Before getting Indapamide, it's essential to have a comprehensive understanding of this medication and its various aspects. This article will provide in-depth information on Indapamide, ensuring you make an informed decision.
We'll look at how Indapamide stacks up against other antihypertensive medications in terms of effectiveness and explore the various applications of this drug. You'll also learn about contraindications, side effects, and potential drug interactions associated with taking Indapamide.
Furthermore, we'll delve into this medication's proper dosage and administration guidelines and tips for safe and effective use. By the end of this post, you will have a clearer idea of why buying Indapamide can be a viable option for managing hypertension.
Table of Contents: Buy Indapamide
- Indapamide: The Diuretic You Need
- What Is Indapamide?
- The Versatility of Indapamide
- Efficacy of Indapamide
- Indapamide vs. Other Antihypertensive Drugs: What's the Difference?
- Indapamide Contraindications: Who Should Avoid It?
- Indapamide: Side Effects to Watch Out For
- Drug Interactions with Indapamide
- Indapamide Dosage and Administration: Take It Right.
- Tips for Safe and Effective Use of Indapamide
- Why Indapamide Is a Considerable Option
- Buy Indapamide
Indapamide: The Diuretic You Need
Indapamide is a diuretic drug that helps reduce blood pressure and manage heart failure by eliminating excess water and salt from your body.
What Is Indapamide?
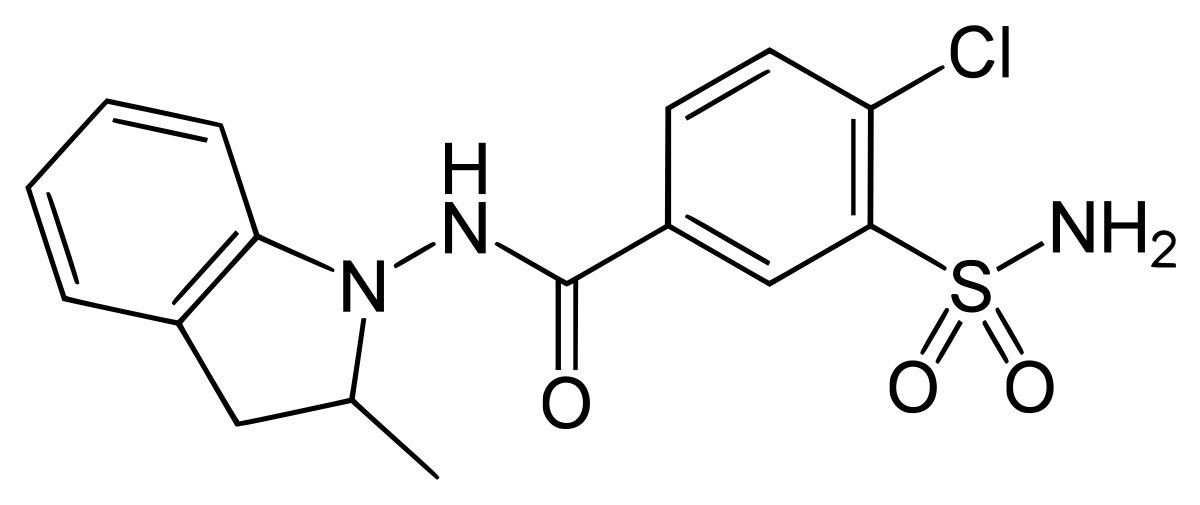
Indapamide is an oral antihypertensive drug introduced in the 1970s, with a unique chemical structure that sets it apart from other thiazide diuretics.
The Structure of Indapamide
Indapamide has a molecular composition featuring a benzene ring linked to a sulfonamido moiety, which grants it further vasodilation properties on blood vessels.
How Indapamide Works:
- Inhibits sodium reabsorption: Indapamide blocks specific proteins responsible for sodium uptake in kidney cells, promoting increased sodium and water excretion into urine.
- Vasodilation: The drug helps relax blood vessel walls by inhibiting calcium influx into smooth muscle cells lining arteries, reducing peripheral vascular resistance and lowering blood pressure levels overall.
Indapamide is crucial in managing hypertension and improving heart health, with various uses, efficacy, and side effects.
The Versatility of Indapamide
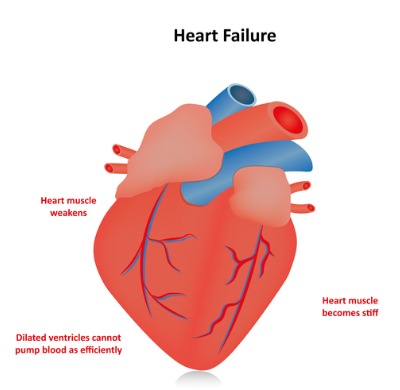
Indapamide, a diuretic med, offers various applications, including controlling hypertension and treating heart failure.
Lowering Blood Pressure
Indapamide helps lower high blood pressure by promoting the excretion of excess salt and water from the body through urine production.

Managing Heart Failure
Indapamide reduces fluid buildup caused by congestive heart failure by increasing urine output and alleviating symptoms such as shortness of breath and swelling in the legs or ankles.
Other Applications
- Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus: Indapamide may help treat nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.
- Calcium Kidney Stones: Indapamide reduces the risk of calcium kidney stone formation.
Indapamide is a valuable medication with potential applications in other medical conditions.
Efficacy of Indapamide
Indapamide is a top choice for treating hypertension because it effectively lowers blood pressure and reduces cardiovascular risks.
Studies show that Indapamide is as good as or better than other antihypertensive drugs, with a lower risk of electrolyte imbalances.
How Effective Is It?
- Blood Pressure Reduction: Indapamide reduces systolic blood pressure by 10-15 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure by 5-10 mmHg, making it practical for mild-to-moderate hypertension.
- Risk Reduction: By lowering high blood pressure, Indapamide decreases the risks of heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease. The HYVET study showed that Indapamide significantly reduced fatal and nonfatal strokes in elderly patients with hypertension.
- Tolerability: Indapamide is well-tolerated by most patients and has a favorable side effect profile compared to other antihypertensive drugs.
Indapamide is a viable option for patients seeking effective blood pressure control and risk reduction.
Indapamide vs. Other Antihypertensive Drugs: What's the Difference?
What are the contrasts between Indapamide and other treatments for high blood pressure?
Different Drug Classes
Indapamide is a thiazide-like diuretic, while other standard classes include beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, and ARBs.
Varying Side Effects
- Diuretics: Indapamide's side effects tend to be milder compared to traditional thiazide diuretics.
- Beta-blockers: These medications may lead to fatigue, cold extremities, or slow heart rate.
- Calcium channel blockers: Potential side effects include swelling in the lower legs or feet and constipation.
- ACE inhibitors: A persistent dry cough is often associated with this drug class.
- ARBs: These drugs are generally well-tolerated but may cause dizziness or elevated potassium levels.
Efficacy and Indications
Indapamide is particularly useful in treating hypertension with concurrent heart failure. At the same time, ACE inhibitors and ARBs are often prescribed for patients with diabetes or kidney disease. essentialortant to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate medication for your specific needs.
Indapamide Contraindications: Who Should Avoid It?
Indapamide is a powerful drug for hypertension and heart failure, but it's not for everyone.
When to Say No to Indapamide:
- Allergy: If you're allergic to Indapamide or sulfonamides, steer clear of this medication.
- Anuria: Indapamide can worsen kidney problems, so it's a no-go for patients with anuria.
- Hepatic encephalopathy: Indapamide can mess with electrolyte balance, so it's not recommended for patients with hepatic encephalopathy.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Pregnant or nursing? Talk to your doctor before taking Indapamide.
Before taking Indapamide, patients with renal impairment, diabetes mellitus, gout, or electrolyte imbalances should consider possible dose adjustments in consultation with their healthcare provider.
Advise your healthcare provider of any medical history before beginning a new medication for safety.
Indapamide: Side Effects to Watch Out For
Indapamide is generally well-tolerated, but knowing the potential side effects is essential.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fatigue or weakness
- Muscle cramps or spasms
- Nausea and vomiting
- Increase in urination frequency
More severe side effects can occur, such as:
- Allergic reactions (rash, itching, swelling)
- Pancreatitis (severe abdominal pain)
Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you experience any severe or persistent symptoms while taking Indapamide.

What Are the Risks?
Indapamide use can cause an imbalance in electrolytes like potassium and sodium levels, leading to hyponatremia (low blood sodium levels) which could cause confusion, seizures, and even coma if left untreated. Patients with kidney conditions should take heed when utilizing this drug because of its diuretic impact on renal capacity.
- Your doctor will monitor your electrolyte levels closely throughout treatment.

Drug Interactions with Indapamide
Are there any potential interactions?
Indapamide can interact with certain drugs and substances, either enhancing or reducing their effectiveness or causing unwanted side effects.
Before taking Indapamide, it is essential to tell your healthcare provider about all medications you are currently using, including prescription and non-prescription drugs, vitamins, supplements, and herbal products.
Everyday drug interactions with Indapamide include:
- Lithium: Indapamide may increase lithium levels in the blood leading to toxicity.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs such as ibuprofen and naproxen can decrease the antihypertensive effect of Indapamide.
- Potassium-sparing diuretics: Combining potassium-sparing diuretics like spironolactone with Indapamide might lead to high potassium levels in the blood (hyperkalemia).
- Digoxin: Digoxin and Indapamide could result in low potassium levels (hypokalemia), increasing the risk of digoxin toxicity.
- Antidiabetic medications: Indapamide's diuretic effect might alter blood sugar control when used with antidiabetic drugs.
Discuss all potential interactions with your healthcare provider before starting indapamide therapy to avoid possible drug interactions and ensure optimal treatment outcomes.
Indapamide Dosage and Administration: Take It Right.
Indapamide is a once-daily oral medication for hypertension and heart failure - take it as your doctor prescribes.

How to Take It?
- Initial dose: Usually 1.25 mg or 2.5 mg taken once daily in the morning.
- Maintenance dose: Your doctor may adjust your dosage based on your response, with a maximum recommended daily dose of 5 mg.
Take it consistently at around the same time each day, swallow tablets whole with a glass of water, and do not crush or chew them.
Missed Dose and Overdose: What to Do?
If you have forgotten to take a dose, make up for it as soon as possible unless the following amount is near; otherwise, proceed with your regular dosing schedule.
In case of an overdose (which can lead to symptoms like nausea/vomiting/dizziness), seek immediate medical attention or contact a local poison control center.
Tips for Safe and Effective Use of Indapamide
When taking Indapamide, follow these guidelines for safe and effective use:
Lifestyle Changes to Enhance Indapamide Effectiveness
- Eat healthy: A balanced diet with fruits, veggies, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy can lower blood pressure.
- Get moving: Regular exercise for 30 minutes most days of the week can improve hypertension management.
- Avoid booze: Limit alcohol intake to prevent increased blood pressure levels.
- Quit smoking: Smoking cessation reduces the risk of heart disease associated with high blood pressure.

Monitoring Your Health While on Indapamide
Track your progress by monitoring your blood pressure regularly with an at-home device or healthcare professional, and maintain a logbook of readings to observe trends over time.
Communicating with Your Healthcare Provider
Maintain open communication with your physician and inform them of any adverse reactions, worries, or variations in your overall health. Your healthcare provider can adjust the dosage or recommend alternative treatments if necessary.
Why Indapamide Is a Considerable Option
Indapamide is the superhero of hypertension and heart failure management, with unique properties make it stand out among other antihypertensive medications.
- Potent diuretic action: Indapamide's ability to reduce fluid retention in the body helps lower blood pressure effectively, making it perfect for those with high blood pressure caused by excess fluid volume.
- Vasodilatory effects: Indapamide also has vasodilatory effects that help relax blood vessels, further reducing blood pressure levels and setting it apart from many other antihypertensive drugs.
- Favorable side effect profile: Most patients generally well-tolerated Indapamide, with fewer adverse reactions than other antihypertensives (source). Before beginning any new medication, consult your healthcare provider about potential risks and benefits.
- Dosage flexibility: Different dosage strengths allow healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans according to individual patient needs, ensuring optimal efficacy while minimizing potential side effects.
Incorporating lifestyle changes alongside indapamide therapy can further enhance its effectiveness, so eat healthy, exercise, limit alcohol intake, and quit smoking to support your overall cardiovascular health.
Buy Indapamide
Want to lower your blood pressure? Indapamide might do the trick, but make sure you know the ins and outs of its uses, side effects, and dosage before you buy.
Don't be a hero - always consult your healthcare provider before taking any medication, including Indapamide, to avoid potential risks or complications.