Propafenone
- I. Introduction to Propafenone
- II. How Propafenone Works
- III. Authorized Uses of Propafenone
- IV. Off-label Uses of Propafenone
- V. Propafenone Dosage and Administration
- VI. Composition of Propafenone
- VII. Storage and Handling Precautions for Propafenone
- VIII. Interactions with Propafenone
- IX. Warnings and Contraindications for Propafenone Use
- X. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
- XI. Common and Serious Side Effects of Propafenone
- XII. Propafenone Overdose
I. Introduction to Propafenone
A. Overview and Clinical Use
Propafenone, which belongs to the Class IC agents, is commonly used in cardiology to treat specific cardiac arrhythmias. These include atrial fibrillation and paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. The primary purpose of this medication is to help restore a heart rhythm and enhance the overall quality of life for individuals affected by these challenging heart conditions.
B. History and Development
Propafenone has been around since the 1980s. It was first used for medical purposes in 1980. Knoll Pharmaceuticals initially developed this drug. It gained approval from the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1989. Since then, researchers have conducted studies on Propafenone, contributing to a better understanding of its effectiveness and safety.
C. General Mechanism of Action
Propafenone works by interfering with the sodium channels in the heart's cells. This interference slows down the activation and transmission of signals within these cells. As a result, Propafenone helps to regulate heartbeats and maintain a more consistent rhythm in the heart.
II. How Propafenone Works
A. Detailed Mechanism of Action
When we dive into the details, Propafenone works in ways. It acts as a sodium channel blocker, which hinders the inward sodium current (INa). This slows down the increase in electrical activity in cardiac cells. As a result, it decreases the speed at which signals travel through the ventricular myocardium leading to its strong ability to treat irregular heart rhythms. It also has selective blocking effects on beta-adrenoreceptors, contributing to its therapeutic benefits.
B. Role in Cardiac Function
Propafenone is a medication for maintaining normal heart function. Its main goal is to regulate the heartbeat in cases where the heart rhythm is fast or irregular. Propafenone reduces the chance of dangerous arrhythmias by slowing down the signals that trigger heartbeats. This positive effect helps the heart pump blood effectively, relieving symptoms and enhancing overall cardiac performance.
C. Effect on Abnormal Heart Rhythms
Propafenone has shown therapeutic benefits in the treatment of abnormal heart rhythms. Conditions like fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia often occur due to rapid electrical signaling in the heart. Propafenone, by blocking sodium channels, can help correct these rhythms. It effectively slows signal conduction, reduces heartbeats, and assists in restoring a normal rhythm. This not provides relief from symptoms but also improves the prognosis for patients with these conditions.
III. Authorized Uses of Propafenone
Treatment of Supraventricular Arrhythmias
Propafenone is prescribed to help prevent the recurrence of heartbeats like atrial fibrillation (AF) in patients without any underlying structural heart conditions.
Here is a reference for you to check out:
: Propafenone: MedlinePlus Drug Information
Usage in Ventricular Arrhythmias
In its tablet form, this medication helps control and reduce the chances of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias, like sustained VT (ventricular tachycardia) or VF (ventricular fibrillation).
Here is a reference for you to check out:
: Propafenone: MedlinePlus Drug Information
Preventive Role in Recurrent Atrial Fibrillation
It has been found that this treatment is similarly effective to quinidine, flecainide, procainamide, and sotalol in preventing the recurrence of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (PAF) and maintaining a normal heart rhythm after successful cardioversion.
Here is a reference for you to check out:
: Propafenone: MedlinePlus Drug Information
IV. Off-label Uses of Propafenone
Propafenone in Non-cardiac Conditions
Propafenone has been prescribed for conditions beyond its approved uses, including bipolar disorder, diabetic nerve pain, complex regional pain syndrome (chronic arm or leg pain after injury or surgery), attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), restless leg syndrome, trigeminal neuralgia (a type of chronic facial pain), migraine and drug and alcohol withdrawal seizures.
Here is a reference for you to check out:
: Propafenone: MedlinePlus Drug Information
Research and Controversies
The use of propafenone for cardioversion of atrial fibrillation or flutter has been observed, even though it is not an approved indication for this medication12.
Here are some references for you to check out:
1: Arrhythmias - Treatment summaries - BNF - NICE 2: Atrial fibrillation: Cardioversion - UpToDate
Future Potential Applications
Propafenone can control various supraventricular tachycardias (SVTs), including focal atrial tachycardia and junctional tachycardia12.
Here are some references for you to check out:
1: ESC Guidelines on Supraventricular Arrhythmias - European Society of Cardiology 2: Focal atrial tachycardia - Symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment | BMJ Best Practice
V. Propafenone Dosage and Administration
A. Standard Dosage Guidelines
The usual starting dose for Propafenone in adults ranges from 150 to 300 milligrams every eight hours. However, the exact dosage may differ based on the patient's weight, kidney function, and the specific heart condition being treated. It's important to remember that the maximum daily dose should not go beyond 900 milligrams to avoid any effects.
B. Individualized Dosage Adjustments
Like other medications, the dosage of Propafenone may need to be adjusted individually depending on how the patient responds. It is common to make changes in dosage for patients with liver or kidney problems, as these organs are essential in how the drug's processed and eliminated from the body. In addition, adjustments may also be necessary for patients who experience effects at standard doses, have other existing health conditions, or are taking other medications simultaneously. It's crucial to consult a healthcare professional who can guide and determine the suitable dosage for each patient's situation.
C. Role of Healthcare Provider in Administration
Healthcare professionals play a role in ensuring the safe use of Propafenone. Their expertise is essential in determining the dosage, making necessary adjustments if needed, and monitoring how patients respond to the medication. Additionally, they offer guidance on handling missed doses administering the drug correctly, and managing any potential side effects. Their advice helps maximize the effectiveness of Propafenone while minimizing any risks involved.
VI. Composition of Propafenone
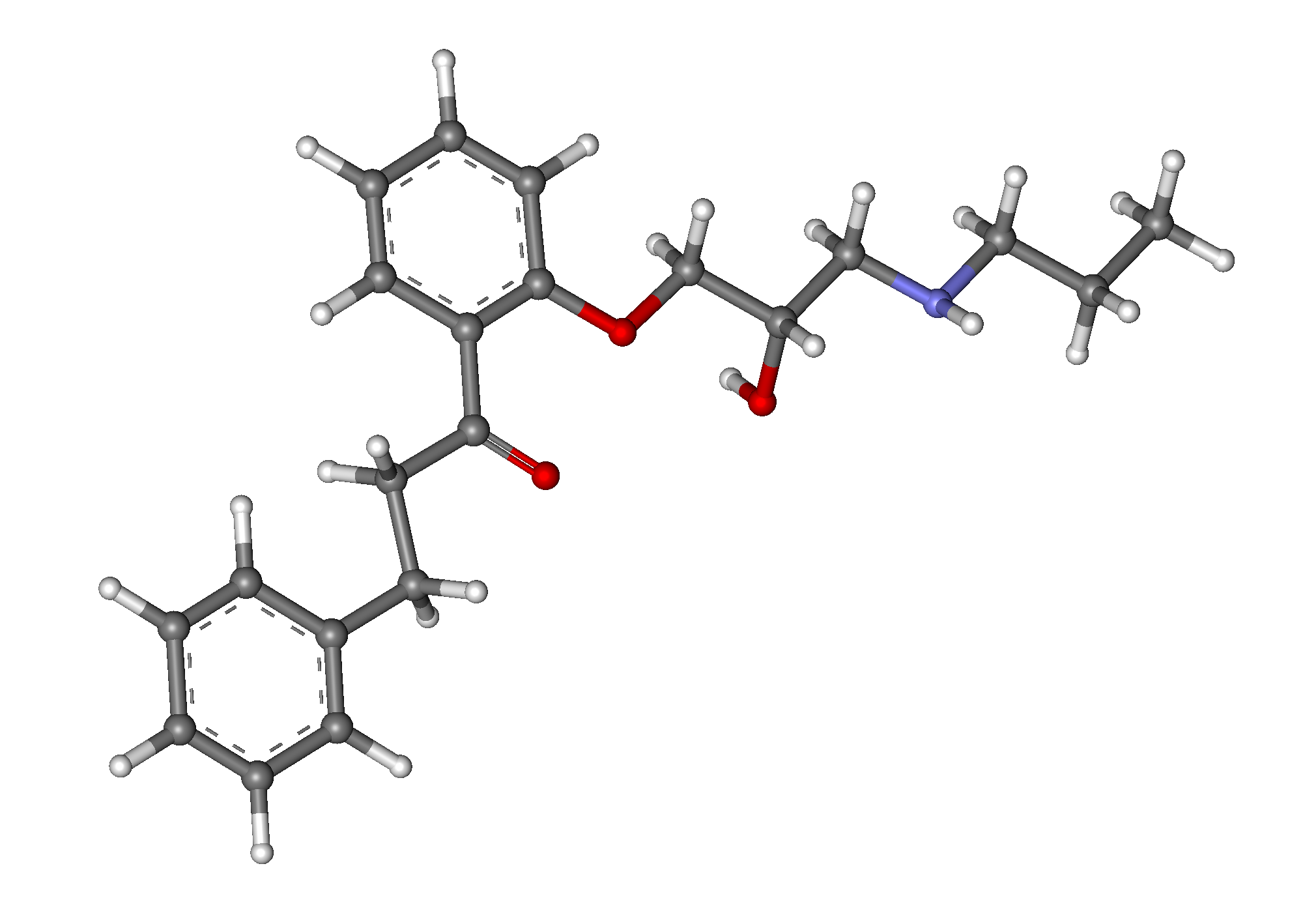
A. Active Ingredients and Their Roles
The main active component found in Propafenone is, not surprisingly, known as Propafenone hydrochloride. This substance works by blocking the sodium channels in the heart, which helps slow the transmission of signals. As a result, it helps to regulate and stabilize the heart's rhythm playing a role in the therapeutic effects of Propafenone.
B. Inactive Ingredients and Their Importance
In addition, the element Propafenone also consists of various inactive ingredients or excipients. These substances include corn starch, hypromellose, and magnesium stearate. While these components may not directly impact therapy, they deliver the medication effectively by aiding absorption and maintaining drug stability. Consequently, they contribute significantly to the effectiveness of Propafenone.
VII. Storage and Handling Precautions for Propafenone
A. Recommended Storage Conditions
Propafenone should be stored at a temperature for humans, typically between 20 to 25 degrees Celsius. Keeping it in the container away from children and pets and protected from direct light and moisture is essential. By storing it, we can ensure that the drug remains effective and safe for use over an extended period.
B. Safety Precautions in Handling and Disposal
When using Propafenone, avoiding getting it in your eyes, mouth, or nose is essential. Remember to wash your hands after handling the medication. If you accidentally come into contact with it seek medical advice. When disposing of Propafenone, follow the pharmaceutical disposal guidelines to minimize any environmental impact.
C. Stability and Shelf-life
The composition and how Propafenone is stored determine its stability and shelf life. If you keep it as recommended, Propafenone will stay stable and effective until its expiration date, typically a few years from when it was made. However, if this period has passed or the medication was not appropriately stored, it should not be. You should arrange for proper disposal.
VIII. Interactions with Propafenone
A. Drug-Drug Interactions
When taking Propafenone, being cautious of interactions with certain medications is essential. These interactions can have effects, such as increasing the risk of side effects or reducing the effectiveness of both drugs. Some specific medicines that can cause interactions include Ritonavir or other potent CYP3A4 inhibitors, which may lead to higher levels of Propafenone in the bloodstream. Drugs that prolong the QT interval should also be used with caution as they can potentially worsen arrhythmias. It's also worth noting that beta blockers can enhance the effects on heart contractility and atrioventricular conduction when combined with Propafenone. Therefore it is crucial to inform healthcare providers about all medications being taken, including, over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
B. Drug-Food Interactions
Some types of food might impact how Propafenone's absorbed or works in the body. For instance, grapefruit juice can raise the levels of Propafenone by blocking CYP3A4, an enzyme that breaks down the drug. Therefore patients should avoid consuming grapefruit or grapefruit juice while taking this medication unless specifically instructed otherwise by their healthcare professional.
C. Impact of Comorbid Conditions
Comorbidities influence how effective and safe Propafenone is. If a patient has liver or kidney disease, their dosage may need to be adjusted because the way their body metabolizes and eliminates the drug can be affected. Additionally, individuals with heart conditions, like heart failure or a previous heart attack, should be cautious when using Propafenone as it could potentially worsen these conditions.
IX. Warnings and Contraindications for Propafenone Use
A. Absolute Contraindications
There are conditions where it is strongly advised not to use Propafenone. These include cases of shock, sick sinus syndrome (except in patients with an artificial pacemaker), uncontrolled heart failure, and severe electrolyte imbalance. In these situations, the potential risks associated with using Propafenone are significantly greater than any benefits it may have.
B. Relative Contraindications
In situations, it is essential to exercise caution when considering using Propafenone. The potential advantages and disadvantages should be thoroughly evaluated. Some factors that suggest being mindful include a history of heart attack, breastfeeding, significant liver or kidney problems, and taking medications that inhibit CYP2D6. Ultimately the decision to prescribe Propafenone should be made on a basis after carefully assessing each case.
C. Important Warnings and Adverse Reactions
Propafenone can potentially lead to some side effects, such as developing or intensifying arrhythmias. Additionally, it might cause severe but still bothersome effects like dizziness, feelings of nausea, or a metallic taste, in the mouth. Patients need to be informed about these adverse reactions and promptly reach out to their healthcare provider if they encounter any of them.
X. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
A. Administration to the Elderly
Elderly individuals might have a sensitivity, to Propafenone and the drug may take longer to leave their system. As a result, it might be necessary to begin with a dose, make adjustments gradually and closely monitor their response.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Propafenone should only be used during pregnancy if the benefits outweigh any risks to the baby. It is essential to consider the impact of the drug, on both the mother's health and the well-being of her nursing infant when deciding whether to continue breastfeeding or stop taking the medication.

C. Administration to Children
The safety and effectiveness of Propafenone in children have not been established, It is not currently recommended for use in this age group.
XI. Common and Serious Side Effects of Propafenone
A. Overview of Propafenone Side Effects
Like any medication, the use of Propafenone can cause severe side effects. These potential adverse reactions can vary in intensity ranging from mild and easily manageable to severe and possibly life-threatening. Patients and healthcare providers must be aware of these side effects to address any concerns and take action when necessary promptly.
B. Most Common Side Effects and Their Management
Propafenone may lead to some side effects, such as feeling dizzy or lightheaded, experiencing nausea or vomiting, having an unusual taste in the mouth, constipation, and headaches. These side effects are usually mild. Tend to diminish as your body gets accustomed to the medication. However, you should contact your healthcare provider if they continue or worsen. Prescription remedies and lifestyle changes can often assist in managing these commonly experienced side effects.
C. Serious Side Effects and Emergency Interventions
Common but severe side effects of Propafenone necessitate immediate medical attention. These may include experiencing breathing or shortness of breath, irregular heartbeats, chest discomfort or tightness, sudden weight gain, and swelling in the hands, ankles, or feet (known as edema). If any of these symptoms manifest, it is crucial to seek emergency assistance promptly. These symptoms might indicate a reaction to the medication or an aggravation of an existing heart condition.
XII. Propafenone Overdose
A. Signs and Symptoms of Overdose
An overdose of Propafenone can happen if a patient exceeds the recommended dosage or if the medication builds up in the body due to difficulties with metabolism or elimination. Signs of an overdose may include experiencing dizziness or fainting, having an unusually slow or fast heartbeat having seizures, or even losing consciousness.
B. Immediate Actions and Emergency Treatment
If you suspect an overdose, it's crucial to seek medical help. Contact your poison control center or emergency services right away. Treating a Propafenone overdose primarily involves providing support and addressing symptoms to maintain bodily functions. This may include monitoring the heart performing lavage, administering activated charcoal, and giving intravenous fluids.
C. Long-term Consequences and Follow-up Care
The long-term effects of taking much Propafenone will vary depending on how severe the overdose was and how quickly it was treated. In some situations, there might not be any lasting consequences. However, if the overdose is powerful, it could potentially cause harm to the heart or other organs. It is essential to monitor the patient's recovery and take steps to prevent future overdoses. This may involve monitoring their medication schedule, adjusting their dosage if necessary, or even considering alternative medications.