Zovirax Injection
- Introduction to Zovirax Injection
- Composition of Zovirax Injection
- Uses of Zovirax Injection
- Off-Label Uses of Zovirax Injection
- How Zovirax Injection Works
- Dosage and Administration of Zovirax Injection
- Common Side Effects of Zovirax Injection
- Severe Side Effects and Complications
- Important Precautions with Zovirax Injection
- Contraindications of Zovirax Injection
- Acyclovir interactions
- Administration Considerations for Special Populations
- Warnings and Precautions for Zovirax Injection
- Careful Administration and Monitoring
- Overdose Management and Emergency Measures
- Storage and Handling of Zovirax Injection
Introduction to Zovirax Injection
Overview of Zovirax Injection
The Zovirax Injection contains the substance acyclovir and is tailored for addressing certain viral infections effectively and efficiently in the body system. Doctors usually recommend this injection, for treating herpes related infections as it offers properties to control and lessen the impact of the infection promptly. Designed as a solution for use, in urgent situations needing quick antiviral treatment.
Originating in the 1970s, acyclovir was introduced as an advancement in antiviral treatment, specifically targeting herpesviruses with therapeutic benefits in mind. Designed to address the necessity for a substance that could impede DNA replication while sparing host cells from impacts, this innovation transformed the antiviral therapy landscape. Acyclovir's efficacy in providing patients with relief, coupled with its recognized safety record, played a role in its widespread adoption within contemporary medical practices.
Importance of Zovirax in Treating Viral Infections
In a setting, Zovirax Injection is crucial for treating viral infections like herpes simplex virus (HSV). Because of its effectiveness against both HSV and varicella zoster virus (VZV), it is especially valuable for those with weakened systems who are vulnerable to complications. By stopping the replication of viruses, Zovirax helps reduce symptoms and the risk of transmission, resulting in advantages during critical situations.
Composition of Zovirax Injection
Active Ingredient: Acyclovir
The primary ingredient in Zovirax Injection is acyclovir, a synthetic purine nucleoside analog with potent antiviral properties. Acyclovir interferes with viral DNA synthesis, specifically targeting infected cells while sparing normal host cells. This selectivity makes acyclovir a preferred choice for viral infections requiring intravenous intervention.
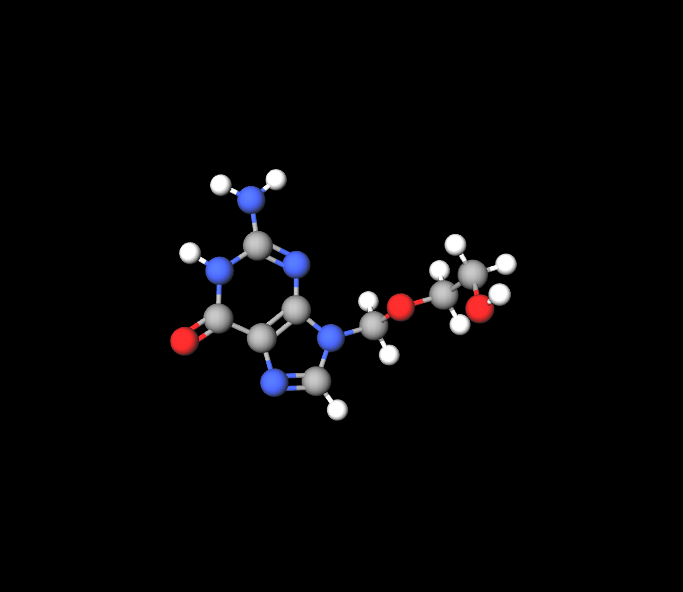
Inactive Ingredients and Formulation
Apart from acyclovir itself, Zovirax Injection contains substances that help keep the solution stable to ensure safe and effective administration of the medication.The inactive ingredients are meticulously combined to preserve the potency of the ingredient and assist in delivering it to the targeted tissues.
Available Strengths and Concentrations
The Zovirax Injection comes in strengths to customize the dosage according to the seriousness of the infection and the specific needs of the patients body functions.This adaptability enables treatment, for age groups such, as children and elderly individuals who might need accurate dose modifications.
Topical acyclovir
Topical acyclovir is prescribed to manage the manifestations of herpes simplex virus infections affecting the skin, mucous membranes, and genital region.
Acyclovir and ibuprofen
Ibuprofen will increase the level or effect of acyclovir by acidic (anionic) drug competition for renal tubular clearance.
Valacyclovir vs acyclovir
Valacyclovir and the other drugs work against viruses; however, valacyclovir offers a period of effectiveness that allows for less frequent daily doses—this is its primary benefit.
Docosanol vs acyclovir
Acyclovir is effective in treating health issues such as sores, genital herpes, shingles, and chickenpox infections; it is also used to manage herpes simplex encephalic. Docosanol is used to treat cold sores.
Famciclovir vs acyclovir
In immunocompromised patients, both Famciclovir and acyclovir work well for treating genital herpes infections. Famciclovir might offer pain relief and quicker healing for herpes zoster compared to acyclovir.
Mupirocin vs acyclovir
Mupirocin is an antibiotic that helps stop bacteria from multiplying on the skin and is commonly used to treat skin ailments like impetigo. Acyclovir is prescribed to combat infections triggered by strains of viruses such as shingles and chickenpox, along with herpes simplex virus infections.
Uses of Zovirax Injection
Primary Uses in Treating Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) Infections
Doctors often recommend Zovirax Injection to address herpes simplex virus infections when oral medication isn't enough to control the symptoms caused by both HSV types and alleviate symptoms, like sores and widespread viral effects, throughout the body.
Application in Treating Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV) Infections
This injection is also used to treat patients at risk from varicella zoster infections, such as shingles in adults and chickenpox in individuals. It helps by stopping the virus from multiplying and effectively decreases pain and the risk of issues.
Use in Immunocompromised Patients
People with weakened systems, like those going through chemotherapy or living with HIV/AIDS, frequently depend on Zovirax Injections to fight off infections effectively. The strong antiviral properties of the medication help lower the chances of extended infections and severe issues.
Role in Preventing and Treating Herpes Encephalitis
Zovirax Injection crucially supports the treatment of herpes encephalitis, as it addresses this brain condition that can be life-threatening but uncommon. The prompt use of acyclovir can help minimize any harm and highlight the necessity of receiving treatment.
Use in Neonatal HSV Infections
Zovirax Injection is crucial for newborns with HSV as it helps control the spread of the virus and safeguards their developing systems in care settings where its versatility and significance, for vulnerable patients, are evident.
Off-Label Uses of Zovirax Injection
Investigational Use for Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Infections
Studies have been looking into whether Zovirax Injection could help with cytomegalovirus infections beyond its use case. Ongoing research is examining the advantages of using acyclovir to treat CMV in individuals with weakened systems.
Use in Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Related Conditions
In situations, Zovirax Injection has been used to treat Epstein Barr virus infections to alleviate symptoms linked to EB. This unconventional application is especially thought about in cases or, for patients, severe issues.
Off-Label Use for Severe Cases of Acute Viral Infections
Zovirax Injection is sometimes used in ways to treat viral infections that suddenly appear acute in nature. This demonstrates its versatility, as an treatment, in emergency medical settings.
How Zovirax Injection Works
Mechanism of Action: DNA Polymerase Inhibition
Acyclovir works by blocking the activity of DNA polymerase, an enzyme required for creating viral DNA chains. This process stops the virus from multiplying, enabling the system to better control and clear the infection.
Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability
When administered intravenously, acyclovir reaches systemic circulation rapidly, with high bioavailability. It is widely distributed in bodily fluids and achieves therapeutic concentrations quickly, making it an efficient treatment for acute viral infections.
Duration of Effectiveness and Onset of Action
Upon receiving Zovirax Injection into the system, it shows results within an hour.The period of its effectiveness can vary for hours determined by patient factors, like kidney function and immune health status.
When compared to one another, acyclovir stands out for its effectiveness and safety record. This comparison emphasizes the strength of Zovirax Injection as a choice for treating infections with targeted antiviral treatment.
Acyclovir half-life
The average time it takes for acyclovir to diminish by half in adults is 2-3 hours while in newborns it ranges from 3-4 hours.
Dosage and Administration of Zovirax Injection
Recommended Dosage for Different Age Groups
The amount to take differs depending on your age category; there are instructions for adults and children of different ages. Even newborns have their own guidelines to follow! Tailoring the dosage individually guarantees safety and effectiveness across all groups. This is especially crucial for those who may be more vulnerable.
Adjustments for Renal Impairment and Liver Conditions
Dosage adjustments are essential for patients with renal or hepatic impairment. Renal function monitoring is often conducted before administration to prevent accumulation and toxicity.
Methods of Administration: Intravenous and Intramuscular
Zovirax Injection is typically administered intravenously. An intramuscular route may be considered in certain cases, though IV administration provides more rapid and consistent delivery.
Step-by-Step Administration Procedure
- Prepare the solution according to the manufacturer's instructions.
- Ensure the patient is hydrated to minimize renal toxicity risks.
- Administer the injection over an appropriate duration to avoid irritation.
Duration of Treatment for Various Infections
The length of treatment varies based on the type of infection and can last anywhere from a day to several weeks. Doctors track the patient's improvement to decide whether prolonged therapy is required.
Common Side Effects of Zovirax Injection
Local Reactions at Injection Site
Common side effects include mild pain or inflammation at the injection site. These reactions are usually transient and resolve within hours of administration.
Gastrointestinal Effects (Nausea, Vomiting)
Some patients may experience feelings of nausea or vomiting, which can usually be managed with changes in how the medication is given or by using medications to help reduce these symptoms.
Neurological Effects (Dizziness, Headache)
Zovirax Injection can cause mild neurological symptoms, including dizziness or headache. These effects are typically short-lived and rarely severe.
Renal-Related Effects (Increased Serum Creatinine)
Acyclovir can impact renal function, particularly if hydration is inadequate. Monitoring serum creatinine levels helps prevent renal-related adverse effects ensuring safe administration for at-risk patients.
Valacyclovir vs acyclovir side effects
Valacyclovir and Zovirax share side effects, like headache and nausea; they can also cause vomiting and rash in some cases. On the other hand, Valtrex may lead to discomfort,cold symptoms,liver enzyme elevation, reduced white blood cell count, joint pain, and dizziness, which are not commonly seen with Zovirax.
Severe Side Effects and Complications
Rare But Serious Neurological Reactions
While uncommon, Zovirax Injection may provoke neurological severe reactions in some individuals. Patients could experience symptoms such as hallucinations, confusion, or even seizures. These adverse effects are typically associated with higher doses, underlying neurological conditions, or renal impairment, which can increase drug concentration in the body.
Renal Toxicity and Nephrotoxicity Risks
Due to toxicity concerns, Zovirax Injection can cause kidney damage in individuals with existing kidney issues. Acyclovir has the potential to form crystals in the kidney tubules and harm the kidneys. Hydration is crucial during treatment to avoid kidney problems by helping to eliminate the drug through the kidneys and lowering the chances of the effects occurring.
Allergic Reactions and Hypersensitivity
Some individuals might show responses or heightened sensitivity to Zovirax Injection. Treatment therapy could be necessary in case of indications of hypersensitivity such as inflammation, breathing difficulties, or a sudden decline in blood pressure it's crucial to stop the injection and seek medical assistance immediately.
Signs of Overdose and Toxicity
An overdose of Zovirax Injection can lead to severe toxicity, manifesting as nausea, renal dysfunction, or neurological disturbances. Patients displaying these symptoms require urgent medical attention, including cessation of the drug and supportive care. Hemodialysis may be necessary in cases of severe overdose to remove acyclovir from the bloodstream effectively.
Important Precautions with Zovirax Injection
Monitoring for Renal Function and Hydration
It's important to have kidney function tests to avoid kidney damage caused by acyclovir when using Zovirax Injection so make sure patients stay hydrated before and during treatment to lower the risk of kidney problems related to the medication by helping the body remove the drug and reducing acyclovir levels in the kidneys.
Neurological Monitoring for High-Dose Administration
Close neurological monitoring is advised for patients receiving high doses. Symptoms like dizziness, tremors, or mental confusion should be noted, as they can indicate early signs of neurotoxicity. Dosage adjustments or alternative therapies may be required for patients displaying neurological symptoms.
Signs to Monitor for Allergic Reactions
Healthcare providers should be vigilant for any signs of allergic reaction, including skin irritation, respiratory distress, or swelling. These signs necessitate prompt intervention to avoid severe allergic responses. Patients should also be informed of potential symptoms and should report immediately if they occur.
Reducing Risk of Adverse Effects through Correct Dosage
Precise dosage calculation considering the patient's weight and kidney function is essential to reduce reactions effectively.
Contraindications of Zovirax Injection
Absolute Contraindications: Allergy to Acyclovir or Related Compounds
Individuals with a known allergy to acyclovir or other compounds in the same family should avoid Zovirax Injection. Hypersensitivity to the drug could lead to life-threatening reactions, thus making this an absolute contraindication.
Conditions Warranting Avoidance of Zovirax Injection
Individuals, with kidney problems or a history of issues should steer clear of using Zovirax Injection to prevent the likelihood of facing severe adverse reactions; instead consider exploring alternative treatment options.
Relative Contraindications in Patients with Specific Comorbidities
Patients, with conditions such as epilepsy or liver issues and those, with weakened systems should use Zovirax Injection cautiously as it may require dosage adjustments and close monitoring to prevent any complications.
Acyclovir interactions
Overview of Drugs That May Interact with Zovirax
The Zovirax Injection may interact with medications that affect kidney function or share common metabolic processes, which could impact effectiveness or raise the risk of side effects.
Effect of Interaction on Efficacy and Side Effects
Concurrent use of other drugs can either potentiate or inhibit Zovirax's antiviral effects. Interactions may enhance renal toxicity or decrease the drug's effectiveness, particularly if administered with nephrotoxic agents.
Probenecid, a medication that affects renal excretion, can increase acyclovir blood levels, potentially leading to toxicity. Care should also be taken when using Zovirax with other antivirals, as this may result in synergistic toxicity or reduced therapeutic effect.
Managing Interactions through Dosage Adjustments
When interactions are unavoidable, dosage adjustments or additional monitoring may be required. Close collaboration between healthcare providers is essential to effectively manage and mitigate the effects of drug interactions.
Administration Considerations for Special Populations
Administration to Elderly Patients: Adjustments and Precautions
In elderly patients, renal function typically declines, necessitating dosage adjustments for Zovirax Injection. Regular monitoring and cautious dosing are advised to prevent accumulation of the drug, reducing the risk of adverse effects.
Administration to Pregnant Women: Safety and Risk Factors
Although Zovirax Injection is generally considered safe in pregnancy, it should only be administered when necessary. The potential risks to the fetus must be balanced against the therapeutic benefits, with dosage carefully managed under medical supervision.
Nursing Mothers: Effects on Breast Milk and Infant Health
Acyclovir is known to pass into breast milk, albeit in small amounts. Nursing mothers receiving Zovirax Injection should be monitored to ensure that exposure does not adversely affect the infant.

Administration to Children and Infants: Dosage Guidelines and Safety
Zovirax Injection is used to treat severe viral infections in children and infants. Dosage is weight-based, and monitoring is essential to ensure safety and efficacy, particularly in neonates and young children with underdeveloped renal function.
Warnings and Precautions for Zovirax Injection
Key Warnings for Safe Use of Zovirax Injection
Important cautions regarding Zovirax Injection involve the risk of neurotoxicity and kidney function decline. There is a need to closely observe patients for any indications of reactions in groups, at higher risk.
Risks Associated with Incorrect Dosage
Improper administration of Zovirax Injection can result in issues such as overdosing and inadequate management of infections. Take care to administer the dosage to ensure treatment, with minimal adverse effects.
Special Warnings for Patients with Renal Impairment
Patients with renal impairment require careful consideration before receiving Zovirax Injection. Dosage adjustments and enhanced monitoring can help reduce the risk of nephrotoxicity, which is more common in individuals with compromised renal function.
General Safety Precautions
General safety measures include ensuring adequate hydration and regularly assessing renal function. Patients should also be informed of potential side effects and instructed to report symptoms immediately.
Acyclovir and alcohol
It is commonly advised to steer clear of alcohol when using acyclovir, even though alcohol doesn't directly interact with it because alcohol can weaken the system and hamper your body's ability to combat infections effectively.
Careful Administration and Monitoring
Guidelines for Careful Administration in At-Risk Populations
For patients at higher risk, such as the elderly or those with comorbidities, Zovirax Injection should be administered with caution. Dosing should be conservative, with regular monitoring to detect any adverse effects early.
Acyclovir nursing considerations
Before administering this medication, warn the patient about the possibility of developing headaches. Acyclovir has a low bioavailability and is slowly absorbed by the GI tract. This medication may cause symptoms of GI distress, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Parameters to Monitor During Treatment (e.g., renal function, CNS effects)
Monitoring aspects such, as kidney function tests and observations of the nervous system and ensuring adequate hydration levels are crucial, in evaluating how patients are reacting to treatment and avoiding any risks of toxicity.
Role of Healthcare Providers in Ensuring Safe Use
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in overseeing safe administration. Regular assessments, patient education, and prompt intervention for adverse effects are essential to maximizing the benefits of Zovirax Injection.
Acyclovir foods to avoid
Stick to simple meals and do not eat rich or spicy food. It might help to take your medicine after you have eaten. If you're being sick, try small, frequent sips of water to avoid dehydration. Signs of dehydration include peeing less than usual or having dark, strong-smelling pee.
Overdose Management and Emergency Measures
Symptoms of Zovirax Injection Overdose
Overdose symptoms may include severe nausea, acute renal failure, or neurological disturbances. Immediate medical attention is necessary to address and mitigate overdose effects.
Immediate Steps and Emergency Protocols
In case of overdose, immediate cessation of Zovirax Injection and supportive care are essential. Emergency protocols often include fluid resuscitation and close monitoring of vital signs and renal function.
Treatment Options for Overdose and Toxicity
Hemodialysis is an effective option for removing excess acyclovir from the blood in cases of severe overdose. Additional supportive measures may be taken based on symptom severity and patient condition.

Storage and Handling of Zovirax Injection
Recommended Storage Conditions for Stability
Make sure to keep Zovirax Injection in a place with a steady room temperature to ensure it stays effective and doesn't lose its potency due to exposure to cold temperatures.
Protecting from Light and Temperature Variations
Shielding the injection from sunlight and extreme temperature fluctuations is crucial to maintaining the effectiveness of the ingredients and ensuring the solution works as intended.
Proper Disposal of Unused and Expired Zovirax Injection
Properly dispose of any unused or expired Zovirax injection following the guidelines in your area to prevent hazards or unintentional exposure to others.
Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers should follow standard handling precautions to avoid accidental exposure. To minimize risks, personal protective equipment (PPE) may be required when preparing and administering the injection.