Betahistine Hydrochloride
- I. Introduction to Betahistine Hydrochloride
- II. Composition and Properties of Betahistine Hydrochloride
- III. Mechanism of Action: How Betahistine Hydrochloride Works
- IV. Betahistine Dihydrochloride uses
- V. Betahistine Dihydrochloride Off-Label Uses
- VI. Betahistine Dihydrochloride Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- VII. Special Considerations in Administration
- VIII. Potential Drug Interactions
- IX. Betahistine Hydrochloride side effects
- X. Warnings and Contraindications
- XI. Important Precautions and Safety Information
- XII. Overdose Management
- XIII. Storage and Stability of Betahistine Hydrochloride
- XIV. Handling Precautions for Betahistine Hydrochloride
I. Introduction to Betahistine Hydrochloride
Overview of Betahistine Hydrochloride
Betahistine hydrochloride is a man-made version of histamine that is mostly used to treat vestibular disorders. This substance helps enhance blood flow in the ear, reducing issues like dizziness and ringing in the ears.
Historical context and development
Betahistine was created in the mid 20th century with the aim of treating Menieres disease. Its popularity and widespread adoption were supported by clinical trials that showcased its efficacy and safety.
II. Composition and Properties of Betahistine Hydrochloride
Chemical structure and formulation
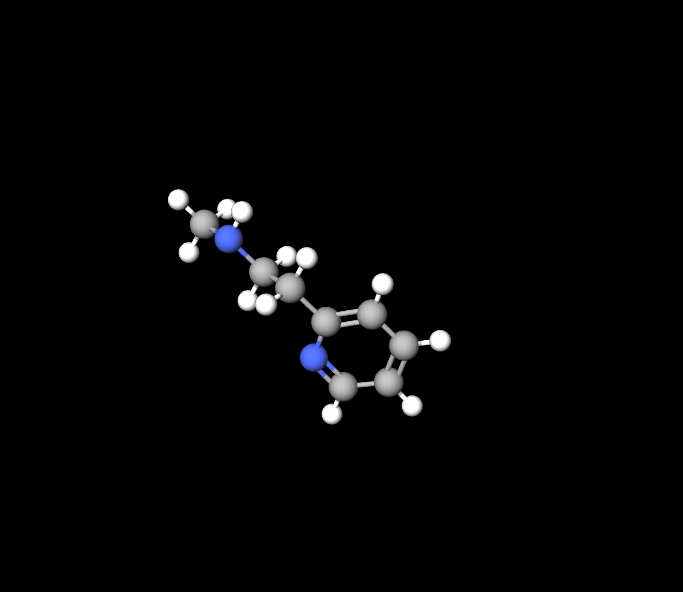
Betahistine hydrochloride is known for its structure, C8H12N2.HCl, which makes it suitable for different methods of administration, such as tablets or liquid solutions.
Pharmacological properties
- Boosts histamine turnover and release.
- It helps regulate the pressure within the inner ear fluid.
III. Mechanism of Action: How Betahistine Hydrochloride Works
Understanding the pharmacodynamics
Betahistine works by imitating histamines effects attaching to H1 and inhibiting H3 receptors in the inner ear and central nervous system. This process encourages blood vessel dilation. Helps regulate the firing rates of neurons.
The role in vestibular compensation
This medication helps restore balance by speeding up vestibular compensation, which's the brains adjustment to inner ear changes after injury or illness.
How soon does Betahistine start working?
Typically, you'll need to take Betahistine three times a day with 6 to 8 hours between doses. It might take a few weeks after starting betahistine before you see any improvements. Some common side effects include headaches, nausea or indigestion. They are usually mild and short-lived.
IV. Betahistine Dihydrochloride uses
Betahistine for Meniere's disease
Betahistine for vertigo and associated symptoms
V. Betahistine Dihydrochloride Off-Label Uses
Exploring non-standard applications in clinical practice
Evidence and studies supporting off-label use
Recent research indicates that Betahistine could play a role in improving blood circulation to the brain, offering a new avenue for addressing cognitive issues and dementia.
VI. Betahistine Dihydrochloride Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Betahistine dose adults
The usual recommended dosage varies between 8 mg and 48 mg per day, split into two or three doses based on the seriousness of the symptoms and how the patient responds to treatment.
Betahistine dose for vertigo
Betahistine is available in tablets of either 8mg or 16mg. Typically, patients begin with a dose of 16mg three times daily spaced out by 6 to 8 hours. Once your symptoms are managed well, your physician might lower the dosage to 8mg three times per day.

Adjustments for specific populations
Patients with kidney or liver issues may need their medication doses adjusted. It's important to keep a close eye on them to ensure the treatment is working as well as possible.
How long should I take betahistine for vertigo?
For results, it is recommended to take betahistine consistently for 3 to 8 weeks at a dosage of 32 to 36 mg per day. There doesn't appear to be benefits on average from higher doses of up to 48 mg/day or extended treatment periods lasting up to 4 months.
VII. Special Considerations in Administration
Administration to elderly patients
Older individuals might need reduced doses because they could be more sensitive to the medication and have health conditions.
Considerations for pregnant women and nursing mothers
Although there is no information available regarding its safety, during pregnancy and breastfeeding, Betahistine should be taken only if the advantages outweigh the possible drawbacks.
Guidelines for pediatric use
It is generally advised against using Betahistine in individuals under 18 years old because there isn't complete information available about its safety and effectiveness.
VIII. Potential Drug Interactions
Common and significant interactions
Interactions between antihistamines and MAO inhibitors might impact the way Betahistine works in the body.
Managing co-administration with other medications
Healthcare professionals need to monitor patients for any negative reactions and adjust medication as needed to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Betahistine vs Meclizine
Betahistine has been shown to be more beneficial than promethazine in alleviating symptoms. The effectiveness of Betahistine for treatment may decline if taken with Meclizine.
IX. Betahistine Hydrochloride side effects
Common side effects encountered
Patients who are prescribed Betahistine Hydrochloride might encounter side effects, with the most common ones being minor digestive issues, like feeling nauseous, having indigestion, and sometimes experiencing headaches. These symptoms typically pass on their own without requiring any intervention.
Managing adverse reactions
- Providing relief through symptom management is important.
- It may be required to change the dosage with oversight to address severe symptoms effectively.
- Regularly monitoring the patient's status can help prevent any worsening side effects from occurring.
Reporting side effects
Healthcare professionals are advised to notify the regulatory authorities of any negative reactions to guarantee thorough monitoring after a product is, on the market. Patients should also be educated on reporting any side effects they may encounter while undergoing treatment.
Betahistine weight loss
The ability of betahistine to aid in weight loss is connected to its impact on the hypothalamus and liver, leading to increased thermogenesis and decreased food consumption. A randomized controlled trial involving 48 women who were treated with both olanzapine and betahistine showed a 37% decrease in average weight gain among those in the betahistine group.
Betahistine withdrawal
After stopping Betahistine for a day, the patient's posture returned to normal. She felt fine. It's important not to stop taking Betahistine even if you start feeling better, as symptoms could come back or worsen in certain situations.
Betahistine Alternative over the counter
Dramamine (dimenhydrinate) is an antihistamine that helps lessen the impact of histamine a chemical, in the body. It is commonly used to prevent feelings of nausea, vomiting and dizziness associated with motion sickness. On the hand Antivert (meclizine) is prescribed to alleviate symptoms of dizziness and spinning related to vertigo.
X. Warnings and Contraindications
Absolute contraindications for use
Patients with pheochromocytoma should not take betahistine hydrochloride because it could increase blood pressure. Moreover, people who have an allergic reaction to Betahistine or any of its ingredients should steer clear of using it.
Risks associated with various health conditions
Patients who have asthma or a past peptic ulcer disease should be careful when using Betahistine since it could worsen these conditions. Additionally, the vasodilatory effects of the medication might intensify symptoms in individuals with issues.
XI. Important Precautions and Safety Information
Monitoring requirements
It is recommended to check vital signs and symptoms, especially for individuals at higher risk of experiencing side effects. Additionally, it is important to evaluate liver and kidney function during extended treatment.
Precautions for handling and administration
Healthcare professionals need to ensure that patients take the correct amount of medication and follow their treatment plans accurately to prevent accidental over or underdosing. It's also important for healthcare providers to teach patients how to take their medications for the best treatment results.
Teva Betahistine 2
TEVA BETAHISTINE is prescribed to lessen the occurrences of recurring vertigo (dizziness) linked to Ménières disease. This medication falls under the category of analogues and is believed to function by improving blood circulation in the inner ear thereby reducing pressure buildup.
XII. Overdose Management
Symptoms of overdose
Signs of taking much Betahistine can lead to significant feelings of queasiness, drowsiness, and, in extreme situations heart-related issues like low blood pressure or rapid heartbeat.
Steps for immediate management and treatment
In case of an overdose, it's vital to get help right away. The treatment involves providing support and addressing symptoms like stomach pumping and keeping an eye on the patient's heart and breathing to help stabilize their condition.
XIII. Storage and Stability of Betahistine Hydrochloride
Recommended storage conditions
Make sure to keep the medicine in a dry place at room temperature and away, from direct sunlight to ensure it works effectively.
Shelf life and disposal methods
Betahistine Hydrochloride usually remains effective for around two to three years after it has been manufactured. It is important to dispose of any unused medication correctly in accordance, with local regulations to avoid causing harm to the environment.
XIV. Handling Precautions for Betahistine Hydrochloride
Safe handling practices
Please handle Betahistine cautiously to avoid exposure to powder or dust, as it could potentially cause irritation in the tract or eyes.

Preventative measures for accidental exposure
It is advisable to wear personal protective gear, like gloves and masks, when dealing with significant amounts of Betahistine, particularly in an uncontrolled setting.