Rosiglitazone/glimepiride
- 1. Introduction to Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride
- 2. Uses of Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride
- 3. Composition and Formulation
- 4. How Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride Works in the Body
- 5. Dosage and Administration
- 6. Storage and Handling Precautions
- 7. Side Effects of Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride
- 8. Drug Interactions
- 9. Warnings and Contraindications
- 10. Careful Administration in Special Populations
- 11. Overdosage: Recognition and Management
- 12. Important Precautions for Safe Use
- 14. Handling Precautions
1. Introduction to Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride
Overview of Rosiglitazone and Glimepiride
Rosiglitazone and Glimepiride are medications for managing type 2 diabetes when used together in treatment plans. They work together to improve insulin sensitivity and regulate glucose metabolism; rosiglitazone is classified as a thiazolidinedione, while Glimepiride falls under the category of sulfonylureas.
Historical Development and Approval
Rosiglitazone made its debut in the 1990's after receiving FDA recognition, for its effectiveness in enhancing insulin resistance levels while Glimepiride was approved earlier in 1995 for its ability to stimulate insulin secretion in the pancreas.The pairing of these two medications was intended to offer a strategy, for managing diabetes.
Combination Therapy: Why Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride?
This pairing targets how diabetes affects the body's functions; rosiglitazone increases sensitivity to insulin in tissues, and Glimepiride boosts insulin production by beta cells. This holistic approach aids in managing blood sugar levels over time.
Mechanism of Action: Dual Approach to Diabetes Treatment
Rosiglitazone works by binding to receptors in cells known as PPAR gamma receptors to enhance the uptake of glucose in the body tissues. In contrast to this mechanism of action is how Glimepiride functions. It blocks ATP potassium channels in beta cells, which triggers insulin release. When these two medications are used together, their effects synergize, leading to the management of blood sugar levels and a decrease in episodes of blood sugar levels.
2. Uses of Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride
Primary Indications: Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride is recommended for individuals with type 2 diabetes who have not reached blood sugar levels with a treatment option alone. It serves as a treatment method for care and is especially beneficial, for those who do not respond well to insulin therapy.
Long-term Glycemic Control: How it Helps Manage Blood Sugar
When focusing on improving both how the body responds to insulin and how much insulin it produces naturally at the time, with this combination approach helps in maintaining blood sugar levels consistently over a period of time.The frequent application also plays a role, in reducing the risks of complications linked to term high blood sugar levels like nerve damage and eye issues.
Improving Insulin Sensitivity and Beta-cell Function
Rosiglitazone enhances the uptake of glucose in the areas of the body by lowering insulin resistance; meanwhile, Glimepiride stimulates the release of insulin in the pancreas to maintain beta cell function intact. This combined approach helps slow down the progression of the disease and decreases reliance on insulin medication.
Off-label Uses: Emerging Research and Applications
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Rosiglitazone has demonstrated potential, in trials, to decrease liver buildup in individuals with NAFL disease. A treatment possibility that extends beyond just diabetes management.
3. Composition and Formulation
Active Ingredients: Rosiglitazone and Glimepiride
The key components of this combined treatment include Rosiglitazone and Glimepiride, each of which helps manage blood sugar levels.
Available Dosage Forms: Tablet Strengths and Combinations
Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride comes in tablet form with strengths, like 8mg / 6mg or 10mg / 8mg options to cater to patient requirements, for dosages.
Inactive Ingredients and Their Role
Other components, like binders and fillers, play a role in maintaining the effectiveness and absorption of the substances in a formulation.
Glipizide vs glimepiride
Glimepiride was linked to a decreased chance of experiencing episodes and showed better blood sugar management than glipizide; it also led to less weight gain than other sulfonylureas on the market.
Glimepiride and metformin
Glimepiride is prescribed for managing blood sugar levels resulting from type 2 diabetes either by itself or along with insulin or another oral medication like metformin. In type 2 diabetes cases where the pancreas produces insulin struggles to transport sugar effectively to the body's cells for functionality.
Glyburide vs glimepiride
Glimepiride significantly reduces blood sugar levels within 4 hours of taking the medication, with fewer and milder impacts on cardiovascular functions compared to glibenclamide (glyburide). The pharmacokinetics of glimepiride remain largely unchanged in individuals with kidney or liver conditions.
Glimepiride vs jardiance
There was no variation in the FMD alterations between the groups receiving empagliflozin and glimepiride medication.
Ozempic and glimepiride
Taking Ozempic might result in decreased blood sugar (hypoglycemia), especially when combined with sulfonylurea (glimepiride, glyburide, glipizide) or insulin, which can be serious and may lead to death.
4. How Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride Works in the Body
Glimepiride: Stimulating Pancreatic Insulin Secretion
Glimepiride functions by blocking potassium channels within the beta cells of the pancreas which results in a rise in insulin secretion levels. This effect is dependent on glucose levels. It helps lower the chances of experiencing hypoglycemia.
Rosiglitazone: Enhancing Insulin Sensitivity in Muscle and Fat Cells
Rosiglitazone acts on PPAR gamma receptors found in muscles and fat cells to enhance the uptake and use of glucose in the body; this can lead to a decrease in blood sugar levels. It is especially beneficial for patients with insulin resistance.
Time to Onset and Duration of Action
The blend starts to take effect shortly after it is given and reaches its impact in 4 to 6 weeks. Rosiglitazone's lasting impact guarantees glucose levels over time, while Glimepiride offers rapid relief for high blood sugar levels.
5. Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosage Guidelines for Adults
The typical initial dosage for Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride is one tablet. It can be modified according to the patient's blood sugar levels and how they respond to the treatment.
Dosage Adjustments Based on Blood Glucose Levels
It's important to keep track of your fasting blood sugar and HBA ₁ C levels to make sure everything is, in check and adjust your dosage as needed to avoid blood sugar or poor glucose control.
Administration Instructions: With or Without Food?
You can choose to consume the medication, with or without food; however, having it during meals might help decrease any issues, like nausea.
Titration and Maintenance Dosing: Achieving Optimal Glycemic Control
It is advisable to adjust the dosage by increasing it every two weeks until it reaches the desired level of blood sugar control without experiencing any side effects.
Missed Dose Instructions
If you forget to take a dose of the medication and remember later, it's almost time for your dose anyway. Just skip the missed one and continue with your usual dosing schedule.
6. Storage and Handling Precautions
Recommended Storage Conditions
Remember to store Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride in a dry location where it is shielded against moisture and direct sunlight at temperatures below 25°C.
Proper Disposal of Expired or Unused Medication
Follow the guidelines for getting rid of unused tablets instead of flushing them down the toilet or throwing them in the regular household garbage.
Safety Precautions for Handling the Medication
Remember to wash your hands after touching the medication if you're splitting tablets—it helps prevent contamination and is a good hygiene practice for both patients and caregivers.
7. Side Effects of Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride
Overview of Common and Serious Side Effects
When Rosiglitazone and Glimepiride are used together, it can cause a variety of side effects ranging from minor to severe. Everyday side effects may comprise of stomach discomfort. Feeling lightheaded whereas critical issues revolve around potential heart related risks and liver problems.
Risk of Weight Gain and Fluid Retention
Rosiglitazone may cause retention, resulting in weight gain, a side effect that is worrisome for individuals with heart failure.

Liver Function Abnormalities: Monitoring Requirements
It is advisable to have tests for liver function to catch any signs of liver damage early because Rosiglitazone could worsen existing liver problems.
Hypoglycemia: Recognizing Symptoms and Managing Risks
Glimepiride has the potential to raise blood sugar levels in individuals who skip meals or engage in exercise routines. The presence of symptoms, like sweating, difficulty concentrating, and heart palpitations, should be a signal to consume carbohydrates.
7.1 Common Side Effects
Gastrointestinal Disturbances: Nausea, Vomiting, Diarrhea
Frequent gastrointestinal side effects are common but tend to improve with medication use; it is advisable for patients to consume the medication along with food to reduce any discomfort they may experience.
Dizziness and Headaches
In the first few weeks of treatment, you might experience dizziness or headaches as your body gets used to the medication.
Edema and Swelling of Extremities
Swelling in the legs is an outcome of taking Rosiglitazone. In serious situations, changing the dosage or stopping it might be necessary.
Respiratory Infections
Some individuals undergoing the combined treatment experience occurrences of respiratory tract infections.
Glimepiride side effects
- Difficulty with swallowing
- fast heartbeat
- hives
- itching
- puffiness, or swelling of the eyelids or around the eyes, face, lips, or tongue,
- shortness of breath,
- skin rash,
- tightness in the chest
Glimepiride side effects weight gain
After beginning treatment, with glimepiride medication for diabetes management patients typically gain around 5 pounds on average in weight over time as a side effect of the medication itself it is essential to note that when using any diabetes medication such, as glimepiride it is crucial to maintain a diet and engage in physical activity to achieve optimal outcomes this approach can also assist in avoiding weight gain associated with the treatment
7.2 Serious Side Effects and Warnings
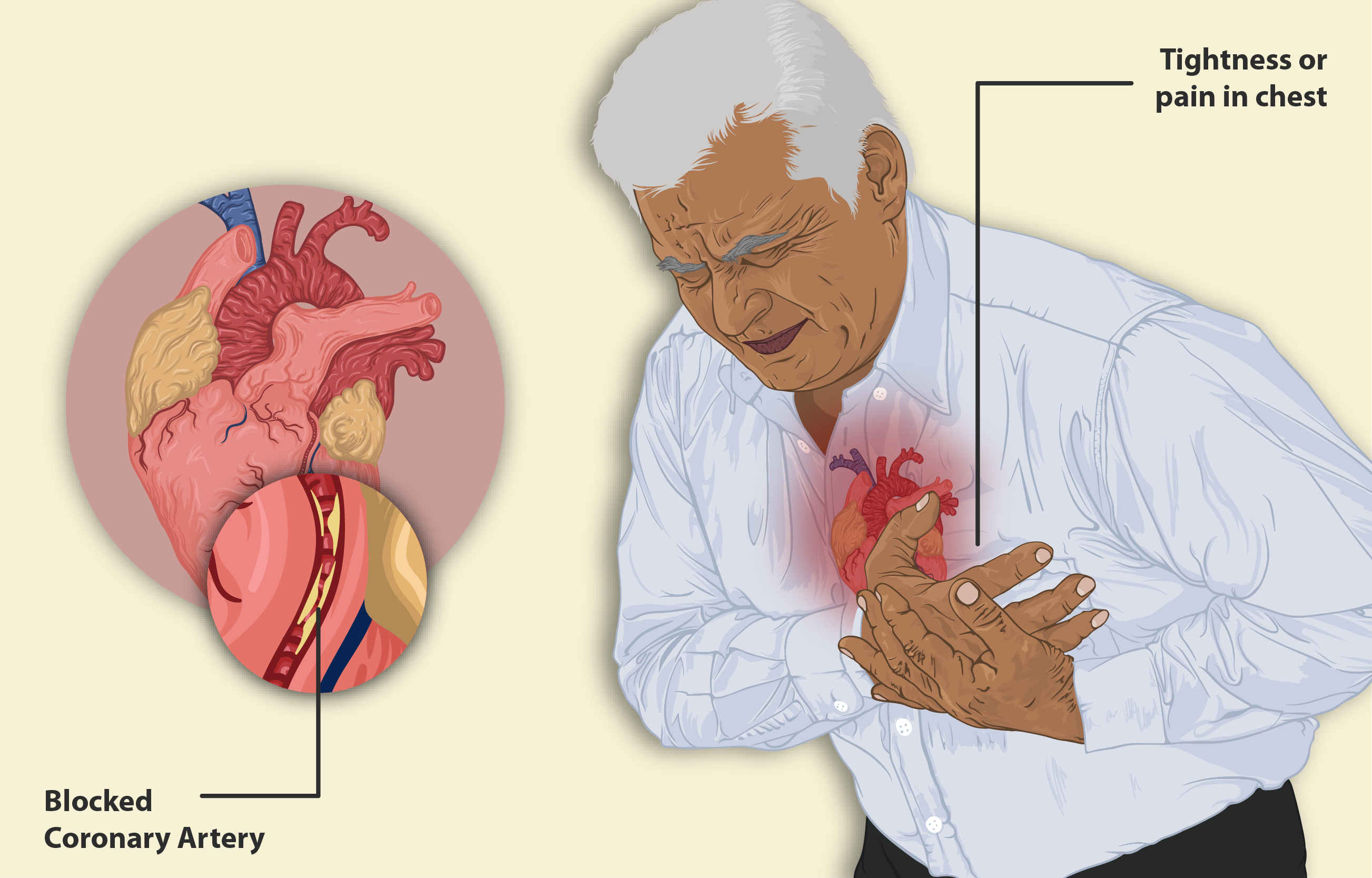
Cardiovascular Risks: Heart Failure and Myocardial Infarction
Individuals who have a background of heart-related issues should be careful when considering Rosiglitazone due to its association with a likelihood of heart failure and heart attack occurrences.
Bone Fractures and Osteoporosis: Risk in Long-term Use
Using Rosiglitazone for a period may raise the chances of bone fractures in women specifically; doctors might suggest taking extra calcium and vitamin D to help mitigate this risk.
Hypoglycemia-Induced Coma: Identifying Early Signs
Severe low blood sugar levels may result in a coma or seizures, so individuals and caregivers need to be educated on spotting signs and taking timely action.
Severe Allergic Reactions: Rash, Itching, Anaphylaxis
In cases of medication reactions, occurrences like rash and itching should prompt stopping the drug right away and seeking medical help for symptoms such as swelling and breathing difficulties.
8. Drug Interactions
Major Drug Interactions: Medications to Avoid
Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride may have interactions with medications that could change how well they work or increase the chances of experiencing side effects. It's important to avoid taking them with CYP2C8 inhibitors like gemfibrozil, as this can greatly increase Rosiglitazone levels. Similarly, medications, like rifampin, that boost this enzyme could make it less effective. Given these interactions it's crucial to monitor or consider treatment options.
Interaction with Other Diabetes Medications
When taking metformin with medications like insulin or insulin secretagogues, it may lead to a higher risk of experiencing hypoglycemia, so it's important to be cautious when adjusting doses to avoid lowering blood sugar levels too much. The use of metformin together with Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride can be beneficial for targeting hepatic glucose production, but you should make sure to monitor your glucose levels regularly while on this combination treatment.
Food and Alcohol Interactions: Guidelines for Safe Consumption
It is recommended to take Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride with food to reduce stomach discomfort caused by the medication's effects on the system. When it comes to alcohol consumption with these medications, though, it's important to be cautious as it can worsen blood sugar levels when taken along with Glimepiride. Excessive drinking may also heighten the risks associated with liver issues related to Rosiglitazone. Patients should be informed about the importance of moderation and regular checkups for their well-being.
Monitoring Requirements for Patients on Multiple Medications
Patients who are prescribed medications that need monitoring are those with long-term conditions, like high blood pressure or heart disease, as drug interactions can significantly impact liver function and cardiovascular health outcomes. It's crucial to check liver function and blood glucose levels to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the treatment regimen.
9. Warnings and Contraindications
Patients with Heart Failure: Contraindications and Warnings
Patients with a history of severe congestive heart failure (Class III or IV, according to NYHA) should avoid using Rosiglitazone as it may result in fluid retention and worsen symptoms of heart failure. Clinicians need to evaluate patients' heart health before starting treatment, paying attention to those with existing heart conditions.
Risk of Liver Disease: Precautions for Liver Function Monitoring
Rosiglitazone has been linked to liver-related issues such as liver damage and toxicity. Concerns have been raised regarding its impact on the liver function tests that should be done before starting treatment and afterward to monitor for any abnormalities or signs of liver problems, which could lead to the need to stop the treatment if necessary.
Contraindications in Patients with Severe Renal Impairment
Patients with kidney issues should avoid taking Glimepiride because it is mainly eliminated through the kidneys and can lead to prolonged blood sugar levels in such situations; therefore, other treatment choices are necessary.
Black Box Warning: Cardiovascular Risk with Rosiglitazone
Rosiglitazone is marked with caution regarding its heart-related dangers, specifically a higher chance of heart attacks. Individuals, with an incidence of heart disease or who're vulnerable, to cardiovascular issues should steer clear of this medication or consider its usage only after a thorough assessment of the pros and cons.
10. Careful Administration in Special Populations
10.1 Administration in Elderly Patients
Adjusting Doses for Age-Related Renal or Hepatic Function Decline
As people get older, their kidneys and liver may not work as before, so doctors may need to adjust medication doses to prevent build-up and potential side effects from medications being more robust in the body of older patients. It's essential to keep an eye on kidney and liver function in individuals to avoid any problems that could arise.
Increased Risk of Hypoglycemia in the Elderly Population
Older individuals face an increased susceptibility to blood sugar levels because of factors such as decreased kidney function and the likelihood of taking multiple medications simultaneously. It is crucial to adjust medication doses and monitor blood sugar levels to lower the chances of experiencing severe episodes of hypoglycemia.
10.2 Administration in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Safety Data on Use During Pregnancy: Risk-Benefit Assessment
Safety information about using Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride while pregnant is insufficiently reliable at the time, as data sources in this regard are scarce. Now, it appears only animal testing has revealed some conceivable dangers, like potential harm to the fetus, which implies that caution should be exercised when deciding whether to use the medication during pregnancy, and it is usually advised to consider other treatment options instead.
Lactation: Can Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride Be Used During Breastfeeding?
It remains uncertain if Rosiglitazone or Glimepiride is passed into breast milk as of yet unknown. With the risk of causing effects on breastfeeding babies, mothers are encouraged to stop nursing or taking the medication based on how essential it is for the mother.
10.3 Administration in Pediatric Patients
Clinical Data on Efficacy and Safety in Children and Adolescents
Limited clinical information exists regarding the safety and effectiveness of Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride in children and adolescents, leading to the medication not being commonly advised for this age group due to a lack of evidence supporting its benefits and safety profile.
Off-label Use in Pediatric Populations
Some healthcare providers have looked into using Rosiglitazone, off-label in kids with insulin resistance syndromes; Guidelines do not strongly back it and needs more research.
11. Overdosage: Recognition and Management
Symptoms of Overdose: Hypoglycemia, Hepatotoxicity, and Cardiovascular Events
Taking too much Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride could result in low blood sugar levels with symptoms like confusion and sweating, which may lead to uncontrollable shaking and seizures as well. Moreover, liver problems could show up as yellowing of the skin or unusual liver enzyme levels. It is important to note heart-related issues such as heartbeats or worsening of heart failure conditions.
Glimepiride max dose
The highest amount you can take in a day is 6mg. Your doctor will monitor any adjustments to your dosage through blood sugar level checks.
Immediate Interventions for Overdose Cases
When someone experiences blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia), it is advised to give them glucose immediately to help raise their blood sugar levels quickly and effectively. If a person is unconscious due to hypoglycemia, don't administer glucose intravenously for action. For conditions like liver damage and heart-related symptoms, it's crucial to admit the patient to the hospital for observation and necessary care.
Emergency Treatment Protocols
In cases of overdose situations when someone has taken much of a substance recently, stomach pumping might be thought about as a course of action to take if it happened not long ago. The person should also receive fluids through a vein, and additional supportive actions must be taken, such as keeping an eye on any irregular heart rhythms or other heart-related issues.
12. Important Precautions for Safe Use
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels Regularly
Patients taking Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride should check their blood sugar levels to prevent low blood sugar levels. Based on the results, they should make changes to their diet, physical activity routine, and medication.
Importance of Adherence to Diet and Exercise
Maintaining a diet and sticking to an exercise routine are vital in managing type 2 diabetes, alongside medication, to improve insulin sensitivity and control blood sugar levels effectively.
Recognizing Signs of Heart Failure Early
Patients need to be informed about how to identify symptoms of heart failure, like weight gain or swelling and difficulty breathing, early on to help prevent the condition from worsening rapidly. Timely medical care is crucial in managing heart failure cases involving Rosiglitazone intake.
Precautions for Patients with Liver or Kidney Disease
Individuals with existing liver or kidney conditions, need supervision in their care regimen. Regular liver function assessments are crucial to monitor for any indications of jaundice or unusual enzyme levels that may necessitate a reassessment of the treatment plan.
14. Handling Precautions
Handling Guidelines for Healthcare Providers
Healthcare professionals need to be careful when handling Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride tablets. They should take precautions when dividing doses of the medication by wearing gloves to avoid contact and practicing proper hand hygiene.
Instructions for Patients: Safe Storage and Use at Home
Remember to keep Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride in a dry place, out of reach of children and pets, without crushing or chewing the tablets. Adhere to the dosage to avoid over- or underdosing.
Special Considerations for Healthcare Workers
Healthcare providers who prescribe Rosiglitazone/Glimepiride should be mindful of the side effects and closely observe their patients' conditions.It is important to exercise caution when treating groups like the elderly or individuals with existing health conditions.
Rosiglitazone/glimepiride FAQ
- When to take glimepiride?
- How long does it take for glimepiride to work?
- How to take glimepiride?
- How much glimepiride can you take in a day?
- When is the best time to take glimepiride?
- When should I take glimepiride and metformin?
- How long does glimepiride stay in your system?
- What should you avoid while taking glimepiride?
- How long does it take for glimepiride to start working?
- What is the difference between glimepiride and glipizide?
- How much does glimepiride lower blood sugar?
- What is rosiglitazone used for?
- How is rosiglitazone administered?
- How rosiglitazone works?
- Can rosiglitazone cause heart problems?
- What are rosiglitazone used for?
- When to take glimepiride?
- How long does it take for glimepiride to work?
- How to take glimepiride?
- How much glimepiride can you take in a day?
- When is the best time to take glimepiride?
- When should I take glimepiride and metformin?
- How long does glimepiride stay in your system?
- What should you avoid while taking glimepiride?
- How long does it take for glimepiride to start working?
- What is the difference between glimepiride and glipizide?
- How much does glimepiride lower blood sugar?
- What is rosiglitazone used for?
- How is rosiglitazone administered?
- How rosiglitazone works?
- Can rosiglitazone cause heart problems?
- What are rosiglitazone used for?
When to take glimepiride?
Most individuals prefer to consume it in the morning alongside their morning meal or breakfast routine; however, if breakfast is skipped, ensure that it is taken with the meal of the day at a specific time each day as prescribed for optimal results. For easier consumption, remember to ingest the tablets whole with a sip of water.
How long does it take for glimepiride to work?
Glimepiride can lower blood sugar within 2 to 3 hours of taking it even though you might not notice any changes, especially when you are not experiencing diabetes symptoms; however, it's crucial to continue the medication regimen as prescribed by your healthcare provider to maintain blood sugar levels. The usual adverse effects include nausea, vomiting, and stomach discomfort in addition, to the risk of blood glucose) In some cases, it is due to glimepiride usage.
How to take glimepiride?
You typically need to consume glimepiride, and it is advisable to take it along with a meal for better absorption in your system; most individuals opt to do so in the morning with their breakfast meal or their first meal of the day if breakfast is skipped.
How much glimepiride can you take in a day?
Adults typically begin with a 1mg dose daily. May have their dosage adjusted by the doctor over several weeks or months to reach a standard 4mg daily dose limit with a maximum of 6mg, per day.
When is the best time to take glimepiride?
You should usually take glimepiride daily. Remember to have it with food—typically in the morning with your breakfast or with your first meal if you skip breakfast.
When should I take glimepiride and metformin?
Glimepiride is prescribed for managing blood sugar levels resulting from type 2 diabetes either on its own or alongside insulin or other oral medications, like metformin.
How long does glimepiride stay in your system?
Glimepiride typically begins to lower blood sugar levels within 2 to 3 hours of taking a dose and can remain effective for up to a day. If Glimepiride's efficacy decreases over time, your healthcare provider might consider raising the dosage or incorporating another diabetes medication, like metformin, into your treatment regimen.
What should you avoid while taking glimepiride?
Remember to steer clear of alcohol, as it can reduce blood sugar levels and potentially disrupt your diabetes management plan. Also, be cautious with sunlight and tanning beds while taking Glimepiride, as it may increase your vulnerability to sunburn.
How long does it take for glimepiride to start working?
Glimepiride typically begins to lower blood sugar levels within 2 to 2 hours after taking a dose. Its effects can last for up to a day before requiring another dose adjustment by your doctor, either by increasing the dosage or incorporating additional diabetic medications like metformin into your treatment regimen.
What is the difference between glimepiride and glipizide?
In one-year trials, glimepiride showed effectiveness compared to glibenclamide and glipizide; nonetheless, it seems that glimepiride leads to a reduction in blood sugar compared to glipizide during the initial weeks of treatment.
How much does glimepiride lower blood sugar?
Glimepiride and other sulfonyluareas have been known to lower A ̇ levels by around
What is rosiglitazone used for?
Rosiglitazone is prescribed for managing type 2 diabetes either on its own or in combination with medications, like metformin or sulfonylureas, while being accompanied by a diet and regular exercise to regulate blood sugar levels effectively.
How is rosiglitazone administered?
Patients could begin taking 4 mg of the medication a day or in two doses initially and adjust the dosage based on their response over 8 to 12 weeks by increasing it to 8 mg daily if needed due to insufficient reduction in fasting plasma glucose levels.
How rosiglitazone works?
Rosiglitazone belongs to a group of drugs known as thiazolidinediones that aid in boosting the body's response to insulin, which is a component of regulating blood sugar levels.
Can rosiglitazone cause heart problems?
Thiazolidinediones, like rosiglitazone, may worsen congestive heart failure symptoms in patients taking the medication; hence, it is important to monitor for signs such as weight gain or shortness of breath and consider stopping the therapy if such symptoms occur after initiating or adjusting the dose.
What are rosiglitazone used for?
Rosiglitazone is a medication prescribed for managing type 2 diabetes. It can be taken alone or in combination with medications like metformin or sulfonylureas, along with adhering to a diet and regular exercise regimen to regulate blood sugar levels effectively.
When to take glimepiride?
Most individuals commonly consume it in the morning alongside their breakfast meal; if you happen to skip breakfast or regularly decide not to start your day with a meal thing in the morning be sure to accompany your first meal of the day with it instead as a replacement plan throughout the week ahead, for consistency purposes and routine formation habits; aim for a consistent time slot each day for consumption to establish a daily habit that works best for you; remember to ingest the tablets whole and wash them down with a sip of water as you do so to ensure proper intake and absorption into your system effectively.
How long does it take for glimepiride to work?
Glimepiride can lower blood sugar levels within 2 to 3 hours after taking it, even though you may not notice any changes, especially when you don't exhibit diabetes symptoms; however, it's crucial to continue with the medication regimen as prescribed by your healthcare provider for results and management of the condition. Common adverse effects associated with glimepiride include nausea and stomach discomfort along, with diarrhea while occasionally leading to episodes of blood sugar known as hypoglycemia.
How to take glimepiride?
You typically need to take glimepiride daily and should do so while having a meal. For individuals, this involves taking it in the morning alongside breakfast; if you skip breakfast, then be sure to take it during your first meal of the day.
How much glimepiride can you take in a day?
Adults typically begin with a starting dose of 1mg per day. Their dosage may be gradually increased by the doctor over weeks or months to reach a standard dose of 4mg daily, with a maximum limit of 6mg per day.
When is the best time to take glimepiride?
You typically need to take glimepiride with a meal. Many individuals choose to take it during their morning breakfast or with their first meal of the day if they skip breakfast.
When should I take glimepiride and metformin?
Glimepiride is prescribed for managing blood sugar levels resulting from type 2 diabetes either as a treatment or in conjunction with insulin or another oral medication, like metformin.
How long does glimepiride stay in your system?
Glimepiride typically begins to lower blood sugar levels within 2 to 2 hours of taking a dose and can continue to be effective for up to a day afterward. If Glimepiride seems to lose its effectiveness over time, your doctor might consider raising the dosage or incorporating another medication, like metformin, into your treatment regimen.
What should you avoid while taking glimepiride?
Steer clear of alcohol as it can reduce blood sugar levels and potentially disrupt your diabetes management plan; also, try to minimize your exposure to sunlight and tanning beds because Glimepiride might increase your susceptibility to sunburn.
How long does it take for glimepiride to start working?
Glimepiride typically begins to lower blood sugar levels within 2 to 3 hours of taking a dose. It can remain effective for up to 24 hours durationally before necessitating a potential dose adjustment or the addition of another diabetic medication, like metformin, per your doctor's recommendation if its efficacy diminishes over time.
What is the difference between glimepiride and glipizide?
Glimepiride showed effectiveness compared to glibenclamide and glipizide in studies conducted over a year. However, glimepiride seems to lower blood sugar levels more than glipizide during the initial weeks of treatment.
How much does glimepiride lower blood sugar?
Glimepiride and other sulfonylureas can lower AIC levels by 150 basis points.
What is rosiglitazone used for?
Rosiglitazone is prescribed for managing type 2 diabetes either on its own or in combination with medications, like metformin or sulfonylureas, as part of a regimen that also includes a diet and regular physical activity to regulate blood sugar levels.
How is rosiglitazone administered?
Patients may start taking 4 mg of the medication a day or split into two doses initially. Then based on their response, after 8 to 12 weeks by observing the decrease, in fasting plasma glucose (FPG) the dosage can be raised to 8 mg daily if needed.
How rosiglitazone works?
Rosiglitazone belongs to a category of drugs known as thiazolidinediones and functions by enhancing the body's response to insulin, a component that regulates blood sugar levels.
Can rosiglitazone cause heart problems?
Rosiglitazone and other thiazolidinediones may worsen congestive heart failure symptoms in patients taking them for diabetes treatment purposes, like weight gain or difficulty breathing signals possible heart failure issues necessitating discontinuation of the medication after monitoring and adjusting the dosage as needed.
What are rosiglitazone used for?
Rosiglitazone is prescribed for managing type 2 diabetes either on its own or in combination with medications like metformin or sulfonylureas. It is complemented by a diet and regular exercise to regulate blood sugar levels effectively.












