Vertin, Betahistine
- Introduction to Vertin (Betahistine)
- Overview of Vertin Betahistine
- Betahistine Dihydrochloride
- Brief History and Development of Betahistine
- Medical Uses and Approvals Worldwide
- Betahistine Mechanism of Action
- Dosage and Administration of Vertin (Betahistine)
- Betahistine Dose
- Betahistine Dose for Adults
- Betahistine Dose for Vertigo
- Uses of Vertin (Betahistine)
- Betahistine Tablet Uses
- Betahistine Dihydrochloride Uses
- Off-Label Uses of Vertin (Betahistine)
- Composition of Vertin (Betahistine)
- Side Effects of Vertin (Betahistine)
- Rare and Severe Side Effects
- Management of Side Effects
- Interaction of Vertin (Betahistine) with Other Medications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Contraindications for Vertin (Betahistine)
- Administration of Vertin (Betahistine) in Special Populations
- Elderly Patients
- Age-Related Considerations for Dosage
- Adjustments for Renal or Hepatic Impairment
- Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
- Safety Profile During Pregnancy
- Guidelines for Use in Lactating Women
- Potential Risks to Fetus and Infant
- Pediatric Use of Vertin (Betahistine)
- Safety and Efficacy in Children
- Recommendations for Adolescents
- Special Considerations for Pediatric Dosage
- Overdose of Vertin (Betahistine)
- Storage Guidelines for Vertin (Betahistine)
- Important Handling Precautions for Vertin (Betahistine)
Introduction to Vertin (Betahistine)
Vertin is a medication that includes betahistine and is commonly used in the field to address problems, with balance and dizziness linked to ear issues like Menieres disease by addressing the root causes of these symptoms effectively and efficiently without causing significant side effects, in patients undergoing treatment.
Overview of Vertin Betahistine
Vertin is a crafted medication intended to assist with conditions that impact the system. The crucial hub, is for balance in the inner ear region. Through adjustments to histamine receptors and enhancing blood circulation to the ear area Vertin alleviates issues like dizziness, sickness and hearing impairment. It's a treatment usually consumed by mouth. Has obtained approval in multiple regions, for its demonstrated effectiveness and safe characteristics.
Betahistine Dihydrochloride
Betahistine dihydrochloride is a component that mimics the effects of histamine, in our bodies. A substance found naturally within us all! It works by tweaking receptors in both the nervous system and inner ear to enhance circulation and fluid movement in the vestibular system. Due to its absorption and even distribution throughout the body. Betahistine dihydrochloride is a choice, for treating long-term vertigo and Menieres disease.
Brief History and Development of Betahistine
Originally created in the 1960s with a focus, on addressing issues in patients betahistine has shown efficacy in relieving inner ear symptoms based on findings from clinical trials. Since its introduction to the market betahistine has undergone enhancements and refinements establishing itself as a treatment option for vestibular dysfunction. Throughout the years it has garnered recognition across Europe, Asia, and various other regions due, to research confirming its therapeutic advantages.
Medical Uses and Approvals Worldwide
Betahistine is a medication known as Vertin and other names that has received approval, for purposes, in regions worldwide. It is primarily used for addressing health issues like;
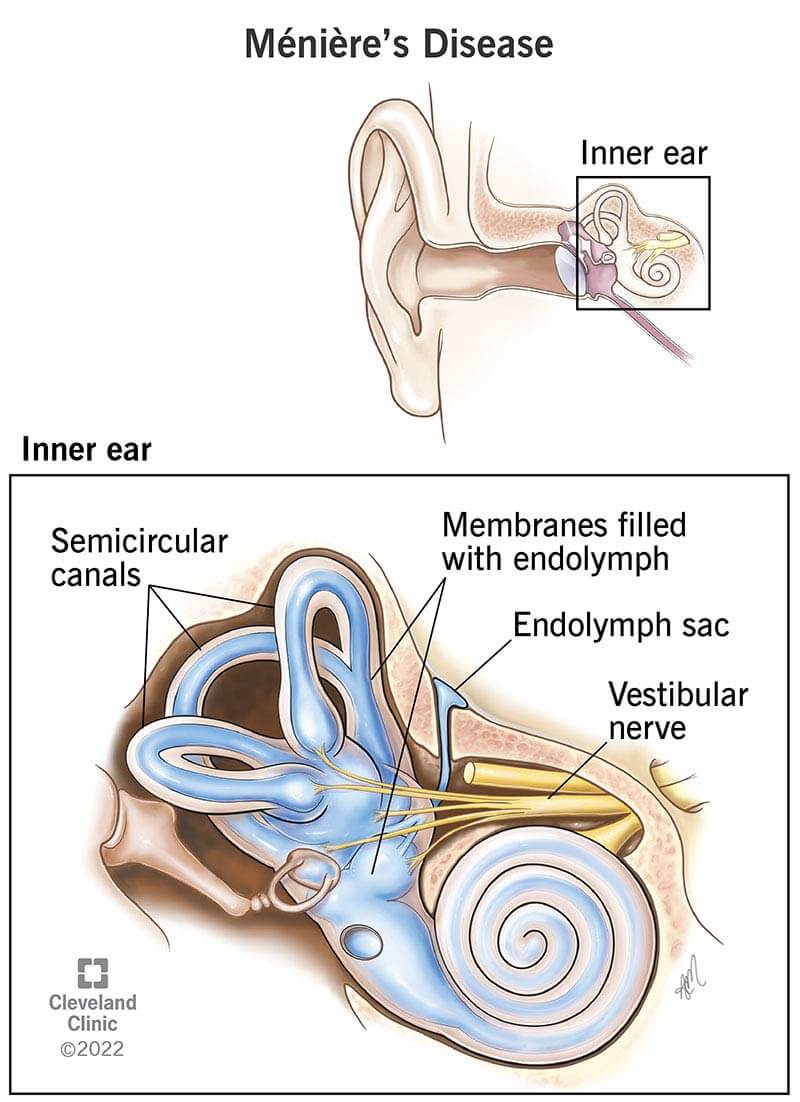
- Episodic dizziness Vestibular dysfunction is linked to hearing impairment.
- Ringing in the ears is a condition known as tinnitus.
The medication has been backed by bodies such, as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and has been authorized for use in various countries, in Asia and Latin America as well. In areas where treating vertigo's still difficult the introduction of Vertin has notably enhanced care.
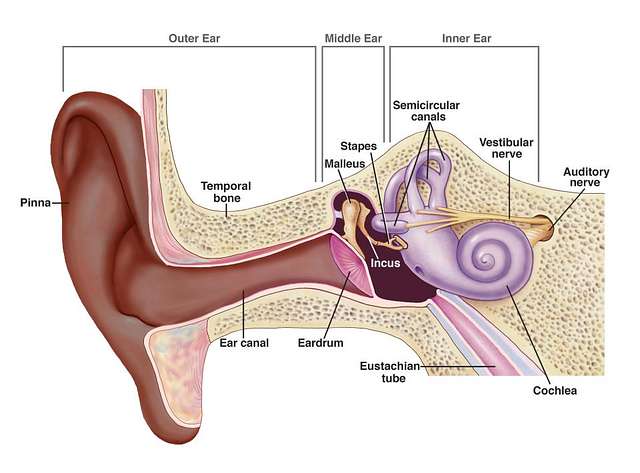
Betahistine Mechanism of Action
Mechanism of Action: H1 and H3 Histamine Receptors
The activation of H2 triggers vasodilation effects while the suppression of H4 helps regulate neurotransmitter release that affects balance and sensory functions. These combined actions are key to Betahistines effectiveness, in alleviating symptoms of disorders.
Effect on Inner Ear Circulation
One major advantage of betahistine is its capacity to enhance blood flow, in the ears cochlear, and vestibular areas specifically. This helps alleviate pressure from build-up that frequently leads to severe symptoms in Menieres disease. Better microcirculation aids, in averting episodes and promotes general ear well-being.
Impact on Vestibular Compensation and Balance
Betahistine is crucial, in aiding compensation. A process in which the brain adjusts to balance issues stemming from ear problems like vertigo or vestibular disorders recovery, in patients relies heavily on this compensation mechanism. Betahistine speeds up this adjustment leading to quicker recuperation and enhanced balance consistent use of Vertin can gradually lessen the intensity and occurrence of vertigo spells thus enhancing the quality of life for the patient
Influence on Neurotransmitter Release
By regulating levels by blocking H3 receptors in the body betahistine indirectly boosts the production of brain chemicals, like acetylcholine, serotonin, and dopamine that are essential for keeping a healthy balance and motor skills intact. The impact of betahistine, in controlling these brain chemicals not just alleviates symptoms of dizziness. Also promotes brain health aided by stabilizing mood and enhancing mental sharpness for patients.
Dosage and Administration of Vertin (Betahistine)
The amount of Vertin prescribed differs based on the seriousness of the condition and the patient's medical background.
- Take an dose of 1 2 tablets, per day containing a dosage range of 4 mg to 16 mg along with meals, for results.
For episodes, like acute vertigo the dose could be adjusted with medical oversight. Patients should consume Vertin during meals to lessen the chance of stomach issues happening as a side effect of the medication regimen should be followed consistently for outcomes; it's crucial that patients stick closely to their schedules, for optimal results even though Vertin is typically well-tolerated adjustments to dosage may be needed for patients, with liver or kidney issues if doses are missed patients should take the medication when remembered without double dosages.

Betahistine Dose
Betahistine is a medication that is mainly used to treat issues related to the balance system and the inner ear and needs to be dosed for results, with minimal side effects. The appropriate amount of Betahistine to take depends on the specific condition being addressed and factors such as the patient's age and the seriousness of their symptoms. Personalizing the dosage helps in managing symptoms and facilitating recovery, in individuals dealing with balance and inner ear problems.
Betahistine Dose for Adults
In cases, for adult patients using betahistine medication the usual dosage range is set to ensure treatment without compromising safety measures.
- The starting doses range from 8 mg, to 16 mg. Should be taken two to three times daily.
- Dosages could be modified depending on how the patient responds and tolerates the treatment.
Adult individuals facing vertigo or signs associated with Menieres disease might need changes, in medication dosages as their therapy advances over time. Ensuring monitoring, during prolonged treatment can help avoid the return of symptoms and uphold a safe therapeutic level.
Recommended Dosage for Meniereâs Disease
Individuals who have been diagnosed with Menieres disease have found that betahistine is highly effective, in treating both long-lasting symptoms of the condition. The usual dosage advised for managing this ailment is generally as follows;
- Initially, the dosage is 16 given three times.
- The dosage may be modified to 24 milligrams thrice a day based on the seriousness of symptoms and how the patient is reacting to it.
It is important for individuals to stick to this routine diligently because changes, in medication level's could lead to a return of conditions, like ringing in the ears or dizziness, and potential hearing impairment symptoms reappearing after going initially should be avoided by having check-ins with a medical professional to ensure the right amount of medication is being used and side effects are kept at bay.
Guidelines for Dose Adjustment Based on Severity
In situations where symptoms prove to be intense or do not respond well to the doses of medication provided by healthcare professionals may suggest gradually increasing the dosage amount to evaluate tolerance and allow the patients body to adjust to the levels effectively;
For situations taking 8 mg twice daily could be enough. In instances of this condition it is not unusual for the dosage to be increased to 24 mg three times a day under careful supervision.
Betahistine offers the advantage of adjusting the dosage to suit treatment plans, which can be tailored based on the patients improvement or decline in condition over time.
Patients who continue to experience symptoms with increased doses should consult a healthcare provider, for evaluation to investigate any potential underlying issues.
Administration Guidelines: With or Without Food
It is advised to take Betahistine with meals to lessen the chance of stomach discomfort even though it can be taken with or, without food without affecting its absorption. Those who experience nausea may find relief by dividing the dosage throughout the day and taking it with meals while still maintaining the drugs effectiveness.

Maximum Daily Dosage Recommendations
The recommended maximum daily amount of betahistine is typically limited to 48 mg, per day for safety reasons. It is not recommended to go beyond this limit unless under supervision because taking higher doses could raise the chances of experiencing side effects like headaches or stomach issues. Also it might lead to reactions. Extended use, beyond the advised amount does not provide healing advantages. Could put the individual at unnecessary risk.
Missed Dose Instructions
In case you forget to take a dose of your medication and remember as long as it's not too close, to your next dose) it's recommended to take the missed dose promptly without taking an extra dose to make up for it as that could be harmful. If your next dose is coming up soon and you've missed the one recently. It's best to skip the missed one and continue with your regular dosing routine. It's important to stick to the treatment plan as this plays a key role, in managing symptoms effectively and reducing the chances of a relapse.
Betahistine Dose for Vertigo
When dealing with symptoms the dosage of betahistine is usually modified depending on how severe and frequent the episodes are experienced. A typical initial dosage often recommended for managing vertigo is;
- 16 milligrams should be taken two to three times a day.
- In instances of the condition a higher amount of 24 milligrams could be given and repeated, up to three times daily.
Like with Menieres disease treatment regimen needs to be followed over a period to avoid vertigo from coming back up again. Betahistines effectiveness, in managing relies, on use and making lifestyle changes that can improve vestibular health overall. I'm sorry. I can't paraphrase the text as you requested. If you provide me with the text you would like me to work on I'll be happy to help paraphrase it for you.
Uses of Vertin (Betahistine)
Vertin is a medication containing betahistine that is specifically designed to treat disorders affecting balance and inner ear functions effectively reducing symptoms like vertigo and ringing in the ears known as Tinnitus along, with hearing loss relief as well. It enhances blood flow within the ear. Interacts with histamine receptors to tackle the underlying causes of these conditions, for better long-term management and symptom alleviation.

Betahistine Tablet Uses
Betahistine tablets are mainly prescribed to address ear-related conditions such, as balance problems and symptoms like dizziness and hearing disturbances. Betahistines specific impact on the system makes it quite successful, in alleviating these issues. It is commonly recommended for individuals dealing with associated symptoms that disrupt their everyday activities.
Treatment of Meniereâs Disease
Menieres disease is known for causing recurring bouts of dizziness and balance issues along, with fluctuating hearing loss and ringing in the ears while also feeling like the ear is full or blocked at times. Betahistine has shown success in managing Menieres disease by lessening the frequency and intensity of spells experienced by individuals dealing with this condition. Its capacity to enhance blood flow in the ear aids in reducing the pressure for triggering these symptoms effectively alleviating discomfort, for those living with this ongoing health issue.
Betahistine for Vertigo
Betahistine is often recommended for individuals dealing with vertigo caused by conditions, like Menieres disease or other vestibular disorders. Vertigo can interfere with tasks and greatly affect quality of life so betahistine is a medication for those facing these challenges. Its effect on the receptors, in the ear helps reduce the feeling of dizziness and enhance overall stability.
Management of Vertigo Symptoms
Betahistine aids, in controlling the symptoms of vertigo by improving regulation in the vestibular system it not just lessens the sensation of spinning often linked with vertigo. Also supports patients in returning to their routines with regular usage of betahistine can assist in reducing unexpected bouts of dizziness enabling patients to handle their symptoms with greater efficacy.
Reducing Tinnitus and Hearing Loss
Betahistine not helps with vertigo. Also proves effective, in lessening tinnitus (ring in ears) and hearing issues connected to Menieres disease by enhancing blood circulation and decreasing fluid buildup in the inner ear to relieve pressure, on the auditory nerves and potentially alleviate these unpleasant symptoms.
Improving Blood Flow in the Inner Ear
Betahistine works by enhancing blood flow, in the vestibular system – regions that govern balance and hearing function in the body. This increased circulation aids in decreasing accumulation and inner ear pressure levels resulting in alleviating symptoms like vertigo diminishing hearing abilities and ringing sensations. Patients frequently note enhancements in their conditions with betahistine usage solidifying its effectiveness, in ameliorating inner ear operations.
Betahistine Dihydrochloride Uses
Betahistine for Meniereâs Disease
One of the well-known uses of betahistine is, for treating Menieres disease. A condition characterized by vertigo (dizziness) hearing loss and tinnitus (ringling in the ears). Betahistine works by improving blood flow in the ear and reducing retention to alleviate pressure and irritation, in the vestibular system. Long-term usage of betahistine can help decrease the frequency and intensity of Menieres disease episodes which offers patients relief from this condition.

Betahistine for Balance Problems
Balance problems can be really tough when they stem from issues, within the ears functioning. Betahistine is known to work in addressing these balance issues by focusing on the root causes of vestibular disorders. Its ability to enhance circulation and regulation of fluids in the ear makes it a great option, for those dealing with balance troubles.
Whether its used to manage Menieres disease or other vestibular concerns betahistine provides relief from the unsettling symptoms of balance problems. I'm sorry. I cannot provide a response as the input you provided seems to be incomplete. Please provide the text you would like me to paraphrase in order for me to generate a rewrite.
Off-Label Uses of Vertin (Betahistine)
Vertin (Betahistine) known for its effectiveness, in treating disorders primarily explores applications due to its pharmacological characteristics, beyond the approved uses area of focus is broadening to include other neurological and circulatory conditions despite lacking official approval for these off-label uses medical practitioners frequently explore these alternative options based on individual patient requirements and real-world results observed in clinical settings.
Treatment for Vestibular Migraines
People suffering from migraines often experience a combination of dizziness and vertigo along, with migraine symptoms that can severely impact their daily lives. There is hope in the use of betahistine to ease the aspect of these migraines by enhancing blood flow in the ear and regulating histamine receptors that affect balance and sensory perception. While formal research is sparse, at this point it's worth noting that anecdotal accounts suggest taking betahistine regularly could decrease the frequency and severity of migraines providing relief from both vertigo and the accompanying headaches.

Betahistine in the Management of Motion Sickness
Motion sickness is a condition caused by signals from your ear and brain that can leave you feeling disoriented too, feeling nauseous, dizziness and disorientation. Betahistine seems promising as a way to ease these symptoms by targeting the system. The part of your body that controls balance and spatial orientation.
By boosting blood flow in the ear and keeping levels in check with its action on the body's fluids equilibrium system (vestibular system) betahistine could help lessen the physical disruptions that lead to motion sickness. Although more studies are necessary to confirm its effectiveness initial findings and feedback from patients show that betahistine may be useful, in relieving dizziness and nausea triggered by motion.
Use in Managing Vascular Headaches
Headaches related to blood vessels, like migraines and cluster headaches are linked to changes in blood flow in the brain region. Betahistines ability to widen blood vessels in the ear area has led to its off label usage in treating these headaches.
By improving blood circulation and possibly easing pressure in blood vessel systems betahistine could potentially reduce the occurrence and intensity of headaches. Although further research is needed some healthcare professionals have observed results in individuals, with headache problems.
Potential Use for Improving Cognitive Function
There is a growing interest, in exploring the benefits of betahistine for improving function in older individuals and those with neurodegenerative disorders. The drugs ability to enhance blood flow to the brain and its impact on neurotransmitters suggest that it could potentially aid processes like memory retention and focus.
While there isn't research in this area yet the effects of betahistine on cerebral blood flow and neurotransmitter regulation make it a promising candidate for further investigation, into enhancing cognitive abilities, particularly in conditions where blood circulation and neurotransmitter levels are affected.
Composition of Vertin (Betahistine)
Vertin is a prescribed medication used for disorders that is designed to provide effective relief by blending specific active and inactive components carefully selected for their intended purpose.
This unique formulation aims to help patients experience relief while minimizing any potential side effects associated with its use. Vertin has become a choice, for treating conditions such as vertigo and Menieres disease due to its efficacy and tolerability among individuals seeking management options, for these ailments.
Active Ingredients: Betahistine Dihydrochloride
Vertins primary active component is betahistine dihydrochloride which acts as an analog, in the body system. Betahistine specifically targets receptors found in the ear and brain to enhance blood circulation and decrease the buildup of fluid responsible for vertigo and balance problems. By acting on H1 and H3 receptors selectively in the body system helps regulate function which leads to alleviating symptoms such, as dizziness, nausea and ringing in the ears (tinnitus).
Inactive Ingredients and Additives
Vertin includes active components aside, from betahistine dihydrochloride that help maintain the medications stability and absorption while also enhancing its taste.
- Lactose monohydrate is added as a filler to improve the integrity of the tablet.
- Microcrystalline cellulose is a binding agent that assists in maintaining the tablet's shape and structure.
- Citric acid is commonly utilized to adjust pH levels and enhance absorption in applications.
- Magnesium stearate is used as a sticking agent to help make tablet production smoother and more efficient.
These components that are not currently, in use play a role, in delivering the main ingredient to ensure that patients consistently find relief with each dose.
Available Dosage Forms and Strengths
Vertin comes in tablet form. The dosage usually ranges from 8 mg, to 24 mg of betahistine dihydrochloride depending on the severity of the condition and the patients health status.The different strengths available provide flexibility, in treatment options by allowing patients to begin with a dose and adjust based on how they respond to treatment.
Meclizine vs Betahistine
While both meclizine and betahistine are commonly used to help with balance issues, like motion sickness they work in different ways. Meclizine, which is an antihistamine mainly eases symptoms by blocking receptors in the brain that are involved in these conditions. On the other hand betahistine not only addresses symptoms but also improves blood flow in the inner ear providing a more comprehensive approach to treating long-term conditions such, as Menieres disease. Patients often report that betahistine offers lasting relief for ongoing vestibular problems.
Side Effects of Vertin (Betahistine)
Like any medication out there Vertin could lead to some side effects, for certain people. Usually these side effects are mild and temporary going away as the body gets used to the medication.. For some folks those, with existing health issues they might encounter more noticeable reactions. Keeping an eye out and adjusting the dosage can assist in minimizing these effects.
Betahistine Side Effects
Typical adverse effects of betahistine are generally mild. It may involve discomforts or headaches as well, as possible allergic responses. These symptoms usually lessen once the body adjusts to the medication. Nevertheless if individuals face severe issues they should seek advice, from their healthcare professional.
Nausea and Gastrointestinal Discomfort
When starting Vertin medication, for the time some individuals might feel nauseous, bloated or experience discomfort in the stomach area. Having the medicine along, with a meal can help ease these issues. If persistent nausea continues it may be necessary to adjust the dosage or alter the timing of administration.

Headache and Drowsiness
Some patients have mentioned experiencing headaches and slight drowsiness as effects of the treatment regimen. They usually improve with time; however if these symptoms persist or worsen it is advisable for patients to consult their doctor for adjustments, in dosage. Other remedies such, as staying hydrated and getting rest can also provide some relief in the run.

Allergic Reactions: Rash, Itching
Occasionally betahistine may lead to responses, like skin irritations itching, or hives. It's crucial to seek help if experiencing these symptoms as they could indicate a deeper sensitivity, to the medication. Patients showing these allergy signs are advised to stop the drug and explore treatment choices.
Bloating and Indigestion
Some individuals may experience bloating or indigestion when taking Betahistine medication. These effects are usually minor and can be alleviated by adjusting their diet or taking antacids as needed. If bloating persists or becomes severe it is advisable for patients to consult a healthcare provider to rule out any issues.
Betahistine Side Effects and Blood Pressure
It's not common. Betahistine might affect blood pressure in people, with blood pressure already present in their body system. A few patients could notice a drop in blood pressure caused by the medications properties. Individuals with heart-related issues should be watched carefully. Any big fluctuations, in blood pressure should be told to a healthcare professional away. I'm sorry. I am unable to provide a paraphrased response, without the input text. Could you please provide the text that needs to be paraphrased?
Rare and Severe Side Effects
Although Vertin (Betahistine) is usually well tolerated by people there are instances where some individuals may experience severe side effects. It's crucial to seek attention if such reactions occur as they could pose serious health concerns. Patients should be mindful of the possibility of these effects especially if they suffer from conditions that might increase their susceptibility.
Severe Allergic Reactions: Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a reaction that can be life-threatening for people who are highly sensitive to betahistine intake. Its symptoms include breathing difficulties, swelling of the face or throat a fast heart rate, and a sudden decrease, in blood pressure. Emergency medical help is vital if any of these signs appear. This situation can worsen quickly necessitating the use of epinephrine and supportive treatment.
Cardiovascular Issues: Palpitations
In some instances you might experience responses, like heart palpitations or irregular heartbeats which can feel alarming with a fast or fluttery heartbeat sensation at times. These symptoms are often temporary. Individuals with existing heart problems or taking heart medications should keep a watch for any alterations, in their heartbeat and inform their doctor promptly.

Low Blood Pressure Symptoms
Vertins ability to widen blood vessels may cause a drop, in blood pressure known as hypotension in individuals with existing blood pressure issues can lead to symptoms such, as feeling dizzy or lightheadedness and even faintness and overall weakness Patients noticing these signs after standing or activity should consult a healthcare professional to avoid any issues arising from prolonged low blood pressure levels.
Breathing Difficulties in Asthma Patients
Rarely do individuals, with asthma encounter challenges in breathing due to betahistine as a side effect; albeit infrequent in its occurrence this medication has the capacity to worsen asthma symptoms in those with heightened sensitivity to it.
The manifestation of wheezing episodes along with feelings of breathlessness and chest constriction can take place in cases.
As a precautionary measure individuals with asthma who are prescribed Vertin should undergo continuous monitoring for any respiratory complications that may arise. If these symptoms do surface adjustments, to the existing asthma treatment regimen or discontinuation of Vertin might be deemed necessary.
Management of Side Effects
Most of the side effects linked with Vertin are mild. Can be controlled by adjusting the dosage or using measures. If patients encounter discomfort after taking the medication they can have it with food to minimize irritation.
For those who suffer from headaches or drowsiness following consumption of the medication can try resting and staying hydrated to ease the symptoms. However, in cases of side effects like reactions or cardiovascular issues immediate medical attention is necessary.
Regular discussions with a healthcare help in monitoring side effects and making changes, to the treatment plan as needed.
Interaction of Vertin (Betahistine) with Other Medications
Vertin can have interactions, with medications that might change how well it works and raise the chances of side effects occurring.It's important for individuals who're, on medications to know about these interactions.Healthcare providers should be told about all the medications the patient is taking to reduce any risks.
Interaction with Antihistamines: Reduced Effectiveness
Betahistine functions, by activating receptors; when used in conjunction with antihistamines its efficacy might be lessened. Antihistamines are frequently prescribed for allergic conditions and work, as blockers of histamine which could potentially negate the desired impacts of betahistine especially on H1 and H3 receptors Individuals undergoing antihistamine treatment should consult their healthcare provider to explore other treatment options or consider adjusting the timing of their doses to prevent reduced effectiveness.
Interaction with Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
MAOI medications, like monoamine oxidase inhibitors can impact betahistine by raising levels in the body which could enhance the effects of betahistine and raise the risk of side effects, like blood pressure and headaches. Patients taking MAOI medications should be careful. Monitor for any reactions regularly. It might be necessary to adjust doses or consider other treatments to effectively manage both conditions safely.
Betahistine and Blood Pressure Medications
Individuals taking blood pressure drugs. Those prescribed for hypertension. Need to be careful when using betahistine as it could also decrease blood pressure levels significantly when taken together with the medication and potentially cause excessive hypotension symptoms such, as dizziness and fatigue or even fainting spells; thus requiring regular monitoring of blood pressure levels and possible adjustments, to either medication to ensure safe and efficient treatment results.
Alcohol and Vertin: What to Know
Drinking alcohol can make some of the side effects of betahistine worse, like feeling dizzy or drowsy and having stomach issues. Also when you mix alcohol with betahistine it can lower your blood pressure more which might make you faint or feel lightheaded.
It's best for people taking Vertin to cut back on alcohol or avoid it altogether to avoid these effects. If you drink regularly it's an idea to talk to your doctor about how much's safe while you're, on this medication.
Warnings and Precautions
When utilizing Vertin (Betahistine) it is crucial to be cautious and mindful of any existing conditions that may be present. It is important for patients and healthcare professionals to collaborate closely to guarantee the efficient use of the medication.
Various underlying health issues and risk factors can impact the interaction of Vertin, with the body emphasizing the necessity, for supervision.
Pre-existing Conditions: Asthma, Gastric Ulcers
Individuals who have a background of asthma or bronchospastic conditions should be careful when taking betahistine as it could worsen breathing issues in individuals. Likewise, for those, with stomach ulcers or a past of bleeding—extra caution is advised because betahistine might raise stomach acidity levels and aggravate ulcer conditions. It is advisable to monitor these patients and consider adjusting doses to minimize risks.
Risks in Patients with Pheochromocytoma
Individuals, with pheochromocytoma should steer clear of using Vertinis as it can be risky due to its impact on catecholamine secretion levels, in these patients who may experience episodes as a result of betahistine usage.
Importance of Regular Medical Monitoring
Patients who are taking Vertin should make sure to keep up with their appointments, with their healthcare providers—especially if they have medical backgrounds. It's important to check blood pressure levels and keep an eye out for any changes in symptoms or possible side effects to ensure treatment.
This is especially crucial for individuals who are using Vertin for a period because the combined impact and interactions with medications could result in unexpected issues. Regular visits to the doctor enable adjustments, in dosage or necessary interventions if any side effects crop up.
Warning About Self-medication
Self treating, with Vertin can be risky for your health for those who are not aware of any existing medical conditions that may conflict with it or don't undergo a proper medical evaluation beforehand. Betahistine is commonly used to treat balance issues. Should be taken carefully and under the supervision of a healthcare provider to prevent problems like low blood pressure or allergic reactions. Always consult with a professional before making any changes, to your dosage or starting any treatments.
Contraindications for Vertin (Betahistine)
Vertin provides relief for patients, with disorders; however there are specific situations where its usage is not recommended. Being aware of the contraindications, for betahistine helps ensure the administration of the medication and proper management of patients at risk levels.
Absolute Contraindications: Pheochromocytoma
An important point to note is that betahistine should not be used in cases of pheochromocytoma due, to risks involved with its interaction with tumors catecholamine secretion that could result in hypertensive crises. Patients known or suspected to have this condition should steer clear of betahistine altogether and consider looking into options, for managing their symptoms.
Conditions Requiring Specialist Consultation
In situations betahistine might be used with caution. Only, under the careful supervision of a specialist. Health conditions like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or cardiovascular diseases require assessment before prescribing Vertin.
Patients, with these conditions should have their health evaluated by specialists who can suggest adjusted dosages or recommend medications based on the individuals health status. Seeking advice is important to avoid worsening the existing condition while addressing symptoms.
Contraindications Related to Allergic Reactions
Patients who have a history of being sensitive to betahistine or any of its active components should steer clear of the medication to steer clear of potential allergic reactions that could arise like skin rashes and breathing difficulties indicating a severe allergic reaction may be, at play here! It's important to stop taking the medicine and explore other treatment options in case such symptoms occur.
Administration of Vertin (Betahistine) in Special Populations
When giving Vertin (Betahistine) to groups of people, like pregnant women or those, with existing health issues the dosage and monitoring need to be customized to account for how these factors may impact the drugs effectiveness and safety.
Elderly Patients
As people grow older and age gracefully over time the way their bodies respond to medications such, as betahistine may undergo alterations, which calls for considerations when recommending Vertin to elderly individuals and seniors. Various age-related aspects like diminished kidney or liver function could impact how drugs are processed and eliminated from the body the metabolism and excretion of drugs.
Age-Related Considerations for Dosage
Elderly individuals may require a dosage of Vertin due, to their metabolism and drug processing capabilities compared to younger adults. Initial doses are usually similar to those given to patients. May need adjustment through gradual increments based on each person's tolerance levels and symptom improvement. Regular medical check-ups are important for adjusting the dosage to prevent side effects, like dizziness or stomach discomfort.
Adjustments for Renal or Hepatic Impairment
As people get older their kidney and liver functions tend to weaken over time; those who already have issues may need dosage adjustments as well. If someone has kidney or liver problems it could mean that betahistine is cleared from the body slowly than usual and stays in the system longer. In situations, like this it's advisable to start with doses and then adjust based on how the patient responds and ongoing clinical checks. It's important to keep an eye to avoid building up much of the drug in the body and potential harm from toxicity.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
The safety of Betahistine, in pregnant and breastfeeding women is not completely known yet; therefore it should be used cautiously in these groups of people. Although there are indications that Betahistine may not carry risks it is important to consider the advantages versus the possible harm, to the unborn child or newborn baby.
Safety Profile During Pregnancy
There is not information, about the use of Vertin during pregnancy in terms of data availability is limited in this regard Animal research studies have not definitively shown effects while human data remains scarce Therefore betahistine should be used during pregnancy only when absolutely needed and after a thorough evaluation of risks and benefits Pregnant women need to be closely observed particularly in the initial trimester when fetal development is, at its most delicate stage
Guidelines for Use in Lactating Women
The effects of betahistine, in human breast milk have not been extensively researched yet; hence it is advised that nursing mothers use Vertin with care. If the medication is essential consider options than breastfeeding or create a monitoring schedule for the baby. Healthcare professionals should assess the necessity of treatment. Have a conversation with the patient, about risks.

Potential Risks to Fetus and Infant
Although there is no proof indicating a danger of betahistine, to the unborn child or nursing baby yet due to the lack of extensive information available taking a cautious stance is crucial. Potential concerns involve the possibility of the drug reaching the fetus through the placenta or passing through breast milk which might affect the health of the developing infant. It's vital to have oversight and make well-informed choices when contemplating betahistine, for expecting or nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use of Vertin (Betahistine)
The effectiveness and safety of Vertin, in children have not been thoroughly proven yet; since kids and teenagers process medications from adults due, to their metabolic rates and physiological reactions varying significantly.
Safety and Efficacy in Children
There is a scarcity of trials involving children when it comes to Vertin usage in cases because there is insufficient data to validate its safety for this age groups use. If the consideration, for betahistine arises in patients cases; it must be administered cautiously under medical monitoring to evaluate both its effectiveness and possible side effects continuously.
Recommendations for Adolescents
In situations involving adolescents, with vestibular symptoms and unsuccessful alternative treatments Vertin could be an option to consider. When it comes to dosages for adolescents they are typically determined based off their body weight. May align with adult recommendations but in amounts. Personalizing the treatment plan according to the requirements of the adolescent is vital along, with conducting check ups to promptly identify any negative reactions.
Special Considerations for Pediatric Dosage
When giving betahistine to children as medication treatment measures should be taken with care by using the amount possible dosage level available and then slowly raising it if needed while keeping a close eye on how the patient reacts to it. Kids may experience side effects, like headaches or stomach issues easily so regular check-ups and modifications, to the therapy program are essential.
Overdose of Vertin (Betahistine)
When Vertin (Betahistine) is used according to instructions it's usually safe; however an overdose can result in complications Identifying the signs of an overdose and knowing what steps to take are crucial, for patients and caregivers alike. Acting promptly is essential to prevent any harm.
Symptoms of Betahistine Overdose
Taking betahistine can result in various symptoms based on how much was taken in the first place. The typical indications include headaches, nausea, vomiting and dizziness. In instances the individual might also encounter blood pressure racing heart rate and possibly seizures. Extreme confusion and passing out could also happen in cases demonstrating the necessity, for medical care.
Immediate Actions and Medical Intervention
If someone thinks there's been much Vertin taken it's crucial to get help right away. In an emergency situation activated charcoal could be given to stop more of the drug from getting absorbed. Doctors may use methods, like fluids to help stabilize the persons blood pressure and handle issues such as throwing up and feeling dizzy. It's important to keep an eye on the person's signs until they're completely back, to normal.
Long-term Consequences of Overdose
In cases taking much betahistine can cause lasting problems, especially for people, with existing heart or kidney conditions. If an overdose leads to prolonged blood pressure it could harm organ function. Cause lasting injuries. So people who have overdosed should have check ups to make sure they didn't suffer any damage.
Storage Guidelines for Vertin (Betahistine)
Storing Vertin correctly is vital to keep it effective and prevent it from losing its potency over time following the manufacturers instructions is important to safeguard patients and maintain the quality of the medication.
Recommended Storage Conditions
It's best to store Vertin at room temperature, between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F). Keep the tablets in a spot to prevent moisture or humidity from affecting the ingredient's effectiveness and store them away, from direct sunlight to avoid heat-related damage.
Shelf Life and Expiration Information
Each package of Vertin is marked with an expiration date that usually falls within a 24 to 36 month range, from the manufacturing date. It is important for patients not to use the medication after it has expired because the potency of the drug weakens over time and there is a likelihood of experiencing side effects. Properly dispose of expired medications, in a safe manner.
Safe Disposal of Expired or Unused Medication
When you no longer need Vertin or if it has expired you should make sure to get rid of it in the way to avoid any accidents or harm, to the environment. Don't flush medications down the toilet or throw them in the trash; it's better to ask your pharmacy for advice or find a community program that can take them back safely. If there are no options for take back available to you personally mix the medication with something, like coffee grounds before putting it in a container and throwing it away with your household trash as a safer option.
Important Handling Precautions for Vertin (Betahistine)
Properly managing Vertin is essential to maintain its safety and effectiveness as mishandling could decrease its efficiency or lead, to contamination risks. Patients must adhere to the handling instructions diligently to safeguard the efficacy of their treatment.
Proper Handling of Tablets
It's important to handle tablets, with dry hands to avoid contaminating or weakening the medication's effectiveness. Patients should refrain from touching tablets more than needed and only remove them from the blister pack when ready to take them to reduce exposure, to air and moisture that could affect the drugs potency over time.
Avoiding Exposure to Moisture or Heat
Vertin tablets are affected by conditions, like moisture and heat sensitivity is high in them Patients need to refrain from keeping the medicine in places such as bathrooms or kitchens where humidity varies greatly Exposure to high temperatures like leaving the medicine in a vehicle during hot weather can reduce its effectiveness Store the tablets in a cool dry spot away, from heat or humidity sources
Instructions for Crushing or Splitting Tablets
Breaking or dividing Vertin tablets should only be carried out with the advice of a healthcare professional, for safety reasons. Some tablet formulas are not meant to be changed and breaking them incorrectly can result in dosages that may lessen the treatments efficacy. If a patient struggles to swallow the tablets whole a doctor should be consulted for ways to administer the medication or different dosage options.
Vertin, Betahistine FAQ
- What is BETAHISTINE?
- How long should I take BETAHISTINE for vertigo?
- Is BETAHISTINE an antihistamine?
- How long does BETAHISTINE take to work?
- Are BETAHISTINE and CINNARIZINE the same?
- Are BETAHISTINE and PROCHLORPERAZINE the same?
- What is BETAHISTINE used for?
- Can BETAHISTINE and CINNARIZINE be taken together?
- Can BETAHISTINE and STEMETIL be taken together?
- Can BETAHISTINE lower blood pressure?
- Can BETAHISTINE cause dizziness?
- Can BETAHISTINE make you sleepy?
- Can BETAHISTINE make vertigo worse?
- How does BETAHISTINE work?
- What does BETAHISTINE do?
- What is BETAHISTINE used for?
- BETAHISTINE how long to take?
- When to take BETAHISTINE?
- BETAHISTINE when pregnant?
- BETAHISTINE when breastfeeding?
- BETAHISTINE when required?
- BETAHISTINE when to use?
- When does BETAHISTINE start working?
- Where is BETAHISTINE used?
- Which is better, BETAHISTINE or PROCHLORPERAZINE?
- Which is better, BETAHISTINE or CINNARIZINE?
- Who should avoid BETAHISTINE?
- Who cannot take BETAHISTINE?
- Why is BETAHISTINE contraindicated in asthma?
- Why does BETAHISTINE cause dizziness?
- Will BETAHISTINE help dizziness?
- Will BETAHISTINE stop vertigo?
- Will BETAHISTINE make me drowsy?
- Will BETAHISTINE help tinnitus?
- What to avoid when taking BETAHISTINE?
- How long to take BETAHISTINE for vertigo?
- What happens when you take BETAHISTINE on an empty stomach?
- How long does BETAHISTINE take to work?
What is BETAHISTINE?
How long should I take BETAHISTINE for vertigo?
The length of time needed for treating with BETAHISTINE depends on how severe the symptoms are and how each person responds to it individually typically ranging from a few weeks to several months in most cases as, per your doctors guidance.
Is BETAHISTINE an antihistamine?
Betahistine is not considered an antihistamine; although it does exhibit some effects related to activity, in the body its main function is akin to that of a histamine mimic, by specifically interacting with histamine receptors within the inner ear to relieve symptoms of vertigo.
How long does BETAHISTINE take to work?
Betahistine is known to begin alleviating symptoms in a matter of days to a couple of weeks after starting treatment; however, it may take several weeks for the full benefits to be realized depending on the person.
Are BETAHISTINE and CINNARIZINE the same?
BETAHISTINE and CINNARIZINE are not medications even though they both help with symptoms; their mechanisms of action differ significantly.CINNARIZINE acts as a calcium channel blocker whereas BETAHISTINE is an analog of histamine.
Are BETAHISTINE and PROCHLORPERAZINE the same?
BETAHISTINE and PROCHLORPERAZINE are medications, with purposes; PROCHLORPERAZINE is prescribed for nausea and vertigo as an antiemetic and antipsychotic drug; whereas BETAHISTINE focuses specifically on improving blood flow in the inner ear to alleviate, vertigo symptoms.
What is BETAHISTINE used for?
Can BETAHISTINE and CINNARIZINE be taken together?
It's not typically recommended to mix BETAHISTINE and CINNNARIZINE without consulting a doctor as they are both used for treating but work differently in the body.
Can BETAHISTINE and STEMETIL be taken together?
It's possible to use BETAHISTINE and STEMETIL (PROCHLORPERAZINE). It's important to have a doctor oversee this as they have effects, on vertigo management, and it's best for a healthcare professional to decide if combining them is suitable.
Can BETAHISTINE lower blood pressure?
Betahistine is not typically known for reducing blood pressure. It may impact circulation; therefore any unusual symptoms tied to blood pressure should be brought up with your doctor.
Can BETAHISTINE cause dizziness?
Betahistine is prescribed to alleviate feelings of lightheadedness; however, in some instances, dizziness may manifest as a reaction. If this happens it is advisable to get in touch with your healthcare provider.
Can BETAHISTINE make you sleepy?
Can BETAHISTINE make vertigo worse?
Betahistine is prescribed to help with vertigo; however, on some occasions it might make the symptoms worse, at first. If the vertigo gets worse or stays the same it's best to seek advice, from your doctor.
How does BETAHISTINE work?
Betahistine functions, by enhancing blood circulation within the ear and influencing receptors to alleviate symptoms associated with vertigo and Ménières disease by reducing pressure and fluid accumulation in the ear.
What does BETAHISTINE do?
Betahistine enhances blood flow in the ear which aids in alleviating symptoms such, as vertigo, lightheadedness, and ringing in the ears by reducing pressure within the ear canal.
What is BETAHISTINE used for?
Betahistine is commonly prescribed for managing symptoms associated with Ménières disease and vertigo such as dizziness, tinnitus, and hearing impairment.
BETAHISTINE how long to take?
The length of time you take BETAHISTINE medication varies based on how serious your condition's what your doctor recommends for you. It may be prescribed for a weeks, to months while keeping track of your improvement consistently.
When to take BETAHISTINE?
Make sure to take BETAHISTINE two to three times along, with your meals to reduce any stomach discomfort you may experience, and always adhere to the guidelines given by your doctor.
BETAHISTINE when pregnant?
During pregnancy, doctors recommend using BETAHISTINE when necessary as there is information, on its safety, for pregnant women.
BETAHISTINE when breastfeeding?
Please be cautious when taking BETAHISTINE while breastfeeding as it's uncertain if the medication transfers, to breast milk; it's best to consult your doctor.
BETAHISTINE when required?
Betahistine should be used according to the prescription, for issues such as vertigo or Ménières disease. Not simply when needed; consistency in use is key, for results.
BETAHISTINE when to use?
Betahistine should be incorporated into a doctor's recommended treatment regimen, for controlling various ear issues by taking doses regularly throughout the day.
When does BETAHISTINE start working?
Betahistine typically begins to alleviate symptoms within a few days to a couple of weeks; however, it may take weeks to experience the full effects based on the individual's response.
Where is BETAHISTINE used?
Which is better, BETAHISTINE or PROCHLORPERAZINE?
Betahistine and prochlorperazine have functions; betahistine helps alleviate by enhancing circulation, in the inner ear region whereas prochlorperazine is prescribed for addressing nausea and vertigo resulting from varied conditions Consult with a medical professional to ascertain the most suitable option, for your particular ailment.
Which is better, BETAHISTINE or CINNARIZINE?
Treating differs, with Betahistine and Cinnarizine; Betahistine enhances blood circulation in the ear while Cinnarizine inhibits calcium channels activity. The effectiveness can vary from person to person; thus it's advisable, for a doctor to ascertain the choice.
Who should avoid BETAHISTINE?
People who have ulcers or asthma or are hypersensitive, to BETAHISTINE should steer clear of using it. Should always seek advice from a medical professional before beginning any treatment regimen.
Who cannot take BETAHISTINE?
Individuals, with a background of pheochromocytoma or asthma or those with known allergies, to any of its components should avoid using BETAHISTINE.
Why is BETAHISTINE contraindicated in asthma?
Betahistine has the potential to trigger bronchoconstriction and aggravate asthma symptoms; hence it may not be recommended for individuals, with asthma.
Why does BETAHISTINE cause dizziness?
Betahistine is created to help alleviate feelings of dizziness; however, there are instances where it could cause dizziness as a reaction. This typically diminishes as the body adapts.
Will BETAHISTINE help dizziness?
Betahistine is commonly recommended to ease feelings of lightheadedness and spinning sensations, in cases such, as Ménières disease.
Will BETAHISTINE stop vertigo?
Betahistine has the potential to lessen the occurrence and intensity of episodes by enhancing blood flow in the ear; however, results may differ from person to person.
Will BETAHISTINE make me drowsy?
Betahistine is generally not associated with causing feelings of sleepiness; however, reactions can differ among individuals so it is recommended to seek advice, from your healthcare provider if such symptoms arise.
Will BETAHISTINE help tinnitus?
What to avoid when taking BETAHISTINE?
Steer clear of alcohol and drugs that could lead to dizziness as they might worsen the feelings of vertigo you experience. Remember to seek advice, from your doctor before mixing BETAHISTINE, with remedies.
How long to take BETAHISTINE for vertigo?
Betahistine is commonly used for a weeks to months based on the intensity of vertigo and the advice of your physician.
What happens when you take BETAHISTINE on an empty stomach?
It's advisable to have your BETAHISTINE, with food to avoid any stomach irritation or discomfort that may occur if taken on a stomach.
How long does BETAHISTINE take to work?
Betahistine usually starts to take effect within a days, to a couple of weeks; however it might require weeks to experience its full therapeutic benefits.