Cefotaxime
I. Introduction
Cefotaxime, a figure in the realm of antibiotics, has undergone significant advancements since its inception. As a member of the cephalosporin family, its distinctive physical and chemical characteristics have made it an invaluable asset in the fight against infections.
History and Development of Cefotaxime
Cefotaxime originated in the 1970s when the medical community urgently required powerful antibiotics to combat bacteria that were becoming resistant. Once it was synthesized, it quickly became a leading choice for clinicians, offering them a defense against these pathogens.
Classification and Basic Properties of the Drug
Belonging to the third-generation cephalosporins group, Cefotaxime is known for its range of effectiveness. It has a beta-lactam ring that helps it stay unaffected by beta-lactamase enzymes, giving it an advantage over antibiotics.
II. Uses
Cefotaxime is widely known for its effectiveness in treating critical conditions making it highly regarded in the medical field.
Primary Medical Conditions it Treats
Cefotaxime is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic that is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including septicemia, meningitis, respiratory tract infections, and urinary tract infections 123.
Here are the HTML links to the references:
1: Cefotaxime: Dosage, Mechanism/Onset of Action, Half-Life - Medicine.com 2: Cefotaxime: View Uses, Side Effects and Medicines | 1mg 3: Cephalosporins | Treatment summaries | BNF | NICE
Spectrum of Bacterial Coverage
Its wide range of effectiveness primarily focuses on combating Gram bacteria but also exhibits notable effectiveness against specific Gram-positive pathogens. This dual mechanism of action makes it a favored option in treatment approaches.
III. How it Works
To truly grasp the capabilities of Cefotaxime, it is essential to explore how it operates within the body.
Mechanism of Action in the Body
When Cefotaxime is given, it attaches to the penicillin-binding proteins found on the wall of cells. This attachment hampers the cell wall synthesis, ultimately causing the bacteria to die.
Bacterial Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibition
Disrupting the cell wall is a clever tactic that renders the bacterial cell defenseless and unstable, ultimately causing it to break apart and be destroyed.
IV. Dosage and Administration
Administering Cefotaxime should be done carefully, considering the patient's medical situation.
General Guidelines for Adult Patients
Usually, for grown-ups the recommended dose is generally between 1 to 2 grams, given either through an IV or an injection, into the muscle every 6 to 8 hours. However, the frequency and dosage may vary depending on how severe the infection is.
Adjustments Based on Specific Medical Conditions
Patients who have problems with their kidneys may need to have their doses adjusted. It is crucial to check the levels of certain substances in the blood of these individuals to prevent any possible harmful effects.
V. Composition
Cefotaxime possesses its qualities due to its inherent composition.
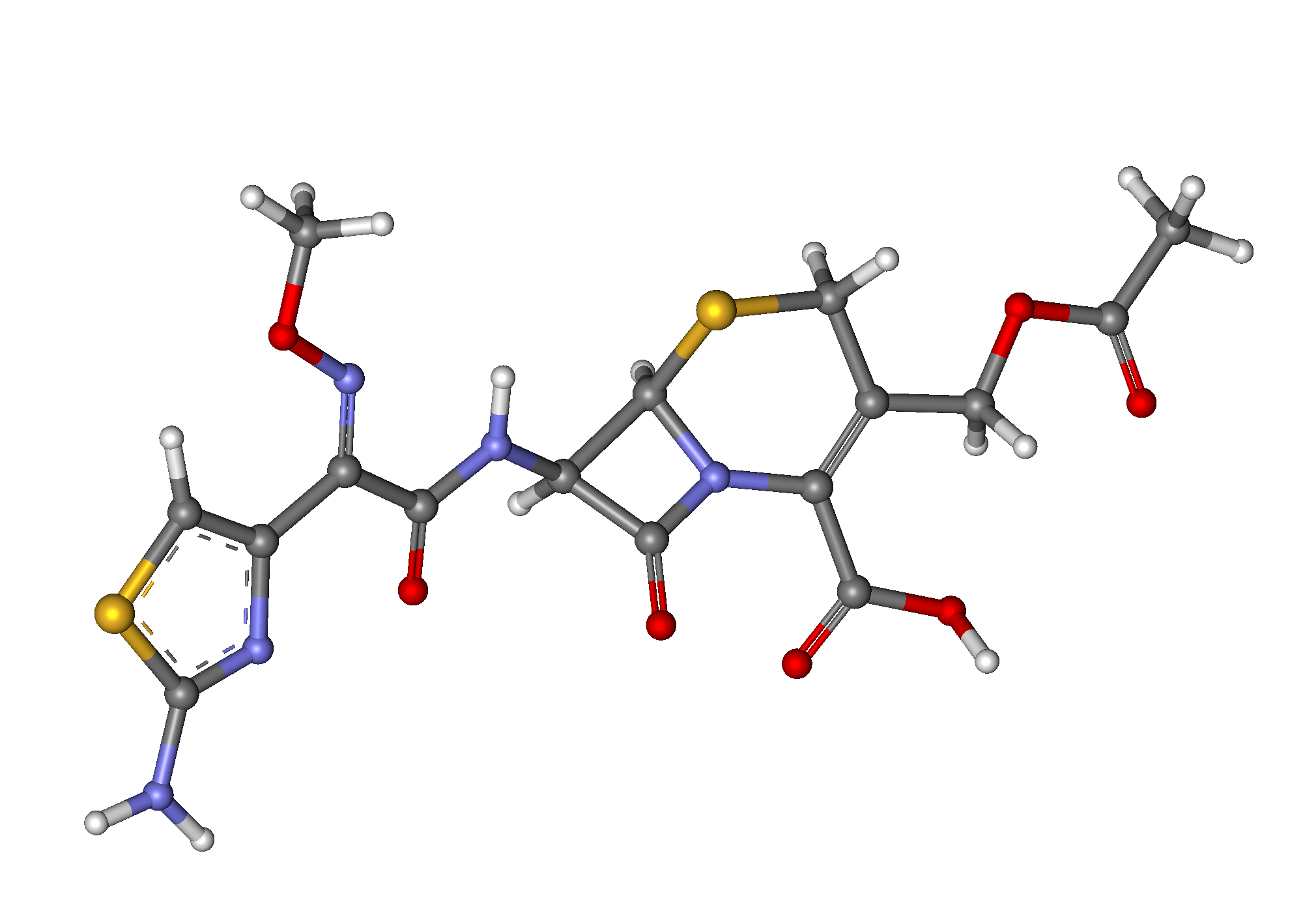
Active and Inactive Ingredients
The main ingredient in this product is Cefotaxime sodium. Additionally, there are inactive ingredients, such as sodium carbonate, that help stabilize the pH when it is mixed.
Formulations Available in the Market
Cefotaxime is mainly sold as a powder that must be mixed with a liquid before being injected into the body through IV) or intramuscular (IM) administration. Many known pharmaceutical companies have versions of this vital medication, guaranteeing that healthcare professionals always have reliable access to it.
VI. Off-Label Use
Sometimes doctors may use Cefotaxime for conditions beyond what it's officially approved for based on their practical experience and research findings.
Conditions not Officially Approved but Treated with Cefotaxime
Cefotaxime is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic that is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including septicemia, meningitis, respiratory tract infections, and urinary tract infections 1. Although Cefotaxime has not been officially approved for treating diseases other than the ones mentioned above, research studies have investigated its potential in treating Lyme disease and certain types of uncommon pneumonia 23.
Here are the HTML links to the references:
1: Cefotaxime: Dosage, Mechanism/Onset of Action, Half-Life - Medicine.com 2: Lyme Co-Infections: What Is Mycoplasma Pneumoniae? 3: Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Lyme Disease
Research Supporting Off-label Uses
Cefotaxime has been widely studied in off-label conditions, with numerous research papers, peer-reviewed journals, and clinical trials supporting its effectiveness. These findings highlight the versatility of Cefotaxime in treating medical conditions.
VII. Side Effects
Similar to any medication, Cefotaxime comes with a range of potential side effects varying from mild to more serious, in nature.
a. Common Side Effects
Digestive issues can show up as feelings of nausea the urge to vomit or experiencing diarrhea. If one reacts they may notice symptoms, like hives, itching, or swelling. Skin rashes can appear as either irritated patches or pus-filled eruptions.
b. Less Common and Severe Side Effects
Commonly, but still worth mentioning, a few people may encounter specific effects such as Neurological complications, including seizures or tremors. Concerns: Symptoms may vary from palpitations to more severe cardiac irregularities.
VIII. Interaction
To fully unleash the power of Cefotaxime, it is essential to be cautious about how it interacts with medications.

Drugs that Interfere with Cefotaxime's Efficacy
Some types of diuretics like furosemide or certain drugs that can harm the kidneys, such as aminoglycosides, have the potential to affect how Cefotaxime is excreted by the kidneys and its effectiveness.
Recommendations when using Concomitant Drugs
When following a treatment plan that involves these medications, it is advisable to undergo kidney function tests and potentially make necessary adjustments to the dosage of Cefotaxime.
IX. Warning
Given the advantages, it is crucial to proceed carefully and be aware of the possible drawbacks connected to Cefotaxime.
Potential Risks of Long-term Use
Extended use of Cefotaxime may increase the risk of individuals developing infections or superinfections caused by bacteria that are resistant to Cefotaxime's effects.
Situations where Heightened Caution is Required
Patients with a record of gastrointestinal disorders, particularly colitis, should receive Cefotaxime with caution while closely monitoring for any indications of bowel disturbances.
X. Contraindication
Conditions where Cefotaxime should not be used
Ensuring that Cefotaxime is suitable for the patient's medical situation is crucial. There are circumstances where giving Cefotaxime may not be recommended.
Allergies and Hypersensitivity Reactions
Individuals who show a reaction to antibiotics in the cephalosporin class or have experienced severe hypersensitivity reactions to similar medications should avoid using Cefotaxime.
XI. Careful Administration
Considerations for Patients with Liver or Kidney Problems
The liver and kidneys have a role in how Cefotaxime is broken down and eliminated from the body. Therefore, for patients with liver or kidney problems, it may be necessary to adjust the dosage or extend the time between doses.
Monitoring Requirements for Certain Patients
For patients who have medical conditions or are taking a combination of medications, it is essential to regularly check their kidney and liver functions and blood counts. This monitoring is crucial for their care.
XII. Important Precautions
When to Avoid Alcohol or Certain Foods
Although Cefotaxime usually has no known interactions with alcohol, it is advisable to refrain from alcohol consumption while undergoing treatment. This precaution helps ensure that the medication works effectively and minimizes the risk of any reactions.
Activities to be Cautious of While on the Drug
Patients taking Cefotaxime should be cautious when driving, operating machinery, or engaging in tasks that demand constant focus. This is particularly important if they experience feelings of dizziness or fatigue as a result of the medication.
Administration to Specific Populations
a. Administration to Elderly
Updated Dosage Recommendations: Due to age-related decline in kidney function, the elderly may require longer or longer intervals between doses. Monitoring for Side Effects Related to Aging: Older adults may be more vulnerable to drug-induced kidney and liver damage. Careful monitoring is necessary.
b. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Safety Considerations During Pregnancy: Cefotaxime should only be given to women if the benefits outweigh the potential risks to the unborn baby. Although no harmful effects on development have been reported, it is still important to exercise caution. Transfer to Breast Milk and Potential Risks to the Baby: While Cefotaxime can pass into breast milk, the amount is minimal. However, nursing mothers should decide to stop breastfeeding or avoid taking Cefotaxime, considering how necessary the medication is for their well-being.
c. Administration to Children
Pediatric Dosage Recommendations; Children and newborns frequently need to modify their dosage according to their weight and age. Factors to Keep in Mind and Potential Side Effects in Children: Pediatric patients may encounter side effects, such as increased irritability or cryogenic reactions, necessitating careful monitoring.
XIII. Overdosage
Symptoms of Cefotaxime Overdose
An overdose can lead to neurological effects like seizures, encephalopathy, or even a coma. This is particularly true for patients who have insufficiencies.
Immediate Actions and Treatments
In the event of an overdose, it is crucial to seek medical help. The primary focus of treatment is to support maintaining breathing, circulation, and airway function. Hemodialysis can be used to speed up the elimination of Cefotaxime in cases of overdose.
XIV. Storage
Proper Storage Temperature and Conditions
Cefotaxime should be stored at room temperature away from light and moisture. It's best to keep it in its packaging until you're ready to use it again.
Shelf-life and Expiry Considerations
Make sure to check the expiration date mentioned on the package. After reconstitution, it is essential to use Cefotaxime solutions. Any leftover solution should be discarded within 24 hours if stored at room temperature.
XV. Handling Precautions
Safe Handling and Disposal
To reduce the chances of exposure, it is essential always to follow aseptic procedures when preparing and administering Cefotaxime. Regulations for pharmaceutical waste management should appropriately dispose of any expired or unused solutions.
Precautions to Prevent Contamination
Keep the vials or containers sealed until you're ready to use them. Once you open them, use the solution promptly to prevent contamination. Before administering the solution, always visually check for any particles or changes in color.