Before committing to taking Sulfasalazine, it is essential to be well-informed about the medication and its effects. This article will delve into Sulfasalazine therapy, providing valuable insights for patients who may benefit from its use.
We'll begin by discussing what Sulfasalazine is and how it was developed. Next, we'll examine the mechanism of action behind Sulfasalazine in treating various inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. We will also discuss the benefits associated with using this drug.
Furthermore, our discussion will cover essential aspects like pharmacology and potential side effects that one should be aware of when buying Sulfasalazine. Additionally, we'll highlight any possible interactions with other medications that might affect your treatment plan. Finally, we'll weigh the pros and cons of incorporating Sulfasalazine into your daily routine while offering guidance on dosage administration.
Understanding all these aspects thoroughly before deciding to buy Sulfasalazine or starting treatment can help ensure a successful outcome in managing your condition effectively while minimizing the risks involved.
Table Of Contents: Buy Sulfasalazine
- The Development of Sulfasalazine
- What is Sulfasalazine?
- Understanding How Sulfasalazine Works
- Benefits of Sulfasalazine
- The Pharmacology of Sulfasalazine
- Side Effects
- Understanding Interactions
- Weighing the Pros and Cons of Sulfasalazine
- Dosage and Administration
- Life with Sulfasalazine
- Is Sulfasalazine Right for You?
- Buy Sulfasalazine
The Development of Sulfasalazine
Sulfasalazine has a rich history dating to its initial discovery in the 1930s. It was first developed as an antibiotic for treating bacterial infections but soon gained attention for its anti-inflammatory properties. Researchers found that sulfasalazine could effectively reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms associated with rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis.
Over the years, numerous clinical trials have been conducted better to understand the drug's efficacy and safety profile. These studies have helped establish sulfasalazine as a trusted treatment option for patients suffering from inflammatory conditions.
- 1941: The first study on sulfasalazine's effectiveness in treating rheumatoid arthritis was published by Dr. Nanna Svartz, who observed significant improvements in her patients' condition after administering the drug.
- 1958: Sulfasalazine received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to manage ulcerative colitis symptoms.
- The late 1980s: Further research led to FDA approval of sulfasalazine specifically for treating rheumatoid arthritis.
In addition to these milestones, ongoing research explores new potential uses for this versatile medication. For example, recent studies suggest that it may be beneficial in managing other autoimmune disorders, such as psoriatic arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis (source). As our understanding of sulfasalazine expands, so does its potential to improve the lives of patients with various inflammatory conditions.
If you are considering sulfasalazine therapy, it is essential to consult with your healthcare provider to determine if it is the right treatment option for you.
What is Sulfasalazine?
Sulfasalazine is a medication that has been used for over 60 years to treat inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. It was first developed in the 1950s by Dr. Nanna Svartz, a Swedish physician who discovered its anti-inflammatory properties while studying patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
What is Sulfasalazine Used For?
Sulfasalazine works by reducing inflammation in the body, which helps alleviate symptoms of various inflammatory diseases, including:
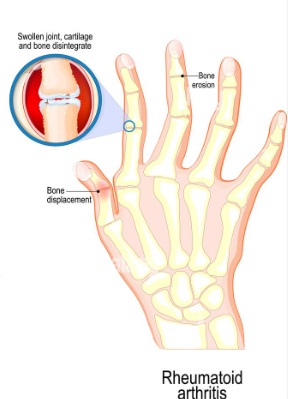
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: This condition causes joint pain and stiffness due to inflammation. Studies have shown that sulfasalazine therapy can help reduce these symptoms and improve the overall quality of life for people with this condition.
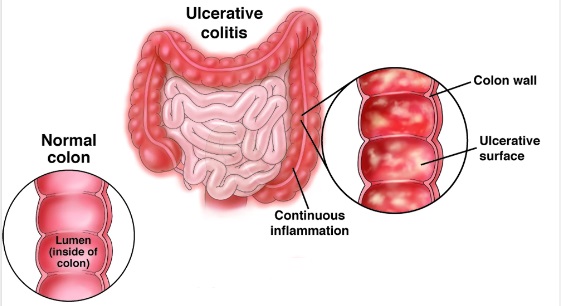
- Ulcerative Colitis: This is an inflammatory bowel disease that affects the colon and rectum, causing diarrhea, abdominal pain, and cramping, among other symptoms. Sulfasalazine has been found effective at inducing remission from active ulcerative colitis.
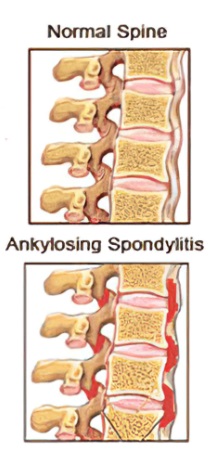
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: This type of arthritis primarily affects the spine but can also affect other joints, leading to stiffness, pain, and reduced mobility. Research shows that sulfasalazine may help reduce spinal inflammation associated with this condition.
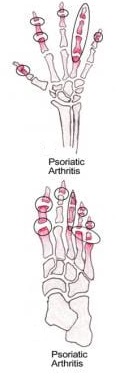
- Psoriatic Arthritis: This type of arthritis occurs in some people with psoriasis - a skin condition characterized by red patches covered with white scales on different body parts. Sulfasalazine could be helpful because it reduces inflammation throughout your body, including areas affected by psoriasis.
Understanding How Sulfasalazine Works
Sulfasalazine is a medication that belongs to the class of drugs known as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Sulfasalazine has anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties, making it an effective treatment for various inflammatory conditions. To understand how sulfasalazine works, let's explore its mechanism of action and effects on the body in greater detail.
When taken orally, sulfasalazine undergoes intestinal cleavage, which breaks down the drug into two active components: 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) and sulfapyridine. The exact mechanism through which these components exert their therapeutic effects remains unclear; however, several theories exist:
- Inhibition of prostaglandins: Both 5-ASA and sulfapyridine are thought to inhibit the production of prostaglandins - chemicals responsible for inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis (source). Reducing prostaglandin levels, they help alleviate pain and swelling associated with these conditions.
- Action on immune cells: Some studies suggest that 5-ASA may affect immune cells like T-cells by suppressing their activation or proliferation (source). 5-ASA's ability to suppress immune cell activation and proliferation and its antioxidant properties, which may protect cells from oxidative stress damage, could contribute to reduced inflammation in patients suffering from autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis.
- Oxidative stress reduction: 5-ASA has been shown to possess antioxidant properties, which may help protect cells from damage caused by oxidative stress in inflammatory conditions (source). This could contribute to its therapeutic effects in treating ulcerative colitis and rheumatoid arthritis.
In summary, sulfasalazine breaks down into two active components that target inflammation through various pathways. Despite its uncertain mechanisms, sulfasalazine has been proven to be a successful treatment for the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis.
Benefits of Sulfasalazine
Sulfasalazine is a versatile medication with numerous benefits for patients suffering from inflammatory conditions. Sulfasalazine is also used to treat other inflammatory diseases, such as RA and ulcerative colitis.
Easing Inflammation: Sulfasalazine in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation in the joints, leading to pain and stiffness. Sulfasalazine has been shown to effectively reduce inflammation and slow down the progression of RA by suppressing the immune system's overactive response. This leads to decreased joint swelling, improved mobility, and better quality of life for those with this debilitating condition.
The Role of Sulfasalazine in Treating Ulcerative Colitis
Sulfasalazine has been proven advantageous in managing ulcerative colitis (UC), an inflammatory bowel disorder distinguished by irritation and sores within the colon. By reducing intestinal inflammation, sulfasalazine helps alleviate symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and rectal bleeding commonly experienced by UC patients. Furthermore, long-term use can help maintain remission periods where symptoms are minimal or absent altogether.
When else Sulfasalazine might be prescribed
- Ankylosing spondylitis: A form of spinal arthritis causing chronic back pain; sulfasalazine can help manage symptoms.
- Psoriatic arthritis: A type of arthritis affecting some people with psoriasis, sulfasalazine may be prescribed to alleviate joint pain and inflammation.
- Juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Sulfasalazine can help control symptoms in children suffering from chronic arthritis.
In summary, the benefits of sulfasalazine extend beyond its primary uses for rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis, making it a valuable medication for managing various inflammatory conditions such as sulfasalazine therapy, rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis.
The Pharmacology of Sulfasalazine
Gaining a thorough understanding of the pharmacology of sulfasalazine is essential for those looking to make an educated choice regarding their therapy. Research has revealed important information about this medication and its potential advantages.
Pharmacokinetics
Sulfasalazine is a prodrug, meaning it must be metabolized in the body to produce its active components: 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) and sulfapyridine. Most oral sulfasalazine remains intact until it reaches the colon, where bacteria break it down into these two compounds. Approximately 60% of an administered dose becomes systemically available as sulfapyridine, while most remaining 40% stays within the gastrointestinal tract as 5-ASA.
Mechanism of Action
Although researchers are still working to understand sulfasalazine's mechanism of action fully, they believe that both active components play a role in reducing inflammation. Sulfapyridine has been shown to suppress immune system activity by inhibiting certain enzymes involved in inflammatory processes, whereas 5-ASA acts locally within the gut lining to reduce inflammation directly at its source.

Efficacy in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Ulcerative Colitis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Clinical trials have demonstrated that sulfasalazine can significantly improve symptoms such as joint pain, swelling, and stiffness when compared with placebo or other treatments like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Ulcerative Colitis: Studies have shown that sulfasalazine effectively induces and maintains remission of ulcerative colitis, with response rates ranging from 40% to 80%. A meta-analysis concluded that it was more effective than a placebo and comparable to other 5-ASA compounds.
In summary, the pharmacology of sulfasalazine provides a solid foundation for its use as an anti-inflammatory agent in treating rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis.
Side Effects
Sulfasalazine is a medication that can effectively treat conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. However, like all medications, it comes with potential side effects.

The Potential Side Effects of Sulfasalazine
Some of the most common side effects associated with sulfasalazine therapy include:
- Nausea or vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Dizziness or headache
- Mouth sores or ulcers
- Rash or itching skin
In rare cases, more severe side effects may occur. These can include:
- Blood Disorders: Aplastic Anemia (A condition where your body stops producing new blood cells)
- Liver Problems: Hepatitis (Inflammation in the liver)
- Kidney problems: Kidney stones formation due to crystallization.
If you experience any unusual symptoms while taking sulfasalazine therapy, it's essential to contact your doctor right away. They will be able to advise you on whether you should continue taking the medication and what steps you should take next.
Taking Precautions When Using Sulfasalazine Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis & Ulcerative Colitis Treatment:
To minimize the risk of developing severe side effects from using a sulfasalazine treatment plan for RA and UC management, patients must follow these precautions:
- Regular Blood Tests: To monitor blood cell count and liver function tests
- Avoid Alcohol Consumption: As it may increase the risk of liver damage.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to avoid kidney stone formation due to crystallization.
If you have concerns about sulfasalazine therapy's side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. They can help you understand what to expect and how best to manage any symptoms that may arise during treatment.
Sources: Mayo Clinic - Sulfasalazine Side EffectsArthritis Foundation - Sulfasalazine (Azulfidine)
Understanding Interactions
It is essential to be aware of any possible interactions with other medications or supplements when utilizing Sulfasalazine. Drug interactions can alter the effectiveness of your treatment and increase the risk of side effects. Before starting Sulfasalazine, inform your healthcare provider about all prescription and over-the-counter medications, vitamins, and herbal products you are currently taking.
Some common drugs that may interact with Sulfasalazine include:
- Digoxin: Concurrent use may decrease digoxin absorption, leading to reduced efficacy.
- Methotrexate: Co-administration can increase methotrexate toxicity due to decreased renal clearance.
- Folic acid antagonists: The concomitant use might result in folate deficiency as sulfasalazine inhibits folic acid absorption.
- Anticoagulants: There have been reports of prolonged prothrombin time when using anticoagulants like warfarin and sulfasalazine.
Inform your physician if you have a past of renal or liver issues, asthma, porphyria (a metabolic disorder), G6PD deficiency, or any blood-related disorders, as these may necessitate modifications to your therapy. Inform your physician if you have had issues with the kidneys, liver, asthma, porphyria (an enzyme issue), G6PD lack, or any other blood disorders since these conditions may necessitate changes to your treatment program.
Regularly monitoring your progress and checking for side effects while taking Sulfasalazine is essential. It is crucial to seek professional guidance when adjusting medications or dosages to ensure Sulfasalazine's safe and effective use. Always consult with a healthcare professional before changing your medications or dosages.
Weighing the Pros and Cons of Sulfasalazine
It is necessary to evaluate the potential advantages and drawbacks before deciding whether or not sulfasalazine use is appropriate. This section will discuss some of the pros and cons of sulfasalazine use.

Pros:
- Efficacy in treating inflammatory conditions: As mentioned earlier, sulfasalazine has proven effective in managing rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis symptoms by reducing inflammation.
- Affordability: Sulfasalazine is often more affordable than other medications used for similar purposes, such as biologics or newer disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
- Fewer side effects than alternative treatments: While all medications have potential side effects, many patients experience fewer adverse reactions with sulfasalazine than alternatives like corticosteroids or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Cons:
- Potential side effects: Some people may experience gastrointestinal issues, headaches, skin rashes, or liver problems while taking sulfasalazine. Discuss possible side effects and interactions with your doctor before starting treatment.
- Possible interactions with other medications: strong Sulfasalazine can interact negatively with certain drugs like warfarin or digoxin. Be sure to inform your healthcare provider about all prescription and over-the-counter medications you're currently taking so they can assess potential interactions before prescribing this drug.
- Slow onset of action: strong Sulfasalazine may take several weeks to months before its full effects are noticeable. Patients may be disappointed by the lack of quick results when using sulfasalazine to treat their symptoms.
In conclusion, sulfasalazine offers many benefits in treating inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis. However, it's crucial to consider potential side effects and interactions with other medications when deciding if this drug is right for you. Before beginning any new treatment plan, it is essential to seek medical advice.
Dosage and Administration
Following your doctor's instructions is essential when taking Sulfasalazine for proper dosage and administration. This article offers a summary of the dosages typically recommended for various conditions and guidance on how to take Sulfasalazine correctly.

How much Sulfasalazine should you take?
The appropriate dosage of Sulfasalazine varies depending on age, weight, and the specific condition being treated. For adults with rheumatoid arthritis, initial doses typically range from 500 mg to 1 g per day, gradually increasing over several weeks to a maintenance dose of 2-3 g daily. In contrast, patients with ulcerative colitis may start at a higher amount (up to 4 g daily) before tapering down once symptoms improve.
A Guide to Administering Sulfasalazine: Getting it Right
- Take with food: To minimize gastrointestinal side effects like nausea or stomach pain, always take Sulfasalazine tablets or capsules with food or milk.
- Maintain consistent timing: Try taking your doses around the same time each day to maintain stable blood levels of the drug and optimize its effectiveness.
- Frequent sips: If you're using an oral suspension form of this medication, shake the bottle well before each use and measure the dose carefully using a particular measuring device. Drink plenty of fluids to help reduce the risk of kidney stones, a rare side effect of Sulfasalazine.
- Monitor progress: Regular blood tests may be required during treatment to monitor your response to the medication and check for potential side effects. Always keep your scheduled appointments with healthcare providers.
In conclusion, following your doctor's instructions regarding dosage and administration when taking Sulfasalazine is crucial. By doing so, you'll increase its effectiveness while minimizing any potential risks or side effects.
Life with Sulfasalazine
Incorporating sulfasalazine into your daily routine can be crucial in managing conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. It is essential to heed your physician's advice regarding dosage, usage instructions, and necessary precautions. Here are some tips to help you integrate this medication seamlessly into your life:
- Create a schedule: Consistency is critical when taking sulfasalazine. Set reminders on your phone or use a pill organizer to ensure you take the medication simultaneously daily.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can help minimize potential side effects such as gastrointestinal issues. The Mayo Clinic recommends about 3.7 liters (125 ounces) for men and 2.7 liters (91 ounces) for women daily.
- Maintain open communication with your healthcare team: Regularly updating your doctor on how you feel while taking sulfasalazine will allow them to make any necessary adjustments to optimize treatment outcomes.
Contact your healthcare provider for advice and support if you have any queries or issues related to taking sulfasalazine. They may recommend additional resources, such as patient support groups or educational materials, that can provide valuable information and encouragement during this journey.
Beyond medication management, it's important to consider lifestyle changes that complement pharmacological treatments - including maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity tailored to individual abilities (according to the Arthritis Foundation), and managing stress through relaxation techniques or counseling. These steps can contribute to overall well-being and improve the quality of life for individuals with chronic conditions.

Is Sulfasalazine Right for You?
If you are suffering from rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis, psoriatic arthritis, or ankylosing spondylitis, your doctor may recommend sulfasalazine therapy. However, before starting this medication, assessing whether it suits you is essential.
Precautions to Take: Assessing Your Suitability for Sulfasalazine
Before taking sulfasalazine, your healthcare provider will consider several factors, such as:
- Your medical history and current health status
- Allergies or hypersensitivity reactions to sulfa drugs
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding status (sulfasalazine can harm the fetus)
- Kidney disease or liver disease
- Blood disorders such as anemia and leukopenia
You should also inform your doctor if you have ongoing infections since sulfasalazine can weaken the immune system. In addition, this medication may interact with other drugs you are currently taking, so make sure that all medications, including over-the-counter medicines and supplements, are disclosed.
Discussing Sulfasalazine with Your Doctor
Your doctor will explain how sulfasalazine treats inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis. They will also discuss potential side effects of the drug, including nausea, vomiting, headache, and rash.
If they determine that sulfasalazine is appropriate for you after considering all relevant factors, then they will prescribe a dosage explicitly tailored to meet your needs. Instructions on taking the medicine properly must be followed strictly not to compromise its effectiveness.
Remember, sulfasalazine is not for everyone. Your doctor will help you weigh the pros and cons of taking this medication so that you can make an informed decision on whether it's right for you.
If you have concerns about sulfasalazine therapy, do not hesitate to ask your healthcare provider. They are there to help answer all questions and address any worries that may arise during treatment.
Incorporating Sulfasalazine into your routine
Sulfasalazine should be taken with food or a full glass of water to minimize stomach upset. Doses must be taken regularly as your doctor prescribes since missing doses could reduce drug efficacy.
Conclusion
Sulfasalazine is a powerful anti-inflammatory agent used in treating several conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis, among others. Before starting this medication, however, one must assess their suitability based on factors like medical history, allergies, current health status, etc. If determined appropriate after consultation with your healthcare provider, instructions on how best to take the medicine must be followed strictly not to compromise its effectiveness.
Buy Sulfasalazine
In conclusion, Sulfasalazine is a medication used to treat inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. It works by reducing inflammation in the body. Although it may have potential side effects and interactions with other medications, Sulfasalazine can still be an effective treatment option for those who need it.
If you are considering buying Sulfasalazine, consult your doctor first to see if it's the right sulfasalazine therapy for you. Once you have a prescription, Buy-Pharma offers affordable options for purchasing this medication online.
Take control of your health today and buy Sulfasalazine from Buy-Pharma!