Havrix Injection
- I. Introduction to Havrix Injection
- II. Uses of Havrix Injection
- III. Off-label Uses of Havrix Injection
- IV. How Havrix Injection Works
- V. Dosage and Administration
- VI. Composition of Havrix Injection
- VII. Havrix side effects
- VIII. Common Side Effects of Havrix Injection
- IX. Rare and Serious Side Effects of Havrix Injection
- X. Drug Interactions with Havrix Injection
- XI. Warnings and Precautions for Havrix Injection
- XII. Contraindications for Havrix Injection
- XIII. Special Precautions in the Elderly
- XIV. Administration During Pregnancy and Nursing
- XV. Administration in Children
- XVI. Overdosage of Havrix Injection
- XVII. Handling and Storage of Havrix Injection
- XVIII. Important Precautions for Handling Havrix
I. Introduction to Havrix Injection
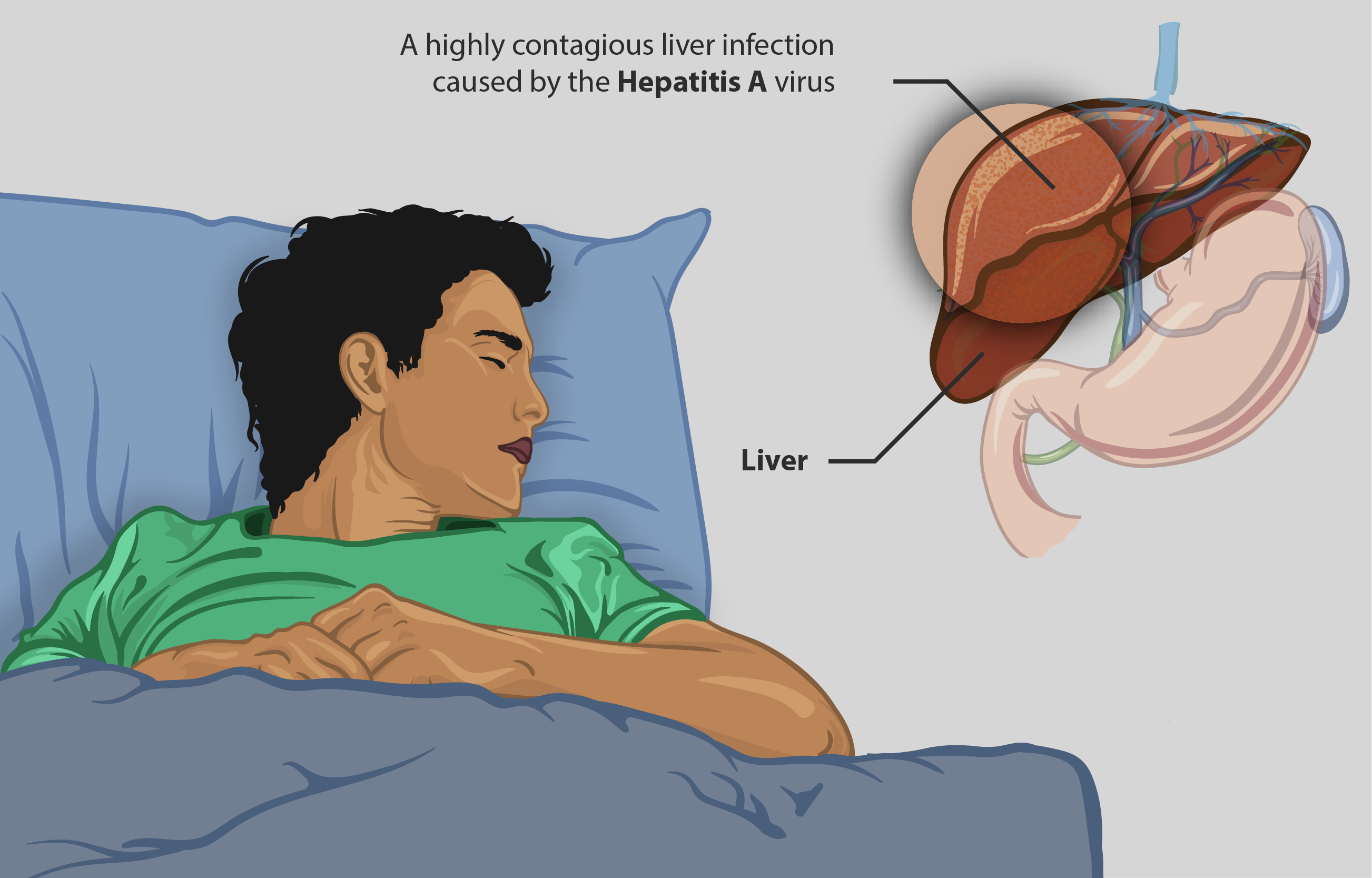
Havrix is a vaccine designed to prevent Hepatitis A, an acute liver infection caused by the Hepatitis A virus (HAV). This injection is a critical preventive measure, offering immunity to individuals at risk of exposure. Hepatitis A is primarily spread through contaminated food and water, making the vaccine particularly important for people traveling to regions where the virus is common.
Hepatitis A affects millions globally each year. According to the World Health Organization, approximately 1.4 million new cases occur annually, emphasizing the significance of vaccinations like Havrix. The vaccine is essential in global public health strategies, particularly in areas with poor sanitation.
- Designed to prevent Hepatitis A infection
- Offers long-lasting immunity
- Recommended for travelers to high-risk areas
II. Uses of Havrix Injection
The primary indication for Havrix is the prevention of Hepatitis A infection. The vaccine is highly effective in creating immunity in those who are vaccinated, protecting them from contracting the virus if exposed. Havrix is recommended for both children and adults, especially those living in or traveling to areas where Hepatitis A is prevalent.
Havrix is also crucial for individuals in endemic regions where Hepatitis A is a constant threat. It is often recommended for international travelers, food handlers, and healthcare workers who may be exposed to the virus through their occupation. In these scenarios, the vaccine serves as a pre-exposure prophylaxis, safeguarding individuals before potential exposure to HAV.
III. Off-label Uses of Havrix Injection
While Havrix is primarily indicated for Hepatitis A prevention, it is sometimes utilized off-label in outbreak control situations. In the case of an outbreak in a localized community or institution, administering the vaccine can help halt the spread of the virus.
In immunocompromised patients, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or living with HIV, Havrix may be used off-label. These individuals are often at higher risk of severe complications from Hepatitis A, making early vaccination essential. Additionally, those with chronic liver disease may be recommended for off-label use to protect their already vulnerable liver from further damage caused by HAV.

IV. How Havrix Injection Works
Havrix works by stimulating the immune system to produce antibodies against Hepatitis A. These antibodies will recognize and neutralize the virus if the vaccinated individual is exposed. The vaccine contains inactivated Hepatitis A virus, which cannot cause infection but is sufficient to trigger an immune response.
The duration of immunity following vaccination can last for several years. In most cases, individuals receiving the initial dose and a booster shot maintain immunity for up to 20 years. The vaccine is also effective at reducing transmission rates by decreasing the number of susceptible hosts in a population.
V. Dosage and Administration
The appropriate amount of Havrix to take differs depending on the age group.
Havrix schedule
For grown ups the usual amount is 1 ml given as an injection, into the muscle and a follow up shot after 6 to 12 months is recommended. Children usually get a dose of around 0.s ml following the schedule of a shot followed by a booster. The vaccine is injected into the deltoid muscle in the arm. If a dose is skipped, it's best to take it as soon as possible. However even if there's a delay, in following the schedule some protection is still provided by the vaccine.
Havrix pediatric dose
VI. Composition of Havrix Injection
The active ingredient in Havrix is a Hepatitis A virus, which is not infectious but can trigger an immune response in the body. Aluminum hydroxide is also an adjuvant to enhance the response and preservatives to ensure vaccine stability. It's important for individuals with allergies to know the ingredients of Havrix. If someone is allergic to any of the components, in the vaccine they should refrain from using it to avoid reactions.
Vaqta vs havrix
The Vaqta vaccine generates a amount of anti HAV antibodies compared to Havrix vaccine results, in terms of antibody concentration are especially notable when Vaqtam is administered as a booster shot after crossover immunization The implications of higher levels of anti HAV antibodies for long term protection remain uncertain.
VII. Havrix side effects
Like all vaccines, Havrix can cause side effects. Most are mild and short-lived, but serious reactions can occur in rare cases. The side effects can be categorized based on their severity and frequency. Immediate reactions, such as localized pain at the injection site, are common, while delayed reactions like fever may occur a few days after the injection.
Recognizing the signs of an adverse reaction is crucial, especially if severe symptoms like difficulty breathing or swelling occur, as these may indicate an allergic response that requires immediate medical attention.
VIII. Common Side Effects of Havrix Injection
- Pain, swelling, or redness at the injection site
- Fatigue and mild fever
- Headache
- Nausea or gastrointestinal discomfort
These side effects are generally mild and resolve within a few days without the need for medical intervention. Pain at the injection site is the most frequently reported side effect and is usually short-lived. Headaches and gastrointestinal symptoms can also occur but tend to be transient.
IX. Rare and Serious Side Effects of Havrix Injection
Though uncommon, serious side effects such as severe allergic reactions may occur. Signs of anaphylaxis include hives, difficulty breathing, and swelling of the face or throat. Immediate medical attention is required if these symptoms develop.
In extremely rare instances, neurological side effects like Guillain-Barra syndrome, a condition affecting the nervous system, have been reported. Individuals with a history of severe allergic reactions to vaccines should consult their healthcare provider before receiving Havrix.
X. Drug Interactions with Havrix Injection
Havrix injection, like many vaccines, can interact with other medications and vaccines, influencing the body's immune response. It is essential to understand these interactions to ensure optimal efficacy and avoid complications.
When administered alongside other vaccines, such as the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) or varicella vaccines, there is no significant impact on immune responses. However, the vaccines should be injected into different sites to minimize local reactions.
Concurrent use with immunosuppressants, including corticosteroids, cytotoxic drugs, or treatments for autoimmune conditions, may reduce the effectiveness of the Havrix vaccine. Immunosuppressants can dampen the body's ability to develop a strong immune response, making it crucial to monitor the vaccine's efficacy in patients under such therapies.
- Limited interaction with most vaccines when administered at separate sites
- Immunosuppressants may reduce the immune response to the vaccine
- Monitor patients receiving immunomodulatory drugs
XI. Warnings and Precautions for Havrix Injection
Before receiving Havrix, patients must be evaluated for specific risk factors. Certain conditions require caution to prevent adverse effects. Individuals with moderate to severe illness, for instance, should postpone vaccination until they have fully recovered. Fever, infections, or acute disease can exacerbate vaccine reactions or skew its efficacy.
Patients with underlying medical conditions, such as liver disease or immune system disorders, require close monitoring after vaccination. Hepatitis A vaccination in these populations is essential due to their increased susceptibility to severe infections, but careful monitoring helps mitigate risks. Patients with a history of severe allergic reactions to vaccines or vaccine components should avoid the Havrix injection to prevent life-threatening allergic responses.
XII. Contraindications for Havrix Injection
Severe allergic reactions to any component of Havrix constitute an absolute contraindication. Individuals with hypersensitivity to the vaccine's excipients, including neomycin, or those who have previously experienced anaphylaxis after a Hepatitis A vaccine dose should avoid receiving Havrix. Immediate hypersensitivity reactions require prompt medical intervention.
In addition to allergies, some patients must postpone the vaccine due to ongoing medical conditions. Immune-compromised individuals, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or organ transplantation, may not respond adequately to the vaccine. In such cases, healthcare providers should weigh the benefits of vaccination against the risk of a diminished immune response.
XIII. Special Precautions in the Elderly
Vaccination in the elderly presents specific challenges. While Havrix is generally well-tolerated in older adults, dosing and close monitoring adjustments may be necessary. The immune system weakens with age, potentially altering the vaccine's efficacy. However, older adults are at higher risk of complications from Hepatitis A, making vaccination particularly important.
A thorough risk-benefit analysis should be conducted before vaccinating elderly patients, especially those with multiple comorbidities or weakened immune systems. In some cases, booster doses may be required to ensure sustained immunity.
- Adjustments in dosing may be needed for elderly patients
- Monitor closely for adverse reactions in this population
- High-risk groups benefit significantly from vaccination
XIV. Administration During Pregnancy and Nursing
The safety of Havrix in pregnancy is a critical consideration. While the vaccine is classified under FDA Pregnancy Category C, meaning there is no conclusive evidence of harm to the fetus, it should be administered only if clearly needed. Pregnant women at high risk of Hepatitis A exposure, such as those traveling to endemic regions, should consult their healthcare provider to weigh the risks and benefits.
Havrix is considered safe for breastfeeding women. There is no evidence that the vaccine's components are secreted in breast milk. Vaccination may even confer some level of passive immunity on the infant, offering added protection. Pregnant travelers, especially those headed to high-risk areas, should prioritize vaccination in consultation with their physician.
XV. Administration in Children
Havrix has been proven safe and effective in pediatric populations. The vaccine is recommended for children, particularly those living in or traveling to areas with a high prevalence of Hepatitis A. The dosing schedule typically involves two doses, with the first administered after 12 months of age and a booster dose 6 to 12 months later.
When used in conjunction with other routine childhood vaccines, Havrix does not interfere with the immune response. Pediatricians can safely administer the vaccine alongside others, such as the MMR or DTaP vaccines, ensuring comprehensive immunization during early childhood.
XVI. Overdosage of Havrix Injection
Overdose with Havrix is rare, but it can occur if multiple doses are administered in a short period. Symptoms of an overdose are generally mild and may include enhanced local reactions such as pain, swelling, or redness at the injection site. Other symptoms could include fatigue, fever, or mild systemic effects.
Treatment for an overdose is typically supportive, focusing on alleviating symptoms. Any adverse event resulting from an overdose should be promptly reported to healthcare authorities to monitor for potential complications. In most cases, an accidental overdose does not result in severe long-term consequences.
XVII. Handling and Storage of Havrix Injection
Proper handling and storage of Havrix are critical to maintaining its efficacy. The vaccine must be stored between 2°C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F). It should never be frozen, as freezing may degrade the inactivated virus, rendering the vaccine ineffective.
Healthcare providers should follow strict guidelines when handling Havrix. This includes checking expiration dates, ensuring vaccines are stored in temperature-controlled environments, and maintaining sterile conditions during administration. Proper disposal of vaccine vials and needles is essential to prevent contamination and accidental injury.
- Store between 2°C and 8°C, do not freeze
- Maintain sterile conditions during handling and administration
- Proper disposal of vials and needles is crucial
XVIII. Important Precautions for Handling Havrix
Healthcare professionals must adhere to safety protocols when handling and administering Havrix. These precautions include ensuring the vaccine is administered under sterile conditions to prevent infections. Healthcare workers should also be trained to identify and manage adverse reactions effectively, ensuring prompt intervention.
Avoiding contamination is paramount. Once the vaccine vial is opened, it must be handled with extreme care to avoid bacterial contamination. If any contamination occurs, the vial should be discarded immediately to prevent complications in the vaccinated individual.
- Strict adherence to safety protocols is essential
- Ensure sterile conditions to prevent infections
- Proper training for healthcare workers is crucial for safe administration
Havrix Injection FAQ
- What is the minimum interval between the first and second doses of either havrix or vaqta?
- What is havrix?
- When is the havrix vaccine schedule for adults?
- What is havrix junior monodose vaccine?
- What is havrix monodose vaccine?
- How long is havrix good for?
- Can havrix be given after vaqta?
- How long can havrix be out of the fridge?
- Can havrix be given with other vaccines?
- Can havrix be given to adults?
- Can havrix and engerix be given together?
- Are havrix and avaxim the same?
- Are havrix and vaqta interchangeable?
- How to give havrix injection?
- Havrix how often?
- Havrix how long does it last?
What is the minimum interval between the first and second doses of either havrix or vaqta?
ACIP's recommendations regarding hepatitis A vaccination suggest that individuals between the ages of 1 and 18 who have not been vaccinated should get two doses of the hepatitis A vaccine with a gap of 6 months between doses. If someone received their dose at 12 months or older, they should get their dose at least six months after the first one.
What is havrix?
HAVRIX is recommended for protecting against hepatitis caused by the hepatitis A virus (HAV). It is authorized for individuals aged 12 months and above. The initial vaccination is ideally given 2 weeks before potential HAV exposure occurs, and it is important to shake before use.
When is the havrix vaccine schedule for adults?
For adults, the initial vaccination involves a 1-milliliter shot followed by a booster shot of the amount given at least 6 to 12 months later in the deltoid area of the arm. The injection is available, in prefilled TIP Lok syringes with a volume of 0
What is havrix junior monodose vaccine?
The Havrix Junior Monodose vaccine includes the deactivated hepatitis A virus and is designed to strengthen the system to prevent hepatitis A infection in children and teenagers aged 1 to 15.
What is havrix monodose vaccine?
The Havrix Monodose vaccine comprises the hepatitis A virus. It is utilized to bolster the system in adults and adolescents aged 16 and above, helping guard against hepatitis A infection by triggering an immune response without causing the actual infection itself since the virus within the vaccine is inactive.
How long is havrix good for?
After receiving a shot of the HAVRIX vaccine against hepatitis A virus infection, you will be protected for a minimum of one year, which can be extended with a booster dose administered six to one year after the initial dose. This will ensure prolonged protection expected to endure up to 20 years, as per estimates by health experts; your physician will offer guidance regarding any necessity for supplementary doses.
Can havrix be given after vaqta?
It's a good idea to stick with the vaccine brand for your entire vaccination series whenever you can manage it; however, if that's not feasible, then it's fine to switch between brands for subsequent doses (for example, following HAVRIX with VAQUA or vice versa).
How long can havrix be out of the fridge?
The stability information suggests that Havrix remains stable at temperatures of, up to 25°C for a period of 3 days to assist healthcare providers during temperature deviations.
Can havrix be given with other vaccines?
HAVRIX can be given at the time as a globulin; however, if other vaccines or immune globulin need to be administered simultaneously, they should be injected using separate syringes and at different locations on the body.
Can havrix be given to adults?
For individuals who're 16 years old and above. The recommended amount of HAVRIX 1440 is 1mL for each dose.The injection of HAVRIX into adults and older children would be administered in the upper arm muscle, while for infants, it would be injected into the thigh muscle. There may be cases where individuals, with bleeding disorders might require the dose to be administered under the skin).
Can havrix and engerix be given together?
HAVRIX can be given at the time as globulin. If other vaccines or immune globulin need to be administered simultaneously, syringes and injection sites are important.HAVRIX should not be mixed with any vaccine or product in the syringe.
Are havrix and avaxim the same?
Avaxim and Havrix are both vaccines with aluminum adjuvants; however, they differ in the amount of aluminum they contain. Avaxim has 0..03 mg of aluminum hydroxide in a 0..05 mL dose for children, and Havrix has 0..05 mg of aluminum hydroxide in a 0..05 mL dose for children.
Are havrix and vaqta interchangeable?
It is recommended that the patient stick with the brand of vaccine for the treatment course; however, if this isn't feasible, Vaccines from different brands can be swapped out for the second dose (for instance, VAQTAA could be administered as a follow-up to an initial HAVRIX shot and vice versa).
How to give havrix injection?
Please inject HAVRIX into the muscle only. Avoid the region to ensure an effective response. Avoid administering HAVRIX intravenously or through the skin.
Havrix how often?
After receiving a shot of the HAVRIX vaccine, hepatitis A protection lasts for a minimum of 1 year, with long-term protection provided by a second booster dose administered 6 to 10 months later. This could potentially offer protection for up to 20 years, as recommended by your healthcare provider regarding the necessity of booster doses.
Havrix how long does it last?
After receiving one shot of the HAVRIX vaccine, hepatitis A prevention will last for a minimum of one year, with protection following a booster dose administered 6 to 121 months later, which is anticipated to provide immunity for up to 20 years, as recommended by your physician, who will guide you on the necessity of additional doses.












