Desogestrel/ Ethinyl Estradiol
- Introduction
- Composition and Formulation
- Mechanism of Action: How Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol Works
- Primary Uses and Benefits
- Off-Label Uses and Alternative Applications
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
- Drug Interactions and Contraindications
- Storage, Handling, and Safety Measures
- Warnings, Precautions, and Careful Administration
- Special Considerations for Unique Populations
- Overdose and Emergency Management
- Handling Precautions in Clinical and Home Settings
Introduction
Overview of Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol
Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol represents an advanced dual-hormone formulation acclaimed for its robust contraceptive efficacy and intricate endocrine modulation. This composite preparation amalgamates a potent progestin with a synthetic estrogen to orchestrate a precise reproductive equilibrium.
- Exhibits a meticulously engineered pharmacological profile.
- Ensures high bioavailability with a refined absorption pattern.
- Offers a synergistic balance, underpinning its therapeutic reliability.
A judicious blend of active agents ensures optimal reproductive suppression and menstrual regulation.
Historical Development and Medical Significance
The genesis of Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol is steeped in scientific innovation and iterative clinical enhancements. Initially developed to rectify the limitations of earlier contraceptive methods, it has evolved through rigorous empirical trials and methodical refinements.
- Introduced in the late 20th century amidst a paradigm shift in hormonal therapies.
- Pioneered to mitigate adverse effects and elevate patient compliance.
- Instrumental in transforming contraceptive practices worldwide.
Its historical journey is emblematic of progressive breakthroughs in gynecological therapeutics.
Composition and Formulation
Chemical Structure and Active Ingredients
At the molecular echelon, the formulation is distinguished by its intricately designed chemical architecture. The active constituents include:
- Desogestrel: A highly potent progestin derivative that exerts anti-gonadotropic effects.
- Ethinyl Estradiol: A synthetic estrogen known for its augmented stability and bioactivity.
This meticulous synthesis ensures a harmonious interplay between the components, fostering superior clinical outcomes.
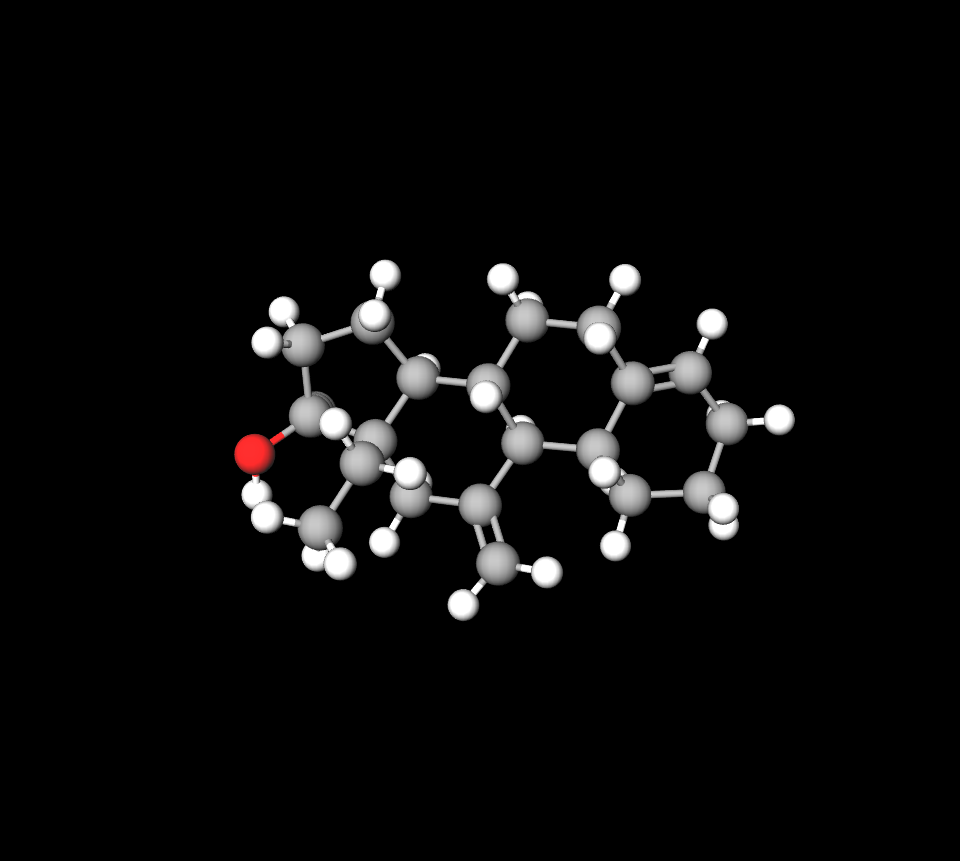
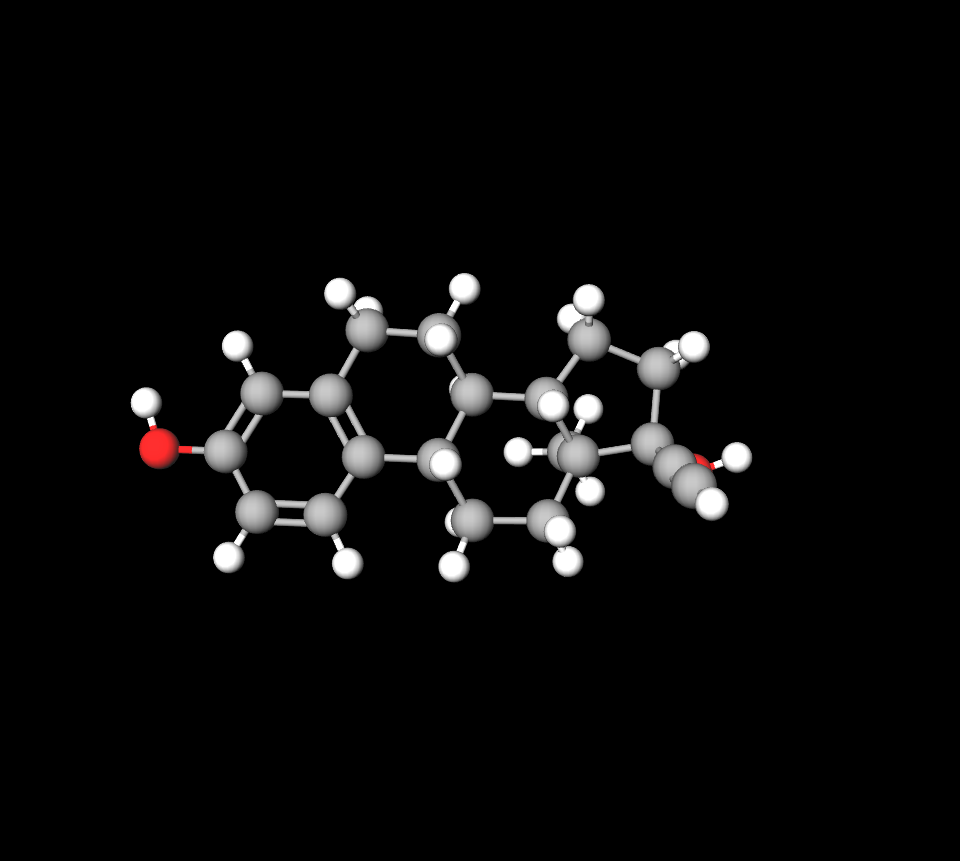
Inactive Components and Excipients
Complementary to the active ingredients, a constellation of inactive components fortifies the formulation. These excipients are selected to:
- Guarantee uniform tablet integrity and consistent dosage distribution.
- Enhance the dissolution rate and bioavailability.
- Preserve the formulation against physical and chemical degradation.
The inclusion of such inert substances is pivotal in maintaining the overall therapeutic efficacy.
Pharmaceutical Formulations and Dosage Forms
Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol is dispensed in multiple pharmaceutical forms, each tailored to optimize delivery and patient adherence. Key dosage forms encompass:
- Oral Tablets: Engineered for daily ingestion with precise dosing intervals.
- Transdermal Patches: Offering alternative administration routes for enhanced convenience.
- Investigational Forms: Under continuous research to explore novel delivery systems.
These diverse formulations underscore the compound's adaptability across clinical scenarios.
Mechanism of Action: How Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol Works
Hormonal Regulation and Contraceptive Effects
The principal mechanism involves a sophisticated hormonal regulation that precludes ovulation and induces an inhospitable endometrial environment.
- Suppresses the luteinizing hormone surge, thereby inhibiting follicular maturation.
- Enhances cervical mucus viscosity, impeding sperm penetration.
- Modulates endometrial receptivity to thwart implantation.
This multifaceted approach culminates in a formidable contraceptive effect.

Impact on Ovulation and Menstrual Cycle Control
The formulation exerts decisive control over the ovarian cycle. It achieves:
- Interruption of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis.
- Regularization of menstrual intervals and mitigation of breakthrough bleeding.
- Preservation of cyclical hormonal equilibrium.
Both succinct and expansive in its regulatory capabilities, the compound affords predictability in menstrual management.
Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Considerations
Pharmacokinetic studies reveal a rapid onset of action with a sustained plasma concentration, while pharmacodynamic attributes include:
- Consistent metabolic pathways with minimal interindividual variability.
- Steady-state kinetics ensuring enduring contraceptive efficacy.
- Robust receptor binding affinities that underpin its clinical potency.
These dimensions collectively enhance the compound's therapeutic index.
Primary Uses and Benefits
Oral Contraceptive Effectiveness and Pregnancy Prevention
Primarily, Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol is revered for its exceptional role in pregnancy prevention. A synthesis of both brevity and elaboration:
- Reliable inhibition of ovulation.
- Substantial reduction in pregnancy risk when administered correctly.
- Validated through extensive clinical trials demonstrating superior efficacy.
The dual-hormone mechanism forms an impregnable barrier to conception.

Regulation of Menstrual Cycles and Alleviation of Dysmenorrhea
The formulation facilitates regular menstrual cycles while alleviating the severity of dysmenorrhea. It offers:
- Mitigation of heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Reduction in the intensity of menstrual cramps.
- Enhanced predictability of menstrual intervals.
A nuanced approach that affords both symptomatic relief and cycle regularity.
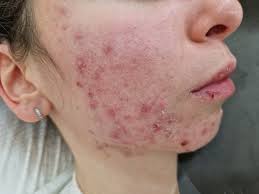
Management of Hormonal Imbalances and Acne
- Normalization of androgen levels.
- Reduction in sebaceous gland hyperactivity.
- Improvement in overall dermal clarity and texture.
Its ancillary benefits contribute substantially to holistic dermatological care.
Role in Treating Menstrual Disorders
Beyond contraception, the compound addresses an array of menstrual disorders.
- Amelioration of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) symptoms.
- Control over irregular and heavy menstrual cycles.
- Stabilization of cyclical hormonal variations.
Such versatility renders it indispensable in modern gynecological management.

Off-Label Uses and Alternative Applications
Hormonal Therapy Beyond Contraception
Off-label Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol extends its utility into broader hormonal therapy applications. It is utilized in:
- Adjunctive treatments in hormone replacement therapy.
- Regulation of endocrine dysfunctions beyond reproductive health.
- Support in transgender hormone regimens under specialized protocols.
This versatility is emblematic of its far-reaching clinical potential.
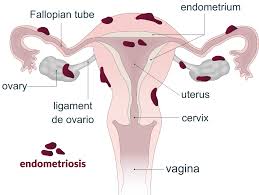
Treatment Options for Endometriosis and Related Pain
Emerging clinical evidence advocates its off-label use in alleviating endometriosis-related discomfort. It functions by:
- Inhibiting ectopic endometrial tissue proliferation.
- Attenuating chronic pelvic pain and inflammatory responses.
- Enhancing quality of life through symptomatic relief.
Its application in this domain exemplifies innovative therapeutic adaptation.
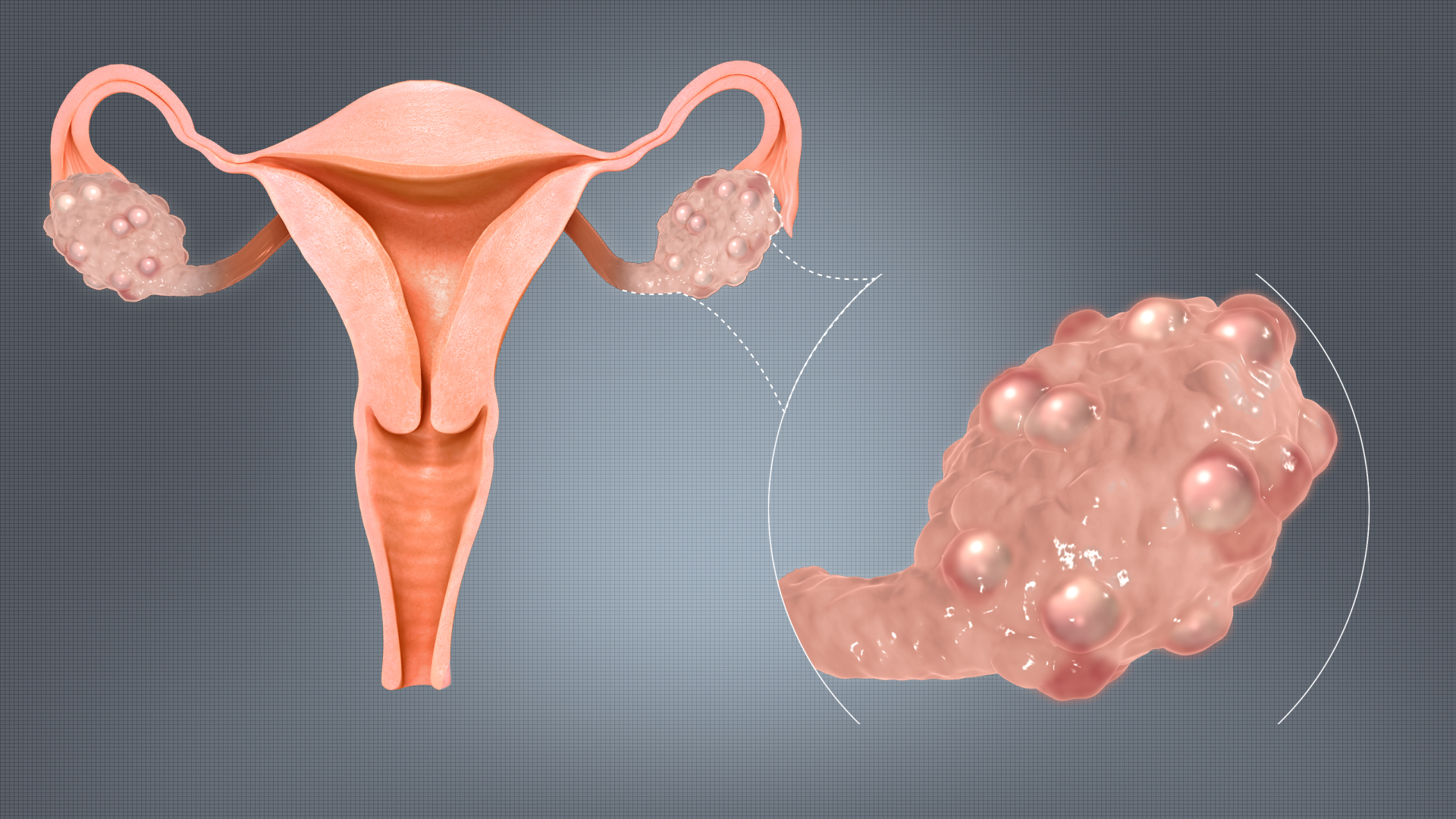
Potential Use in Managing Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Preliminary data indicates a promising role in the management of PCOS. Its benefits include:
- Regularization of menstrual cycles.
- Reduction in hyperandrogenic symptoms.
- Improvement in metabolic indices associated with the syndrome.
This potential application warrants further clinical scrutiny.
Other Reproductive Health Applications
Additional off-label applications span various reproductive health challenges. Considerations involve:
- Management of abnormal uterine bleeding.
- Adjunct therapy in cases of endometrial hyperplasia.
- Restoration of hormonal equilibrium in complex gynecological conditions.
Such alternative uses broaden its clinical spectrum significantly.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Standard Dosing Regimens and Treatment Cycles
Standard dosing regimens are rigorously formulated to maximize clinical efficacy while minimizing adverse effects. Typically:
- Administered daily with strict adherence to cycle timing.
- Cyclic dosing synchronized with the menstrual calendar.
- Dosage tailored to individual pharmacokinetic profiles.
This regimen is underpinned by robust clinical protocols.
Step-by-Step Administration Instructions
A methodical approach to administration is essential for optimal therapeutic outcomes. The recommended procedure involves:
- Initiation on the first day of the menstrual cycle.
- Consistent dosing at the same time each day.
- Meticulous adherence to the prescribed treatment plan.
Such systematic guidance ensures maximal efficacy.
Adjustments for Different Age Groups and Health Conditions
Dosing adjustments are imperative to accommodate age-related and pathophysiological variances. Considerations include:
- Modified regimens for geriatric patients with altered pharmacodynamics.
- Special adjustments for individuals with hepatic or renal impairments.
- Customization in the presence of concomitant chronic conditions.
Tailored modifications safeguard patient safety and optimize outcomes.
Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Common Side Effects
Nausea and Gastrointestinal Discomfort
Patients may experience episodic nausea and mild gastrointestinal perturbations. These manifestations:
- Typically subside with continued therapy.
- May be mitigated with dietary adjustments.
- Require minimal intervention in most cases.
Short-lived discomfort often resolves spontaneously.
Headaches and Migraines
Headaches, ranging from mild cephalalgia to debilitating migraines, can emerge as a side effect.
- Often correlated with hormonal fluctuations.
- May necessitate symptomatic treatment or dosage review.
- Occasional episodes warrant clinical reassessment.
The frequency and intensity vary among patients.

Breast Tenderness and Mood Swings
Breast tenderness and emotional lability are among the frequently encountered side effects.
- May present as transient discomfort and mood fluctuations.
- Typically diminish as the body acclimates to the regimen.
- Requiring empathetic patient counseling.
These effects are generally self-limiting.
Identification of Rare and Severe Side Effects
Although infrequent, severe adverse events require immediate clinical attention. Such events include:
- Thromboembolic complications.
- Severe hypersensitivity reactions.
- Marked hepatic dysfunction.
Prompt recognition is essential to avert significant morbidity.
Drug Interactions and Contraindications
Overview of Potential Drug Interactions
Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol may exhibit pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interactions with concomitant medications.
- Interactions may alter its metabolic clearance.
- Potential attenuation of contraceptive efficacy.
- Increased risk for adverse reactions when combined with certain agents.
A thorough medication reconciliation is imperative before initiation.
Interaction with Enzyme-Inducing Medications
Enzyme-inducing medications can accelerate the metabolic degradation of the active components. Considerations include:
- Antiepileptics and certain antibiotics are known for enzyme induction.
- Potential need for dosage readjustment.
- Vigilant monitoring of therapeutic efficacy.
Such interactions may compromise contraceptive reliability.
Contraindications in Specific Patient Populations
Certain clinical scenarios preclude the use of Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol. Contraindications include:
- History of thromboembolic events or clotting disorders.
- Severe hepatic insufficiency or active liver disease.
- Documented hypersensitivity to any formulation components.
Strict adherence to contraindications is essential for patient safety.
Guidance on Managing Concomitant Therapies
Co-administration with other therapeutic agents necessitates a cautious approach. Recommended practices include:
- Comprehensive review of all concurrent medications.
- Tailored adjustments to mitigate potential interactions.
- Collaborative management involving specialist consultation when required.
Strategic oversight ensures optimal therapeutic synergy.
Storage, Handling, and Safety Measures
Optimal Storage Conditions and Shelf Life
Maintaining the integrity of Desogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol hinges on adherence to precise storage guidelines. Key recommendations:
- Store in a cool, dry environment, shielded from direct sunlight.
- Maintain within the recommended temperature range.
- Observe expiration dates rigorously to ensure efficacy.
Such meticulous storage practices preserve its therapeutic potency.
Handling Precautions for Pharmacists and Healthcare Providers
Safe handling protocols are paramount for both dispensing and administration. Healthcare providers should:
- Employ protective measures to avoid contamination.
- Follow established protocols for accurate dispensing.
- Monitor environmental factors that could compromise the medication.
Rigorous adherence to these protocols safeguards patient health.
Warnings, Precautions, and Careful Administration
Important Warnings and Black Box Information
The administration of this pharmaceutical compound necessitates an astute awareness of its inherent warnings and explicit black box advisories. Clinicians must assimilate:
- Unambiguous contraindications documented in the product's labeling.
- Vigilant observation of potential thromboembolic events.
- Alertness to any emergent hepatic perturbations or hypersensitivity reactions.
It is imperative to recognize that these warnings are not merely advisory but constitute critical determinants of safe clinical practice.

Critical Precautions for High-Risk Groups
Specialized precautions must be exercised when administering this therapy to patients with predisposing risk factors. These high-risk groups include individuals with:
- Pre-existing cardiovascular abnormalities.
- History of coagulopathies or endocrine irregularities.
- Concurrent comorbidities that may exacerbate adverse reactions.
Short and deliberate interventions are advised to circumvent potential complications.
Special Considerations for Unique Populations
Administration to Elderly Patients
Older women, particularly those over 35 and especially those who smoke, have a significantly increased risk of serious cardiovascular side effects from combined oral contraceptives.
These risks include:
- Blood clots (thrombosis)
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- The risk of these complications increases with age.
Older women are also more likely to have other health conditions that can be made worse by oral contraceptives, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
The therapeutic profile in pregnancy and lactation necessitates a delicate balance between efficacy and safety. Considerations include:
- Safety Profile During Pregnancy: Exposure to these hormones during pregnancy can pose potential risks to the developing fetus. While epidemiological data may not always show a definitive increased risk of birth defects when inadvertently taken in early pregnancy, there are still risks, and animal studies have shown potential for fetal harm.
- Recommendations for Breastfeeding Mothers: Assess the excretion of the medication in breast milk and potential neonatal exposure. Recommendations should be framed within the context of minimizing infant risk while addressing maternal needs.
Both short-term interventions and long-term vigilance are pivotal.
Administration to Children and Adolescents
Pediatric administration requires particular sensitivity to developmental pharmacodynamics. Key areas of focus include:
- Pediatric Dosing Considerations: Desogestrel/ethinyl estradiol is generally not appropriate for pre-pubertal children. These medications are designed to affect hormonal processes related to the menstrual cycle and ovulation, which are not yet active in very young children. Giving hormonal medications to very young children can have unpredictable and potentially harmful effects on their development.
- Monitoring Growth, Development, and Side Effects: Regular evaluations to ensure that the therapeutic intervention does not impede normal developmental trajectories. Constant monitoring aids in early detection of adverse effects.
Both succinct directives and comprehensive developmental assessments are necessary.
Overdose and Emergency Management
Recognizing Symptoms of Overdose
The clinical presentation of an overdose may manifest with a spectrum of nonspecific and overt symptoms. Clinicians should be alert to:
- Severe gastrointestinal distress.
- Marked neurological disorientation.
- Acute cardiovascular instability.
Timely recognition is crucial, as even subtle signs may presage a more serious toxicological event.
Immediate Response and Emergency Treatment Protocols
Rapid intervention following an overdose is indispensable. The emergency response protocol should include:
- Immediate cessation of the medication.
- Supportive care measures to stabilize vital parameters.
- Administration of specific antidotes where applicable.
Swift, decisive action combined with well-structured emergency procedures can significantly mitigate morbidity.
Handling Precautions in Clinical and Home Settings
Best Practices for Safe Medication Handling
Optimal safety in both clinical and domestic environments is achieved through adherence to established handling protocols. Best practices include:
- Utilization of protective gear during preparation and administration.
- Strict compliance with sanitation standards.
- Regular staff training and competency assessments.
Concise procedural checklists complement comprehensive safety frameworks.
Strategies for Minimizing Risk and Ensuring Safety
Implementing multifaceted risk minimization strategies fortifies the safety of therapeutic regimens. Recommended strategies encompass:
- Regular audits of medication handling processes.
- Integration of digital monitoring systems.
- Continuous feedback loops between patients and healthcare providers.
Combining rapid-response measures with long-term risk assessments ensures a resilient safety infrastructure.
Desogestrel/ Ethinyl Estradiol FAQ
- What does desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol do?
- Is desogestrel good for PCOS?
- What are the side effects of desogestrel?
- What are the benefits of taking desogestrel?
- When is the best time to take desogestrel?
- What are the benefits of ethinyl estradiol?
- Can I take desogestrel on my period?
- What will happen if I stop taking desogestrel?
- Can you get pregnant on desogestrel?
- Can desogestrel cause ovarian cysts?
- What does spotting look like?
- Do you gain weight on desogestrel?
- What type of pill is desogestrel?
- What is the use of desogestrel ethinyl estradiol?
- What are the health benefits of desogestrel?
- Can I stop my period with desogestrel?
- What happens when you stop taking ethinyl estradiol?
- Can you bleed when taking desogestrel?
- Is desogestrel good for PMS?
- Can you get pregnant if you miss one desogestrel pill?
- Why am I still getting a period on desogestrel?
- How to tell if pregnant on desogestrel?
- Is desogestrel safe?
- Is desogestrel good for PCOS?
- Do you still ovulate on desogestrel?
- What are the side effects of desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets?
- What are the side effects of desogestrel?
- What are the benefits of taking desogestrel pills?
- When is the best time to take desogestrel?
- How long does it take for estradiol to stop bleeding?
- What happens to your body when you stop taking desogestrel?
- When is the best time to take ethinyl estradiol?
What does desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol do?
Desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol together are utilized to avoid pregnancy by acting as a pill that encompasses both desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol hormones; when consumed correctly as per directions laid out in the prescription statement, it aids in preventing conception by impeding the full maturation of a woman's egg each menstrual cycle.
Is desogestrel good for PCOS?
Yes
What are the side effects of desogestrel?
Irregularities in the cycle changes in mood, increased weight, skin reactions, nausea, decreased libido, headaches, and altered moods are some of the reported side effects associated with breast abnormalities treatment.
What are the benefits of taking desogestrel?
The desogestrel pill might be able to reduce period pain and discomfort during ovulation.
When is the best time to take desogestrel?
within 12 hours of the time you usually take it
What are the benefits of ethinyl estradiol?
The medication works by stopping ovulation and preventing pregnancy. It can also be prescribed for managing acne and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD). It falls under the category of contraceptives. Consists of a blend of estrogen and progestin hormones.
Can I take desogestrel on my period?
You have the flexibility to begin taking the progestogen pill at any point during your cycle.
What will happen if I stop taking desogestrel?
Most women typically resume ovulation within a month after discontinuing a combined birth control pill or around 17 days after stopping a desogestrel-containing minipill.
Can you get pregnant on desogestrel?
While it's highly improbable to occur, some slim possibility exists of getting pregnant while using the progestogen pill. If this situation arises, no evidence suggests any harm to your baby from taking the pill.
Can desogestrel cause ovarian cysts?
A few women might encounter significant adverse reactions, such, as ovarian cysts.
What does spotting look like?
Spotting refers to bleeding that may appear as pinkish or reddish spots or even brownish in color.
Do you gain weight on desogestrel?
Than 10% of women might face weight gain when using a pill that includes desogestrel.
What type of pill is desogestrel?
Desogestrel is a progestogen pill often referred to as a mini pill and can be up to 99 percent effective when used correctly.
What is the use of desogestrel ethinyl estradiol?
This type of hormone medication is commonly taken to avoid getting pregnant and includes two hormones. Progestin and estrogen are in it. Apart from their birth control effects, these pills can also help regulate your cycles, reduce bleeding and pain, lower the chances of ovarian cysts formation, and even improve acne conditions.
What are the health benefits of desogestrel?
Taking the progestogen pill with desogestrel can assist with alleviating ovulation discomfort since it inhibits ovulation for 97 percent of users, effectively reducing the associated pain due to the absence of ovulation activity.
Can I stop my period with desogestrel?
Some people notice an increase in the frequency of their periods. Encounter spotting between cycles when taking desogestrel-based mini pills. It is believed that desogestrel may have a chance of inducing amenorrhea (cessation of menstruation) though this effect is expected to be temporary.
What happens when you stop taking ethinyl estradiol?
skin breakouts, like acne; putting on pounds; experiencing headaches; dealing with menstrual cycles; irregular menstrual cycles or missing periods altogether; and feeling changes, in emotions.
Can you bleed when taking desogestrel?
Irregular bleeding in the area can happen when using Desogestrel.
Is desogestrel good for PMS?
They are typically employed solely for addressing PMS symptoms with the supervision of a gynecologist.
Can you get pregnant if you miss one desogestrel pill?
If you forget to take your desogestrel pill and its been over 12 hours since your time you may not be fully protected from pregnancy.
Why am I still getting a period on desogestrel?
Body might continue to ovulate as normal
How to tell if pregnant on desogestrel?
A late period, bleeding during implantation, breast tenderness or alterations, fatigue, feeling queasy and dislikings towards foods, headaches and the urge to urinate frequently.
Is desogestrel safe?
There might be a rise in the chance of developing breast cancer in women who are currently using or have recently used progestogen birth control methods.
Is desogestrel good for PCOS?
Yes
Do you still ovulate on desogestrel?
The progestogen pill containing desogestrel has the ability to prevent ovulation well.
What are the side effects of desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets?
Experiencing reactions can manifest as skin rash or itching. May include hives or swelling in areas, like the face or tongue. Detect signs of a blood clot if you encounter pain or swelling in your leg along with symptoms, like shortness of breath or chest pain. Be aware of gallbladder issues which may cause stomach pain accompanied by feelings of nausea and vomiting along with feverish symptoms.
What are the side effects of desogestrel?
Some warning signs to look out for include the presence of breast lumps or changes, in mood like feelings of sadness getting worse. Additionally experiencing stomach or abdominal pain should be taken seriously. Any unusual alterations in bleeding patterns such as spotting or sudden heavy flow could raise concern. Other worrisome symptoms to watch for are urine and yellow eyes.
What are the benefits of taking desogestrel pills?
The desogestrel pill could potentially provide relief for cramps and discomfort during ovulation around the middle of the cycle.
When is the best time to take desogestrel?
Within 12 hours of the time you usually take it
How long does it take for estradiol to stop bleeding?
1 week
What happens to your body when you stop taking desogestrel?
It may take a while for your body to adjust to not taking birth control pills. You might observe bleeding between periods or experience menstrual flow and cramps. There could also be a recurrence of any mood swings and bloating that you had before you started taking the pill. Additionally you may notice differences, like increased hair growth,new acne breakouts and fluctuations in weight.
When is the best time to take ethinyl estradiol?
Your physician might suggest starting your medication either on the day of your period (known as Day 1 start) or on the Sunday following the start of your period (known as Sunday start).