Theophylline Syrup
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Composition of Theophylline Syrup
- 3. Uses of Theophylline Syrup
- 4. Off-Label Uses of Theophylline
- 5. How Theophylline Works
- 6. Dosage and Administration
- Theophylline and Guaifenesin cough syrup
- Theophylline and caffeine
- 7. Administration to Specific Populations
- 8. Side Effects of Theophylline Syrup
- 9. Important Precautions and Warnings
- 10. Handling and Storage of Theophylline Syrup
- 11. Overdose and Emergency Management
1. Introduction
Overview of Theophylline Syrup
Theophylline Syrup is commonly recommended as a bronchodilator for managing asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Its main purpose is to help relax the muscles around the airways, allowing airflow into the lungs and making breathing easier for individuals with breathing difficulties.
Brief History of Theophylline Use in Medical Treatments
Since the 1900s, Theophylline, a substance originating from xanthine found in tea and cocoa beans, has been employed in the field of medicine. Its progression in application showcases notable developments in comprehending respiratory conditions and how they are treated with medications.
2. Composition of Theophylline Syrup
Active Ingredients and Their Functions
Theophylline is an ingredient that acts as a strong bronchodilator. It works by blocking phosphodiesterase, which results in higher cAMP levels and the subsequent relaxation of smooth muscles.
Role of Excipients in Theophylline Syrup
- Stabilizers are added over time to maintain the effectiveness of the syrup.
- Preservatives are also included to prevent any growth and ensure the product remains safe for consumption, throughout its storage period.
3. Uses of Theophylline Syrup
Primary Indications in Respiratory Conditions
Efficacy in Treating Asthma and COPD
4. Off-Label Uses of Theophylline
Exploring Lesser-Known Applications
-
Other Investigational Uses:
- Beyond its established indications, Theophylline is being investigated for potential benefits in managing:
- Sleep Apnea
- Pulmonary Hypertension
- Heart Failure1.
- Beyond its established indications, Theophylline is being investigated for potential benefits in managing:
Theophylline for dogs
-
Uses of Theophylline for Dogs and Cats:
- Bronchodilation: Theophylline relaxes bronchial muscles, leading to the dilation of airways. It helps in conditions such as asthma, chronic bronchitis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Tracheobronchial Disorders: Specifically in dogs, Theophylline is employed to manage tracheobronchial disorders like tracheal collapse and chronic bronchitis.
- Collapsing Trachea: It is used to address collapsing trachea within the chest.
- Adjunct Treatment: Theophylline can be an adjunct treatment in heart failure and other lung diseases123.
-
Effectiveness Compared to Glucocorticoids:
- While Theophylline is beneficial, its effectiveness falls short when compared to glucocorticoids (such as prednisone). Glucocorticoids are more potent in managing certain respiratory conditions1.
Clinical Studies Supporting Off-Label Use
5. How Theophylline Works
Mechanism of Action in Bronchodilation
The way Theophylline works includes more than inhibiting phosphodiesterase. It also involves blocking adenosine receptors, which helps with its ability to open up the airways.
Effects on Respiratory Muscles and Airflow
The medication boosts the power and stamina of the muscles used for breathing, resulting in airflow and less fatigue in those muscles.
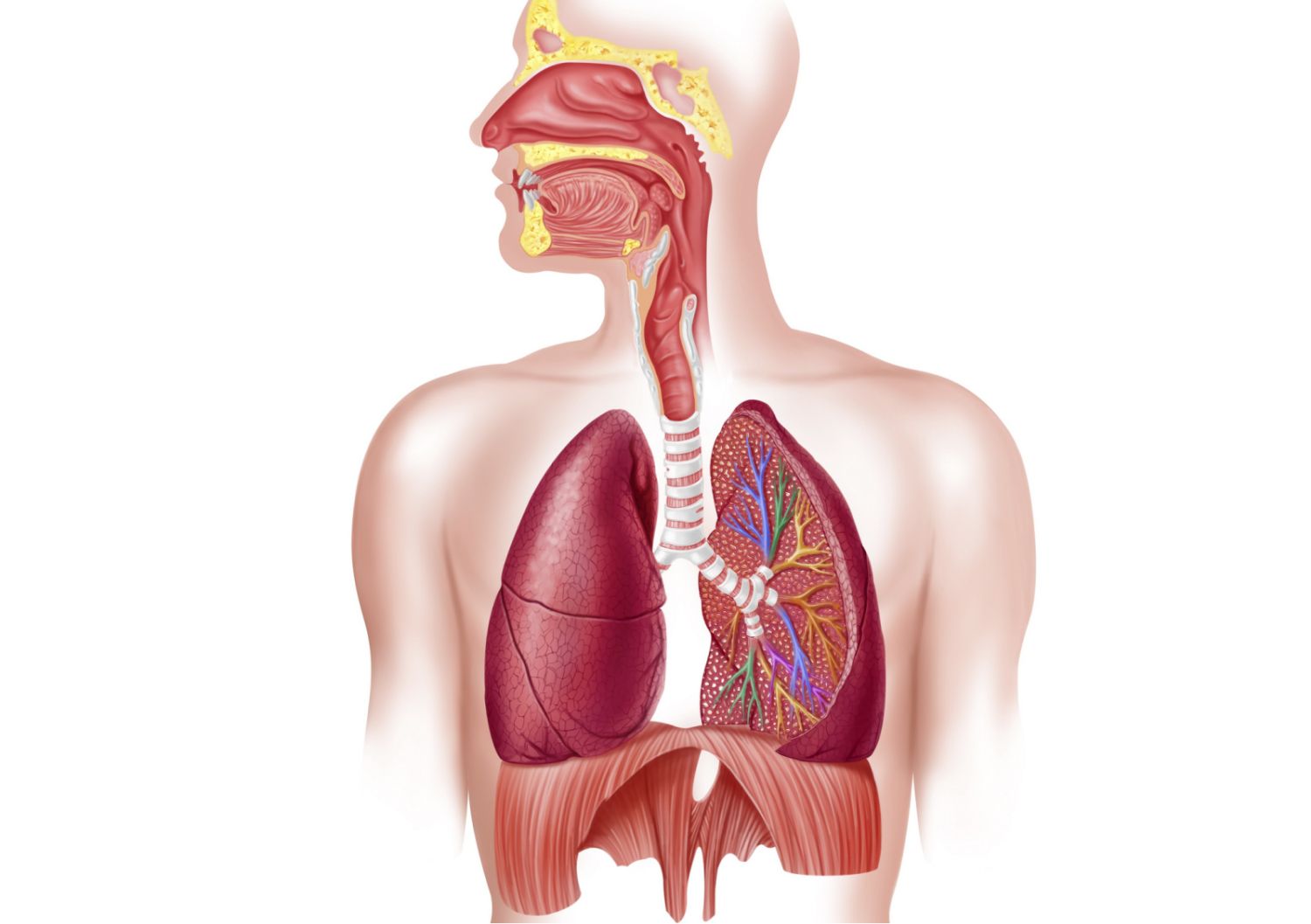
Theophylline toxicity
Toxic levels are typically defined as being 20 micrograms per milliliter or above. However, harmful effects may still occur within normal therapeutic ranges. Symptoms such as heart rhythm disturbances, seizures, and fatality may manifest when levels reach 80 to 100 micrograms per milliliter. Chronic toxicity could emerge at concentrations ranging from 40 to 60 micrograms per milliliter.
6. Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosages for Different Age Groups
The amount of Theophylline Syrup needed depends on the age of the individual, taking into account precautions for children and older adults to prevent any harmful effects.
Instructions for Optimal Consumption
For best results and to reduce potential side effects, it is recommended that you take Theophylline on an empty stomach either one hour before or two hours after eating.
Theophylline and Guaifenesin cough syrup
The combination of Theophylline and guaifenesin is prescribed for managing asthma symptoms, chronic bronchitis, and emphysema. This medication helps alleviate coughing, wheezing, difficulty breathing and shortness of breath.
Theophylline and caffeine
Combining these medications could heighten theophylline's side effects, leading to symptoms like nausea, vomiting, difficulty sleeping, shaking, feeling agitated, irregular heartbeats, and seizures. It's best to steer clear of consuming beverages or snacks with caffeine content, such as coffee, tea, soda, and chocolate.
7. Administration to Specific Populations
Administration to Elderly Patients
Monitoring Theophylline blood levels is essential in patients because they are more prone to experiencing adverse reactions.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
While Theophylline is usually considered safe it is essential to use it under medical supervision to prevent any possible harm to the unborn baby or newborn.
Administration to Children
Children require dosing instructions for quicker metabolism and different body sizes.
8. Side Effects of Theophylline Syrup
Common Side Effects and Management
Typical symptoms may consist of feeling queasy, experiencing stomach upset, and having a headache. These effects are usually mild. It can be controlled by adjusting the dosage or providing supportive treatment.
Serious Adverse Reactions and Emergency Response
Severe responses, like heart rhythm irregularities, seizures, and extreme allergic reactions, demand medical attention and may necessitate hospital care.
9. Important Precautions and Warnings
Interactions with Other Medications
Theophylline has the ability to interact with different types of medications, requiring careful monitoring.
- Specifically it has interactions with fluoroquinolone antibiotics and certain antifungal drugs, which can increase its levels in the blood and raise the risk of toxicity.
- Combining it with beta-blockers may reduce the effects. It is not recommended to use xanthines at the same time due to the possibility of cumulative effects.
Contraindications and Risk Factors
Theophylline should not be used in patients who are hypersensitive to xanthine derivatives. Additionally, individuals with health issues like active peptic ulcer disease, uncontrolled epilepsy, and certain cardiac arrhythmias should steer clear of using it. Factors such as age, liver problems, and existing pulmonary conditions need to be taken into account before prescribing Theophylline due to the increased risk of side effects and dosing complexities they may pose.
10. Handling and Storage of Theophylline Syrup
Storage Conditions to Preserve Efficacy
- It's crucial to store Theophylline Syrup to ensure it stays effective:
- Store it in a cool, dry place away from sunlight and moisture.
- Avoid keeping it in the bathroom or near a sink, as heat and humidity can affect its potency.

Handling Precautions for Safety
Remember to securely close the bottle after use to keep it safe and free from contamination. For the syrup to work effectively, make sure to use it before the expiration date indicated on the bottle.
11. Overdose and Emergency Management
Signs and Symptoms of Overdosage
Identifying the indications of an overdose of Theophylline is crucial for efficient treatment. Common signs typically consist of nausea, vomiting, persistent headaches and irregular heartbeats. In cases seizures might manifest, requiring urgent medical attention.
Immediate Actions and Antidote Information
If someone overdoses the initial action is to stop giving Theophylline and get medical help. The main treatment includes actions, like washing out the stomach and giving activated charcoal to reduce absorption. IV fluids and electrolytes are given to help the patient stabilize. Its important to keep an eye on their heart and breathing functions.