Carvistar, Carvedilol
- Introduction to Carvistar (Carvedilol)
- How Carvistar (Carvedilol) Works
- Primary Uses of Carvistar (Carvedilol)
- Off-label Uses of Carvistar (Carvedilol)
- Composition of Carvistar (Carvedilol)
- Active Ingredients: Carvedilol
- Inactive Components
- Available Formulations and Strengths
- Carvedilol Half-Life
- Carvedilol vs Metoprolol
- Propranolol vs Carvedilol
- Amlodipine and Carvedilol
- Carvedilol Phosphate
- Carvedilol vs Losartan
- Carvedilol vs Lisinopril
- Atenolol to Carvedilol Conversion
- Carvedilol and Albuterol
- Colchicine and Carvedilol
- Carvedilol Testosterone
- Entresto vs Carvedilol
- Carvedilol Dosage and Administration
- Side Effects of Carvedilol
- Serious Side Effects of Carvistar (Carvedilol)
- Management of Side Effects
- Contraindications for Carvistar (Carvedilol)
- Warnings and Precautions with Carvistar (Carvedilol)
- Caution in Patients with Diabetes (Masking Hypoglycemia Symptoms)
- Risk of Abrupt Withdrawal and Rebound Hypertension
- Carvedilol Impact on heart failure patients with Renal function
- Monitoring of Liver Enzymes and Signs of Liver Toxicity
- Foods to Avoid When Taking Carvedilol
- Carvedilol Withdrawal Symptoms
- Switching from Metoprolol to Carvedilol
- Carvedilol and Bananas
- Carvedilol and Alcohol
- Carvedilol and Grapefruit
- Interactions with Other Medications
- Careful Administration of Carvistar (Carvedilol)
- Administration to Special Populations
- Administration to Children
- Overdosage of Carvistar (Carvedilol)
- Storage and Handling Precautions
Introduction to Carvistar (Carvedilol)
Carvedilol or commonly known as Carvestar is a known medication, for treating various cardiovascular disorders. It works by targeting pathways in the body to reduce strain on the heart and blood vessels resultantly improving heart function and overall cardiovascular well-being. This unique mechanism of action makes it a crucial treatment option for individuals dealing with long-term heart problems or hypertension, this underlines its importance, in interventions.
Overview of Carvistar
Carvestar falls into a group of drugs called beta blockers. It is specifically a selective blocker of beta and alpha-adrenergic receptors. Unlike beta blockers, Carvestar has an action, by targeting both the beta receptors in the heart and the alpha receptors in the blood vessels. This unique approach expands its benefits and distinguishes it from similar medications. Carvedilol is mainly prescribed for conditions, like blood pressure, heart failure, and other heart-related issues to help patients effectively manage their symptoms and enhance their quality of life.
Carvedilol's Therapeutic Classification
Carvedilol falls under the category of medications known as selective beta-blockers, with alpha-blocking properties which play a crucial role, in how Carvistar affects the body's functions. By not targeting one type of receptor Carvedilol affects various pathways within the cardiovascular system making its therapeutic scope wider. Its ability to interact with multiple receptors aids in easing the hearts workload and regulating blood circulation across the system.
History and Development of Carvedilol
Carvedilol was created in the century to tackle high blood pressure and heart failure more effectively than single receptor beta blockers could manage alone Researchers developed Carvedilol as a compound that could engage with both beta and alpha 1 receptors Its original use, for heart failure treatment grew as further research showed its effectiveness, in treating hypertension and other heart-related issues
Importance of Carvedilol in Cardiovascular Treatments
Carvedilol has become a treatment, in medicine due to its effectiveness in controlling heart rate and lowering vascular resistance while protecting against specific heart-related incidents. It is crucially beneficial for individuals with heart failure by decreasing hospitalization risks and enhancing survival rates and overall quality of life significantly appreciated for its multi targeted approach in managing various cardiovascular risks concurrently Carvedilol plays a key role, in comprehensive cardiovascular treatment strategies.
How Carvistar (Carvedilol) Works
Carvedilol Mechanism of Action
Carvedilol works by blocking both beta and alpha 1 receptors to slow down the heart rate and relax blood vessels rather than making them beat faster or constricting them as usual signals would do so. By easing the heart's workload and enhancing blood circulation through this inhibition of signals release Carvedilol provides an effect, for individuals, with high blood pressure by effectively reducing their blood pressure levels.
Carvedilol as a Non-Selective Beta-Blocker
Carvedilol works on both receptors (beta-1 and beta-2) as a selective beta blocker instead of just targeting the heart's beta receptors, like selective beta blockers do in the heart alone. Its non-selective feature allows it to affect systems such as the system. This wide range of effects helps effectively reduce blood pressure. Control heart related issues for individuals, with requirements this comprehensive action goes beyond what standard beta blockers can offer.
Mechanism of Action in Reducing Blood Pressure
Carvedilol is efficient, in reducing blood pressure by relaxing blood vessels and decreasing activity effectively which ultimately eases the circulation of blood throughout the body due to its alpha-blocking mechanism that lessens resistance. This reduced resistance translates to strain on the heart in pumping blood naturally resulting in blood pressure levels. Furthermore, the beta-blocking characteristics play a role, in reducing heart rate which contributes to the management of blood pressure and alleviates the burden on the heart.
Dual Action: Beta-Blocker and Alpha-1 Blocker Effects
Carvedilol's effectiveness stems from its ability to target both beta and alpha receptors simultaneously. Reducing the heart rate helps to lower the heart's oxygen requirements. Decreased vascular resistance helps the blood flow smoothly through the arteries and veins. Enhanced cardiac performance, by reducing the strain, on the heart's functions. This two-fold effect sets this heart medication apart as it offers a rounded method, for addressing blood pressure and heart failure symptoms simultaneously.
Impact on Heart Rate, Cardiac Output, and Vascular Resistance
Carvedilol has a variety of impacts, on the system that influence aspects of heart performance. By slowing down the heart rate and preventing strain on the heart muscle is advantageous for individuals dealing with heart failure. Moreover, the reduction in performance achieved by its beta blocker traits helps in lowering the amount of blood that the heart has to pump reducing strain. Additionally, the decrease in resistance eases blood flow without hindrance reducing the likelihood of complications, like blood clots, and improving circulation to organs. Carvedilol's ranging effects serve as evidence of its versatility, as a medication, for heart health issues.
Primary Uses of Carvistar (Carvedilol)
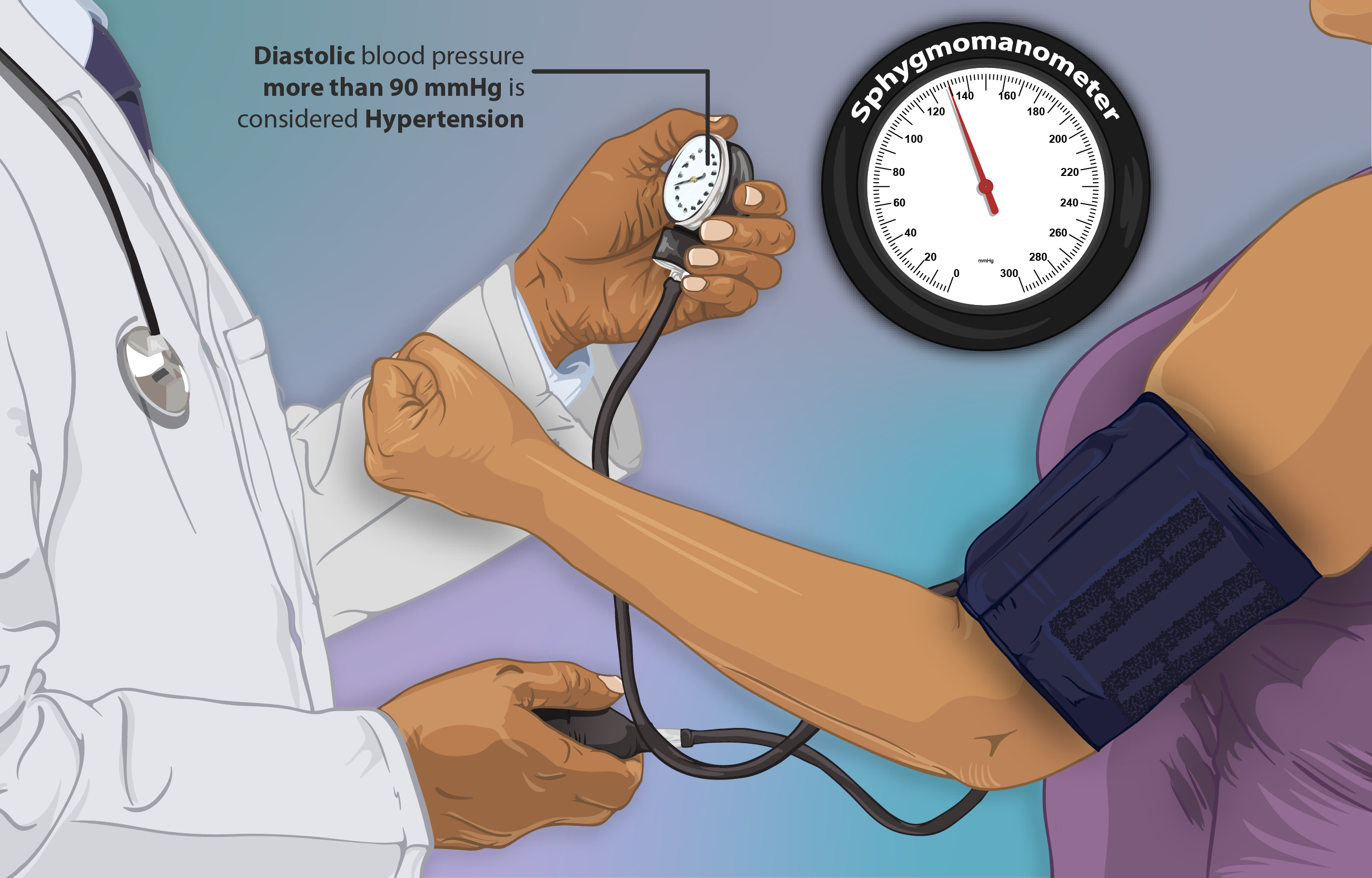
Treatment of Hypertension
Carvedilol, from Carvistar is crucial in treating hypertension due to its way of blocking receptors in the body's system. By targeting both alpha and beta receptors it helps vascular resistance and blood pressure effectively, this results in an approach to managing blood pressure. Moreover, Carvedilol's capacity to decrease output adds another layer to it's ability to lower blood pressure. Patients may notice a decrease, in their blood pressure levels reducing the chances of complications related to hypertension.
Management of Heart Failure (CHF)
In individuals suffering from heart failure (CHF) Carvestar serves as an aid, in easing the burden on the heart by lowering the heart rate and regulating blood pressure effectively to enable the heart to function more efficiently and with reduced stress levels. For those, with a heart muscle condition Carvestar provides an avenue for enhancing ejection fraction and overall cardiac performance. The advantages of using Carvestar in managing CHf include ;
- Increased heart function leading to blood flow, throughout the body.
- Experienced symptoms, like feeling out of breath and tiredness.
- Hospitalization rates, for heart failure have decreased recently.
- These benefits position it as a treatment choice, in protocols, for managing heart failure.
Use in Left Ventricular Dysfunction Post-Myocardial Infarction (Post-MI)
After someone has experienced a heart attack ( infarction) CarviStar plays a role, in caring for the patient by helping the heart’s main pumping chamber. The left ventricle recover effectively. Following a heart attack left dysfunction can. Potentially progress to chronic heart failure without proper treatment.CarviStar’s capability to lessen stress on the heart supports the restoration of function. Enhances survival rates, in the long term.In cases following a heart attack (post MI) carvedilol can;
- Help the heart work better by cutting down on the need, for oxygen.
- Avoid any damage, to the heart muscle.
- Minimize the chances of experiencing heart attacks, in the future.
Therefore it is often recommended as part of a treatment strategy after experiencing a heart attack.
Reducing Risk of Stroke and Heart Attack
Carvistar is also used as a measure, for people facing a risk of stroke and heart attack by managing blood pressure and heart rate effectively to tackle the key factors leading to these vascular issues. Studies have demonstrated that consistent use of carvedilol can decrease the likelihood of stroke and heart attacks in high-risk individuals with a disease background. Its holistic approach towards managing blood pressure plays a role, in minimizing the risks associated with events.
Carvedilol for Anxiety
Although Carvistar is commonly known for its effects, on the heart's health aspects primarily; it has also shown advantages in alleviating symptoms of anxiety too. By obstructing the beta receptor's action mechanism; it can help alleviate some of the body's responses linked to anxiety like a fast heartbeat and increased blood pressure levels. While it may not be the go-to choice for treating anxiety from the start; its soothing impact, on the heart system could provide comfort in situations where anxiety significantly affects heart function or blood pressure levels.

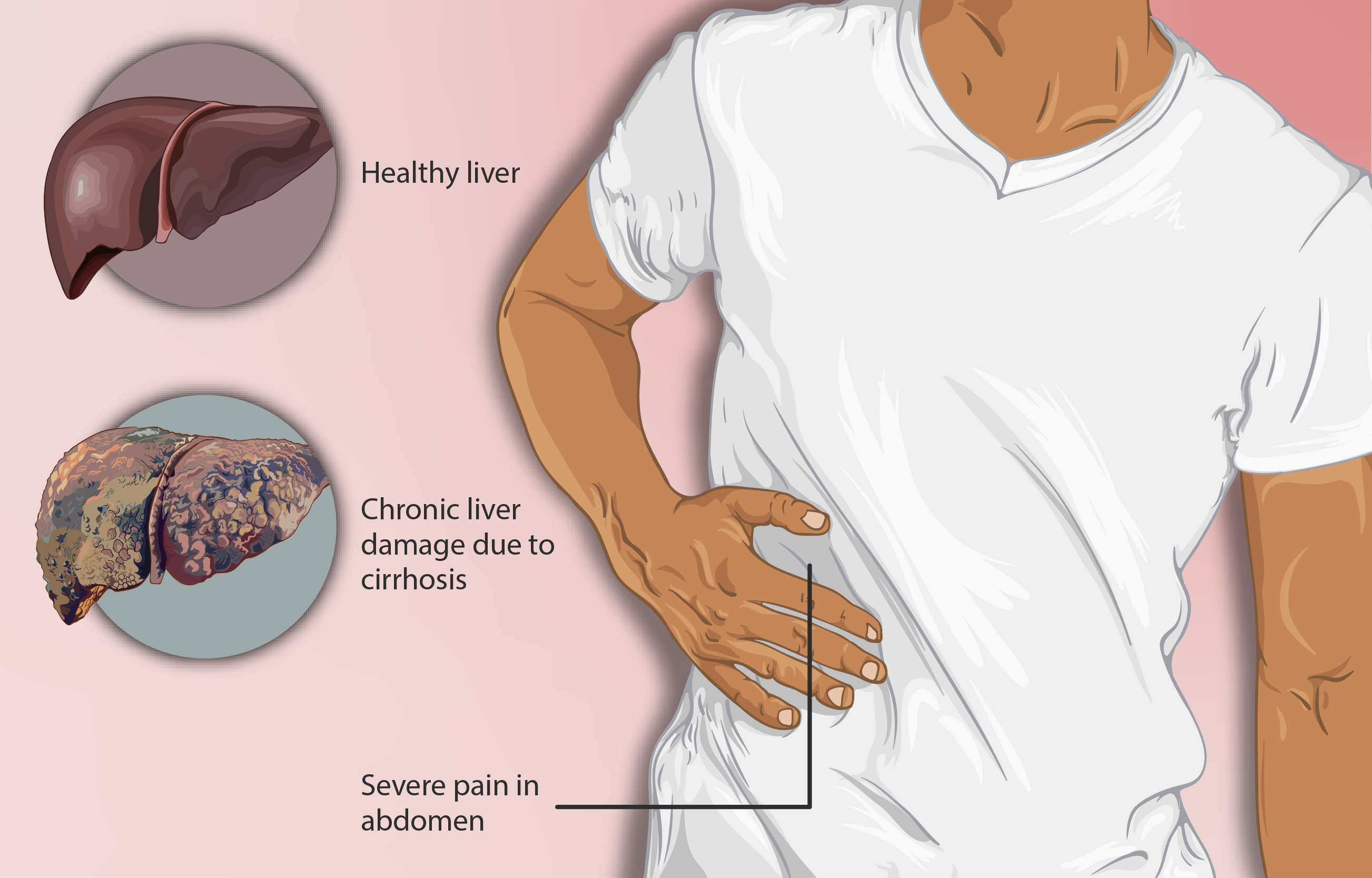
Carvedilol for Esophageal Varices
Carvedilol offers benefits, in treating varices linked to liver cirrhosis by lowering portal hypertension and alleviating pressure in the esophageal veins to lessen the risk of variceal bleeding—a dangerous complication for cirrhotic individuals. The effectiveness of Carvistar in reducing vein pressure positions it as a choice, for addressing this critical issue and offering essential vascular support to prevent bleeding incidents effectively.
Propranolol vs. Carvedilol for Anxiety
While both propranolol and carvedilol can be used to treat anxiety symptoms; the two medications have mechanisms of action that set's them apart, from each other. Propranolol operates as a beta blocker that primarily targets receptors and is commonly prescribed for managing anxiety disorders. On the other hand; Carvedilols dual impact on alpha and beta receptors allows for a range of effects compared to propranolol. Propranolol is often preferred for its relief in situations of performance anxiety; whereas carvedilol's lasting effects may be more advantageous in treating anxiety related to underlying cardiovascular conditions, like hypertension.
Carvedilol and Liver Cirrhosis
Patients suffering from liver cirrhosis greatly benefit from carvedilol's effectiveness, in lowering vein pressure levels. An aspect of managing this condition is complications such as ascites and esophageal varices caused by elevated portal pressure. Carvedilol works by reducing resistance and easing hypertension to mitigate the severity of these associated problems for individuals with cirrhosis. Not only does carvedilol help regulate blood pressure, in patients but also acts as a preventive measure to impede the progression of issues related to portal hypertension.
Off-label Uses of Carvistar (Carvedilol)
Prevention of Variceal Bleeding in Cirrhotic Patients
Carvedilol is a medication that blocks both alpha-adrenergic receptors and shows promise in preventing variceal bleeding, in cirrhosis patients. For those with liver conditions portal hypertension can cause the development of varices delicate blood vessels are susceptible to rupture. Carvedilols ability to lower pressure makes it a valuable tool, in managing this serious complication. By working in two ways to decrease both blood pressure and portal hypertension Carvedilol helps lessen the risk of bleeding. For individuals suffering from cirrhosis of the liver. This provides a life-saving method using medication to reduce the need, for interventions.
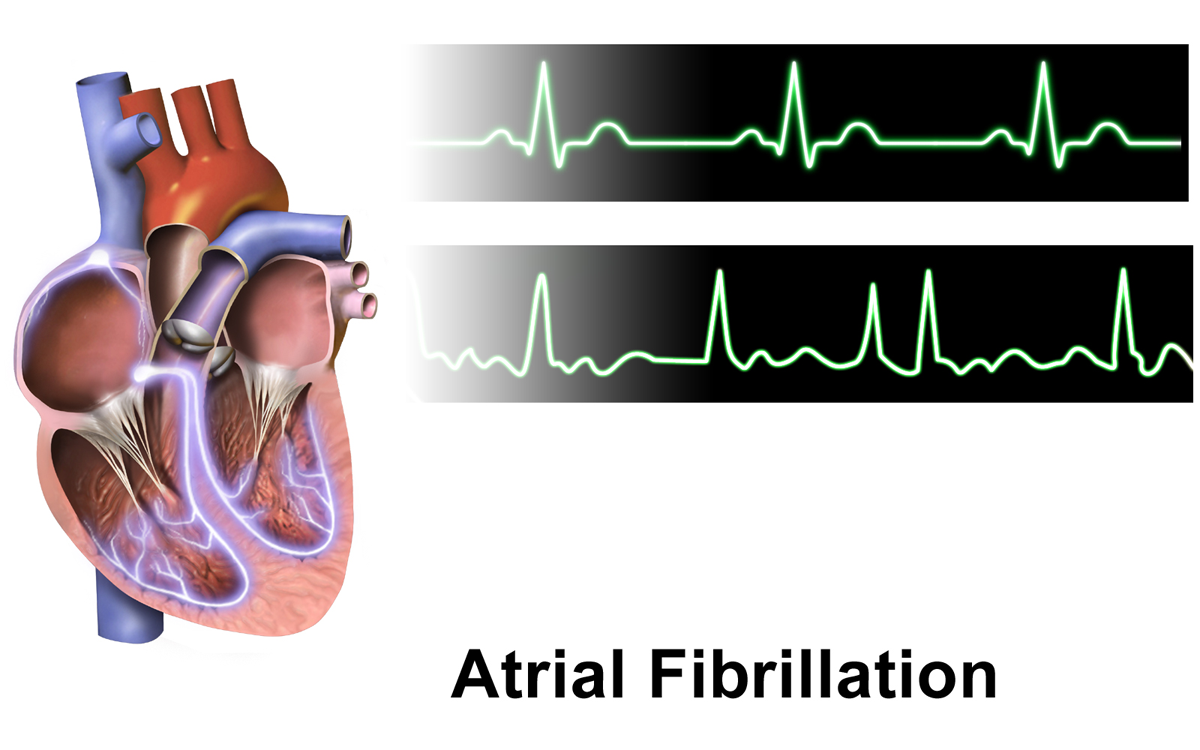
Management of Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation is a common heart condition known for its sometimes fast heartbeat rhythms, in the realm of cardiovascular health care field Carvedilol has been investigated as a method for managing atrial fibrillation because it can help regulate heart rate and decrease instances of irregular heartbeats. By inhibiting adrenergic stimulation carvedilol contributes to controlling how the ventricles respond thus preventing the heart from beating too rapidly. Moreover, its ability to block alpha receptors can improve blood circulation and oxygen levels which aids in lessening the overall impact of atrial fibrillation, on the body Benefits of using Carivistar for managing fibrillation are numerous such as;
- Decrease in heart rate during episodes.
- Avoiding instances of heartbeats.
- Enhancing the hearts pumping capacity in hearts facing challenges.
Carvestaris features add to its effectiveness, in treating fibrillation. Provide an additional option, alongside traditional therapies.
Use in Angina Pectoris
Chest pain caused by decreased blood flow, to the heart known as angina is an issue among individuals with artery disease. Carvedilol has become an off-label choice for treating angina as it eases the strain on the heart and boosts the oxygen supply to heart tissue. By lowering heart rate and lessening heart muscle contraction strength carvedilol reduces the oxygen needs of the heart especially important for those dealing with angina. Furthermore, the medication's vasodilation properties enhance blood flow in arteries leading to a decrease, in angina symptoms. Carvistars advantages, for individuals, with angina might involve;
- The occurrence and severity of angina episodes have reduced.
- Enhanced ability to withstand activity.
- Improved quality of life as symptoms are alleviated.
Carvestars benefits make it a valuable option, for aiding in managing angina pectoris symptoms in individuals who need a treatment strategy.
Potential Benefits in Diabetic Patients
Carvedilol has demonstrated potential, in enhancing the well-being of individuals beyond just managing blood pressure levels according to studies conducted on Carvestars effects in diabetic patients with a high risk of heart issues. Studies suggest that carvedilol could offer metabolic advantages by reducing insulin resistance. A worry associated with beta-blockers. Unlike some beta blockers that can negatively impact glucose tolerance carvedilol seems to have an even positive influence on glucose metabolism making it a preferred option for diabetic individuals requiring beta-blocker treatment. Carvestar is seen as beneficial, for patients at risk of cardiovascular complications.
- Enhanced control of blood pressure while maintaining blood sugar levels.
- Potential ways to reduce the impact of insulin resistance.
- A decrease, in stress can be good, for the health of our blood vessels.
Carvitstars positive effects, on metabolism and its support for heart health make it a viable alternative for individuals, in need of cardiovascular assistance.
Composition of Carvistar (Carvedilol)
Active Ingredients: Carvedilol
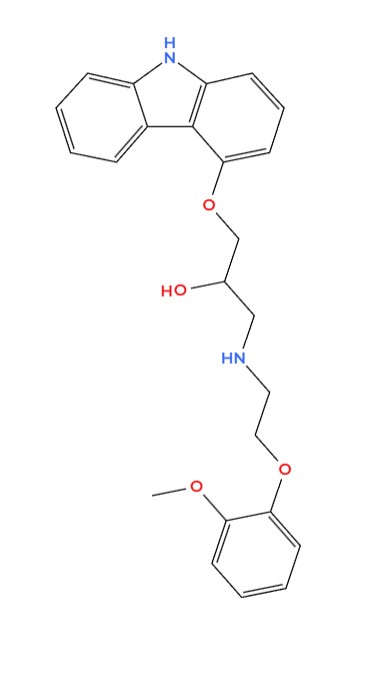
Carvistar contains carvedilol as the component which is a beta-adrenergic blocker that also has alpha-blocking properties It functions by blocking certain receptors in the heart and blood vessels resulting in slowing the heart rate and lowering vascular resistance The dual impact of carvedilol, on both beta and alpha receptors makes it a powerful treatment, for controlling high blood pressure heart failure and various heart-related issues Its comprehensive mode of operation sets it apart from conventional beta blockers providing a wider range of therapeutic benefits
Inactive Components
Carivstars formula contains active components that help in delivering and maintaining the effectiveness of the main ingredient, which could include;
- Microcrystalline cellulose is utilized to maintain the shape and durability of tablets.
- Using lactose monohydrate, in the pill adds bulk. Improves its size and feel.
- Silicon dioxide helps keep the tablet dry and ensures its durability, over time.
- Magnesium stearate helps in the manufacturing process by preventing ingredients from sticking during production.
Although these elements do not directly impact the effectiveness of the medication itself they are crucial, in upholding the standards of quality, uniformity, and practicality, in every dosage.
Available Formulations and Strengths
Carvisar comes in forms and potencies to cater to treatment depending on the patient's health status and reaction, to the treatment regimen The typical strengths consist of;
- 3.125 mg tablets
- 6.25 mg tablets
- 12.5 mg tablets
- 25 mg tablets
Different versions of medications make it easier to get the dose and adjust slowly to maximize the effects, on health conditions, like heart issues based on patient's medical background and current health status.
Carvedilol Half-Life
Carvedilol typically stays in the body for around 6 to 10 hours before being eliminated through metabolism and other bodily processes that vary from person, to person. This shorter half-life means that it is necessary to take the medication twice a day in order to keep a level of the drug in the bloodstream and ensure that its benefits remain constant. In individuals, with liver issues, the half-life may be longer making it important to adjust the dosage carefully to prevent any effects.
Carvedilol vs Metoprolol
Carvedilol and metoprolol belong to the category of medications known as beta-blockers; however, they have differences, in how they work and their medical uses. Metoprolol primarily targets the heart as a beta–blocker that focuses on beta–1 receptors while carvedilol has an effect by blocking both beta and alpha receptors impacting both the heart and blood vessels.
This dual mechanism of action allows carvedilol to provide control over blood pressure and support for the vasculature, which is especially beneficial for patients with heart failure. On the other hand, metoprolol may be preferred for individuals who need a specific focus, on the heart without affecting peripheral areas.
Propranolol vs Carvedilol
Propranolol and carvedilol are both beta blockers, with some similarities; however they differ in that carvedilol does not possess alpha-blocking properties like propranolol does. Carvedilol's wider range of uses extends to managing hypertension and heart failure compared to propranolol which is better suited for anxiety and migraine prevention. The vascular effects of carvedilol make it particularly beneficial, for conditions where the regulation of blood pressure's crucial. For patients requiring support treated with carvedilol can provide a comprehensive solution.
Amlodipine and Carvedilol
Sometimes doctors prescribe a combination of amlodipine and carvedilol to better manage blood pressure levels in patients. The way amlodipine operates is, by relaxing the blood vessels while carvedilol decreases the heart rate and lowers resistance in the arteries. This combination results in an effect where amlodipine strong vasodilation is enhanced by carvedilol heart rate adjustment. This two-pronged strategy is particularly beneficial for individuals who need treatment, for blood pressure.
Carvedilol Phosphate
Carvedilol phosphate is a kind of carvedilol that releases the medication slowly over a day to make it easier for patients to take just one dose every day and keep their blood levels steady, with fewer doses required.
Carvedilol vs Losartan
Carvedilol functions, as a beta blocker with alpha-blocking capabilities while losartan acts as an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB). Both medications effectively reduce blood pressure using mechanisms; losartan blocks angiotensin II receptors to lessen vasoconstriction and lower blood pressure; carvedilol achieves results by blocking beta and alpha receptors simultaneously. For individuals with heart failure conditions, carvedilol may offer benefits compared to losartan which could be more suitable for individuals, with kidney problems.
Carvedilol vs Lisinopril
Lisinopril and carvedilol work differently, in lowering blood pressure – Lisinopril blocks the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II while carvedilol reduces heart rate and vascular resistance for the purpose of decreasing blood pressure levels in individuals needing treatment, for hypertension or related conditions.
Atenolol to Carvedilol Conversion
Switching from atenolol to carvedilol needs to be done due, to differences in dosages and actions between the two medications. Carvedilol having an effect compared to the beta blocker selectivity of atengolols action. In practice when transitioning to carvedilol from atenolol it is advisable to start with a dosage and then adjust gradually while keeping an eye out for any potential side effects. Such changes are usually made with the aim of widening the scope of treatment for conditions, like blood pressure or heart failure where the alpha-blocking feature of carvedilol proves beneficial.
Carvedilol and Albuterol
Albuterol is often used to treat asthma as a beta 2 agonist. Due to its blocking of receptors, it may have interactions with carvedilol, which could reduce the bronchodilatory effects of albuterol when used together, leading to the need for close monitoring of patients, on both medications and considering alternative treatments if respiratory function is affected.
Colchicine and Carvedilol
Colchicine is a medication mainly prescribed for gout to reduce inflammation and may impact how carvedilol is metabolized when taken together with it. It's important to be cautious as colchicine can influence the liver enzymes, for processing carvedilol which may result in either lower levels, in the bloodstream. To manage this interaction effectively it is crucial to make dosage changes to ensure the treatment remains effective and reduce any negative consequences.
Carvedilol Testosterone
Research suggests that carvedilol could potentially impact testosterone levels in a manner, for some individuals. There are instances where the use of carvedilol has been linked to a decrease in testosterone levels among patients. This decrease could result in symptoms like fatigue or weakened muscle strength. Is typically mild and may not be of concern from a clinical standpoint. Nevertheless, it is important to keep an eye on these effects in patients, with existing imbalances or symptoms indicating low testosterone levels.
Entresto vs Carvedilol
Entresto blend of sacubitril and valsartan varies, from carvedilol in its ingredients and effects. When used for heart failure patients the main goal of Entrestois to ease the burden on the heart by hampering neprilysin activity and blocking angiotensin II receptors. On the other hand carvedilolis are designed to target beta and alpha receptors in order to reduce blood pressure and heart rate. In some cases, doctors may recommend a combination of Entrestowell known for its benefits, for the hearts, and carvedilol to achieve optimal results in treating heart failure.
Carvedilol Dosage and Administration
Recommended Starting Dosage for Hypertension
Carvedilol is commonly started at a dose, in patients with high blood pressure to check for tolerance and reduce possible side effects. It is usually prescribed at 6.25 mg twice a day to establish a level of the medication for controlling blood pressure without straining the heart too much. The dosage can be adjusted over time depending on how the patients blood pressure responds and how well they tolerate the medication. Regular monitoring, during the stages is crucial to ensure that the treatment is effective and prevent the lowering of blood pressure.
Adjustments in Dosing for Heart Failure
For individuals, with heart failure conditions and needing carvedilol treatment initiation is usually done step by step starting at 3.125 mg twice daily to help the heart adjust to the effects of the medication, on heart rate and contractility After adapting to the dose adjustments may be made every two weeks aiming for a dosage range of 12.5 mg daily Depending on patient tolerance and treatment objectives higher doses may be considered but close monitoring is essential to prevent worsening heart failure symptoms.
Dose Titration Based on Patient Response
Carvedilol dosages are tailored to each patient's needs and are adjusted according to how the patient responds and tolerates the medication dose over time. Clinicians typically evaluate the patient's response, within one to two weeks of starting treatment. Make adjustments to the dosage as needed. This careful approach aims to achieve the desired benefits while minimizing any side effects.
Monitoring factors such as blood pressure changes heart rate levels and improvements in symptoms help guide the adjustment of dosages. In patients, with heart failure carvedilol dosage increases are done gradually and systematically to prevent the worsening of their condition and ensure that the heart adjusts effectively to the medication's effects.
Guidelines for Taking Carvistar with or Without Food
Carvedilol should be consumed with food to improve absorption and lower the chances of hypotension—a side effect related to beta-blocker medications. Food presence helps in slowing down the absorption of the medicine which results in a release and prevents decreases, in blood pressure while standing up. Patients should adhere to a routine of taking this medication at intervals during meal times, for plasma levels and effective management of blood pressure. By following these instructions diligently patients can maximize the benefits of carvedilol.
Carvedilol Dosage for High Blood Pressure
For people, with blood pressure conditions who are prescribed carvedilol medication to control their blood pressure level's the initial dose is usually 6.25 mg is taken twice a day which is consistent with the starting dose for treating hypertension. The dosage may be adjusted based on how the individual responds to the treatment and their blood pressure readings gradually increasing to a maximum of 25 mg taken daily for management.
In situations higher doses might be required; however careful monitoring is important to prevent lowering of blood pressure or decreased heart rate. Carvedilols' unique ability to act on both beta and alpha receptors makes them highly effective in achieving desired blood pressure targets, with doses.
Carvedilol Max Dose
The highest suggested amount of carvedilol can differ depending on the ailment being addressed. The maximum dosage, for hypertension is commonly set at 50 mg per day in two doses. When dealing with heart failure a lower maximum dose is usually observed at 25 mg twice daily. Going beyond these limits is uncommon. Usually reserved for situations where specialists are overseeing the treatment process since elevated doses heighten the likelihood of experiencing effects, like lightheadedness, tiredness and low blood pressure.
Carvedilol Dosage for Anxiety
While it's not a treatment, for anxiety on its own carvedilol might be considered in situations where anxiety noticeably affects heart rate or blood pressure. The typical dosage for anxiety tends to be cautious typically falling within the range of 3.125 mg to 6.25 mg once or twice a day. This modest amount delivers beta-blocking benefits to ease symptoms without affecting blood pressure or inducing tiredness. Nonetheless, carvedilol is generally reserved for anxiety management in individuals, with accompanying heart conditions.
Carvedilol Dose for Hypertension
To treat hypertension effectively with carvedilol medication regimen typically starts at 6.25 mg daily. May be adjusted based on blood pressure levels, for the best outcomes. Doses can be raised up to 25 mg daily if needed. The specific dosage varies for each patient based on factors like existing health issues and how well they respond to the drug. When adjusting dosage healthcare providers take into account any signs of blood pressure or slow heart rate to find the balance, between controlling blood pressure effectively and minimizing unwanted side effects.
Side Effects of Carvedilol
Dizziness and Lightheadedness
Carvedilol often causes dizziness or feeling light-headed as a side effect when standing up quickly due, to a decrease, in blood pressure known as orthostatic hypotension Patients may feel off balance or may have brief episodes of vertigo especially when starting with the medication This side effect usually lessens as the body gets used to the medicine over time
Fatigue and Lethargy
Patients often mention feeling tired when they use carvedilol medication since it is a beta blocker that lowers heart rate and slows down functions overall leading to fatigue symptoms, in some cases during the stage of treatment. Making changes, to the dosage or when the medicine is taken might help reduce this fatigue and make it easier to go about tasks.
Bradycardia
Carvedilol's effect, on heart rate, can cause bradycardia, it is a condition characterized by a heartbeat rate. Though a decreased heart rate is advantageous in lessening the stress on the heart muscles; low rates can lead to feelings like dizziness and respiratory issues. It is vital to monitor patient's heart rates to avoid bradycardia from becoming a medical concern, especially for individuals, with existing heart rhythm problems.
Hypotension and Fainting
Carvedilol's strong ability to lower blood pressure can occasionally cause hypotension in patients resulting in feelings of dizziness or lightheadedness. In some situations this drop, in blood pressure may lead to episodes of fainting. Particularly when a patient is dehydrated or standing for extended periods. It is recommended that patients take their time when transitioning from sitting or lying down positions and ensure they stay well hydrated to minimize the risk of occurrences.
Carvedilol Side Effects: Weight Gain
Putting on weight could happen as a surprise when taking carvedilol for those dealing with heart failure issues due, to fluid retention linked to beta blockers effects. Being watchful, for indications of swelling in the legs or feet is crucial since fluid buildup may signal complications. At times besides using carvedilol diet pills could be recommended to deal with this side effect.
Carvedilol Side Effects in Elderly
The older population is more vulnerable, to the side effects of carvedilol since they might feel more sensitive to changes in blood pressure and a decrease in heart rate than younger individuals do. Signs like feeling lightheadedness or tiredness and having a heart rate can be more noticeable, among patients which could raise the chances of falling and facing other issues. It is usually advised to make changes in dosage and keep a check for patients to lessen these risks.
Carvedilol Hair Loss
Hair loss is not common, but it is experienced by an individuals who are, on carvedilol medication. When the body's hormonal or metabolic balance is affected by the influence of the drug causing what is known as drug-induced alopecia. Typically reversible once the medication is stopped; however those facing this concern may want to seek advice, from their healthcare provider regarding options or supportive therapies.
Serious Side Effects of Carvistar (Carvedilol)
Signs of Worsening Heart Failure
Carvedilol is commonly prescribed for the treatment of heart failure; however, it may unexpectedly exacerbate symptoms in individuals during the stages of therapy. If experiencing heightened breathlessness or swelling in the limbs along, with weight gain while on carvedilol therapy could suggest a deterioration, in heart failure condition. In situations seeking medical assessment is crucial to potentially modify the medication dosage or explore other treatment options.
Symptoms of Liver Dysfunction
Carvedilol may cause liver issues that are rare but could lead to liver dysfunction in instances. You might experience symptoms, like skin or eyes (jaundice) urine that looks like tea or cola coloration, and discomfort or ache in the upper right abdomen region. These signs could indicate complications with the liver. Regular checks of liver function are recommended for individuals undergoing treatment, with carvedilol drug particularly if they have existing liver problems this helps in the detection of any liver impairments.`
Severe Allergic Reactions (Anaphylaxis)
Carvedilol may trigger responses, in rare cases like anaphylaxis which could lead to symptoms such as facial or throat swelling along with breathing difficulties and severe skin rashes necessitating prompt emergency care attention. Clients who are aware of their allergies or sensitivities should exercise caution. Notify their healthcare provider prior, to commencing Carivstar treatment.
Bronchospasm and Respiratory Complications in Asthma Patients
Carvedilol's broad beta-blocking effects may trigger bronchospasm in individuals, with asthma or respiratory issues which can worsen breathing problems by causing wheeziness or shortness of breath. For individuals with asthma the disadvantages of using carvedilol may outweigh the advantages and doctors often suggest medications, with cardio properties as a better option.
Carvedilol Side Effects: Erectile Dysfunction
Some male patients using carvedilol may experience erectile dysfunction (ED) as a side effect of the medication, due to its effects on blood flow and hormonal balance that can affect erection maintenance capabilities over time This issue could impact one's quality of life and individuals facing ED are encouraged to talk about possible solutions or other treatment options, with their healthcare provider.
Management of Side Effects
Managing side effects effectively is important, for individuals using Carvedilol (Carvedilol). It's essential to strike a balance between reaping the benefits of the medication and minimizing any discomfort that may arise from side effects like dizziness or tiredness which tend to fade as the body gets used to the treatment routine. Practical approaches such as getting up from a seated position and staying well hydrated can help alleviate these symptoms along with adjusting when the medication is taken throughout the day.
For patients encountering issues like bradycardia or low blood pressure while, on Carvedilol treatment may find relief by either reducing the dosage or gradually adjusting it with monitoring from healthcare providers. Regularly communicating with healthcare professionals enables adjustments that can greatly enhance the tolerability of treatment side effects such, as weight gain from retention or hair loss and erectile dysfunction in rare cases.
Making changes and potentially adding diuretics can be beneficial for side effects, like weight gain. Patients experiencing hair loss or erectile dysfunction should discuss options or supportive treatments with their healthcare provider. Effective management and monitoring are crucial to ensure that the benefits of carvedilol outweigh any reactions.
Contraindications for Carvistar (Carvedilol)
Contraindicated in Patients with Asthma or Bronchospastic Conditions
Carvistar should not be used by individuals, with asthma or bronchospastic conditions because of its selective beta-blocking characteristics which can cause bronchoconstriction by blocking beta receptors in the lungs and exacerbating breathing problems for asthma sufferers This could result in complications like bronchospasm or breathing difficulties Patients, with issues are usually encouraged to explore other treatment options that do not jeopardize lung function to ensure safe and efficient care while maintaining respiratory health.
Severe Liver Impairment
Severe liver damage is a reason to avoid using carvedilol because the liver processes this medication in the body. Individuals, with liver problems might have carvedilol in their system which can result in stronger side effects and potential harm. Doctors often suggest liver function tests before starting treatment to check if the liver can handle the medication safely. If the liver isn't functioning enough for processing of drugs, like carvedilol other treatment options that are easier for the liver to handle are recommended instead.
Cardiogenic Shock or Severe Bradycardia
Carvistar should not be used in patients, with shock or severe bradycardia because it can make these conditions worse by slowing down the heart rate and reducing cardiac function even more. The beta-blocking effects of Carvedilol slow down the heart rate which could be risky for those with reduced heart function. In shock when the heart's unable to pump adequate blood to meet the body's demands and adding Carvedilol can make hemodynamic stability worse. Patients with bradycardia or low output states should consider medications that do not have a negative effect, on heart rate.
Known Hypersensitivity to Carvedilol
Individuals who have shown sensitivity, to carvedilol should steer clear of the medication to steer clear of reactions that might occur from skin irritations to severe anaphylactic responses causing swelling and breathing difficulties with potential life-threatening complications included in the mix. For those with known allergies to the drug must inform their healthcare providers to opt for alternative medication options. Keeping an eye by monitoring and understanding patient history plays a crucial role, in preventing negative consequences linked to hypersensitivity conditions.
Warnings and Precautions with Carvistar (Carvedilol)
Caution in Patients with Diabetes (Masking Hypoglycemia Symptoms)
Carvedilol (known as Carvistar) should be used with caution, in individuals with diabetes since it might hide signs of blood sugar levels like rapid heart rate and tremors which are typically seen in such situations. Users with diabetes are encouraged to check their blood sugar levels and watch out for less noticeable symptoms such, as sweating or sudden confusion that could indicate low blood sugar. Collaborating closely with healthcare to make adjustments to diabetes medication can assist in reducing this risk factor.
Risk of Abrupt Withdrawal and Rebound Hypertension
Suddenly stopping Carvistar could result in a rebound effect that spikes blood pressure and heart rate—a condition termed rebound hypertension—which can strain the heart and pose risks of angina or even heart attacks, for individuals, with issues conditions It is advised to slowly decrease carvedilol under medical guidance to prevent these complications Allowing the body to adapt gradually reduces the chances of negative heart-related incidents
Carvedilol Impact on heart failure patients with Renal function
Carvedilol could affect the functioning of the kidneys, in individuals with heart failure. This is because it lowers blood pressure and changes how blood flows in the body; hence it may decrease kidney perfusion. Resulting in kidney issues.It's advisable for patients with existing kidney problems or heart failure to undergo tests to check their kidney function and to keep an eye out for any changes in filtration rates. At times adjustments in medication dosage or extra support, for the kidneys might be required to ensure that the kidneys are functioning well.
Monitoring of Liver Enzymes and Signs of Liver Toxicity
It is recommended to keep an eye, on liver enzyme levels in individuals undergoing treatment with Carvistar since carvedilol has been linked to cases of liver damage. Signs of liver problems like yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice) colored urine and pain in the abdomen should be reported promptly for medical assessment. Regular testing of liver function can help identify signs of toxicity on so that appropriate action can be taken in time. For patients, with liver function conditions it may be worth exploring treatments that are less likely to affect the liver to prevent potential harm to the liver.
Foods to Avoid When Taking Carvedilol
For those using carvedilol it's important to be mindful of factors that can impact its absorption and effectiveness such, as certain types of foods.
- Be cautious, with grapefruit. Grapefruit juice as they could affect how carvedilol is processed in your body which may lead to levels of the medication, in your blood and increase the possibility of experiencing side effects.
- Eating bananas may increase the effects of beta blockers by causing an excess of potassium in your body which could result in hyperglycemia.
- Alcohol can enhance the blood pressure-lowering effects of carvedilol. May result in dizziness or fainting when standing up.
Patients should be advised to talk to their healthcare provider about making changes to their diet that can improve the effectiveness of carvedilol and minimize any effects, from interactions.
Carvedilol Withdrawal Symptoms
When stopping carvedilol medication after long-term use it's advisable to do to prevent possible rebound effects, like a faster heart rate and higher blood pressure as well as a potential return of angina symptoms In serious situations suddenly quitting may lead to a hypertensive crisis or heart-related issues It's best to slowly taper off the dosage, under controlled conditions giving the body time to adjust and reducing the chances of sudden stoppage risks
Switching from Metoprolol to Carvedilol
Switch from metoprolol to carvedilol requires dosage adjustments because these drugs vary in how they target receptors and how long they stay active despite both being beta blockers; while metoprolol mainly affects beta 1 receptors, in the heart (cardio-selective) carvedilol acts on both beta and alpha receptors.
To make this transition smoothly and safely for patients without causing blood pressure or slow heart rate (bradycardia) doctors usually start with a lower dose of carvedilol and monitor its effects closely before making any further adjustments to ensure that the cardiovascular system functions steadily.
Carvedilol and Bananas
Although bananas are usually seen as a food choice due, to their nutrient content such as potassium levels which may interact adversely with carvedilol when consumed excessively by patients taking this medication for various health conditions like heart problems or high blood pressure. Since carvedilol can impact the body's potassium levels by retaining more of it than usual which could result in potassium levels in the bloodstream leading to a condition called hyperkalemia. Where there is too much potassium present in the blood. Therefore patients are generally advised to be mindful of their banana consumption, by keeping it at a level and not to use potassium supplements unless specifically instructed to do so by their healthcare provider who is overseeing their treatment and medical care.
Carvedilol and Alcohol
Drinking alcohol can enhance the blood pressure-lowering impact of carvedilol medication. This leads, to increased feelings of dizziness or lightheadedness and possibly fainting episodes This effect tends to be more noticeable when standing up quickly or changing positions rapidly It is recommended for patients to moderate their alcohol consumption and approach it cautiously at the start of taking carvedilol when the medications ability to lower blood pressure may be more sensitive
Carvedilol and Grapefruit
Consuming grapefruit and grapefruit juice can impact how the body processes carvedilol by interfering with enzymes that handle drug metabolism. This interference could result in levels of carvedilol, in the bloodstream which may heighten the likelihood of experiencing side effects such as drops, in blood pressure and slowed heart rate. To promote levels of carvedilol and minimize the chances of responses it is commonly recommended for individuals to steer clear of grapefruit-related products.
Interactions with Other Medications
Potential Interactions with Calcium Channel Blockers
Carvedilol (Carvistar) has the potential to interact significantly with calcium channel blockers, like verapamil and diltiazem as they work together to affect heart rate and blood pressure levels collectively The use of both types of drugs can lower the functioning of the hearts conduction system which may result in a heart rate or a significant drop in blood pressure when used concurrently Patients who are prescribed both carvedilol and calcium channel blockers need to be monitored and adjustments, to dosages should be done cautiously at the first signs of irregular heartbeats or low blood pressure.
Interaction with Insulin and Oral Hypoglycemics
Carvedilol has the potential to hide signs of blood sugar in individuals which can make managing blood glucose levels more challenging. When combined with insulin or oral hypoglycemic medications; carvedilol might decrease the body's reaction, to blood sugar by dampening warning signals like heart rate. This concealed effect calls for increased awareness in patients; they should regularly check their blood sugar levels. Be alert for more subtle signs of low blood sugar such, as sweating or confusion.
Interactions with Antihypertensive Agents and Risk of Hypotension
When Carvistar is taken alongside medications, for blood pressure like ACE inhibitors or diuretics it can enhance the effects of lowering blood pressure and may result in low blood pressure (hypotension). Patients might experience dizziness, fainting, or orthostatic hypotension if they also use drugs such, as ARBs simultaneously. It is crucial to adjust the dosage and gradually increase it when combining carvedilol with medications to effectively manage hypertension while avoiding excessively low blood pressure levels.
Effects of Carvistar on CYP2D6-Metabolized Drugs
Carvedilol is broken down to some extent by the enzyme CYP 20 D 26; this implies that it might have interactions, with medications that also use this route of metabolism like antidepressants and antipsychotics as well as beta blockers usage along with it may affect the blood concentrations of these drugs either increasing or decreasing their effectiveness; therefore in individuals taking multiple drugs metabolized by CYP2D6 adjustments, to dosages and careful monitoring are advised to prevent unintended effects related to drug processing in the body.
Carvedilol to Metoprolol Succinate Conversion
Transitioning from carvedilol, to metoprolol succinate requires evaluation due to variations, in receptor preferences. How the body processes them differently. Metoprolol succinate mainly targets beta 1 receptors related to the heart while carvedilol affects both alpha and beta receptors influencing heart rate and blood vessel resistance. When switching between these medications it typically begins with a metoprolol dosage. Then adjusts gradually based on how the patient responds to achieve a similar treatment outcome.
Natural Replacement for Carvedilol
For individuals looking for alternatives, to carvedilol medication for heart health support they can explore lifestyle changes and supplements that aid wellness. Adopting modifications like reducing salt intake and increasing potassium levels well as introducing heart-friendly nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids can assist in managing blood pressure effectively. Moreover, natural elements such as extract and magnesium have been recognized for their impact on heart function and may be complementary to traditional treatments, under medical supervision. Nevertheless, it is crucial to seek advice before considering any substitutions as they do not mirror the specific pharmacological effects of carvedilol medication.
Careful Administration of Carvistar (Carvedilol)
Administration in Patients with Renal Impairment
When someone has kidney issues or renal impairment. Needs to take Carvistar medication, like carvedilol with caution because the kidneys affect how the body processes and levels of this drug in the blood. For individuals with kidney problems or reduced kidney function taking carvedilol might build up in the body. Lead to an increased chance of experiencing side effects such as low blood pressure and slow heart rate.
It's recommended to adjust the dosage. Regularly check kidney function parameters when using Carvestar in patients, with compromised kidney function to ensure treatment. If someone has kidney problems or impaired renal function looking into medications that don't heavily involve the kidneys could be an option worth considering for their treatment plan.
Considerations for Patients with Peripheral Vascular Disease
Patients diagnosed with the disease (PVD) need to be careful when taking carvedilol since it could worsen circulation issues by reducing blood flow, to the limbs due to its beta-blocking effect. This may lead to increased discomfort or pain in the extremities. Closely monitoring patients with PVD and making dose adjustments can help maintain treatment effectiveness while minimizing impacts, on peripheral circulation.
Close Monitoring of Heart Failure Patients During Dose Adjustments
Patients, with heart failure need monitoring when starting or changing carvedilol doses to prevent the worsening of their condition. By beginning with a dose and adjusting gradually over time patients hearts can better adjust to the medication. Lower the chances of experiencing more severe heart failure symptoms. It's important to educate patients about recognizing signs of deterioration, like increased difficulty breathing or swelling, and to prompt them to seek help if these symptoms occur.
Risk Management in Patients with Severe Aortic Stenosis
Patients suffering from stenosis need to be cautious when taking carvedilol due, to its effects on blood flow management with potential risks involved in controlling blood pressure levels and cardiac output which may worsen symptoms like chest pain or fainting episodes in such cases; those with this condition should explore alternative treatments that do not heavily impact blood pressure before considering the use of carvedilol under close monitoring, by healthcare professionals specializing in this area.
Administration to Special Populations
Administration to Elderly Patients
When prescribing Carvedilol to patients it's important to take into account age-related changes, in their body functions and metabolism. The kidneys tend to function as people age which can impact how quickly the body eliminates Carvedilol from the system. This may require adjusting the dosage by starting with an amount and gradually increasing it to reduce the risk of side effects. Older adults are often more responsive to Carvedilols effects, in terms of heart rate and blood pressure regulation.
Higher sensitivity could result in heightened reactions, like a heart rate or low blood pressure that require monitoring throughout treatment sessions with carvedilol in elderly patients. Orthostatic hypotension. A sudden decrease in blood pressure when standing up. Is an issue for individuals taking carvedilol. Consistent observation and advice, on slow position changes can lower the chances of falls and feelings of lightheadedness linked with this reaction.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Using carvedilol while pregnant requires an evaluation of the advantages and disadvantages involved in such a decision-making process. Although carvedilol might be essential, for controlling hypertension or heart failure in women its impact on the growth and development of the fetus remains unclear. The choice to utilize carvedilol during pregnancy necessitates a conversation between the expecting mother and her healthcare provider considered the benefits and possible risks to the child. Carvedilol is secreted in breast milk which could potentially pose a threat, to nursing babies. When infants are exposed to carvedilol through breast milk it can lead to symptoms like a decreased heart rate or lower blood pressure.
Nursing mothers should explore treatments with a profile, for infants or monitor the infants cardiovascular status closely if using carvedilol is necessary. In environments nursing considerations involve informing mothers about side effects on the infant such, as sluggishness or feeding difficulties. Interventions, in nursing could also include scheduling follow-up visits to monitor the well-being and growth of babies who have been exposed to carvedilol to promptly detect and address any impacts that may arise.
Administration to Children
Off-Label Use in Pediatric Hypertension
Carvedilol (brand name Carvistar) is typically intended for adults, with hypertension management responsibilities prescribed off-label in children's care situations to tackle high blood pressure issues in a tailored manner for younger patients who may benefit from its dual action properties as a beta and alpha-blocker, in certain scenarios where alternative treatments are ineffective or unsuitable.
Safety Profile and Lack of Extensive Pediatric Studies
The safety characteristics of carvedilol, in children are not as well established as in adults because there are clinical studies and trials involving pediatric patients compared to adults. Current information indicates that carvedilol may work well for controlling blood pressure in children; however the extended-term impacts and complete range of adverse effects in this age group are not entirely known. Doctors proceed with care by weighing the advantages against risks when prescribing carvedilol to children, under specialized monitoring.
Recommended Pediatric Dosing Guidelines
When considering the use of carvedilol, in children's treatment plans. If it's deemed suitable. Doctors usually start with dosages based on the child's weight and health condition. It's common to begin with a dose of 0.05 to 0.1 mg, per kg for children that is given twice a day. This initial dose might be increased gradually while closely watching blood pressure and heart rate to prevent any side effects. Since children can respond differently to medications based on their characteristics and needs; regular check-ups are crucial to adjust dosages and maintain safety throughout the treatment process.
Overdosage of Carvistar (Carvedilol)
Symptoms of Overdose: Bradycardia, Hypotension, Cardiac Arrest
Taking carvedilol could result in serious heart-related issues such, as significant slowing of the heartbeat (bradycardia) and a dangerous drop in blood pressure (hypotension). In instances of an overdose situation with carvedilol can lead to a cardiac arrest episode which is considered an emergency requiring immediate medical attention, by patients or their caregivers if an overdose is suspected.
Carvedilol Overdose Death
Fatalities resulting from an overdose of carvedilol are uncommon. Have been recorded in documented cases where high doses were involved or when prompt medical assistance was not sought timely enough. The likelihood of mortality rises when symptoms such, as bradycardia and hypotension are not properly addressed. Taking action and seeking medical help in the event of an overdose can potentially save lives and emphasize the critical need, for swift intervention.
Immediate Steps in Overdose Management
In the case of detecting an excess of carvedilol ingestion is crucial to act by checking the patient's vital signs and addressing any signs of breathing or heart problems, for stabilization purposes. It is essential to engage emergency services and, in the meantime ensure that the patient's airway remains clear and position them appropriately to avoid any risk of aspiration as a part of supportive measures.
Role of Activated Charcoal and Gastric Lavage
In a setting activated charcoal might be given to bind any leftover carvedilol in the stomach and prevent it from being absorbed into the body. Stomach pumping could also be done if the overdose happened recently. These approaches work best when used after ingesting the drug providing an opportunity to reduce its effects throughout the body.
Supportive Treatments: Atropine, Glucagon, and Intravenous Fluids
Treatment, for an overdose of carvedilol includes interventions.
- To treat bradycardia Atropine is given to help raise the heart rate.
- Glucagon is employed to boost heart muscle strength when beta blocker side effects are strong and do not respond to treatments.
- Intravenous fluids are administered to address blood pressure and assist with circulation in order to stabilize blood pressure levels effectively.
Each of these therapies targets signs of overdose and collaborates to bring back cardiovascular function while averting progression to severe complications.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Proper Storage Conditions for Carvistar Tablets
Store CarviStar tablets, in a place within the temperature range of 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) to keep them potent and effective over time. Taking care to maintain an environment from temperature changes is crucial. Store the medication in its container with the lid tightly closed to shield the tablets from pollutants and uphold their quality over the long haul. By storing CarviStar you can ensure its continued effectiveness and safety for consumption, throughout its lifespan.
Safety Measures for Avoiding Exposure to Heat and Moisture
Exposure to heat and moisture could weaken the stability of Carvistar. Might make it less effective, over time. It's recommended to store the tablets in a place that is not exposed to sunlight and away from heat sources or damp environments like bathrooms, as moisture can quicken the degradation of the components. A cool and dry spot is best suited for keeping the tablets potent and maintaining their benefits.
Guidelines for Safely Discarding Expired or Unused Medication
It's important to dispose of unused Carvistar tablets to avoid accidental ingestion or harming the environment. The recommended approach is to return them to a pharmacy that has a medication take-back program, for compliant disposal. If that's not an option you can mix the tablets with unappealing materials such as coffee grounds or cat litter put them in a plastic bag and throw them in the household trash. It's best to refrain from flushing the medication down the toilet unless advised otherwise as it can cause damage, to water systems. Implementing waste disposal methods can lower the hazards, for others. Safeguard the environment.
Carvistar, Carvedilol FAQ
- How does CARVEDILOL work?
- What is CARVEDILOL?
- What is CARVEDILOL used for?
- What are the serious side effects of CARVEDILOL?
- What foods should be avoided when taking CARVEDILOL?
- Why is CARVEDILOL dosed twice daily?
- What does CARVEDILOL do?
- What are the long-term side effects of CARVEDILOL?
- How much does CARVEDILOL lower blood pressure?
- How long does it take for CARVEDILOL to work?
- What drugs should not be taken with CARVEDILOL?
- What is the most common side effect of CARVEDILOL?
- When to hold CARVEDILOL?
- What are the most common side effects of CARVEDILOL?
- What are the side effects of CARVEDILOL?
- What does CARVEDILOL look like?
- What happens if I miss a dose of CARVEDILOL?
- How long does CARVEDILOL take to work?
- How long does it take CARVEDILOL to work?
- What to avoid when taking CARVEDILOL?
- How long does CARVEDILOL stay in your system?
- What is CARVEDILOL for?
- What should I avoid while taking CARVEDILOL?
- How fast does CARVEDILOL work?
- How long for CARVEDILOL to work?
- What is the main side effect of CARVEDILOL?
- How does CARVEDILOL work?
- How many hours between doses of CARVEDILOL?
- What is a good replacement for CARVEDILOL?
- What is CARVEDILOL used to treat?
- What pain reliever can I take with CARVEDILOL?
- CARVEDILOL how long does it take to work?
- Why take CARVEDILOL and LISINOPRIL together?
- What is a good replacement for CARVEDILOL?
- What does CARVEDILOL do for you?
- How much does CARVEDILOL lower heart rate?
- What to avoid while taking CARVEDILOL?
- What does CARVEDILOL 6.25 mg look like?
- How quickly does CARVEDILOL work?
- What vitamins should you not take with CARVEDILOL?
- CARVEDILOL what is it used for?
- What not to take with CARVEDILOL?
- Foods to eat when taking CARVEDILOL?
- What does CARVEDILOL pill look like?
- What decongestant can I take with CARVEDILOL?
- How much CARVEDILOL is an overdose?
- What is CARVEDILOL prescribed for?
- Why take LOSARTAN and CARVEDILOL together?
- What foods should be avoided when taking CARVEDILOL?
- How to stop taking CARVEDILOL?
- What does a CARVEDILOL pill look like?
- CARVEDILOL how long to work?
- What is CARVEDILOL ER?
- What allergy medicine can I take with CARVEDILOL?
- How do you wean off CARVEDILOL?
- Are CARVEDILOL and METOPROLOL the same?
- Are CARVEDILOL and LISINOPRIL the same?
- Are CARVEDILOL and AMLODIPINE the same?
- Are CARVEDILOL and LOSARTAN the same?
- What are CARVEDILOL tablets used for?
- What are CARVEDILOL side effects?
- Can CARVEDILOL cause bradycardia?
- Can CARVEDILOL cause weight gain?
- Can CARVEDILOL cause anxiety?
- Can CARVEDILOL be taken without food?
- How does CARVEDILOL work?
- Which is better: CARVEDILOL or METOPROLOL?
- Which is better: CARVEDILOL or AMLODIPINE?
- Which is better: CARVEDILOL or LISINOPRIL?
- Which is better: CARVEDILOL or BISOPROLOL?
How does CARVEDILOL work?
What is CARVEDILOL?
Carvedilol is a type of medication known as a beta blocker that also possesses alpha-blocking qualities. It is frequently prescribed for managing blood pressure and heart failure and, for enhancing longevity following a heart attack.
What is CARVEDILOL used for?
Carvedilol is mainly prescribed to manage blood pressure (hypertension) well as, for treating heart failure and enhancing post heart attack survival rates by easing the hearts workload and averting additional harm.
What are the serious side effects of CARVEDILOL?
Carvedilol may cause side effects, like dizziness; fainting; a slow or irregular heartbeat; and signs of heart failure worsening such as swelling; shortness of breath; and unusual weight gain. If you experience any of these symptoms seek medical help promptly.
What foods should be avoided when taking CARVEDILOL?
Its recommended to steer of caffeinated foods and beverages, like coffee and energy drinks when using Carvedilol because they can raise heart rate and blood pressure which might work against the medications purpose.
Why is CARVEDILOL dosed twice daily?
Carvedilol needs to be taken two times a day to keep a presence in the bloodstream so that it can effectively control blood pressure and support heart function all day long.
What does CARVEDILOL do?
Carvedilol lowers the heart rate. Relaxes blood vessels to ease the hearts burden and manage blood pressure effectively while also enhancing heart function in cases of heart failure and lowering the chances of future cardiac issues.
What are the long-term side effects of CARVEDILOL?
Long term usage of Carvedilol may result in symptoms, like tiredness and dizziness as weight gain and occasional deterioration of heart function; it is advisable to have regular check ups, with a healthcare professional to address any lasting impacts.
How much does CARVEDILOL lower blood pressure?
Carvedilol has the potential to effectively lower blood pressure; however the degree of reduction may vary depending on reactions dosage levels used and whether it is administered as a treatment or, in combination, with other medications.
How long does it take for CARVEDILOL to work?
It typically takes 1 to 6 hours for Carvedilol to start showing its effects after the dose administration; however it may require a few weeks of regular usage to observe its full impact, on lowering blood pressure or alleviating symptoms of heart failure.
What drugs should not be taken with CARVEDILOL?
Certain medications, like calcium channel blockers (for example VERAPAMIL) antiarrhythmic drugs and specific antidepressants should be used with caution. Avoided when taking Carvedilol due, to interactions.
What is the most common side effect of CARVEDILOL?
Dizziness is a side effect of Carvedilol. Is often experienced when standing up quickly because of its ability to lower blood pressure.
When to hold CARVEDILOL?
It is advisable to stop taking Carvedilol if the heart rate is bradycardia) blood pressure is low. If experiencing severe dizziness or fainting symptoms. Consult a healthcare before adjusting the dosage in any way.
What are the most common side effects of CARVEDILOL?
The typical adverse reactions of Carvedilol consist of feeling lightheadedness or dizzy spells and tiredness or fatigue; some individuals may also experience blood pressure and occasional gastrointestinal discomfort.
What are the side effects of CARVEDILOL?
Side effects associated with Carvedilol may encompass feelings of lightheadedness and exhaustion as potential instances of lowered blood pressure or weight gain, along with experiences of breathlessness and minor digestive complications to be aware of. In cases where serious side effects arise from the use of Carvedilol could involve irregular heart rhythms or a deterioration, in heart function.
What does CARVEDILOL look like?
Carvedilol tablets usually have oval shapes. Come in different colors depending on the dosage strength they contain – such, as white or blue or yellow hues – and often feature dosage details or a distinct imprint, for identification purposes.
What happens if I miss a dose of CARVEDILOL?
If you forget to take your Carvedilol dose at the time. It's not yet time, for your next dose of medication yet skip the missed dose and continue with your usual dosing schedule without doubling up on doses to compensate for the one you missed.
How long does CARVEDILOL take to work?
It typically takes 1 to 1 to 12 hours for Carvedilol to begin lowering blood pressure however it may require weeks of regular usage, for the full benefits, in treating heart failure to be evident.
How long does it take CARVEDILOL to work?
Carvedilol typically starts to take effect within 1 to 3 hours, for lowering blood pressure levels; however it may take a weeks before its positive effects, on the heart are noticeable.
What to avoid when taking CARVEDILOL?
It's best to steer clear of alcohol and caffeine when taking Carvedilol since they could mess with its ability to regulate blood pressure effectively. Also make sure not to make movements that could lead to dizziness.
How long does CARVEDILOL stay in your system?
Carvedilol has a life of around 6 to 10 hours which implies it can remain in the body for a days duration.Due, to dosages the impact of the medication on blood pressure and heart rate may persist for a period beyond its presence, in the system.
What is CARVEDILOL for?
CARVEDILOL is prescribed for managing hypertension and heart failure while also aiding in enhancing heart attack survival rates by easing the hearts burden and regulating blood pressure levels.
What should I avoid while taking CARVEDILOL?
Refrain from consuming alcohol or caffeine and engaging in activities that demand vigilance until you understand the impact of CARVEDILOL, on your body as they could exacerbate feelings of dizziness or drowsiness.
How fast does CARVEDILOL work?
Usually CARVEDILOL takes 1, to 1 hours to begin reducing blood pressure. It may take a few weeks to see the full benefits, for heart conditions.
How long for CARVEDILOL to work?
The impact of Carvedilol, on blood pressure starts showing up within a couple of hours; however; it may take a weeks of usage to see enhancements, in heart function.
What is the main side effect of CARVEDILOL?
The primary drawback of CARVEDILOL is feeling lightheadedness when getting up fast because of its tendency to lower blood pressure.
How does CARVEDILOL work?
CARVEDILOL functions, by inhibiting beta and alpha receptors in the heart and blood vessels to heart rate and decrease blood pressure It also reduces the workload on the heart This makes it beneficial, for treating heart failure and hypertension
How many hours between doses of CARVEDILOL?
CARVEDILOL is typically ingested every 12 hours or twice daily to ensure a presence of the medication, in the bloodstream.
What is a good replacement for CARVEDILOL?
Consider options besides CARVEDILOL such, as METOPROLOL or BISOPROLOL; however; the appropriate substitute should be decided by a healthcare provider according to the specific requirements of each individual.
What is CARVEDILOL used to treat?
What pain reliever can I take with CARVEDILOL?
It's usually safe to combine ACETAMINOPHEN with CARVEDILOL for pain relief; however it's important to be cautious when using nonsteroidal inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) as they could potentially affect blood pressure regulation.
CARVEDILOL how long does it take to work?
CARVEDILOL usually starts to take effect in 1 to 20 hours for controlling blood pressure and shows its benefits, in treating heart conditions after a weeks.
Why take CARVEDILOL and LISINOPRIL together?
CARVEDILOL and LISINOPRIl are sometimes prescribed in combination as they operate through mechanisms to effectively decrease blood pressure and enhance heart function which's particularly beneficial, in cases of heart failure.
What is a good replacement for CARVEDILOL?
Other options, to CARVEDILOL consist of beta blockers such, as METOPROLOL or ATENOLOL; however switching should be overseen by a professional.
What does CARVEDILOL do for you?
Carvedilol is known for its ability to decrease blood pressure levels and heart rate while also easing the strain, on the heart muscle itself—a treatment for conditions like hypertension and heart failure well, as aiding in post heart attack recovery to enhance survival rates.
How much does CARVEDILOL lower heart rate?
Carvedilol usually decreases the heart rate by around 10 to 20 beats, per minute; however the specific decrease can differ based on how each person reacts and the dosage prescribed.
What to avoid while taking CARVEDILOL?
Refrain from consuming alcohol and caffeine or making posture adjustments when using CARVEDILOL to prevent worsening side effects such, as dizziness and potential interference, with its efficacy.
What does CARVEDILOL 6.25 mg look like?
CARVEDILOL 6 POINT 25 milligrams tablets are typically circular, in shape. Have a coloration, with unique markings that vary based upon the company producing them.
How quickly does CARVEDILOL work?
CARVEDILOL generally begins to take effect in, around 1 to 1½ hours to lower blood pressure; however; it may take a couple of weeks to experience its benefits, for heart failure treatment.
What vitamins should you not take with CARVEDILOL?
It's best to steer of consuming amounts of vitamins such, as vitamin E or K while taking CARVEDILOL since they could impact blood pressure regulation and the efficacy of the medication.Additionally you may want to seek advice from a healthcare professional, for guidance on this matter.
CARVEDILOL what is it used for?
Carvedilol is prescribed for managing blood pressure and heart failure while also aiding in enhancing survival heart attack by lessening the hearts burden and regulating blood pressure.
What not to take with CARVEDILOL?
It's important to steer of medications, like calcium channel blockers and specific antidepressants when taking CARVEDILOL without consulting a healthcare professional since they could have interactions.
Foods to eat when taking CARVEDILOL?
Eating a variety of fruits and vegetables along, with grains and lean proteins can help keep your heart healthy when using CARVEDILOL medication – steer clear of foods high, in sodium.
What does CARVEDILOL pill look like?
CARVEDILOL tablets come in shapes and colors depending upon the dosage and the company that manufactures them; they can be round or oval, in shape. Are typically white or blue, with dosage markings imprinted.
What decongestant can I take with CARVEDILOL?
Its recommended to steer of decongestants that have pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine when taking CARVEDILOL since they could potentially raise your blood pressure levels.Think about discussing with your doctor for options.
How much CARVEDILOL is an overdose?
Taking CARVEDILOL can lead to an overdose when the dosage exceeds the prescribed amount by a significant margin. Signs of an overdose may comprise dizziness, a heart rate and breathing problems; if you suspect an overdose it is crucial to seek urgent medical assistance promptly.
What is CARVEDILOL prescribed for?
Carvedilol is often recommended to control blood pressure and treat heart failure while also lowering the risk of death after a heart attack occurs.
Why take LOSARTAN and CARVEDILOL together?
LOSARTAN and CARVEDILOL are often given in combination as they target pathways to help lower blood pressure and alleviate the hearts workload—an approach, for managing heart failure.
What foods should be avoided when taking CARVEDILOL?
Try to steer clear of foods that're rich, in salt and caffeine or alcohol while on CARVEDILOL since they might hinder its ability to lower blood pressure effectively.
How to stop taking CARVEDILOL?
Before discontinuing CARVEDILOL medication usage and, without supervision is not recommended as it may lead to withdrawal symptoms like a rise, in heart rate or blood pressure.
What does a CARVEDILOL pill look like?
The appearance of CARVEDILOL pills can differ depending upon the manufacturer but they are usually round or oval, in shape and come in colors like white to blue or yellow; sometimes they have markings, for dosage identification.
CARVEDILOL how long to work?
What is CARVEDILOL ER?
CARVEDILOL ER (Extended Release) a version of CARVEDILOL created to release the medicine over a period of time, for daily intake to ensure steady blood levels.
What allergy medicine can I take with CARVEDILOL?
It's usually safe to take allergy meds, like LORTADINE or CETIRIZINE, with CARVEDILOL but steer clear of decongestants containing pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine as they might increase blood pressure levels. Make sure to check with a healthcare provider before mixing medications.
How do you wean off CARVEDILOL?
When stopping CARVEDILOL medication under the guidance of your healthcare providers advice follow a reduction, in dosage to avoid experiencing withdrawal symptoms, like heart rate or blood pressure levels as directed by your doctor.
Are CARVEDILOL and METOPROLOL the same?
CARVEDILOL and METOPROLOL are both beta blockers, with characteristics; CARVEDILOL acts by blocking alpha receptors well as beta receptors, for added blood vessel relaxation effects; whereas METOPROLOL primarily targets beta receptors.
Are CARVEDILOL and LISINOPRIL the same?
CARVEDILOL and LISINOPRIl are not the medicines—CARVEDILOL acts as a beta blocker while LISINOPRIl functions, as an ACE inhibitor. Doctors might recommend both drugs concurrently to harness their combined benefits, in managing blood pressure and heart failure conditions.
Are CARVEDILOL and AMLODIPINE the same?
CARVEDILOL belongs to the beta blocker family of medications. Amlodipine is classified as a calcium channel blocker drug. Both are used to reduce blood pressure; however they function through mechanisms. Are occasionally prescribed in combination, for certain conditions.
Are CARVEDILOL and LOSARTAN the same?
CARVEDILOL and LOSARTAN are not the kind of medicines – CARVEDILOL falls under beta blockers and LOSARTAN is categorized as an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB). They are commonly prescribed in combination to enhance the management of blood pressure efficiently.
What are CARVEDILOL tablets used for?
CARVEDILOL tablets are prescribed for managing blood pressure and heart failure while also aiding in enhancing survival heart attack by lessening the hearts strain and regulating blood pressure levels.
What are CARVEDILOL side effects?
The typical adverse effects of CARVEDILOL consist of feelings of lightheadedness and tiredness, along with issues, like blood pressure and weight increase; in rare instances bradycardia might also occur as a side effect to be mindful of.Severe repercussions could encompass exacerbation of symptoms related to heart failure and irregular heart rhythms well.
Can CARVEDILOL cause bradycardia?
CARVEDILOL has the potential to lead to bradycardia (a decrease, in heart rate) as it functions by slowing down the heart to alleviate blood pressure and lessen the hearts workload impact on it. Remember to keep a check on your pulse and seek advice, from your healthcare provider if it drops excessively low.
Can CARVEDILOL cause weight gain?
Weight gain may happen as a side effect of CARVEDILOL, among individuals diagnosed with heart failure conditions If you notice any sudden increase in weight without explanation consult your healthcare professional, for guidance and support.
Can CARVEDILOL cause anxiety?
Occasionally but not often individuals might encounter feelings of nervousness when taking CARVEDILOL as a medication side effect. Be sure to inform your healthcare provider if you notice any shifts, in your mood.
Can CARVEDILOL be taken without food?
Make sure to take CARVEDILOL with a meal as it helps with absorption and lowers the chances of experiencing side effects such, as feeling lightheaded or having blood pressure.
How does CARVEDILOL work?
CARVEDILOL functions, by obstructing beta and alpha receptors to decrease heart rate and relax blood vessels and ultimately lower blood pressure; hence it is useful, in managing blood pressure and heart failure.
Which is better: CARVEDILOL or METOPROLOL?
CARVEDILOL might be an option, for patients requiring blood vessel relaxation because of its alpha blocking properties; on the other hand METOPROLOL could be preferred for its more specific beta blocking effects.The decision varies based on an individuals health requirements. Should be directed by a healthcare professional.
Which is better: CARVEDILOL or AMLODIPINE?
CARVEDILOL and AMLODIPINE work differently in the body; CARVEDILOL acts as a beta blocker while AMLODIPINE functions, as a calcium channel blocker each tailored to suit the patients health requirements and offering advantages based on individual circumstances.
Which is better: CARVEDILOL or LISINOPRIL?
CARVEDILOL and LISINOPRIL are commonly prescribed together of being directly compared because CARVEDILOL is a beta blocker while LISINOPRIl is an ACE inhibitor; they work together to complement each others effects, in controlling blood pressure and heart conditions.
Which is better: CARVEDILOL or BISOPROLOL?
CARVEDILOL and BISOPROLOL are both types of beta blockers; however CARVEDILOL not blocks receptors but also alpha receptors which helps in lowering blood pressure further compared to BISOPROLOL alone. Depending on the individuals health condition and specific treatment requirements BISOPROLOL might be favored for its selectivity, towards receptors.