Labetalol
- I. Introduction
- II. What is Labetalol?
- III. Uses of Labetalol
- IV. Off-label Uses
- V. How Labetalol Works
- VI. Dosage and Administration
- VII. Administration to Elderly
- VIII. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
- IX. Administration to Children
- X. Composition
- XI. Common Side Effects
- XII. Serious Side Effects and Warnings
- XIII. Contraindications
- XIV. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
- XV. Drug Interactions
- XVI. Overdosage
- XVII. Storage Guidelines
- XVIII. Handling Precautions
- XIX. Conclusion
I. Introduction
Brief Overview of Labetalol
Labetalol is a used medication that falls under the category of adrenergic receptor blockers. It is primarily utilized in treatment, particularly for managing high blood pressure.
Importance in Medical Therapeutics
The medication has received a lot of praise for being practical and taking action. Being a blocker of both beta-adrenergic receptors, it has significant therapeutic benefits for various cardiovascular conditions.
Scope of the Article
This informative article seeks to clarify aspects of Labetalol, including how it works and the recommended ways to administer it.
II. What is Labetalol?
Definition and Class of Drug
Labetalol is a medication that blocks alpha and beta-adrenergic receptors and is mainly used to treat blood pressure.
Historical Background
First introduced in the 1970s, Labetalol has become a component of cardiovascular treatments. Its origins can be traced back to the advancements in receptor-blocking technology.
Forms Available (Tablets, Injection)
Tablets are commonly found in three strengths, including 100 mg, 200 mg, and 300 mg. Injections are typically provided in a concentration of 5 mg per milliliter.
III. Uses of Labetalol
Hypertension
Labetalol is a medication that is commonly used to treat hypertension. It has been found to be effective in managing both systolic and diastolic blood pressure123. Here are some references that provide more information about Labetalol and its use in treating hypertension:
- UpToDate: This article provides detailed information about the use of Labetalol in treating hypertension, including dosages, side effects, and more.
- NHS: The NHS describes how Labetalol works, how it is taken, and its potential side effects.
- CKS: The Clinical Knowledge Summaries (CKS) provides prescribing information for Labetalol, including dosage, contraindications, and side effects.
Chronic Angina
Labetalol is a medication that is commonly used to treat hypertension. It has been found to be effective in managing both systolic and diastolic blood pressure123. Here are some references that provide more information about Labetalol and its use in treating hypertension:
- UpToDate: This article provides detailed information about the use of Labetalol in treating hypertension, including dosages, side effects, and more.
- NHS: The NHS describes how Labetalol works, how it is taken, and its potential side effects.
- CKS: The Clinical Knowledge Summaries (CKS) provides prescribing information for Labetalol, including dosage, contraindications, and side effects.
Perioperative Blood Pressure Management
Labetalol is a medication that is commonly used to temporarily control blood pressure123. Here are some references that provide more information about Labetalol and its use in controlling blood pressure:
- UpToDate: This article provides detailed information about the use of Labetalol in treating hypertension, including dosages, side effects, and more.
- NHS: The NHS describes how Labetalol works, how it is taken, and its potential side effects.
- CKS: The Clinical Knowledge Summaries (CKS) provides prescribing information for Labetalol, including dosage, contraindications, and side effects.
Pre-eclampsia and Eclampsia
Labetalol is a medication that is used to control elevated blood pressure during situations in pregnancy that are linked to pre-eclampsia and eclampsia1. It is a non-selective beta blocker that also selectively blocks alpha-1 adrenergic receptors2. You can find more information about labetalol on the following websites:
- Medscape: Provides comprehensive information about labetalol, including dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more.
- MedlinePlus: Offers detailed drug information about labetalol, including side effects, dosage, and special precautions.
- Sigma Aldrich: Provides information about Labetalol European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard.
- DrugBank Online: Offers information about labetalol’s uses, interactions, and mechanism of action.
IV. Off-label Uses
Migraine Prophylaxis
Labetalol is a medication that is used to control elevated blood pressure during situations in pregnancy that are linked to pre-eclampsia and eclampsia1. It is a non-selective beta blocker that also selectively blocks alpha-1 adrenergic receptors2. You can find more information about labetalol on the following websites:
- Medscape: Provides comprehensive information about labetalol, including dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more.
- MedlinePlus: Offers detailed drug information about labetalol, including side effects, dosage, and special precautions.
- Sigma Aldrich: Provides information about Labetalol European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard.
- DrugBank Online: Offers information about labetalol’s uses, interactions, and mechanism of action.
Portal Hypertension
Labetalol is a medication that is sometimes used by doctors to manage portal hypertension, although it is not commonly used as a mainstream treatment1. It is a beta-blocker that is also prescribed for the treatment of high blood pressure2.
Here is a reference that provides information about Labetalol:
- Society of Hospital Pharmacists of Australia: The Australian Injectable Drugs Handbook contains information about Labetalol1.
Thyroid Crisis Management
Labetalol is a medication that can be used during episodes of hyperthyroid crises to help reduce the activity of the sympathetic nervous system1. It works by blocking β1-β2 adrenergic receptors, which leads to a decrease in blood pressure and heart rate through negative inotropic and chronotropic effects. It also inhibits renin release2.
Here are some references that provide more information on the topic:
- Treatment of paroxysmal sympathetic storm with labetalol: This article discusses the use of labetalol in the treatment of paroxysmal sympathetic storm2.
- HYPERTHYROIDISM AND THE SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM: This article explores the role of the sympathetic nervous system in the hemodynamic changes of hyperthyroidism3.
Glaucoma
Labetalol is a medication that has demonstrated promise in lowering pressure, which can be beneficial in managing glaucoma1. It works by blocking β1-β2 adrenergic receptors, which decreases blood pressure and heart rate through negative inotropic and chronotropic effects. It also inhibits renin release2.
Here are some references that provide more information on the topic:
- Labetalol Disease Interactions - Drugs.com: This page lists 20 disease interactions with labetalol, including glaucoma1.
- Betaxolol: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action | DrugBank Online: This page provides information on betaxolol, another medication used to treat glaucoma2.
- Medications That May Adversely Affect Glaucoma - BrightFocus: This article discusses medications that may adversely affect glaucoma, including beta-blockers like labetalol3.
V. How Labetalol Works
Mechanism of Action
The medication works by blocking the receptors, which helps reduce the smooth muscles' contractile response to catecholamines in blood vessels.
Pharmacodynamics
- Vasodilatation
- Decrease in heart rate
Pharmacokinetics
The drug's absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion influence how quickly it takes effect, reaches its highest concentration in the body and remains active.
Beta-Blocker with Alpha-Blocking Activity
Its distinctive ability to perform two activities simultaneously gives it an advantage in handling various cardiovascular conditions.
VI. Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosage for Adults
The typical recommended dose for adults is usually between 200 to 400 mg per day, which is commonly divided into doses throughout the day.
Route of Administration
- Oral: Tablets
- Intravenous: Injection
Titration Guidelines
Dosage adjustments should be cautiously approached, considering the patient's response and tolerance levels.
VII. Administration to Elderly
Special Considerations
Because of changes in how medications are processed in the body, it may be necessary to adjust the dosage for older adults.
Adjustments in Dosage
It would be wise to start the therapy with doses as a cautious approach.
Monitoring Requirements
It is recommended to monitor blood pressure and renal function.
VIII. Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Risk Category
Labetalol is classified as Pregnancy Category C by the FDA, indicating risks may be involved.
Recommended Guidelines
Only use it when the advantages are more significant than any drawbacks.
Potential Risks to Fetus or Infant
Growth restriction that occurs inside the womb and slow heart rate in babies.
IX. Administration to Children
Safety Profile
Its application in children has been extensively documented, highlighting the importance of careful clinical supervision.
Age-specific Dosage Recommendations
Dosage recommendations can be vague. Typically tailored to each individual, often relying on extensive clinical expertise.
X. Composition
Active Ingredient
Labetalol hydrochloride compound is the active ingredient in Labetalol, and it plays a crucial role in the medication's effectiveness in treating cardiovascular conditions.
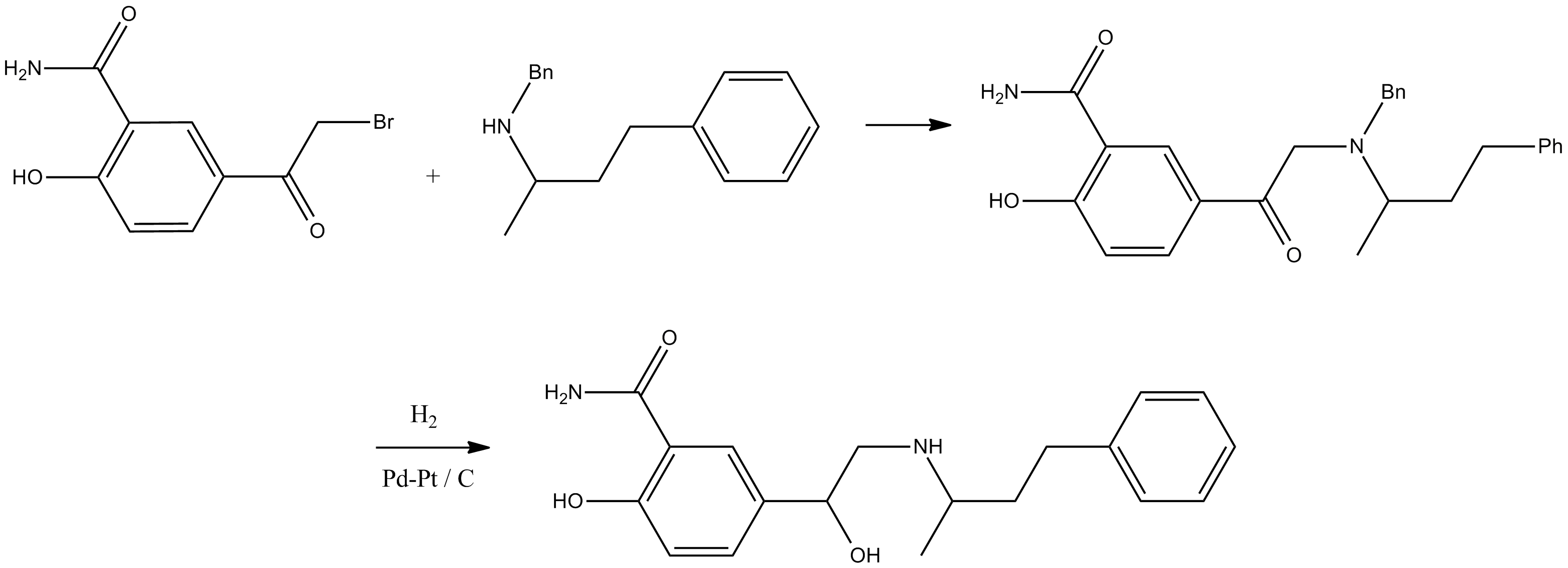
Inactive Ingredients
The formulation includes substances such as magnesium stearate, lactose, and colloidal anhydrous silica. It also contains additives, like sodium lauryl sulfate and crospovidone.
Generics Vs. Brand Names
While Trandate, the known brand name version has undergone thorough evaluation generic alternatives have also been shown to be bioequivalent and are often a more cost-effective choice.
XI. Common Side Effects
List of Most Common Side Effects
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Nausea
Frequency Statistics
Fatigue is reported by around 30% of users, while dizziness is observed in 25% of cases.
Reversible vs. Irreversible Effects
Most of these side effects can be reversed when you stop taking the medication. It's necessary to stay alert for any signs of permanent complications.
XII. Serious Side Effects and Warnings
Cardiovascular Risks
- Orthostatic hypotension
- Bradycardia
Liver Function Abnormalities
Instances of liver enzymes and jaundice have been reported, although they are uncommon occurrences.
Severe Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, are highly uncommon. It can be hazardous.
XIII. Contraindications
Absolute Contraindications
A pre-existing condition of slow heart rate Blockage, in the hearts, signals either second or third degree.
Relative Contraindications
- Chronic lung disease
- Severe hepatic dysfunction
Drug-Induced Contraindications
It is not recommended to use this medication at the time, as certain antipsychotic medications, because it can increase the risk of low blood pressure.
XIV. Careful Administration and Important Precautions
Monitoring Blood Pressure
It is important to have blood pressure checks as part of an effective treatment plan.
Liver and Kidney Function Tests
Regular monitoring of liver and kidney function is essential, for the use of medication.
Avoiding Abrupt Withdrawal
Gradual withdrawal is highly recommended to avoid the risk of rebound hypertension.
XV. Drug Interactions
Common Drug Interactions
- Diuretics
- Calcium channel blockers
Over-the-counter Medicine Interactions
Taking this alongside cough and cold medications that can be bought without a prescription is not recommended because it may raise your blood pressure.
Alcohol and Food Interactions
Drinking alcohol can increase the impact of Labetalol in lowering blood pressure.
XVI. Overdosage
Symptoms of Overdosage
- Profound hypotension
- Respiratory distress

Emergency Management
It is essential to seek medical attention and provide supportive interventions.
Antidotes and Treatment Options
Glucagon has proven to be effective as a remedy.
XVII. Storage Guidelines
Optimal Storage Conditions
- Room temperature away from light and moisture.
Shelf-life
The product can be appropriately stored for a duration of up to 24 months from the date it was manufactured.
Disposal Guidelines
It is essential to follow guidelines, for the proper disposal of expired or unused tablets.
XVIII. Handling Precautions
Safe Handling Procedures
It is essential to handle this in a space with ventilation and away, from any sources of open flames.
Personal Protective Equipment
It is recommended to wear gloves when administering the form.
First Aid Measures in Case of Accidental Exposure
It is advisable to rinse the affected area and seek advice from healthcare professionals.
XIX. Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Labetalol is a useful medication, for treating high blood pressure, and it has many different uses in clinical practice. However, it's essential to be aware that it can also have side effects and may interact with medications.
Clinical Importance of Labetalol
Its distinct way of blocking two types of receptors highlights its importance in treating cardiovascular conditions.
Recommendations for Further Reading and Consultation with Healthcare Providers
To understand Labetalol and its implications in medical treatment, it is recommended to read peer-reviewed articles and seek advice from healthcare professionals.