Famotidine
- I. Introduction to Famotidine
- II. Composition and Structure of Famotidine
- III. How Famotidine Works
- IV. Uses of Famotidine
- V. Off-label Uses of Famotidine
- VI. Dosage and Administration of Famotidine
- VII. Side Effects of Famotidine
- VIII. Interactions with Famotidine
- IX. Warnings and Contraindications of Famotidine Use
- X. Careful Administration of Famotidine
- XI. Special Populations: Administering Famotidine
- XII. Overdosage of Famotidine
- XIII. Storage of Famotidine
- XIV. Handling Precautions for Famotidine
I. Introduction to Famotidine
A. Overview and History of Famotidine
Famotidine is a drug that is widely recognized and utilized. Falls under the category of H2 receptor antagonists. It was first introduced in the 1980s and gained rapid acceptance in the medical community because of its solid and practical ability to treat peptic ulcer disease and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
B. Importance in the Medical Field
An attribute that sets famotidine apart is its exceptional ability to inhibit gastric acid secretion—rendering it an indispensable therapeutic agent. By relieving symptoms associated with excessive acid production, famotidine effectively prevents complications like ulcers or acid-induced esophagitis. Moreover, the significance of famotidine extends beyond this realm through actions like treating allergic reactions and serving as an adjunct therapy for patients with chronic urticaria and showcasing its versatility and prominence in medical practice.
II. Composition and Structure of Famotidine
A. Chemical Components
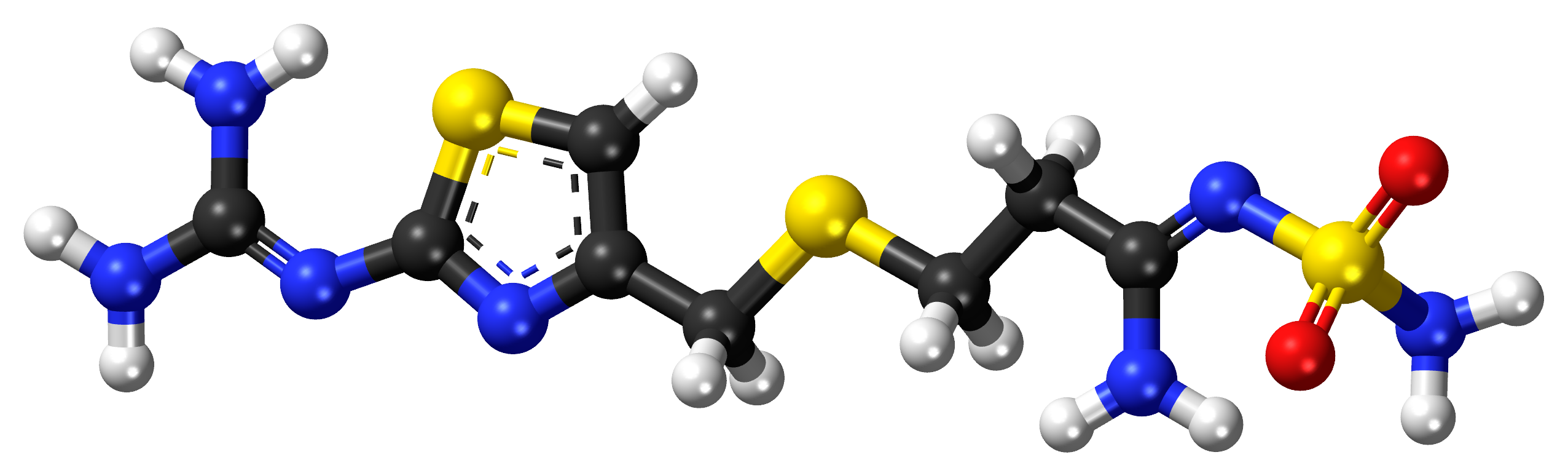
Famotidine is a compound derived from histamine. Possesses distinctive pharmacological properties due to its complex composition of nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, and sulfur atoms. It is represented by the chemical formula C8H15N7O2S3.
B. Mechanisms and Pharmacodynamics
Famotidine functions as a competitive inhibitor of histamine at the H2 receptors, particularly those located on the basolateral membrane of the gastric parietal cells. These parietal cells play a crucial role in producing gastric acid, and by inhibiting their activity, famotidine effectively reduces both the volume and concentration of gastric acid generated.
III. How Famotidine Works
A. Pharmacological Action
Famotidine is categorized as an H2 receptor antagonist. Its primary function is to hinder the activity of histamine. This vital compound stimulates acid production within the stomach by obstructing histamines' pathway to its receptors on the stomach's parietal cells. Famotidine effectively decreases the secretion of gastric acid. Consequently, it relieves symptoms and supports the healing process in various acid-related disorders.
B. Biochemical Interactions
When taken orally, famotidine is absorbed into the bloodstream and travels to the basolateral membrane of the stomach, where the H2 receptors are found. By competitively inhibiting these receptors, famotidine prevents histamine from binding and activating them. This disruption in the biochemical process of gastric acid production leads to a notable decrease in the amount and acidity of stomach secretions, thus offering relief for conditions caused by excess acid.
IV. Uses of Famotidine
A. Approved Indications
Famotidine is a medication that plays a crucial role in treating various gastroenterological conditions. This medication has been approved for the following uses:
- Peptic Ulcer Disease: Famotidine aids in the healing process of both gastric and duodenal ulcers by reducing gastric acid production.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Famotidine relieves the symptoms of heartburn associated with GERD and assists in the healing of esophageal erosion.
- Zollinger Ellison Syndrome: Famotidine can be utilized to manage this rare condition, which is characterized by excessive stomach acid secretion.
- Prevention of Gastric Ulcers: Famotidine is used preventively in critically ill patients or individuals taking NSAIDs to avoid stress-related damage to the mucous membranes.
Here are some references that you can use:
1. Famotidine: Uses, Dosage & Side Effects - Drugs.com
2. Famotidine - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
B. Overview of Beneficial Effects
Famotidine's beneficial effects arise mainly from its ability to decrease gastric acidity. This medicine helps reduce the chances of damage to the esophageal, gastric, and duodenal mucosa caused by acid. Furthermore, it aids in the healing of existing ulcers and alleviates symptoms like heartburn, abdominal discomfort, and nausea. Additionally, its comparatively long half-life permits less frequent dosing enhancing patient adherence.
Here are some references that you can use:
1. Famotidine | Side Effects, Dosage, Uses & More - Healthline
2. Famotidine: 7 things you should know - Drugs.com
V. Off-label Uses of Famotidine
A. Potential Therapeutic Applications
Famotidine is frequently used beyond its approved uses. One notable area is in the treatment of Chronic Urticaria, a persistent skin condition. Some evidence suggests that Famotidine in conjunction with antihistamines can be helpful in managing this condition. Additionally, due to its ability to block histamine, Famotidine may be beneficial in conditions involving mast cell activation, such as Mast Cell Disorders .
Here are some references that you can use:
1. COVID-19: Famotidine, Histamine, Mast Cells, and Mechanisms - Frontiers
2. Acute and Chronic Urticaria: Evaluation and Treatment - American Family Physician
3. Opportunities to target mast cells in inflammatory diseases expand - Nature
B. Efficacy and Safety in Off-label Use
Although there is promising evidence regarding the off-label uses of Famotidine, it is important to acknowledge that these applications are not universally accepted due to limited data. Therefore, the utilization of Famotidine for off-label purposes should only be considered as a last resort after all other treatment options have been explored and should be closely monitored by a healthcare professional. However, it is worth noting that Famotidine has a well-documented safety profile and is generally well tolerated, with rare occurrence of adverse effects .
Here are some references that you can use:
1. Famotidine Monograph for Professionals - Drugs.com
2. Famotidine: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action - DrugBank Online
3. HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION Administration
VI. Dosage and Administration of Famotidine
A. Standard Dosage Guidelines

The dosage of Famotidine can vary depending on the specific condition it is being used to treat. For peptic ulcer disease. A recommended dosage is 40 mg, taken once daily before bedtime for 4 to 8 weeks. In the case of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), taking 20 mg twice daily for a maximum duration of 6 weeks is advised. For Zollinger Ellison Syndrome. The dosage may range anywhere from 20 to 160 mg every 6 hours. Adjustments are made according to how the patient responds. It's important to note that these are general guidelines, and the actual dosage required may vary based on individual patient factors. To ensure proper use. Always carefully follow the instructions provided by a healthcare professional when taking this medication
B. Instructions for Safe Administration
Famotidine can be taken, whether with or without food. Nevertheless if taken on an empty stomach, it may be absorbed at a quicker rate. It is important to note that the tablet form should not be crushed or chewed but rather swallowed whole with a full glass of water. In case a dose is forgotten. It should be taken promptly upon recollection unless it is almost time for the subsequent dose. Under no circumstances should the dosage be doubled in order to compensate for a missed one.
VII. Side Effects of Famotidine
A. Common Side Effects
Although Famotidine is typically well tolerated. It can lead to certain common side effects like headache, dizziness, constipation, or diarrhea. Fortunately, these side effects are typically mild and tend to resolve on their own. However, if they persist or worsen, it is advisable to seek medical attention.
B. Less Common but Serious Side Effects
Serious side effects, although uncommon, may arise and require prompt medical attention. These may manifest as allergic reactions marked by rash, itching, swelling, severe dizziness, or difficulty breathing. Mood changes, including confusion, agitation, or depression, may also occur. Also, easy bruising or bleeding and signs of infection, such as fever or persistent sore throat, should not be taken lightly.
VIII. Interactions with Famotidine
A. Drug-Drug Interactions
Famotidine has the potential to interact with certain medications, which may impact its effectiveness or amplify the chance of experiencing side effects. Significant interactions involve Probenecid, where Famotidine could potentially heighten its blood levels and effects, possibly resulting in toxicity. Additionally, Famotidine can reduce the absorption of Ketoconazole and Itraconazole. Thus diminishing their effectiveness.
B. Drug-Food Interactions
The presence of significant food interactions with famotidine is not established. Nevertheless, it is essential to exercise caution by refraining from consuming alcohol alongside this medication. Alcohol consumption can potentially worsen stomach issues and heighten the risk of bleeding.
IX. Warnings and Contraindications of Famotidine Use
A. Patient Populations at Risk
Although Famotidine is generally considered safe, specific populations need to exercise caution. These populations include individuals who have impaired renal function because their clearance is decreased. They may need dosage adjustments when taking Famotidine. Additionally, individuals with liver disease should also be cautious. While no specific dosage adjustment is necessary careful monitoring is advised. Lastly, individuals with a history of acute porphyria should know that Famotidine might precipitate an acute attack and take necessary precautions.
B. Conditions Warranting Caution
It is essential to exercise caution when administering Famotidine to patients who have gastric malignancy, as this medication has the potential to alleviate symptoms and potentially delay diagnosis. Additionally. Long-term use of Famotidine especially at high doses may pose a potential risk of increasing the likelihood of developing gastric malignancies.
X. Careful Administration of Famotidine
A. Important Precautions to Note
To ensure the safe and effective use of Famotidine, It is essential to take certain precautions. It is advised not to exceed the recommended dosage unless under the guidance of a healthcare professional. If you experience an allergic reaction, it is crucial to discontinue its use immediately and seek prompt medical attention. To avoid any potential interactions. You must inform your healthcare providers about all the medications you are currently taking.
B. Monitoring Parameters during Therapy
Healthcare providers may monitor kidney function, gastric malignancy symptoms, and acute porphyria in at-risk individuals during Famotidine therapy.
XI. Special Populations: Administering Famotidine
A. Administration to the Elderly
Famotidine is considered a safe medication for use in elderly patients. However. It is important to be aware of the potential decline in renal function that can occur with age. Therefore. Dosage adjustments may be required in order to ensure optimal treatment outcomes in this patient population.
B. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
For Famotidine to be used during pregnancy, there must be an apparent necessity and proper healthcare oversight. Its impact on breast milk transmission has not been determined yet. Consequently, nursing mothers are encouraged to consult with a healthcare provider before its administration.
C. Administration to Children
For particular ailments, including peptic ulcer disease, famotidine has been deemed suitable for treatment in children aged one year or older. The appropriate dosage must be determined based on the child's weight. And utmost care must be taken to have a healthcare expert oversee its administration.
XII. Overdosage of Famotidine
A. Potential Risks and Symptoms of Overdosage
Typically speaking, individuals well tolerate Famotidine, and overdosing occurrences are infrequent. Nevertheless, in the event of an overdose, it can escalate the common side effects. Some symptoms that might be observed include arrhythmias, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort.
B. Emergency Measures and Antidotes
If confronted with an overdose scenario, Swift action must be taken by seeking immediate medical intervention to attend to the matter diligently. Treatment predominantly revolves around providing supportive measures that involve inducing vomiting or employing activated charcoal to restrict absorption. It should be noted that no specific antidote has been identified for combating a Famotidine overdose situation.
XIII. Storage of Famotidine
A. Optimal Storage Conditions
To ensure the best possible preservation, storing Famotidine in a cool and dry location that is shielded from direct sunlight is advised. The recommended temperature range is generally between 20°C to 25°C. However, this may differ based on the particular formulation being used.
B. Impact of Incorrect Storage
Improper storage of Famotidine such as subjecting it to high temperatures, humidity, or direct sunlight may cause the medication to degrade. This degradation has the potential to affect its effectiveness and safety negatively.
XIV. Handling Precautions for Famotidine
A. Safe Handling Guidelines
When dealing with Famotidin, It is important to exercise standard precautions. It is crucial not to come into direct contact with the medication using uncovered hands and it is advisable to thoroughly wash your hands both before and after handling it. Furthermore, one should refrain from crushing or breaking the tablet.
B. Disposal Instructions and Environmental Concerns
To prevent accidental ingestion and minimize environmental contamination. It is essential to dispose of unused or expired Famotidine properly. Flushing it down the toilet or pouring it into drains should be avoided. Instead, consult a pharmacist or local waste disposal company for appropriate disposal methods.