare side effects that occur less frequently but can be severe, requiring immediate medical attention or discontinuation of the medication.
Common Side Effects
Muscle Symptoms
Muscle conditions, ranging from muscle pain to severe muscle breakdown, can unfortunately occur as a side effect of certain medications.
Gastrointestinal Issues
The digestive system, with its workings, is often affected by the introduction of drugs. Some common symptoms include
Discomfort or pain in the abdomen.
Feeling nauseous and/or vomiting.
Changes in bowel movements, such as constipation or diarrhea.
Elevated Blood Sugar Levels
Some medications can disrupt the balance of blood sugar levels, leading to blood sugar.
Patients may experience symptoms such as increased thirst or excessive drinking, frequent urination, unexplained fatigue, or feeling tired all the time.
Conclusion
Summary of Pitavastatin's Therapeutic Profile
Pitavastatin, a regarded member of the statin family, has established itself as an effective medication for lowering lipid levels.
Although its ability to reduce risk is widely acknowledged, healthcare professionals should be vigilant about potential side effects.
Future Research and Developments
The field of drug research is constantly changing. As we gain knowledge about genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, there are opportunities to improve the effectiveness of Pitavastatin as a therapy.
Moving forward, our efforts should be directed towards making it safer, with side effects, and developing personalized medicine approaches that are tailored to individual needs.





























