Fusiderm Cream, Fusidic Acid
Introduction
The field of dermatology has greatly benefitted from the introduction of antimicrobial treatments with Fusiderm Cream being a notable example. This cream, containing Fusidic Acid as its component is recognized for its effectiveness in treating skin infections caused by staphylococci and other bacteria.
Staphylococci under the microscope
It symbolizes the intersection of advancements scientific breakthroughs and medical progress. The journey of Fusidic Acid from a laboratory discovery to a component of modern medicine underscores its essential role, in addressing dermatological conditions.
Overview of Fusiderm Cream and Fusidic Acid
Fusiderm Cream offers a ray of hope for people dealing with skin infections by using Fusidic Acid as its main defense, against harmful microbes. This strong antibiotic, obtained from the Fusidium coccineum fungus shows a capability to stop the growth of bacteria helping ease symptoms and speed up healing.
Historical Context and Development of Fusidic Acid
- Discovered during the 1960s Fusidic Acid emerged from research on antibiotics that aimed to introduce innovative modes of action.
- Its unearthing marked an achievement in the fields of microbiology and pharmacology providing a fresh approach to combating drug-resistant bacterial infections.
- The transformation of Fusidic Acid, into a treatment highlights its versatility and lasting importance in the realm of pharmaceuticals.
Importance and Relevance in Modern Medicine
In today's medical field, Fusiderm Cream, which contains Fusidic Acid is a crucial treatment option. Its effectiveness in addressing skin infections while minimizing the development of resistance makes it a popular choice among healthcare providers. The importance of this medicine in healthcare settings is evident in the continuous fight against antibiotic resistance making it a key defense, against bacterial growth.
Composition
Active Ingredients: Fusidic Acid Explained
Fusidic Acid, the ingredient in Fusiderm Cream works through a clever method that interferes with the production of bacterial proteins. This unique approach sets it apart. Plays a role in its effectiveness, in treating skin infections without adding to the widespread problem of antibiotic resistance.
Inactive Components and Their Functions
With Fusidic Acid various inactive components are crucial for making sure the cream works well and is effective in treating skin conditions. These ingredients, such, as stabilizers and emollients improve the cream's feel, stability and ability to be absorbed by the skin making it easier to blend into the skin's defenses.
Pharmacological Classification
Fusidic Acid falls under the category of antibiotics as a bacteriostatic agent that hinders the growth and multiplication of bacteria. Its distinct impact, on protein synthesis sets it apart in a group separating it from other antibiotics that target different aspects.
How It Works
Mechanism of Action: Inhibiting Bacterial Protein Synthesis
Fusidic Acid works by attaching to ribosomes which are the cellular structures that make proteins. This attachment disrupts the movement of molecules during protein production, a stage, in making proteins ultimately halting the growth and reproduction of bacteria.
The Role of Fusidic Acid in Bacterial Cell Membrane Function
Fusidic Acid mainly works by stopping protein synthesis. It also has a subtle impact on the bacterial cell membrane integrity. When it interferes with protein production Fusidic Acid indirectly influences the creation of membrane proteins which are crucial, for the survival and operation of bacteria.
Comparative Analysis with Other Antibacterial Agents
- Fusidic Acid's specific method of blocking protein production provides a benefit by decreasing the chances of resistance developing alongside antibiotics that target different bacteria.
- In contrast to broad-spectrum antibiotics Fusidic Acid has a limited range of effectiveness mainly focusing on Gram-positive bacteria, which helps preserve the body's beneficial bacteria.
- When compared to topical treatments the clinical effectiveness of Fusidic Acid is attributed to its strong impact on particular pathogens highlighting its importance in treating skin infections, with precision.
Uses
Primary Indications: Skin Infections
In the field of dermatology treatments finding remedies for skin infections has always been a top priority. A key focus is using drugs to eliminate harmful bacteria residing in different layers of the skin. Some medications are particularly noteworthy for their effectiveness in offering relief to individuals dealing with bacterial invasions of the skin's outer and inner layers. These infections present a range of symptoms from irritations, to more serious inflammations requiring a strong approach to bring back skin health and balance.
Efficacy in Treating Staphylococcal Infections
Staphylococcal infections(1), caused by Staphylococcus species pose a challenge as they have developed resistance to traditional antibiotics. This resistance makes treating the infections more difficult.
Increases the risk of widespread infection highlighting the importance of finding effective anti-staphylococcal treatments. Some medications have shown results in combating these pathogens providing hope for those affected.
It's impressive how well they can navigate the complexities, within bacteria and render them inactive while minimizing harm to the skin's flora and maintaining its delicate balance.
2. National Library of Medicine - New Weapons to Fight against Staphylococcus aureus Skin Infections
Application in Sycosis Barbae, Folliculitis, and Impetigo
The range of treatments for skin infections is quite diverse covering various conditions affecting the skin and hair follicles. Conditions like sycosis barbae, folliculitis, and impetigo greatly benefit from antimicrobial treatments.
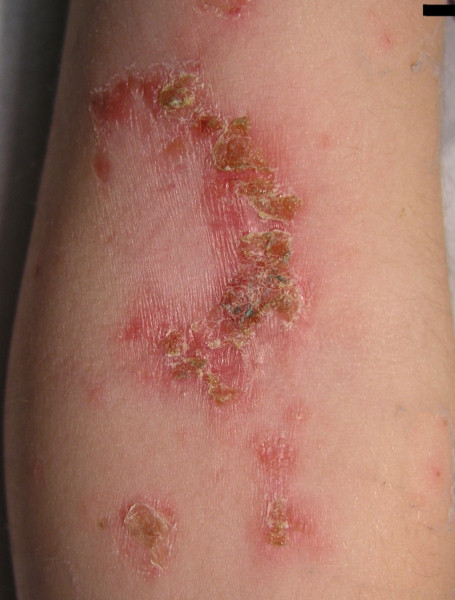
Impetigo
Sycosis barbae(1) typically affects the facial hair areas. Involves inflammation of hair follicles requiring agents that can penetrate these units to combat microbes effectively.
Folliculitis(2), characterized by inflamed hair follicles also needs interventions that can address issues, beneath the skin surface. Impetigo(3), known for its superficial skin lesions demands treatments that can swiftly eliminate the bacteria responsible to prevent further spread.
When treating these conditions selecting the antimicrobial agent depends on whether it is bactericidal (kills bacteria) or bacteriostatic (inhibits bacterial growth) ensuring bacteria are stopped from reproducing.
Using treatments not only eases symptoms but also reduces the risk of spreading infection protecting the health of the wider community.
1. National Library of Medicine - Successful Treatment with Fusidic Acid in a Patient with Folliculitis Decalvans
2. Patient.Info - Folliculitis
1. NHS - Fusidic Acid
Off-Label Use
Expanding the Therapeutic Potential: Dermatological Conditions
In the changing world of medical care, the exploration of new treatment possibilities beyond traditional uses has attracted considerable interest. Dermatological conditions, known for their manifestations and diseases are leading the way in areas where using medications off-label offers hope.
This approach entails using drugs for purposes not originally approved by agencies but backed by emerging research and clinical practice. It represents a blend of creativity and practicality opening up pathways for addressing challenging skin conditions that may not improve with standard therapies.
The decision to use a medication, off-label label is typically based on a review of available literature, personal experiences, and a deep understanding of how the drug works in the body.
Evidence and Case Studies Supporting Off-Label Application
The foundation of off-label use in dermatology is supported by a growing body of evidence including case studies and retrospective analyses. These academic contributions shed light on the effectiveness and safety profiles of medications when used to treat various skin conditions that are not officially approved.
For example drugs initially designed for their inflammatory or immunomodulatory properties have shown success in treating skin issues beyond their intended uses providing relief from symptoms and altering disease progression in cases where standard treatments have failed.
Personal stories and collections of cases have documented the management of complex skin conditions highlighting the potential for using drugs off label to address treatment gaps.
While there are controlled trials available they also support these findings and suggest that certain medications may have wider applications, than originally thought.
Risks and Considerations in Off-Label Prescribing
While using medications in ways not officially approved may bring hope for treatments it also comes with risks and ethical considerations. When prescribing drugs for purposes other than their intended use it's important to carefully weigh the potential benefits against the risks considering factors like side effects the seriousness of the illness and alternative treatment options.
Since there may be a lack of approval gathering comprehensive safety data becomes more challenging highlighting the importance of relying on clinical judgment and obtaining informed consent.
- Healthcare providers should openly discuss with patients the reasons behind off-label drug use as well as its potential advantages and risks.
- It is crucial to monitor and evaluate a patient's response to off-label treatment in line with the ethical principle of avoiding harm. Securing insurance coverage for off-label drug use can be complex.
- May require advocating for patients to receive reimbursement, for treatments that could significantly impact their lives.
Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosage for Adults and Children
The way in which a therapeutic agent is dosed plays a role in its effectiveness as it needs to be carefully adjusted for both adults and children. Healthcare providers have the responsibility to prescribe doses that strike a balance between providing benefits and minimizing any negative effects. When determining the dosage for adults factors such as the severity of the condition the patient's weight and kidney function must be taken into consideration.
On the other hand dosages for children are often calculated based on their body weight or surface area requiring precise modifications to prevent under or over-dosing. This level of accuracy ensures that the medication reaches a concentration, in the body promoting recovery while reducing the risk of toxicity.
Application Techniques for Maximum Efficacy
Maximizing the healing benefits of medications goes beyond the right dose; it involves both the art and science of how they are applied. How a medication is given—whether by mouth on the skin or through injection—plays a role in making sure the drug works well in the body and does its job effectively.
When it comes to applying medications on the skin making sure to spread them over affected areas and following instructions, about covering or exposing the area is key. This careful method helps the medication get absorbed properly and interact with tissues enhancing its healing effects.
Keeping the skin clean and dry before applying medication can really boost how well it gets absorbed for skin treatments. Knowing how to apply a medication is essential to avoid using too little or too much which could make conditions worse instead of better.
Duration of Treatment for Common Conditions
The saying 'sometimes less is better' is frequently relevant when it comes to how a treatment should last aiming for the best possible healing results in the shortest period of time. The length of treatment can vary depending on the condition being treated its severity and how well the patient responds to the medication.
Short interventions might be necessary, for conditions whereas dealing with chronic illnesses might call for longer therapy sessions. It's important to evaluate how effective the treatment is so adjustments can be made to the therapy plan based on how well the patient is doing and their ability to handle it.
Side Effects
Common Side Effects: Local Irritation and Rashes
While medications have their advantages they also come with drawbacks. One common issue in treatments is experiencing local irritation and rashes as the skin reacts to external substances. These reactions, mild and temporary can show up as redness, itching, or peeling.
Although not usually serious they might make patients less likely to stick to their treatment plan and feel satisfied, with it. This highlights the importance of taking steps like adjusting dosage or providing extra care to manage these effects effectively.
Systemic Side Effects: Rare but Significant
Serious side effects, although uncommon in skin treatments are a concern because they can affect overall health. These reactions, which can range from stomach issues to blood-related problems require monitoring, especially for treatments that enter the bloodstream. Identifying risk factors and screening before treatment can help reduce these risks and make the treatment journey safer, for the patient.
- Regularly checking liver and kidney function tests can help prevent toxicity in patients receiving long-term therapy.
- Encouraging patients to report any new or worsening symptoms can facilitate early detection and intervention for potential side effects.
Management and Mitigation of Adverse Reactions
Managing adverse reactions involves approaches, including prevention and treatment. Preventive steps like educating patients and choosing drugs wisely are crucial in reducing side effects. In cases of reactions, personalized strategies, such, as symptom relief or stopping medication need to be applied to manage the effects without compromising the effectiveness of the main treatment.
Important Precautions
Allergic Reactions and Sensitivity Considerations
Allergies and sensitivities are a worry when giving any medication. Before starting treatment it's important to ask the patient about their allergic reactions and sensitivities. This careful approach helps identify any issues and choose safer treatment options. If there's uncertainty, about hypersensitivity conducting patch tests or closely supervising administration may be necessary to keep the patient safe.
Interaction with Other Dermatological Treatments
Using dermatological treatments at the same time can lead to possible interactions between drugs, which may change how effective or toxic the medications are. It's crucial to check the medications a patient is taking, including any, over-the-counter products or supplements to prevent these interactions. Collaborating with healthcare providers helps coordinate treatments improving patient results and reducing the chance of negative side effects.
Precautions for Use in Compromised Skin Integrity
Patients with skin issues like injuries, inflammation, or chronic conditions may experience changes in how their skin absorbs medications. This could result in increased exposure to the medication throughout the body. Cause localized harm. In some cases, it is crucial to be careful when selecting the medication, its strength, and how it is applied based on the individual's skin condition. Continuously monitoring and adjusting the treatment plan is essential to manage the line between effective treatment and safety, for these vulnerable patients.
Contraindications
Absolute Contraindications: Known Hypersensitivity
One of the foundations of ensuring patient safety in medication therapy is the identification and strict adherence to absolute contraindications. An important instance involves a known reaction to a medication or any of its ingredients, which requires its clear exclusion from the list of treatment options.
Allergic reactions, which can range from skin rashes to severe anaphylaxis highlight the importance of conducting a comprehensive patient history assessment before starting any treatment plan. This proactive step plays a role, in prudent clinical practice by protecting patients from potentially harmful consequences.
Relative Contraindications: Liver Disease, Pregnancy, and Lactation
Relative contraindications in contrast to contraindications provide a more detailed view on drug safety by balancing the advantages of treatment with the possible risks in specific patient groups. Notably, individuals with existing liver conditions expectant mothers and nursing mothers fall into categories where the use of medications requires a careful assessment of pros and cons.
For example, medications that are processed by the liver may need dosage adjustments. Might not be recommended at all in cases of liver issues to prevent harmful buildup
- Liver disease can have an impact on how drugs are processed in the body leading to the need for thoughtful evaluation and potential changes in dosages.
- Breastfeeding raises concerns about potential birth defects from drugs and the risk of adverse effects, on newborns or infants.
Interaction with Other Medications
Potential Interactions with Topical and Systemic Agents
The complex maze of drug interactions poses a hurdle for healthcare professionals necessitating a thorough examination of a patient's medication schedule to prevent negative interactions. Both topical and systemic treatments can engage in interactions that impact how they are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and eliminated from the body well as their effectiveness in treating conditions. This intricate situation calls for an approach to patient well-being focusing on improving treatment results while reducing the risk of harmful interactions, between drugs.
Impact on Absorption and Efficacy of Concurrent Medications
When you take medications together it can change how your body processes them affecting how well they work. Some drugs might interfere with how your body absorbs others or speed up the breakdown of drugs making them less effective. These interactions can not only make treatments less effective but also increase the chances of treatment not working or causing harm.
Guidelines for Avoiding Adverse Interactions
With understanding and attentiveness, healthcare professionals can effectively manage drug interactions by following established protocols and suggestions. This includes using drug interaction resources when prescribing medications, closely monitoring reactions and potential side effects, and seeking advice, from pharmacists or experts as needed. By taking this well-informed approach they can prevent harmful drug interactions ultimately safeguarding patient well-being and treatment effectiveness.
Careful Administration
Administration to Elderly: Adjustments and Monitoring
The elderly population with its range of physical characteristics and frequent use of multiple medications requires a customized method for giving medication. Changes in how the body processes and removes drugs due to aging mean that dosages need to be adjusted and any negative effects need to be watched closely. Because this group is more prone to issues caused by medications it's crucial to take a patient-focused approach to treatment, with medications aiming to maximize the benefits while reducing the chances of negative results.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Safety Profile
When giving medications to women and breastfeeding mothers it's crucial to consider the drug's safety, especially its potential harm to the baby and its presence in breast milk. Choosing treatments for these groups follows an approach favoring drugs known for their safety. This idea highlights the importance of prioritizing the health of both the baby and newborn, in deciding on treatment making sure that the advantages of therapy clearly surpass any possible risks.
Administration to Children: Age-Specific Considerations
Kids are not just versions of adults; they have their own specific characteristics when it comes to how drugs move through and affect their bodies. It's crucial to take into account their age when deciding on the dosage, type of medication, and how it's given to ensure they get the best treatment without any harmful side effects. These considerations play a role in providing children with the right care, for their age making sure they benefit from the treatment while staying safe highlighting the careful approach needed in treating children with medications.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Optimal Storage Conditions to Maintain Efficacy
To ensure that medicines remain effective and safe for use it is crucial to store them. Different medications have chemical compositions requiring specific storage conditions to retain their potency and reliability. Factors, like temperature, humidity, and light exposure need monitoring. For example, storing medicines in a dry place out of direct sunlight is often recommended to prevent the breakdown of active ingredients and extend their shelf life.
Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers and Patients
When dealing with pharmaceuticals whether it's healthcare providers or patients it's crucial to handle them with care to ensure safety and prevent any contamination. Wearing protective equipment like gloves might be recommended when giving certain medications to avoid direct contact with the skin or mucous membranes.
It's also important to keep the medication packaging intact until use to shield it from elements and ensure accurate dosing. Always remember to read and adhere to the handling instructions of the medication in order to minimize any risks. Maintaining hand hygiene before and after administering medication is essential, in preventing any cross-contamination.
Disposal Recommendations to Prevent Environmental Impact
Disposing of medications has become a growing issue due to incorrect methods causing water pollution and endangering wildlife. Pharmaceutical substances can linger in the environment highlighting the need for disposal techniques. Various areas provide programs for returning medications. Have designated disposal locations, at pharmacies for safely getting rid of unused or expired medicines. This helps reduce the chances of pollution and stops drugs from getting into the wrong hands.
Overdosage
Symptoms and Signs of Overdosage
Experiencing an overdose is a medical situation that shows various symptoms and signs related to the specific medication being taken. These signs can vary from discomfort to severe life-threatening conditions highlighting the importance of accurate dosing. It's essential to stay alert for any physical or mental reactions, after taking medication as detecting an overdose early can greatly impact the result.
Immediate Actions and Treatment Options
In the case of taking much medication quick action is crucial to minimize negative effects. The first thing to do is to stop the medication and check the patient's signs. Next, provide care and support as needed. If there are antidotes available they can be given if necessary. Making sure the airways are clear giving activated charcoal to absorb the drug and getting medical help are standard procedures. The treatment plan is customized based on the person's condition the substance taken and how severe the overdose is.
Reporting and Documentation of Overdose Incidents
Recording and documenting cases of overdoses is crucial for ensuring safety and enhancing the quality of healthcare. This important procedure enables an examination of the factors that led to the overdose while also adding valuable insights to help prevent similar incidents in the future. Sharing this information with regulatory bodies is essential, for prompt action to address any systemic issues update guidelines, and improve educational resources.
Conclusion
Summarizing the Therapeutic Value of Fusiderm Cream
Fusiderm Cream serves as an example of the progress made in dermatological care providing valuable treatment for skin infections. Its effectiveness, based on the antimicrobial qualities of Fusidic Acid meets an essential requirement in treating issues, like impetigo, folliculitis, and various skin infections caused by susceptible bacteria.
Future Directions in Research and Clinical Use
The evolution of Fusiderm Cream from its creation to clinical application highlights the continuous demand for creative approaches in dermatology. Potential future research paths could include testing out compositions examining combined treatment methods to boost effectiveness or combat resistance and conducting trials to broaden its approved uses. These initiatives are poised to enhance the effectiveness of Fusiderm Cream guaranteeing its continued importance, in treatments.
Key Takeaways for Healthcare Professionals and Patients
Healthcare providers must use Fusiderm Cream carefully adjusting its usage to cases and following dosage and administration guidelines. Patients should focus on adhering to the treatment comprehending the significance of storage and handling instructions and identifying symptoms of possible overdose. These actions collectively promote the efficient utilization of Fusiderm Cream enhancing its healing properties while reducing potential risks.