Entecavir
- I. Introduction
- II. Composition of Entecavir
- III. Uses of Entecavir
- IV. How Entecavir Works
- V. Dosage and Administration
- VI. Common Side Effects
- VII. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
- VIII. Special Populations: Administration Guidelines
- IX. Drug Interactions
- X. Overdosage and Handling Precautions
- XI. Storage Guidelines
- XII. Contraindications and Warnings
I. Introduction
Brief Overview of Entecavir
Entecavir is widely used in treating chronic Hepatitis B infection as an antiviral medication. It falls under the class of drugs called nucleoside analogs.
Importance in Treating Hepatitis B
The importance of treating Hepatitis B cannot be emphasized enough, given its tendency to develop into long-term liver disease or hepatocellular carcinoma. Entecavir serves as a defense against the replication of the virus, thereby slowing down the progression of the disease.
What to Expect from This Article
This article aims to provide an explanation of Entecavir, including its ingredients, applications, how it works, and instructions for usage, among other aspects.
II. Composition of Entecavir
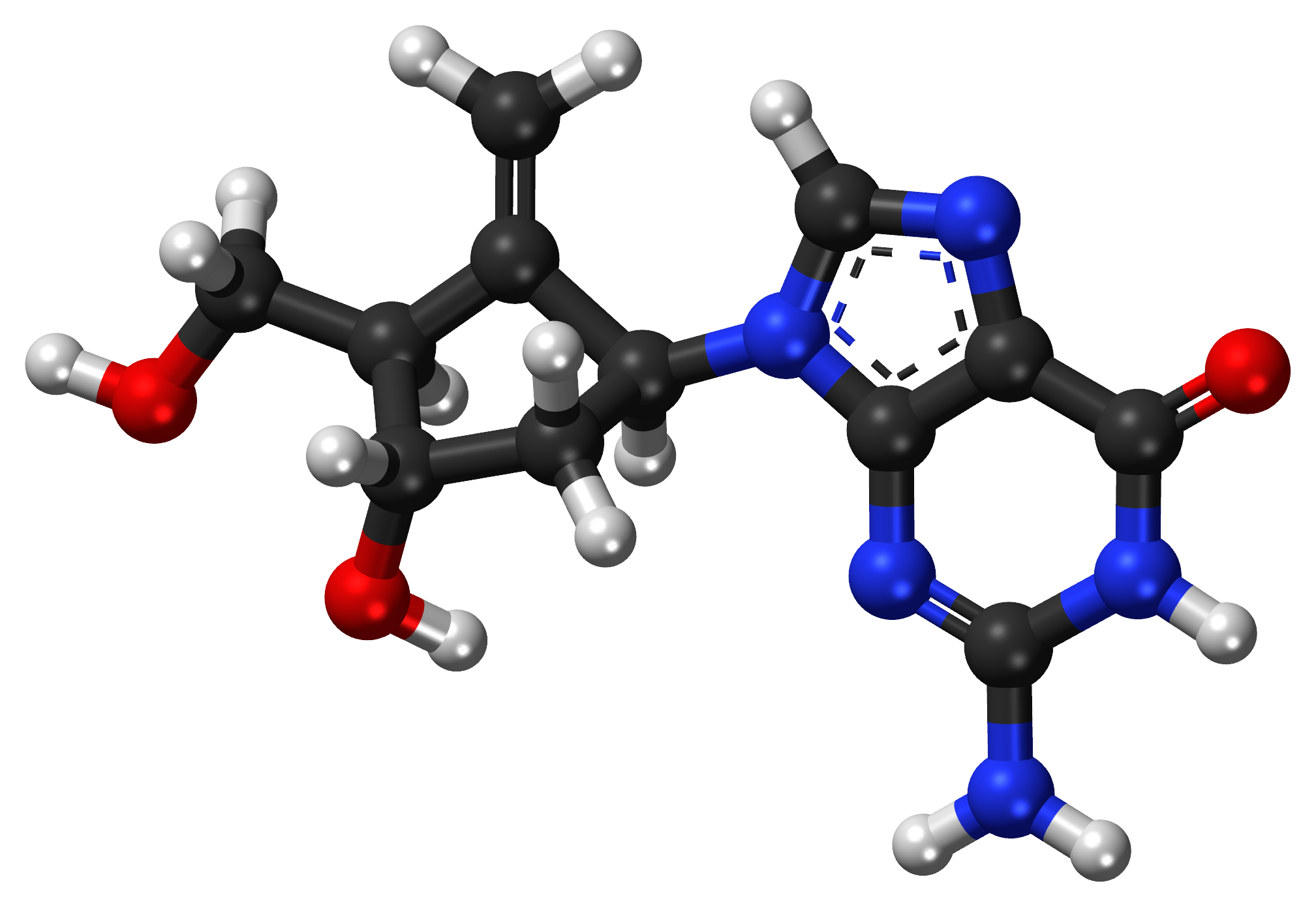
Chemical Structure and Properties
Entecavir possesses an intricate chemical makeup specifically tailored to bind with Hepatitis B polymerase strongly. Its molecular formula is C12H15N5O3.
Active and Inactive Ingredients
Main Ingredient: Entecavir Ingredients; Some other ingredients include lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, and magnesium stearate, among others.
Available Formulations: Tablets and Oral Solution
Entecavir is available in two forms: tablets and a liquid solution. These options cater to the requirements of different groups of patients.
III. Uses of Entecavir
a. FDA-Approved Uses: Chronic Hepatitis B Treatment
In Adults
Entecavir is a nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitor that is commonly used to treat chronic hepatitis B virus infection in adults and children who have evidence of active viral replication and either evidence of persistent elevations in serum aminotransferases (ALT or AST) or histologically active disease 12. It is known for its resistance-preventing solid capabilities 3.
Here are some references that you can use to learn more about Entecavir and its use in treating Hepatitis B:
- Entecavir prophylaxis for hepatitis B virus reactivation in patients with CAR T-cell therapy
- Entecavir: Package Insert - Drugs.com
- Entecavir in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection
In Children
This medication has undergone testing to ensure its effectiveness and safety in children aged 2 and above.
b. Off-Label Uses
Hepatitis B in Co-Infection Scenarios
Entecavir is an antiviral medication primarily used to treat chronic hepatitis B virus infection in adults and children 12. Although it is not officially approved for treating co-infections with Hepatitis B and C or HIV, it has been used in some cases 3.
Here are some references that you can use to learn more about Entecavir and its use in treating Hepatitis B:
- Hepatitis B Virus/HIV Coinfection | NIH - Clinical info
- Entecavir: Package Insert - Drugs.com
- Entecavir in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection
Hepatitis B Prevention for Transplant Patients
Entecavir is an antiviral medication that is primarily used to treat chronic hepatitis B virus infection in adults and children 12. Although it is not officially approved for treating co-infections with Hepatitis B and C or HIV, it has been used in some cases 3. It has also been used to prevent HBV reinfection after liver transplant 4 and to treat chronic hepatitis B virus infection in liver transplant recipients 5.
Here are some references that you can use to learn more about Entecavir and its use in treating Hepatitis B:
- Hepatitis B Virus/HIV Coinfection | NIH - Clinicalinfo
- Entecavir: Package Insert - Drugs.com
- Entecavir in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection
- Entecavir - Wikipedia
- Long-term outcomes of entecavir monotherapy for chronic hepatitis B after liver transplantation: Results up to 8 years
c. Case Studies and Clinical Trials Supporting Use
Entecavir has been shown to be more effective than Lamivudine and other antiviral agents in preventing viral resistance, according to clinical trials 1.
Here are some references that support this claim:
- A randomized clinical trial published in JAMA Network reports a lower incidence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and reactivation in patients seropositive for the hepatitis B surface antigen with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma receiving R-CHOP chemotherapy 1.
- In two large, double-blind, multinational trials, oral entecavir 0.5 mg once daily was more effective than oral lamivudine 100mg once daily in adult nucleoside-naive HBeAg-positive or -negative patients with chronic HBV infection 2.
- Entecavir has a higher potent antiviral efficacy and a lower drug resistance rate than those of Lamivudine in nucleoside-naïve CHB patients 3.
- A study published in The New England Journal of Medicine found that the antiviral efficacy of entecavir was greater than that of lamivudine among patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B 4.
IV. How Entecavir Works
Mechanism of Action
Entecavir hinders the functioning of DNA polymerase, an enzyme, for viral replication, thereby interrupting the viral life cycle.
Role in Inhibiting Hepatitis B Virus Replication
This disruption helps to reduce the replication of the virus, which in turn decreases the amount of the virus in the body and may improve liver health.
Entecavir demonstrates a favorable pharmacokinetic profile and a stronger ability to resist genetic changes that lead to drug resistance compared to other options such, as Lamivudine and Adefovir.
V. Dosage and Administration
a. Recommended Dosage for Adults
It is typically advised for adults to take between 0.5mg and 1mg per day based on assessment.
b. Pediatric Dosage Guidelines
When it comes to children, the dosage is usually adjusted according to their body weight and other factors related to how the medication is processed in their bodies.
c. Dosage Modifications
Renal Impairment
The dosage might need to be adjusted for patients who have insufficiency.
Liver Cirrhosis
Patients with liver cirrhosis might need to be monitored and their dosage adjusted as necessary.
d. Administration Guidelines
Proper Storage Pre-Administration
Store entecavir at room temperature, avoiding exposure to moisture and heat.
Tablet vs. Oral Solution
Patients are free to decide whether they prefer taking the tablet or the oral solution depending on their preference and medical advice.
VI. Common Side Effects
List of Common Side Effects
Some of the adverse effects include feelings of nausea, tiredness, and headaches.
Incidence and Frequency
Most patients only experience adverse effects, and these effects are not expected.
Managing Common Side Effects
Symptomatic treatment and, if needed, adjusting the dosage are some options to improve the situation.
VII. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
Pre-Treatment Screening
Before proceeding with any treatment, it is crucial to conduct an evaluation that explicitly examines liver function tests and viral markers.
Monitoring During Treatment
Regular checkups are essential, especially when it comes to evaluating virological reactions.
Contraindications
Renal Disease
Entecavir should not be used in patients who have kidney problems.
Liver Dysfunction
Likewise, individuals who have decompensated liver disease should avoid using this medication.
Warning Signs to Stop Administration
If there is an increase in liver enzymes or any signs of hypersensitivity, it is essential to stop the treatment right away.
VIII. Special Populations: Administration Guidelines
a. Administration to Elderly Patients
Special Precautions
Monitoring patients is crucial because their renal function declines as they age.
Dose Adjustments
The dosage may need to be adjusted depending on the results of function evaluations.
b. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Known Risks
There is not a lot of data on the risks so it is advisable to only use it if the benefits are more significant than the potential risks.
Recommendations
When it's possible, we should explore options for treating this specific group of people.
c. Administration to Children
Age-Specific Guidelines
Adjusting the dosage is determined by considering the individual's weight and kidney function.
Pediatric Studies and Safety Profile
Research has shown that it is generally safe and effective for children over 2.
IX. Drug Interactions
Known Interactions with Other Medications
Entecavir is generally considered to have a risk of interactions with other medications. However, it is essential to be cautious when using it alongside drugs that may affect its effectiveness and how it is processed in the body. Specifically, medications that impact kidney function can potentially affect the elimination of Entecavir through the kidneys. When using Entecavir in combination with HIV agents like lamivudine, it is essential to exercise caution. It is not advisable to administer Entecavir with nephrotoxic drugs such as aminoglycosides, which can harm the kidneys.
Effects on Lab Tests
Drug interactions have the potential to affect the outcomes of laboratory tests. For example, when it comes to liver function tests, there might be an increase in liver enzyme levels that can be noticed. Similarly, changes in creatinine levels may occur during function tests.
How to Manage Drug Interactions
It is crucial to prioritize pharmacovigilance. Healthcare professionals typically employ a strategy that involves regularly monitoring relevant laboratory indicators, making necessary dosage adjustments, or considering alternative medication options.
X. Overdosage and Handling Precautions
Symptoms of Overdose
Accidental or intentional excessive consumption of Entecavir can lead to the following symptoms; Lactic Acidosis Impaired kidney function Enlarged liver.

Emergency Management
It is crucial to provide medical treatment in such cases. This typically involves performing lavage to reduce absorption and using hemodialysis to improve the elimination of the drug through the kidneys.
Procedures for Proper Handling and Disposal
Giving attention to safety measures dramatically reduces the chances of accidentally taking too much medication. Make sure to store it in a place. When you have expired or unused medication, it's best to dispose of it through pharmaceutical take-back programs.
XI. Storage Guidelines
Optimal Storage Conditions
The effectiveness of Entecavir depends on following storage instructions. It is recommended to store it at room temperature for results. Make sure to keep it from high humidity environments to maintain its quality.
Shelf Life
Entecavir typically maintains its effectiveness for a period of 2 years if stored as recommended.
Guidelines for Discarding Expired Medication
Disposing of expired medication is not a simple task but an essential safety precaution. It's important not to flush them down the toilet. Instead, they should be returned to a pharmaceutical disposal program.
XII. Contraindications and Warnings
Absolute Contraindications
There are situations where Entecavir should not be used. These include having a known allergy to any of the ingredients or having lactose intolerance that has not been treated or managed correctly. This is because lactose is present in the formulation.
Relative Contraindications
These factors are related to the context. Include Existing kidney disorders and Simultaneous use of other medications that can harm the kidneys.
FDA and Health Authority Warnings
The FDA has recently issued a warning label highlighting the risk of Hepatitis B worsening when treatment is stopped abruptly.





























