Singulair
- I. Introduction
- II. Uses of Singulair
- III. How Singulair Works
- IV. Dosage and Administration
- V. Composition
- VI. Side Effects of Singulair
- VII. Common Side Effects
- VIII. Off-Label Uses of Singulair
- IX. Interactions with Other Medications
- X. Warnings and Precautions
- XI. Contraindications
- XII. Careful Administration
- XIII. Important Precautions
- XIV. Special Considerations for Specific Populations
- XV. Overdosage
- XVI. Storage Recommendations
- XVII. Handling Precautions
I. Introduction
Throughout the annals of history, there have been numerous remarkable advancements, including the introduction of Singulair. This medication has revolutionized medicine, particularly in pulmonology and allergy treatment. Its main objective is to offer a therapeutic solution for various respiratory ailments and allergic symptoms.
Historical Development and Discovery of Singulair
Singulair was created through scientific research with the goal of finding a powerful medication to address common respiratory issues. Its development was not a coincidence. Instead, the result of dedicated work from numerous scientists and researchers.
Primary Role in Medical Treatment
Singulair quickly established itself as a practical solution for specific medical conditions. Its primary function is to act as a barrier, fighting against the causes of allergic reactions and providing relief to individuals struggling with respiratory issues.
II. Uses of Singulair
Singulair is a prescription medication that is effective in treating asthma, a chronic respiratory condition that involves narrowed airways and inflammation, often requiring long-term management. It provides relief from symptoms in this situation. Moreover, Singulair is also beneficial for preventing and managing rhinitis. It helps alleviate the nasal congestion, sneezing, and nose associated with allergies, making it a popular choice among many individuals. Additionally, Singulair is useful for addressing exercise-induced bronchoconstriction. This condition can occur after exertion and can impact athletes and fitness enthusiasts. By taking Singulair as a measure, it helps maintain smoother respiratory functions. Overall, Singulair’s versatility makes it an important medication for conditions related to the respiratory system 1.
III. How Singulair Works
Understanding how Singulair works provides insights into its effectiveness as a therapeutic agent.
Mechanism of Action in the Body
When you take Singulair, it doesn't just hide the symptoms; it actually focuses on addressing the problem. It blocks pathways in the body responsible for causing inflammation and triggering allergic reactions.
Role of Leukotriene Receptors
Singulairs' central role is to block leukotriene receptors which are chemical compounds that worsen allergic and inflammatory reactions. By preventing their activity Singulair helps reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms.
IV. Dosage and Administration
To achieve the therapeutic outcomes it is essential to follow specific guidelines when administering Singulair.
Standard Dosage Recommendations
It usually is recommended for adult patients to take a dose of medication unless there are any specific reasons not to. It is important to maintain consistency in dosage and take the medication at the time to achieve the desired results.
Adjustments Based on Patient Factors
Every patient is unique. Variables such as age, existing medical conditions, and body weight may require modifications to the recommended dosage.
Timing and Frequency of Administration
To make sure that Singulair works effectively it's essential to take it preferably at the same time every day. This consistency helps in keeping an amount of the medication in your bloodstream.
V. Composition
Going further into its makeup, Singulair takes pride in its crafted combination.
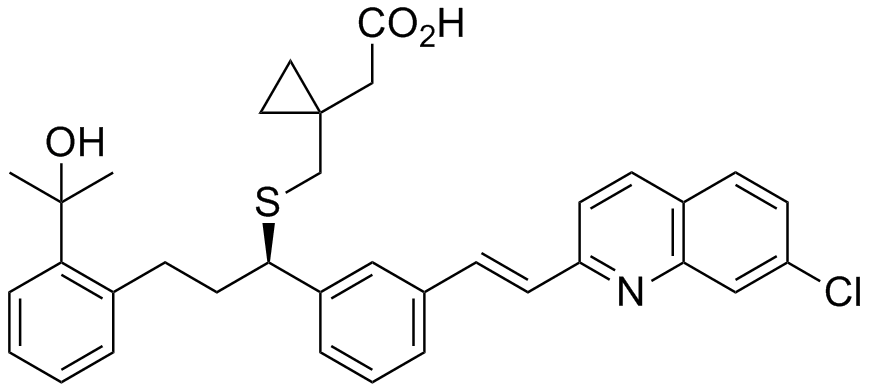
Active Ingredients
Singular therapeutic properties are attributed to its ingredient, montelukast sodium, which effectively targets allergic and inflammatory responses.
Inactive Components
In addition to the ingredient, there are several inactive compounds present. Although they do not directly contribute to the effect of the drug, they play a role in aspects such as drug stability and absorption.
Formulations and Available Strengths
Singulair comes in forms, such as tablets, chewable tablets, and granules designed to meet patients' preferences and age groups. These formulations are available in a range of strengths to accommodate the needs of each patient.
VI. Side Effects of Singulair
Singulair offers hope to individuals, but it's essential to acknowledge that it may have some side effects.
Introduction to Potential Side Effects
Like medications, Singulair can have side effects despite its benefits. Some people may experience symptoms during their treatment with Singulair.
Difference Between Common and Rare Side Effects
Several patients experience side effects commonly encountered, whereas rare side effects occur infrequently and are observed in only a tiny percentage of individuals. Recognizing this difference aids in assessing the level of risk associated with the medication.
VII. Common Side Effects
After taking Singulair, it is expected to experience various difficulties and challenges.
Respiratory Symptoms
Some people may experience symptoms such as coughing, nose congestion, and respiratory tract infections.
Gastrointestinal Disturbances
Some individuals may encounter stomach discomfort, diarrhea, or feelings of nausea, indicating that the medication is affecting their system.
Neurological Side Effects
It is not uncommon to experience headaches, dizziness, or difficulties sleeping as a result of the effects of the drug on the system.
VIII. Off-Label Uses of Singulair
Singulair has been found to have applications beyond its approved uses.
Overview of Unofficial Treatment Applications
Efficacy and Safety in Off-Label Applications
While exploring these uses may seem promising, it is crucial to proceed with caution. It is essential to carefully evaluate Singulair's safety and effectiveness in such situations, which requires thorough patient monitoring and feedback.
IX. Interactions with Other Medications
It's important to understand that medications, although helpful, can sometimes interact with each other. These interactions can. Reduce the effectiveness of the drug or increase adverse side effects.

Potential Risk with Other Asthma Medications
When Singulair is taken together with medications for asthma, its effects might change. This means that the combination of drugs could either work together or against each other, and it may be necessary to adjust the dosages to ensure that they all work well together for treatment.
In situations where microbial infection therapeutics, including antibiotics, antifungals, and antivirals, are involved, it is essential to monitor and potentially adjust the dosage of Singulair due to possible interactions in terms of its pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics.
Other Drug Categories of Concern
In addition to the categories mentioned earlier, there are types of medications like blood thinners, drugs for high blood pressure, or medicines that weaken the immune system, which may have unexpected interactions. It is essential to inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are taking at the time to prevent any potential problems from arising.
X. Warnings and Precautions
Medication treatments, while generally beneficial, require consideration at times. Understanding the situations in which Singulair should be used judiciously is crucial.
Situations when Singulair Should be Used with Caution
Individuals with existing liver conditions, a history of disorders, or currently taking certain medications should exercise caution when considering Singulair.
Monitoring and Signs of Adverse Reactions
Regular clinical evaluations are crucial when taking Singulair. It's essential to detect any signs of mood changes, heart palpitations, or significant digestive issues, on as they could indicate possible adverse reactions.
XI. Contraindications
Sometimes, there may be situations where administering Singulair might not be wise. It is essential to identify these conditions to prioritize the safety and well-being of the patient.
Specific Medical Conditions
Some medical conditions, such as acute liver diseases or specific genetic disorders, may make it inadvisable to use Singulair due, to the increased risk of complications.
Potential Drug Interactions
The simultaneous use of medications, especially those processed by specific liver pathways, could create potential risks. These risks may lead to either build-up of drugs in the body or reduced effectiveness of treatment.
XII. Careful Administration
Administering Singulair requires consideration to maximize its therapeutic benefits and minimize potential risks.
Considerations for Specific Patient Groups
Some patients may need customized Singulair treatment plans due to their physiological characteristics. These specific factors could include age, existing medical conditions, or the functionality of organs.
Monitoring Parameters for Safety
Regularly conducting examinations is crucial to ensure safety. These examinations involve monitoring parameters such as liver function tests, neuropsychiatric evaluations, and respiratory function assessments.
XIII. Important Precautions
To achieve the results from your Singulair treatment, it is essential to take certain precautions.
Adjustments for Patients with Liver Issues
Patients with compromised liver function may require doses of medication or longer intervals between administrations. This is important to prevent drug buildup and potential complications that may follow.
Recommendations for Discontinuation and Signs of Intolerance
If patients experience symptoms such as digestive issues, noticeable changes, in mood, or allergic reactions, it may be necessary to stop taking Singulair. These signs could indicate that the body is not tolerating the medication well.
XIV. Special Considerations for Specific Populations
a. Administration to the Elderly
Elderly individuals frequently experience changes in how their bodies process medications. As a result, it may be necessary to adjust dosages to ensure that the treatment is both safe and effective. It is crucial to monitor for any potential side effects, considering the increased vulnerability of this age group.
b. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Ensuring the safety of the fetus and infant is crucial when administering Singulair to women. It is essential to evaluate the potential risks to the baby compared to the therapeutic advantages. When it comes to pregnancy and breastfeeding, Singulair should only be used if necessary and after analyzing the risks and benefits.
c. Administration to Children
Children undergoing treatment may show different responses due to their developing bodies. It is important to use age doses of medications to ensure the right concentration and prevent potential risks. The safety of using these drugs in patients has been extensively studied, but it is still crucial to remain vigilant.
XV. Overdosage
If someone accidentally or purposely takes much Singulair, it is essential to seek immediate medical help.
Symptoms of Singulair Overdose
Manifestations may encompass gastrointestinal issues, heart palpitations, feelings of drowsiness, or even symptoms related to the nervous system.
Emergency Management and Antidotes
In such situations, it is crucial to perform gastric lavage, provide symptomatic treatment, and closely monitor the patient's condition. Although we don't have an antidote, providing supportive care can help alleviate most potential issues.
XVI. Storage Recommendations
To ensure that Singulair remains effective, it is essential to store it.
Optimal Storage Temperature and Conditions
The medication should be stored where it is shielded from light, preferably at room temperature. It's essential to avoid exposing it to humidity or extreme temperatures as these conditions could potentially impact its effectiveness.
Shelf-life and Expiration
It is crucial to use the product within its recommended shelf life. After it expires, its effectiveness. There may be concerns about its safety.
XVII. Handling Precautions
Singulair is certainly effective in its capabilities but it's essential to be cautious when handling it.
Safety During Administration and Disposal
Taking precautions to minimize contact, wearing gloves when needed, and employing proper disposal techniques can help mitigate environmental and personal risks.
Precautions for Caregivers and Medical Professionals
Caregivers and healthcare professionals need to be informed about the possibility of particles, and they should use masks if required and practice regular hand hygiene after administering any treatments.